Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathology: Course Contents Course Contents
Uploaded by
Raghu VeerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pathology: Course Contents Course Contents
Uploaded by
Raghu VeerCopyright:
Available Formats
PATHOLOGY
Learning Objectives At the end of the course, the learned shall be able to : 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Know the principles of collection, handling, storage and dispatch of clinical samples from patient, in a proper manner, Perform and interpret in a proper manner the basic clinico- pathological procedures, Have an understanding of the common haematological disorders and the investigations necessary to diagnose them and determine their prognosis, Understand the concept of cell injury, the change produces thereby, in different tissues and organs and the body capacity for healing, Understand normal haemostatic mechanism, the derangements of these mechanism and the effect on human system, Understand the etiopathogenesis, the pathological effects, and the clinico pathological correlation of common infectious and non-infectious diseases, Understand the concept of neoplasia with respect to etiology, gross and microscopic features, diagnosis and prognosis in different tissues and organs of the body, Correlate normal and altered morphology (gross and microscopy) of different organ systems in different diseases to the extent needed of understanding of the disease processes and their clinical significance, Have knowledge of common immunological disorders and their effects on human body.
9.
Course contents Course contents 1. Cell injury Cause and mechanism: Ischemic, Toxic and Apoptosis Reversible cell injury: Types, morphology, hyaline, fatty change Irreversible cell injury: Types of necrosis, gangrene Calcification: Dystrophic and metastatic Extracelluler accumulation: Amyloidosis, classification, pathogenesis, morphology 2. Inflammation and repair Acute inflammation: features, causes, vascular and cellular events. Morphological variant of acute inflammation Inflammatory cells and mediators Chronic inflammation: causes, types, non-specific and granulomatous with common examples Wound healing by primary and secondary union, factors promoting and delaying the process and complications Must Desirable know to know
Must Desirable know to know 3. Immunopathology Immune pathology: organization, cells, antibodies and regulations of immune responses Hypersensitivity: types and examples, antibodies and cell mediated tissue injury with examples. Autoimmune disorders like Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Organ transplantation: immunological basis of rejection and graft versus host reaction 4. Infectious diseases Mycobacterial diseases: tuberculosis and leprosy Bacterial diseases: pyogenic, typhoid, dyptheria, gram ve infections, bacillary dysentery, syphilis Viral: polio, herpes, rabies, measles, rickettsial, chlamydial infections Fungal disease and opportunistic infections: Parasitic diseases: malaria, filaria, amoebiasis, kala azar, cystecercosis, hydatid AIDS: etiology, modes of transmission, pathogenesis, pathology, complications, diagnostic procedures and handling of infected materials and health education 5. Circulatory disturbances Oedema: pathogenesis and types Chronic venous congestion: lung, liver, spleen Thrombosis and embolism: formation, fate and effects Infarction: types, common sites, gangrene Shock: pathogenesis, types, morphological chances 6. Growth disturbances Atrophy, hypertrophy, hyperplasia, hypoplasia, metaplasia, malformation, agenesis, dysplasia Neoplasia: causes, classification, histogenesis, biological behaviour, benign and malignant, carcinoma and sarcoma Malignant neoplasia: grades and stages, local and distant spread Carcinogenesis: Environmental carcinogen, chemical, viral, occupational, hereditary and basics of molecular basis of cancer Tumour and host interaction: systemic effects including para neoplastic syndrome , tumour immunology, Laboratory diagnosis: cytology, biopsy, tumour markers Tumours and tumour like conditions of soft tissues 7. Miscalleneous disorders Autosomal and sex-linked disorders with examples
Must Desirable know to know Protein energy malnutrition and vitamin deficiency disorders Radiation injuries Disorders of pigments and mineral metabolism such as billirubin, melanin, haemosiderin 8. Haemetopathology Anaemia: classification and clinical features Nutritional anaemia: Iron deficiency, folic acid/ vit B 12 deficiency anaemia including pernicious anaemia Haemolytic anaemia: classification and investigation Hereditary haemolytic anaemia: thalassemia, sickle cell anaemia, hereditary spherocytosis and G 6 P D deficiency Acquired haemolytic anaemia: Aplastic anemia Haemostatic disorders: platlet deffeciency, ITP, drug induced, secondary Coagulopathies: coagulation factor deffeciency, hemophilia, DIC and anticoagulant control Leucocytic disorders: Leucocytosis, leucopoenia, leucamoid reaction Acute and chronic leukemia: classification and diagnosis Multiple myloma and dysproteinemias Blood transfusion: grouping and cross matching untoward reactions, transmissible infections including HIV and hepatitis Haemolytic anemias: autoimmune, alloimmune, drug induced, microangiopathic and malaria Myelodysplastic syndrome Myelo proliferative disorders: polycythemia, myelofibrosis 9. Cardiovascular pathology Rheumatic heart disease: pathogenesis and morphology Infective endocarditis: causes and pathogenesis Atheroscelorosis and ischemic heart disease: myocardial infarction Hypertension and hypertensive heart disease Congenital heart disease: ASD, VSD, Fallots teratology, Biscuspid aorotic PDA Pericarditis cardiomyopathy 10. Respiratory Pathology Inflammatory diseases of bronchi: chronic bronchitis, bronchial asthma, bronchiectasis
Must Desirable know to know Pneumonias: lobar, broncho, interstitial Lung abscess: etiopathogenesis and morphology Pulmonary tuberculosis: primary and secondary, morphologic types including pleuritis Emphysema: type and pathogenesis Tumors: benign, malignant, squamous cell, oat cell, adeno, etiopathogenesis Structure of bronchial tree and alveolar walls, normal and altered lung function, concepts of obstructive and restrictive lung disorders Nasopharyngeal and laryngeal tumors Occupational lung disorders: anthracosis, silicosis, asbestosis, mesothelioma Atelectasis and hyaline membrane disease. 11. Urinary tract pathology Basics of impaired function and urinalysis Glomerulonephritis: classification, primary proliferative and non proliferative, secondary (SLE, polyarteritis, amyloidosis, diabetes) Nephritic syndrome Acute renal failure: acute tubular and cortical necrosis Pyelonephritis, reflux nephropathy, interstitial nephritis Renal cell tumors: renal cell carcinoma, nephroblastoma Urinary bladder: cystitis, carcinoma Progressive renal failure and end stage renal disease Renal vascular disorders Urinary tract tuberculosis Nephrolithiasis and obstructive nephropathy Renal malformation polycystic kidney 12. Pathology of Gatrointestinal tract Oral pathology: leukoplakia, carcinoma oral cavity and esophagus Peptic ulcer: etiopathogenesis and complications, gastritis types Tumors of stomach: benign, polyp, leiomyoma, malignant, adenocarcinoma, lymphoma Inflammatory disease of small intestine: typhoid, tuberculosis, Crohns disease, appendicitis Inflammatory disease of large intestine: amoebic colitis, bacillary dysentery, ulcerative colitis Large and small intestine tumors: polyps, carcinoid, carcinoma, lymphoma
Must Desirable know to know Pancreatitis Salivary gland ttumors: mixed, adenoids, cystic, warthins Ischemic and pseudomembranous enteroculitis, diverticulitis Malabsorption-coeliac disease, tropical sprue and other causes Pancreatic tumors: endocrine, exocrine and pariampullary 13. Liver and Billiary tract pathology Jaundice: types, apathogenesis and differentiation Hepatitis: acute and chronic, etiology, pathogenesis and pathology Cirrohosis: etiology, classification, pathology, complications Portal hypertension: types and manifestation Diseases of gall bladder: cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, carcinoma Tumors of liver: hepatocelluler, metastatic, tumor markers 14. Lymphoreticular system Lymphadenitis: non-specific, granulomatous Hodgkins and Non-Hodgkins lymphoma, classification, morphology Diseases of spleen: spleenomegaly and effects 15. Reproductive system Diseases of cervix: cervicitis, cervical carcinoma, etiology, cytological diagnosis Hormonal influences and histological apperances of different phases of menstrual cycles and the abnormality associated with it Diseases of uterus: endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma, adenomyosis, smooth muscle tumours Trophoblastic diseases: hydatiform choriocarcinoma Diseases of breast: mastitis, abscess, fibrocystic disease, neoplastic lesions, fibroadenoma, carcinoma, phyllodes tumors Prostate: nodular hyperplasia, carcinoma Ovarian and testicular tumours Carcinoma of penis Pelvic inflammatory disease including salpingitis Genital tuberculosis 16. Osteopathology Osteomyelities: acute, chronic, tuberculosis Metabolic diseases: rickets/osteomalacia, osteoporosis, hyper parathyroidism Tumors: primary, osteosarcoma, osteoclastoma, Ewings sarcoma, chondro sarcoma, metastatic
Must Desirable know to know Arthritis: rheumatoid, osteoid and tuberculosis Healing of fractures 17. Endocrine pathology Diabetes mellitus: types, pathogenesis, pathology Non neoplastic lesion of thyroid: Iodine deficiency goiter, autoimmune thyroiditis, thyrotoxicosis, myxoedema Tumors of thyroid: adenoma, carcinoma: pappilary, follicular, medullary, anaplastic Adrenal disease: cortical hyperplasia, atrophy, tuberculosis, tumors of cortex and medulla Parathyroid hyperplasia and tumors 18. Neuropathology Inflammatory disorders: pyogenic and tuberculous meningitis, brain abscess, tuberculoma CNS tumors-primary glioma and meningioma and metastatic CSF and its disturbances: cerebral oedema, raised intracranial pressure Cerebrovascular disease: atherosclerosis, thrombosis, embolism, aneurysm, hypoxia, infarction and hemorrhage 19. Dermatolopathology Skin tumors: squamous cell, basal cell and melanoma Examination skills Skills 1. Be able to collect, store and transport materials for various pathological tests including histopathology, Cytopathology, clinical pathology, haematology and biochemistry Interpret abnormal laboratory values of common diseases Do complete urine examination including microscopy Do perform and interpret haemoglobin, TLC, DLC, ESR, PCV, bleeding time, clotting time, blood smears and red cell morphology Interpret the peripheral smears of common diseases Do blood grouping and cross matching Adapt universal precautions for self protection against HIV and hepatitis, and counsel the patient P. Indep Under Gui Assist Observe
2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7.
Practical: 1. One-third of allotted practical hours to be devoted to a. Performing a complete urine examination and detecting abnormalities and correlating with pathological changes b. To perform with accuracy and reliability basic haematological estimations : TLC, DLC, peripheral smear, staining, reporting along with history, c. To perform basic lab haematological tests like BT & CT 2. One third of allotted practical hours to be devoted to a. Identify and interpret gross and microscopic features of acute inflammations in organs such as appendix, lungs, meninges, b. Cellular components of chronic and granulomatous inflammation c. Granulation tissue, callous d. Typhoid, tuberculosis, amoebic ulcers in intestine e. Rhinosporidiasis, actinomycosis, mycetoma, molluscum contageosum, f. Amoebic liver abscess, malarial liver and spleen, filarial lymphadenitis, cysticercosis g. Fatty liver and kidney, amyloidosis of spleen, kidney and liver h. Types of necrosis: caseous, cogulative, liquifactive, fat i. Common systemic diseases 3. One third of allotted practical hours to be devoted to a. Discussion of case studies (paper) clinical, gross and microscopic features and other parameters wherever applicable to learn clinico pathological correlations SUGGESTED TOPICS FOR INTEGRATED TEACHING 1. 2. 3. 4. Immunology Deficiency diseases Genetics Integrated seminars a. Rheumatic heart disease b. Ischemic heart disease c. Hypertension and Hypertensive heart disease d. Tuberculosis lung e. Nephrotic syndrome f. Inflammatory disease of small and large bowel g. Cirrhosis h. Metabolic bone disease i. Diabetes mellitus j. HIV/AIDS k. Iron deficiency anaemia l. Jaundice m. Malaria
TEACHING LEARNING METHODS: Structured interactive sessions Small group discussion Practical including demonstrations Problem based exercises Written case scenario Self learning tools Interactive learning e-modules LEARNING RESOURCE MATERIALS Text books Reference books Practical note books Internet resources TIME OF EVALUATION: There should be regular formative assessment. Formative assessment, day-to-day performance should be given greater importance. Examination of Pathology should be at the end of 5th semester and formative assessment in middle of 3rd and 4th semester and summative assessment at the end of 5th semester.
You might also like
- Genetic Diseases of the KidneyFrom EverandGenetic Diseases of the KidneyRichard P. LiftonNo ratings yet
- Understanding Pathology Terms and ConceptsDocument74 pagesUnderstanding Pathology Terms and ConceptsAh ZhangNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 4Document6 pagesLab Activity 4Kayla Mayer100% (2)
- Pathophysiology LESSON PLANDocument9 pagesPathophysiology LESSON PLANLokesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument25 pagesValvular Heart DiseaseRyan VachaparampilNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria in Eco-EnvironmentDocument33 pagesAntibiotic Resistant Bacteria in Eco-Environmentkedar karkiNo ratings yet
- Analytical Epidemiology: Case Control StudyDocument32 pagesAnalytical Epidemiology: Case Control StudydeissuzaNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Basis of CancerDocument31 pagesThe Genetic Basis of Cancerapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Introduction To Endocrinology For Clinical StudentsDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Endocrinology For Clinical StudentsOhwovoriole ToketemuNo ratings yet
- What Should Not You Do in A Research?Document27 pagesWhat Should Not You Do in A Research?Mohd HardyNo ratings yet
- 2018 Overview Digestive System HandoutDocument11 pages2018 Overview Digestive System HandoutdraganNo ratings yet
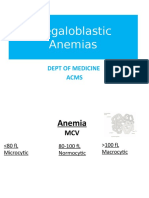
- Megaloblastic Anemias: Dept of Medicine AcmsDocument71 pagesMegaloblastic Anemias: Dept of Medicine Acmskunal ghosh100% (1)
- GI Board ReviewDocument176 pagesGI Board Reviewjosh hagsNo ratings yet
- CASE 28 Recurrent Abdominal PainDocument5 pagesCASE 28 Recurrent Abdominal PainRoseNo ratings yet
- Morbidity and MortalityDocument3 pagesMorbidity and Mortalityadams atebeNo ratings yet
- Videos PathomaDocument3 pagesVideos PathomaMozesCuate0% (1)
- LEC 01 - Principles of EndocrinologyDocument44 pagesLEC 01 - Principles of EndocrinologyIoana Cozma100% (1)
- Cancer Prevention - The Causes and Prevention of Cancer Volume 1 (Cancer Prevention-Cancer Causes) (PDFDrive) PDFDocument338 pagesCancer Prevention - The Causes and Prevention of Cancer Volume 1 (Cancer Prevention-Cancer Causes) (PDFDrive) PDFtheresaNo ratings yet
- Nematode Infections 2019 Student PDFDocument272 pagesNematode Infections 2019 Student PDFCharlene SuliganNo ratings yet
- History Taking2Document25 pagesHistory Taking2Capture UnseenNo ratings yet
- Cellular Adaptations in Growth and DifferentiationDocument32 pagesCellular Adaptations in Growth and Differentiationvinoedhnaidu_rajagopalNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument7 pagesEpithelial TissueJoan PaulineNo ratings yet
- NEUROPATHOLOGY REPORTDocument28 pagesNEUROPATHOLOGY REPORTAnggi WahyuNo ratings yet
- Manage HypoglycemiaDocument57 pagesManage HypoglycemiaAmelia PricopNo ratings yet
- Anatomic Pathology: DR Nancy OkindaDocument8 pagesAnatomic Pathology: DR Nancy OkindaFaryalBalochNo ratings yet
- A Summary of The Chemical Mediators Involve in The Acute Inflammatory Response Is Shown in The Table BelowDocument30 pagesA Summary of The Chemical Mediators Involve in The Acute Inflammatory Response Is Shown in The Table Belowinny100% (1)
- Review of Laboratory and Diagnostic TestsDocument41 pagesReview of Laboratory and Diagnostic TestsPutri Anggraini Rusanti100% (1)
- Medical HistoryDocument167 pagesMedical HistoryPragya Saran100% (1)
- Introduction To History Taking Aims:: Summary of Procedure and NotesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To History Taking Aims:: Summary of Procedure and Notesmj.vinoth@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)Document39 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)Nadya SabrinaNo ratings yet
- Acute Abdomen: Part I: Intestinal Obstruction/Bowel Infarction/ Constipation (And How To Assess and Initiate Management)Document63 pagesAcute Abdomen: Part I: Intestinal Obstruction/Bowel Infarction/ Constipation (And How To Assess and Initiate Management)Rumana IslamNo ratings yet
- Hematological Disorders in Geriatric PatientsDocument18 pagesHematological Disorders in Geriatric PatientsAndre HawkNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic and Nephritic Syndrome - 2008Document65 pagesNephrotic and Nephritic Syndrome - 2008rikasusanti101001201No ratings yet
- Clinical History and Examination of Patients With Infectious DiseaseDocument43 pagesClinical History and Examination of Patients With Infectious DiseaseMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- Neoplasia Patho - 1Document53 pagesNeoplasia Patho - 1Alishba MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Methods Used in EpidemologyDocument53 pagesMethods Used in EpidemologySameera banuNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Study of Disease Patterns in PopulationsDocument22 pagesIntroduction to the Study of Disease Patterns in PopulationsEshan VermaNo ratings yet
- Shankland NHL Lancet Review PDFDocument10 pagesShankland NHL Lancet Review PDFNadhila ByantNo ratings yet
- HepatosplenomegalyDocument52 pagesHepatosplenomegalySundar NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Lymphoma: Pro - Dr.Ahmed EisaDocument45 pagesLymphoma: Pro - Dr.Ahmed EisaOmar Mohammed100% (1)
- NemaoDocument94 pagesNemaoRoxenette Gil Bernales PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Tuberculosis: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument112 pagesPediatric Tuberculosis: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentFenny RahmadaniNo ratings yet
- Base (Path Anatomy) 2014 FIRSTDocument39 pagesBase (Path Anatomy) 2014 FIRSTHarsh NimavatNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 IEN of The Lower Genital TractDocument16 pagesLecture 16 IEN of The Lower Genital TractCharisse Angelica MacedaNo ratings yet
- GastrointestinalDocument104 pagesGastrointestinalNugroho AnisNo ratings yet
- Transplantation: Presented by Santhiya K II M.SC Biotechnology 18PBT014Document54 pagesTransplantation: Presented by Santhiya K II M.SC Biotechnology 18PBT014AbiNo ratings yet
- Antineoplastic Agents 2011 Dental MARCH-1Document41 pagesAntineoplastic Agents 2011 Dental MARCH-1BinayakSwainNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Biochemistry, Volume - T. P. MommsenDocument511 pagesMetabolic Biochemistry, Volume - T. P. MommsenJesus Daniel Morales MarquezNo ratings yet
- Neglected Tropical DiseasesDocument84 pagesNeglected Tropical DiseasesAbhinesh Kr JhaNo ratings yet
- N24: Class #8 Obstructive and Inflammatory Lung Disease: Emphysema Chronic Bronchitis AsthmaDocument42 pagesN24: Class #8 Obstructive and Inflammatory Lung Disease: Emphysema Chronic Bronchitis Asthmadentist40No ratings yet
- Reproductive System Male and FemaleDocument61 pagesReproductive System Male and FemaleAsad KHAN100% (1)
- Autoimmune Disorders: DR Muhammad ZUBAIR Consultant Chemical PathologistDocument52 pagesAutoimmune Disorders: DR Muhammad ZUBAIR Consultant Chemical PathologistZubair YousafNo ratings yet
- Important QuestionsDocument31 pagesImportant QuestionssandeepNo ratings yet
- PATHO Glomerular and Tubulointerstitial DiseaseDocument43 pagesPATHO Glomerular and Tubulointerstitial DiseaseHananya ManroeNo ratings yet
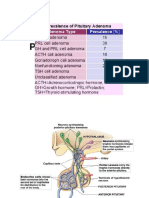
- Pituitary Tumors Engleza 2Document89 pagesPituitary Tumors Engleza 2Achmad Harun MuchsinNo ratings yet
- Managing HIV Patients & HAART Metabolic ComplicationsDocument33 pagesManaging HIV Patients & HAART Metabolic ComplicationsSimeon AdebisiNo ratings yet
- Imuune Thrombocytopenia (Itp)Document34 pagesImuune Thrombocytopenia (Itp)Roshandiep GillNo ratings yet
- Management of Lymphomas: 2018 Indian Expert ConsensusDocument24 pagesManagement of Lymphomas: 2018 Indian Expert ConsensusAndi SusiloNo ratings yet
- Uterus Pathology GuideDocument7 pagesUterus Pathology GuidefadoNo ratings yet
- Faquin Milian System and Molecular Advances in Diagnosis Salivary Gland TumorsDocument87 pagesFaquin Milian System and Molecular Advances in Diagnosis Salivary Gland TumorsJoanna Marie100% (1)
- Guru SiyagDocument34 pagesGuru SiyagRaghu VeerNo ratings yet
- What Is KundaliniDocument25 pagesWhat Is KundaliniRaghu VeerNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedics: Course Content TopicsDocument4 pagesOrthopaedics: Course Content TopicsRaghu VeerNo ratings yet
- Anesthesiology No ChangeDocument3 pagesAnesthesiology No Changeapi-19863548No ratings yet
- Community Medicine 27-03-07Document13 pagesCommunity Medicine 27-03-07Raghu VeerNo ratings yet
- ENTDocument8 pagesENTapi-19863548No ratings yet
- Obstetrics and Gynecology No ChangeDocument6 pagesObstetrics and Gynecology No Changeapi-19863548No ratings yet
- Dermotology NOCHANGEDocument3 pagesDermotology NOCHANGEapi-19863548No ratings yet
- Medicine SkillDocument6 pagesMedicine Skillapi-19863548No ratings yet
- Medicine and Allied SpecialtiesDocument12 pagesMedicine and Allied SpecialtiesRaghu VeerNo ratings yet
- General Surgery 27-03-07Document7 pagesGeneral Surgery 27-03-07Raghu VeerNo ratings yet
- Physiology 27-03-07Document7 pagesPhysiology 27-03-07Raghu VeerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 27 03Document8 pagesPharmacology 27 03Raghu VeerNo ratings yet
- Forensic MedicineDocument6 pagesForensic MedicinenklrathinamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 27 03 07Document9 pagesAnatomy 27 03 07Raghu VeerNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 27 03Document5 pagesMicrobiology 27 03Raghu VeerNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry NO CHANGEDocument6 pagesBiochemistry NO CHANGEapi-19863548No ratings yet
- Medication Safety in LactationDocument30 pagesMedication Safety in Lactationhalima alzadjaliNo ratings yet
- Jonas Salk BiographyDocument3 pagesJonas Salk BiographyhapsNo ratings yet
- The Native American Healing Herbs Bible_ 4 Books in 1_The Complete Herbalist Encyclopedia With Draws.learn the Power of 60 Healing Herbs and Essential Tools.discover 30 Remedies to Boost Wellness.Document194 pagesThe Native American Healing Herbs Bible_ 4 Books in 1_The Complete Herbalist Encyclopedia With Draws.learn the Power of 60 Healing Herbs and Essential Tools.discover 30 Remedies to Boost Wellness.Chris Hannah75% (4)
- First Responder Grant Waiver LetterDocument2 pagesFirst Responder Grant Waiver LetterepraetorianNo ratings yet
- Glossary & Introduction. 4 EditionDocument7 pagesGlossary & Introduction. 4 EditionSilviu MorteanuNo ratings yet
- Undergraduate Manual of Clinical Cases in Obstetrics GynaecologyDocument621 pagesUndergraduate Manual of Clinical Cases in Obstetrics GynaecologyTony StarkNo ratings yet
- Beneficiile Consumului de Alcool PDFDocument9 pagesBeneficiile Consumului de Alcool PDFAndrei AlbuNo ratings yet
- Reach Out.: 3rd EditionDocument100 pagesReach Out.: 3rd EditionMiffyHung100% (1)
- Nurses Role in Health AssessmentDocument5 pagesNurses Role in Health AssessmentKimberly Jane TogñoNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Merit List for DM/MCH/MD Courses July 2022Document15 pagesAIIMS Merit List for DM/MCH/MD Courses July 2022sarath6872No ratings yet
- Healthand Safety Situationsof Garments Workersin Developing Countries AStudyon BangladeshDocument13 pagesHealthand Safety Situationsof Garments Workersin Developing Countries AStudyon BangladeshA FCNo ratings yet
- Haa149Document10 pagesHaa149dadi hartonoNo ratings yet
- Food Contamination Sources 2018Document9 pagesFood Contamination Sources 2018jorge_bustos_1No ratings yet
- Nursing Philosophy FinalDocument7 pagesNursing Philosophy Finalapi-429837528100% (1)
- 2007 DoH Collaborative Recruitment Solutions in Social Care - Getting and Keeping Your WorkforceDocument49 pages2007 DoH Collaborative Recruitment Solutions in Social Care - Getting and Keeping Your WorkforcecarlselbyNo ratings yet
- Skills Fade Literature Review Final Report - PDF 60956354Document38 pagesSkills Fade Literature Review Final Report - PDF 60956354Oscar Garcia AltagraciaNo ratings yet
- Meat Supply Chain Problems & SolutionsDocument8 pagesMeat Supply Chain Problems & SolutionstinuNo ratings yet
- Can Meditation Influence Ans HopmanDocument1 pageCan Meditation Influence Ans HopmanBryan ChenNo ratings yet
- Tricking Kids Into The Perfect ExamDocument2 pagesTricking Kids Into The Perfect ExamLesterNo ratings yet
- Music Therapy PsychiatryDocument59 pagesMusic Therapy PsychiatryAlberto ChicaybanNo ratings yet
- Build Muscle and Strength at HomeDocument17 pagesBuild Muscle and Strength at HomeMuhammad RamaNo ratings yet
- Total Coliform Rule (TCR)Document2 pagesTotal Coliform Rule (TCR)rewerwerwerwewdfsdfNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NCP Template 2Document2 pagesDrug Study NCP Template 2Janico Lanz BernalNo ratings yet
- Colitis, Ulcerative: Whitney D. Lynch Ronald HsuDocument8 pagesColitis, Ulcerative: Whitney D. Lynch Ronald HsuAlexis DF SanchezNo ratings yet
- Casestudy OsuDocument3 pagesCasestudy OsuKinn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Solving AVF Cannulation ChallengesDocument6 pagesSolving AVF Cannulation ChallengesCamille EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument20 pagesAnxiety DisordersAngela BautistaNo ratings yet
- SMLE 2019 Corrections for 10th of September ExamDocument70 pagesSMLE 2019 Corrections for 10th of September ExamRight Ventricle100% (1)
- Catalogo2019 PDFDocument20 pagesCatalogo2019 PDFSora ビリディアナ PhantomhiveNo ratings yet
- Poltekkes Kemenkes Pontianak Created By:: Petresius PikaDocument8 pagesPoltekkes Kemenkes Pontianak Created By:: Petresius Pika서하중No ratings yet