Professional Documents
Culture Documents
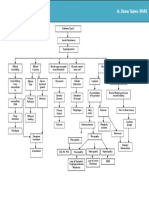
Ideal Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type II
Uploaded by
Mark Anthony YabresOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ideal Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type II
Uploaded by
Mark Anthony YabresCopyright:
Available Formats
Ideal Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type II
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Precipitating factors: frequent or chronic infections eating too much sweets development of glucose intolerance during drug therapy delivery of over 9 lbs infants diet sedentary lifestyle
Predisposing factors: 1. family history of DM 2. obesity 3. Age above 40 Insulin resistance
Exhaustion of beta cells
Insulin production/ decrease secretion of insulin Degradation of proteins
Absorption of glucose by the cell
Breakdown of fat
Cell starvation
Stimulation of hunger mechanism via hypothalamus
Hunger
POLYPHAGIA
FBS 140 mg/dL
HYPERGLYCEMIA
FBS to 180 mg/dL
Nerve Demyelinization
Kidney filtration mechanism impaired
Capillary basement membrane thickening
GLYCOSURIA
NEUROPATHY
Acidity of urine Diffuse glomerular sclerosis Urethral flora NEPHROPATHY
Paresthesias & numbness Impaired pain sensation NON-HEALING ULCERS Delayed wound healing
UTI
Vaginitis
Renal failure End-Stage Renal Disease
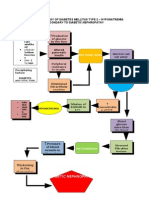
Circulating blood volume Hypovolemia
POLYURIA & ALBUMINURIA
Gangrene
HYPOTENSION & TACHYCARDIA
F & E imbalance
Number of solute relative to water
Potassium ion retention
Sodium ions lost
Cardiac arrythmias DEATH
Tissue dehydration
POLYDIPSIA
Increase viscosity of blood
Capillary basement membrane thickening Abnormal retinal vascular permeability Scarring RETINOPATHY
Thickening of blood vessel walls Occlusion of plaque
Musculoskeletal effects
Impaired glucose absorption in the muscle tissue Joint contractures Myocardial ischemia Myocardial infarction Diminished peripheral pulse
Blood flow blocked
Blood pressure HYPERTENSION
FATIGUE
Blurring of vision Stroke
Blindness blindness
Heart Failure
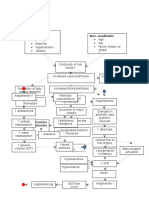
Breakdown of fat
Fatty acids & glycerol ketone bodies in the general circulation hydroxybutyric acid acetoacetic acid Convulsions Metabolic acidosis Acetone breath
Fat content of the blood Hyperlipidemia
Weight Loss
Formation of fatty deposits on the walls of the blood vessels Atherosclerosis
Nausea and vomiting
Abdominal pain
Cellular Potassium
Body attempts to prevent further decrease in pH
Depressed central nervous system
Poor appetite
Cardiac arrhythmias
Kussmauls respirations
Headache
Coma
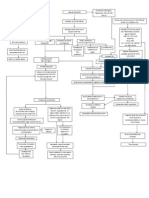
Amino acid in the general circulation Hyperaminoacidemia
Mobilization / degradation of proteins
Decreased urinary nitrogen
Further sodium ion loss
Potassium ion retention
Dehydration
Cardiac arrhythmias DEATH
hunger
You might also like
- Pathophysiology - Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document3 pagesPathophysiology - Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Francis Kevin Sagudo100% (10)
- Patof DMDocument1 pagePatof DMxerwaneNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagramnursing concept maps100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document4 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2jo_annamae4413100% (3)
- DM Type 2 PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesDM Type 2 PathophysiologyuzumakiruleNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of DMRgn Mckl100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of DM IIDocument6 pagesPathophysiology of DM IIJulie SimaurioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document1 pagePathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2faula rocamora100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument7 pagesPathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes MellitusarbyjamesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document5 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2LesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramJhe Lyn82% (11)
- Pathophysiology DMDocument1 pagePathophysiology DMMJ AmarilloNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1Document3 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1CajRofuli100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document6 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Renz Ivan FuntilonNo ratings yet
- Sle FinalDocument41 pagesSle FinalAsniah Hadjiadatu Abdullah100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus: Predisposing and Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus: Predisposing and Precipitating FactorsJerene67% (3)
- Diabetes Mellitus 2Document42 pagesDiabetes Mellitus 2ien84% (19)
- Pathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeDocument1 pagePathophysiology Hemorrhagic StrokeJeffrey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- DM Type II Case StudyDocument28 pagesDM Type II Case StudyRichard Sy67% (3)
- Pathophysiology HypertensionDocument1 pagePathophysiology HypertensionAlinor Abubacar100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)Document1 pagePathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)rexale ria100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5Document21 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Stage 5Kristine Anne Soriano100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CVDDocument1 pagePathophysiology CVDPamela Shiermaine FilomenoNo ratings yet
- Case Study DM TYPE IIDocument16 pagesCase Study DM TYPE IIrose_avy200975% (4)
- Case Study in DMDocument34 pagesCase Study in DMKathrina Marie B. BinaraoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Insipidus Pathophys DiagramDocument1 pageDiabetes Insipidus Pathophys Diagrampaupaulala100% (4)
- Pathophysiology: Precipitating FactorDocument6 pagesPathophysiology: Precipitating FactorMark Anthony YabresNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureIvana Yasmin Bulandres100% (2)
- Chronic Kidney Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiologybilliam123100% (1)
- Case Study About Type II Diabetes MellitusDocument84 pagesCase Study About Type II Diabetes MellitusMark Anthony S. Castillo89% (35)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsLilot Antonio Rodriguez Vinarao100% (5)
- Pathophysiology CKDDocument1 pagePathophysiology CKDReymon Mary JanineNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisDocument4 pagesPathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisCyrus Ortalla RobinNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- CKD PathoDocument5 pagesCKD PathoJohn MIchael AusaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramChristelle GarciaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureTrixia Almendral100% (2)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramMeine MheineNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of HypertensionDocument54 pagesPathophysiology of HypertensionKaloy Kamao100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Diseasekhrizaleeh100% (9)
- Pathophysiology - HyperthyroidismDocument2 pagesPathophysiology - HyperthyroidismCaren Reyes100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Rheumatoid ArthritisGerardeanne ReposarNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus 2Document43 pagesDiabetes Mellitus 2Obed AndalisNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology CHFKim Franzel M. Rabe100% (1)
- Weaknes S/ Fatigue Polyphag IaDocument5 pagesWeaknes S/ Fatigue Polyphag IaEwert Hesketh Nillama PaquinganNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Renal FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Renal FailureHampson Malekano100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Renal Failuresugarmontejo67% (3)
- Anemia PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAnemia PathophysiologyHoney Lorie D. Simbajon67% (6)
- NCP - DMDocument4 pagesNCP - DMMonica Garcia88% (8)
- Pathophysiology of Acute Renal FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Renal Failurekristel_nicole18yaho100% (3)
- Schematic Diag DMDocument1 pageSchematic Diag DMReynaKatNo ratings yet
- Pa ThoDocument1 pagePa ThoDoris Glenn FloresNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument7 pagesPathophysiology of CVAsarzlasco0967% (3)
- End Stage Renal Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDocument2 pagesEnd Stage Renal Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramSharmaine Camille de LeonNo ratings yet
- For Printing Pathophysiology DMDocument1 pageFor Printing Pathophysiology DMkat garciaNo ratings yet
- Nursing care analysis of diabetic retinopathyDocument8 pagesNursing care analysis of diabetic retinopathyDonnabell DayudayNo ratings yet
- Path o PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology Final DMDocument6 pagesPa Tho Physiology Final DMJamil LorcaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY (1)Document2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY (1)Gerome ManantanNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Gynecology and ObstetricsDocument5 pagesInternational Journal of Gynecology and ObstetricsLilian Rahma AnandaNo ratings yet
- IBD MedicationDocument19 pagesIBD MedicationTheghanNo ratings yet
- Pulp CappingDocument3 pagesPulp CappingMeta Anjany FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- What Is Water PollutionDocument13 pagesWhat Is Water PollutiondumitrutudoranNo ratings yet
- Body temperature, vital signs, anthropometric measurementsDocument23 pagesBody temperature, vital signs, anthropometric measurementsWYNE BRENT M CORPUZNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Tot - NR 6classid S.F.ADocument74 pagesPharmacology - Tot - NR 6classid S.F.AcorsairmdNo ratings yet
- Bulimia NervosaDocument17 pagesBulimia NervosaJheanAlphonsineT.Means100% (1)
- Basics of Microvascular SurgeryDocument33 pagesBasics of Microvascular SurgeryPratikshya KothiaNo ratings yet
- EXP 6 - Fecal Coliform Test - StudentDocument8 pagesEXP 6 - Fecal Coliform Test - StudentAbo SmraNo ratings yet
- Kode Gigi BpjsDocument4 pagesKode Gigi Bpjskurnia s100% (1)
- Answers To Questions:: Analysis of SalivaDocument2 pagesAnswers To Questions:: Analysis of Salivaerisseval14No ratings yet
- Berger 1986Document3 pagesBerger 1986kameliasitorusNo ratings yet
- 10.6 Health Issues Related To The Human Circulatory SystemDocument7 pages10.6 Health Issues Related To The Human Circulatory SystemrynNo ratings yet
- The Passive: Solutions Third Edition Upper-IntermediateDocument2 pagesThe Passive: Solutions Third Edition Upper-Intermediatelees10088No ratings yet
- Poultry ParasitesDocument164 pagesPoultry ParasitesGiselle Castro Sabino100% (1)
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocument7 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationKun Adi ReksatamaNo ratings yet
- Secrets of Psychic HealingDocument140 pagesSecrets of Psychic Healingkonoha G100% (39)
- Ramadan Fasting and Infectious Diseases: A Systematic ReviewDocument9 pagesRamadan Fasting and Infectious Diseases: A Systematic ReviewBasel SoudanNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation Options For Intermittent HDDocument10 pagesAnticoagulation Options For Intermittent HDNarinder SharmaNo ratings yet
- Gtbr2016 Main TextDocument214 pagesGtbr2016 Main TextRaimundo Isidro MachavaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Life Cycles on Family HealthDocument27 pagesThe Impact of Life Cycles on Family Healthmarcial_745578124No ratings yet
- Jurnal DMDocument13 pagesJurnal DMidaNo ratings yet
- Medications and Antidotes ChartDocument2 pagesMedications and Antidotes ChartkNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Therapeutic Exercise Foundations and Techniques 6th Edition by KisnerDocument6 pagesTest Bank For Therapeutic Exercise Foundations and Techniques 6th Edition by Kisnera33085258962% (13)
- The Hair Bible A Complete Guide To Health and Care PDFDocument205 pagesThe Hair Bible A Complete Guide To Health and Care PDFDaniel Drop100% (1)
- Microbial GrowthDocument48 pagesMicrobial Growthdreamrose100% (14)
- Maternal Child NursingDocument31 pagesMaternal Child Nursingmatrixtrinity88% (24)
- Pharmacology: Advantages: Rapid Absorption, Convenience, LowDocument53 pagesPharmacology: Advantages: Rapid Absorption, Convenience, LowkrstnkyslNo ratings yet
- IV Push MedicationsDocument67 pagesIV Push Medicationsbtalera100% (1)
- Occupational Health & Safety: Claytons Mid LogisticsDocument20 pagesOccupational Health & Safety: Claytons Mid LogisticsDani PhilipNo ratings yet