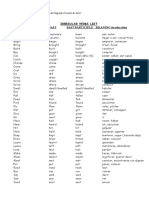
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grammar Present Perfect
Uploaded by
SEISEOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grammar Present Perfect
Uploaded by
SEISECopyright:
Available Formats
The present perfect
The present perfect
1. Formation of the present perfect
1. 1 Formation of the present perfect
Present perfect = present tense of the verb to have + past participle
AFFIRMATIVE I have looked he/she has slept we have worked
QUESTION (+) Have I looked? Has he/she slept? Have we worked?
NEGATIVE I havent looked he/she hasnt slept we havent worked
QUESTION (-) Havent I looked? Hasnt he/she slept? Havent we worked?
2. Use of the present perfect
2.1 Unspecified time before now.
?
PAST
Eg:
PRESENT
FUTURE
Have you ever been in Paris? I've already seen that film. I don't want to see it again. I think Ive met him before.
It doesnt matter when someone does something!
You can use the present perfect with expressions like: ever, never, once, before, already, yet, several times, often, lately, so far, still not, rarely,
The present perfect
You cannot use the present perfect with expressions like: yesterday, last week, that day, five years ago, 2.2 Finished action in an unfinished period.
Period of time
PAST
PRESENT
FUTURE
Eg:
I have seen him (FINISHED ACTION) this evening (UNFINISHED PERIOD this evening has not yet ended!).
means that
She has watched (FINISHED ACTION) the film this weekend. (UNFINISHED PERIOD means that this weekend has not yet ended!)
You can use the present perfect with expressions like: this week, this morning, this winter, if these periods have not yet ended. These periods are called unfinished periods.
2.3 Actions that started in the past and are still continuing.
PAST
Eg:
PRESENT
FUTURE
Paul has not finished his homework. We have lived in the United States for seven years. ( States seven years ago and we are still living there) we started living in the United
FOR = length of time
the action has continued up to now.
for: one year, ages, a weekend, a month,
The present perfect
You have worked at the Bank since 2000. ( you are still working there) you started working at the bank in 2000, and
SINCE = starting time, a precise moment in time then until now. since: Christmas, 1987, seven oclock
the action has continued from
2.4 Actions that happened in the past but have an effect in the present.
PAST
PRESENT
FUTURE
Eg:
Ive not passed my driving test. (= consequently, Im not allowed to drive a car) They have studied English. (= consequently, they know English)
2.5 Actions that happened in the immediate past.
PAST
PRESENT
FUTURE
Eg:
She has just arrived. Hi! We have come to see you! I have just finished my work.
Just is an expression that you can use with the present perfect. It describes an action completed in the immediate past.
The present perfect 3. Gone and been
Note the difference between gone and been: Jack has gone to Canada. Alice has been to Canada. Jack is in Canada now. Alice has been to Canada and come back.
You might also like
- AK GoneWindOneDocument3 pagesAK GoneWindOneSEISENo ratings yet
- Using The Health&Safety TemplateDocument6 pagesUsing The Health&Safety TemplateSEISENo ratings yet
- Qamous AladwatDocument194 pagesQamous AladwatSEISENo ratings yet
- Shakespeare BiographyDocument2 pagesShakespeare BiographyVivek ReddyNo ratings yet
- Connectors: I-Subordinating Conjunctions II-Coordinating Conjunctions III-TransitionsDocument23 pagesConnectors: I-Subordinating Conjunctions II-Coordinating Conjunctions III-TransitionsSEISENo ratings yet
- 1 Outcome Based EducationDocument68 pages1 Outcome Based EducationSEISENo ratings yet
- 06 Shakespeare's LifeDocument9 pages06 Shakespeare's LifeSEISENo ratings yet
- Microsoft Access 2007 Tutorial: Getting StartedDocument49 pagesMicrosoft Access 2007 Tutorial: Getting Startedaqjabbar_pkNo ratings yet
- Item Analysis2Document31 pagesItem Analysis2SEISENo ratings yet
- Conducting Continuous Assessment in Grades 5 To 10Document15 pagesConducting Continuous Assessment in Grades 5 To 10SEISENo ratings yet
- Specifications For End-Of-year Test (September 2010)Document8 pagesSpecifications For End-Of-year Test (September 2010)SEISENo ratings yet
- B04 B65 A3 D 01Document9 pagesB04 B65 A3 D 01SEISENo ratings yet
- Fact SheetDocument1 pageFact SheetSEISENo ratings yet
- Mark Range Letter-Grade DescriptorDocument7 pagesMark Range Letter-Grade DescriptorSEISENo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Open Mind Elementary Unit 02 Grammar 2Document12 pagesOpen Mind Elementary Unit 02 Grammar 2khatuna sharashidzeNo ratings yet
- Sentence Patterns EditedDocument33 pagesSentence Patterns EditedSyahrund MubarackNo ratings yet
- Poimnt of ViewDocument7 pagesPoimnt of ViewElaine Gay MandaNo ratings yet
- U1 - L2 - Modals of AdviceDocument4 pagesU1 - L2 - Modals of AdviceLeo CentenoNo ratings yet
- Total TransformationDocument26 pagesTotal TransformationMd Ridwanul Haque ZawadNo ratings yet
- PrepositionsDocument40 pagesPrepositionsBenedict Lumague50% (2)
- Bob Has Visited His GrandmaDocument3 pagesBob Has Visited His GrandmaTatiana Antacabana de QuispeNo ratings yet
- The Penguin Guide To Plain EnglishDocument1 pageThe Penguin Guide To Plain EnglishIliasNo ratings yet
- Anh303de03 - English Syntax - Morphology - 2331 (Chính TH C)Document5 pagesAnh303de03 - English Syntax - Morphology - 2331 (Chính TH C)Nguyễn Ngọc Quỳnh NhưNo ratings yet
- Spark 2 Grammar PDFDocument150 pagesSpark 2 Grammar PDFDarya BogdanNo ratings yet
- Old English ParadigmsDocument5 pagesOld English ParadigmsLidia Pastrana Diaz100% (1)
- LM 1002 Integrated English II PDFDocument13 pagesLM 1002 Integrated English II PDFLuzviminda A. TajosNo ratings yet
- Vi Yearly Plan English Form 4 2022Document4 pagesVi Yearly Plan English Form 4 2022NURUL HANANI BINTI ABD RAHMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Close Up b2Document15 pagesClose Up b2Lana Saiel AbawiNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument32 pagesModal Verbssusie fallariaNo ratings yet
- Soluções Worksheets 8Document7 pagesSoluções Worksheets 8joanap20030% (1)
- English grammar: reported speechDocument4 pagesEnglish grammar: reported speechAmanda AbbottNo ratings yet
- English Lab WorksheetDocument2 pagesEnglish Lab WorksheetRAMON MENDOZA LOPEZNo ratings yet
- ôn tập TA2Document6 pagesôn tập TA2vungoc24072004No ratings yet
- Vocabulary - and - Grammar - Consolidation - and - Extension 4º PDFDocument46 pagesVocabulary - and - Grammar - Consolidation - and - Extension 4º PDFDavid GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Irregular verbs listDocument3 pagesIrregular verbs listjuan carlosNo ratings yet
- Meeting 6: Talking About: Complaints, Household Chores, Request, Excuse, ApologizeDocument9 pagesMeeting 6: Talking About: Complaints, Household Chores, Request, Excuse, ApologizeAgriel ArsadelNo ratings yet
- Learn Simple Present Tense in 40 WordsDocument6 pagesLearn Simple Present Tense in 40 WordsMade AnomaharsiNo ratings yet
- Giáo Trình READINGDocument68 pagesGiáo Trình READINGDuyên MinhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Modality, Scope and Quantification - Word MapDocument1 pageChapter 7 - Modality, Scope and Quantification - Word MapareszNo ratings yet
- Gramar Chart. Complete. BasicDocument2 pagesGramar Chart. Complete. Basicluis fernando rodriguez ruizNo ratings yet
- English Syntax: Heads and ModifiersDocument34 pagesEnglish Syntax: Heads and ModifiersMustarini Bella Vitiara92% (12)
- Second Quarterly Test in English 4Document4 pagesSecond Quarterly Test in English 4Val AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Common and Proper NounsDocument16 pagesCommon and Proper Nounsdaien quequeNo ratings yet
- Grammar Guide to Parts of Speech in 40 CharactersDocument2 pagesGrammar Guide to Parts of Speech in 40 CharactersHimanshu VasisthaNo ratings yet