Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BTEC HNC - Analytical Methods - Algebraic Methods
Uploaded by
Brendan BurrCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BTEC HNC - Analytical Methods - Algebraic Methods
Uploaded by
Brendan BurrCopyright:
Available Formats
Algebraic
Methods
Analytical Methods for
Engineers
By Brendan Burr
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
Table of Contents
TABLE OF CONTENTS...........................................................2
TASK 1................................................................................5
1.1 Solve the following polynomial division :-......................5
Solution:-.........................................................................................5
Check:-.............................................................................................6
1.2 Solve the following equation using the factor theorem :- 7
Solution:-.........................................................................................7
Check:-.............................................................................................7
1.3 Use the remainder theorem to find the remainder for :-. .8
Solution:-.........................................................................................8
Check:-.............................................................................................8
1.4 Find the remainder for the following expression :- .........9
Solution:-.........................................................................................9
Check:-...........................................................................................10
1.5 Resolve the following into partial fractions :-................11
Solution (a) :-.................................................................................11
Check:-...........................................................................................11
Solution (b) :-.................................................................................12
Check:-...........................................................................................12
Solution (c) :-.................................................................................13
Check:-...........................................................................................13
TASK 2..............................................................................14
2.1 Solve the following equations correct to 2 decimal
places :-............................................................................14
Solution (a) :-.................................................................................14
Check:-...........................................................................................14
Solution (b) :-.................................................................................15
Check:-...........................................................................................15
Solution (c) :-.................................................................................16
Check:-...........................................................................................16
2.2 The voltage across a capacitor at time t is given by :- . 17
Graph and Circuit Diagram :-.........................................................17
Solution (a) :-.................................................................................18
Check:-...........................................................................................18
Solution (b) :-.................................................................................19
Check:-...........................................................................................19
2.3 Evaluate correct to 4 significant figures.......................20
Solution (a) :-.................................................................................20
2
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
Check:-...........................................................................................20
Solution (b) :-.................................................................................21
Check:-...........................................................................................21
2.4 A telegraph wire hangs so that its shape is described
by :-..................................................................................22
Solution :-......................................................................................22
Check:-...........................................................................................23
2.5 If , find values for A and B...........................................24
Solution :-......................................................................................24
Check:-...........................................................................................25
2.6 If find values for P and Q............................................26
Solution :-......................................................................................26
Check:-...........................................................................................26
2.7 Solve the equation correct to 2 d.ps...........................27
Solution :-......................................................................................27
Check:-...........................................................................................29
TASK 3..............................................................................30
3.1 Determine the 15th term of the series 12, 17, 22, 27,.....
........................................................................................30
Solution :-......................................................................................30
Check:-...........................................................................................30
3.2 The sum of the first 10 terms of an arithmetic
progression is 200 and the common difference is 4. Find the
first term of the series.......................................................31
Solution :-......................................................................................31
Check:-...........................................................................................31
3.3 An Oil & Gas Company drills a hole 10 km deep. ...........32
Estimate the cost of drilling if the cost is 1000 for drilling
the first metre with an increase in cost of 200 per metre for
each succeeding metre......................................................32
Solution :-......................................................................................32
Check:-...........................................................................................32
3.4 Determine the 10th term of the series 2, 6, 18, 54,.......33
Solution :-......................................................................................33
Check:-...........................................................................................33
3.5 Find the sum of the first 12 terms of the series 1, 4, 16,
64,....................................................................................34
Solution :-......................................................................................34
Check:-...........................................................................................34
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
3.6 Find the sum to infinity of the series 4, 2, 1, 1/2, 1/4,.....
........................................................................................35
Solution :-......................................................................................35
3.7 Use the Binomial Series to expand ..............................36
Solution :-......................................................................................36
Check:-...........................................................................................36
3.8 (a) Expand the following in ascending powers of x as far
as the term in using the Binomial Series. ..........................37
Solution (a) :-.................................................................................37
Check:-...........................................................................................38
(b) State the limits for which the expansion is valid............38
Solution (b) :-.................................................................................38
TASK 4..............................................................................39
Please refer to Assignment 3 (Calculus)..............................39
EVALUATION.....................................................................40
CONCLUSION.....................................................................40
Books...............................................................................41
Catalogues........................................................................41
Websites...........................................................................41
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
Task 1
1.1 Solve the following polynomial division :6x 2 + 7x 5
x 1
Solution:x 1 6 x 2 + 7 x 5
6 x2
= 6x
x
6x
x 1 6x2 + 7 x 5
6 x x = 6 x2
6 x 1 = 6 x
6 x2 + 7 x 5
6 x2 6x
(Subtracting -6 from 7 gives a new denominator)
0 + 13 x 5
13 x
= 13
x
6 x + 13
x 1 6 x2 7 x 5
13 x = 13 x
13 1 = 13
13 x 5
13 x 13
(Subtracting -13 from -5 leaves the remainder)
0+8
6 x + 13
remainder + 8
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
Check:8
6 x + 13 +
( x 1) =
x 1
6 x 2 6 x + 13 x 13 + 8
6 x 2 +7 x 5
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
1.2 Solve the following equation using the factor theorem :x3
2x 2
x +
2 =
0
Solution:(
3
2
x =1
(1) =1 2 1 1 +2 =0
Hence (x-1) is a factor and x=1 is a root.
(
3
2
x =2
(2) =2 2 2 2 +2 =0
Hence (x-2) is a factor and x=2 is a root.
x = 3 ( 3) = 33 2 32 3 + 2 0
Factors of x begin to predominate at the first term, so move onto
Negative Numbers!
x = 3 ( 3) = 33 2 32 3 + 2 0
x = 2 ( 2) = 23 2 22 2 + 2 0
(
3
2
x =
1
(1) =1 2 1 1 +2 =0
Hence (x+1) is a factor and x=-1 is a root.
Therefore:
x= 1
x= 2
x3
2x2
x+
2 (x
1)(x
2 )(x +
1)
x = 1
Check:Let x = 5 :
x3 2x 2 x + 2
53 ( 2 52 ) 5 + 2 = 72
( x 1)( x 2)( x + 1)
( 5 1)( 5 2)( 5 + 1) = 72
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
1.3 Use the remainder theorem to find the remainder for :3
2
x -6 x + x -5
x-3
Solution:If ax 3 + bx 2 + cx + d is divided by ( x p ) the remainder will be
ap 3 + bp 2 + cp + d .
Therefore:
a=1
b = -6
c=1
p = 3 (After dropping the minus sign)
d = -5
) (
r = 1 33 + 6 32 + (1 3) + ( 5)
r = 27 54 + 3 5
r =
29
Check:x 2 3x 8
x 3 x 3 6x 2 + x 5
x 3 3x 2
0 3x 2 + x 5
0 3x 2 + 9 x
0 + 0 8x 5
0 + 0 8 x + 24
0 + 0 + 0 + 29
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
1.4 Find the remainder for the following expression :(3 x 2 4 x + 2 )
( x + 1)
Solution:x +1 3 x 2 4 x + 2
3x 2
= 3x
x
3x
x + 1 3x 4 x + 2
2
3 x x = 3x 2
3 x 1 = +3x
3x 2 4 x + 2
3x 2 + 3x
0 7x + 2
(The difference between -4 from 3 gives a new denominator)
7x
= 7
x
3x 7
x + 1 3x 4 x + 2
2
7 x = 7 x
7 1 = 7
7x + 2
7x 7
0+9
3x 7
remainder + 9
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
Check:If ax 2 + bx + c is divided by ( x p ) the remainder will be ap 2 + bp + c .
Therefore:
a = +3
b = -4
c = +2
p = -1
r = 3 12 + ( 4 1) + ( 2 )
r =3+ 4+ 2
r =+9
10
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
1.5 Resolve the following into partial fractions :3- x
( x 2 + 3)(x + 3)
(a)
Solution (a) :-
3 x
Ax + B
C
2
+
x + 3 ( x + 3)
x + 3 ( x + 3)
3 x
(Ax
+B )(x +
3) +
(C )(x 2 +3)
Let x = 3 :
3 3 ( ( A 3) + B )( 3 + 3) + ( C ) ( ( 3 3) + 3)
7 =B
Find the coefficients of x on both sides:
4 x 3 = A( x + 1) + B
4 = Ax + A + B
4 =A
4 x 3
( x +1) 2
( x +1) ( x +1) 2
Check:4x 3
( 7 + 1)
25
64
4
7
25
=
2
( 7 + 1) ( 7 + 1) 64
11
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
4x - 3
2
(x + 1 )
(b)
Solution (b) :4x 3
( x + 1)
A
B
+
( x + 1) ( x + 1) 2
A( x + 1)
B ( x + 1)
+
( x + 1)
( x + 1) 2
2
4x 3
4x
3 A(x +
1) +B
Let x = 1 :
( 4 1) 3 = A( 1 + 1) + B
7 =B
Find the coefficients of x on both sides:
4 x 3 = A( x + 1) + B
4 = Ax + A + B
4 =A
4 x 3
4
7
=
2
(
x
+
1
)
( x +1)
( x +1) 2
Check:Let x = 5 :
( 4 5) 3 = 17
( 5 + 1) 2 36
4
( 5 + 1) ( 5 + 1) 2
17
36
12
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
6x - 5
(x - 4)( x + 3)
(c)
Solution (c) :A
B
( x)
+
( x + a )( x + b ) ( x + a ) ( x + b )
6x
5 A(x +
3) +
B (x
4)
Let x = 3 :
( 6 3) 5 = A( 3 + 3) + B( 3 4)
23 = 7 B
B=
23
7
Let x = 3 :
( 6 4) 5 = A( 4 + 3) + B( 4 4)
19 = 7 A
A=
19
7
Therefore:
19
23
6x 5
7 +
7
( x 4)( x + 3) ( x 4) ( x + 3)
Check:Let x = 9 :
( 6 9) 5 = 49
( 9 4)( 9 + 3) 60
19
23
7 +
7 = 49
( 9 4) ( 9 + 3) 60
13
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
Task 2
2.1 Solve the following equations correct to 2 decimal places :(a) ln ( x ) = 5.4
Solution (a) :x = ANTILOG ( 5.4 )
x =
2
2
1
.4
1
to 2 Decimal Places
Check:ln (221 .41
) =5.4
14
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
(b) 5 = 8(1 e 4 )
Solution (b) :Transposing gives:
t
5
=e 4
8
3
=e 4
8
Take Log of both sides:
t
3
LN e 4 = LN
8
Using the Laws of Logs:
LN ( A B ) = LN ( A) + LN ( B )
A
LN = LN ( A) LN ( B )
B
LN A 2 = 2 LN ( A)
( )
So:
t
3
LN ( e ) = LN
4
8
t
3
= LN
4
8
3
t = 4 LN
8
t = 3.923317012
t =
3.92
(Seconds) to 2 Decimal Places
Check:3.92
5 = 81 e 4
15
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
(c) 4 ( y +1) = 2 ( y 2 )
Solution (c) :Take the Log of both sides:
Log 4 ( y +1) = Log 2 ( y 2 )
Log
( A) N
=NLog
( A)
( y + 1) Log 4 = ( y 2) Log 2
Multiply out the brackets
( yLog 4) + ( Log 4) = ( yLog 2) ( 2 Log 2)
2 Log 2 + Log 4 = y ( Log 2 Log 4)
So:
y=
2( Log 4)
( Log 2 Log 4)
to 2 Decimal Places
y =
4.00
Check:4 ( 4 + 1) =
1
64
2 ( 4 2 ) =
1
64
16
Join like terms
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
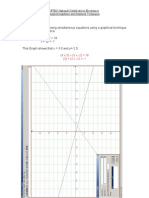
2.2 The voltage across a capacitor at time t is given by :t
v = 10(1 - e- CR )
where C = 10 F and R = 20 k .
Determine :(a)
The time for the voltage to reach 5 V.
(b)
The voltage after 1 mS.
Graph and Circuit Diagram :-
17
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
Solution (a) :C R =
(10 10 ) ( 20 10 ) =
6
=
0.2 S
e
c
o
n
d
s
So:
t
0
5 = 101 e .2
5
= 1 e 0. 2
10
LN ( 0.5) =
t
0 .2
t = 0.2 LN ( 0.5)
t = 0.1386294361
t =
0.13
9
(Seconds) to 3 Decimal Places
Check:0.139
v = 10 1 e 0.2
v=5
18
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
Solution (b) :t
0
If v = 101 e .2 and t = 0.001 then:
0.001
v = 101 e 0.2
v =0.05
Volts
Check:-
19
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
2.3 Evaluate correct to 4 significant figures.
(a)
cosh 2.47
Solution (a) :COSH ( x )
e x + e x
2
e
COSH ( 2.47 )
2.47
+ e 2.47
2
e 2.47 + e 2.47
= 5.953515855
2
C
O
SH
(2.47 ) =5.954
to 4 significant figures
Check:-
20
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
(b)
sinh 1.385
Solution (b) :SINH ( x )
e x e x
2
SINH (1.385 )
e 1.385 e 1.385
2
e 1.385 e 1.385
= 1.872251053
2
SIN
H
(1.385 ) =
1.872
to 4 significant figures
Check:-
21
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
2.4 A telegraph wire hangs so that its shape is described by :x
20
y = 20 ch
Evaluate correct to 3 significant figures the value of y when x is 10.
Solution :y = 20 ch
10
20
y = 20CH ( 0.5)
y = 22 .6
to 3 Significant Figures
22
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
Check:-
23
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
2.5 If 4 e x - 5 e x = A SH x + B CH x , find values for A and B.
Solution : e x ex
RHS of Equation A
2
e x + ex
+ B
2
e x e x
ex ex
A
+ B 2 + 2
2
2
ex
e x
ex
ex
A
+B
+B
2
2
2
2
Collecting the like terms together gives:
B B
A
A
e x + e x + e x e x
2 2
2
2
A B B A
+ e x + e x
2 2 2 2
Factorise by looking at the LHS, giving:
(1) 4 = A + B
2
( 2 ) 5 = B A
2
Multiply both equations by 2, giving:
( 3) 8 = A + B
( 4) 10 = B A
Adding equations (3) and (4) together gives:
2 = 2B
Therefore
B =
24
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
Substituting B back into equation (1) gives:
4=
A 1
+
2
2
8 = A 1
A = 8 +1
So:
A =9
Therefore the equation is:
4e x
5e x
9 SH
(x )
1C
H (x )
Check:Let x = 4 :
4e 4 5e 4 = 218 .3010219
( 9SH 4) + ( 1CH 4 ) = 218 .3010219
25
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
2.6 If P. e x - Q. e x = 2.CH x + 6.SH x find values for P and Q.
Solution :CH ( x ) = COSH ( x ) =
e x ex
+
2
2
1 x 1 x
e + e
2
2
SH ( x ) = SINH ( x ) =
e x + ex
2
e x ex
2
e x ex
2
2
1
1
= e x ex
2
2
So:
1
1
1
2 e x + e x + 6 e x e x
2
2
2
Multiply out the brackets:
e x + e x + 3e x 3e x
4e x 2e x
P= 4
Q= 2
Check:Let x = 9 :
4e 9 2e 9 = 32412
2CH 9 + 6SH 9 = 32412
26
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
2.7 Solve the equation 3.52 CH x + 8.42 SH x = 5.32 correct to 2 d.ps.
Solution :Step 1: replace COSH(x) and SINH(x) with definitions in terms of
EXP(x).
e x + e x
3.52
2
e x e x 2
+ 8.42
= 5.32
2
Step 2: remove the divisor of 2.
3.52 x
8.42 x
e + ex +
e e x = 5.32
2
2
1.76 e x + e x + 4.21 e x e x = 5.32
1.76e x + 1.76e x + 4.21e x 4.21e x = 5.32
Step 3: collect the like terms together.
5.97e x 2.45e x = 5.32
5.97e x 2.45e x 5.32 = 0
Step 4: multiply the LHS by e x .
5.97e x e x 2.45e x e x 5.32e x = 0
( )
2.45 e x + x 5.32e x = 0
( )
2.45e 0 5.32e x = 0
( )
2.45 5.32e x = 0
( )
5.32e x 2.45 = 0
5.97 e x
5.97 e x
5.97 e x
5.97 e x
27
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
This then looks like a Quadratic Equation, where:
y = ex
a = 5.97
b = 5.32
c = .245
5.97 y 2 5.32 y 2.45 = 0
Using the formula for solving Quadratic Equations in terms of y gives:
y=
b b 2 4ac
2a
y=
5.32 5.32 2 4( 5.97 2.45)
2 5.97
y=
5.32 28.3024 4( 14.6265 )
11.94
y=
5.32 86.8084
11.94
y=
5.32 + 9.317102554
11.94
y =
1.225887986
y=
5.32 9.317102554
11.94
y =
0.3
3
4
7
6
5
7
0
8
(this has no real solution so ignore!!!)
28
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
Replacing y with e x gives:
e x = 1.225887986
LNe x = LN (1.225887986 )
x = 0.2036654679
x =
0.20
to 2 Decimal Places
Check:3.5
2 C
H
(0.20 ) +
8.4
2
S
H
(0.20 ) =
5.2
9
(Note with the full answer of x = 0.2036654679 the equation equals
5.319999999, shown in the assignment as 5.32!)
29
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
Task 3
3.1 Determine the 15th term of the series 12, 17, 22, 27,.....
Solution :N
th
Term
=a +(N
1)d
a = 1st Term
d = Common Difference
a=12
d=5
N =15
N 15 = 12 + ( (15 1) 5)
N 15 =82
Check:1
12
2
17
3
22
4
27
5
32
6
37
7
42
8
47
30
9
52
10
57
11
62
12
67
13
72
14
77
15
82
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
3.2 The sum of the first 10 terms of an arithmetic progression is 200 and the
common difference is 4. Find the first term of the series.
Solution :Sn =
n
{2a + ( n 1) d }
2
a= ?
d=4
n = 10
S1 0 = 2 00
200 =
10
{ 2a + (10 1) 4}
2
200
= { 2a + ( 9 4 ) }
5
40 = 2a + 36
40 36 = 2a
4
=a
2
a =2
Check:-
1
2
2
6
3
10
4
14
5
18
6
22
2 + 6 + 10 + 14 + 18 + 22 + 26 + 30 + 34 + 38
= 200
31
7
26
8
30
9
34
10
38
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
3.3 An Oil & Gas Company drills a hole 10 km deep.
Estimate the cost of drilling if the cost is 1000 for drilling the first
metre with an increase in cost of 200 per metre for each succeeding
metre.
Solution :Sn =
n
{2a + ( n 1) d }
2
a = 1,0 00
d = 20 0
n = 1 0,000
S10,0 00 = ?
S10,000 =
S 10 , 000
10,000
{ ( 2 1,000 ) + (10,000 1) 200}
2
=10 ,009 ,000 ,000
Check:-
32
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
3.4 Determine the 10th term of the series 2, 6, 18, 54,....
Solution :The nth term is determined using
ar n 1
a= 2
r= 3
Therefore:
N 10 = ( 2 )( 3)
10 1
N 10 =39366
Check:1
2
2
6
3
18
4
54
5
162
6
486
33
7
1458
8
4374
9
10
13122 39366
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
3.5 Find the sum of the first 12 terms of the series 1, 4, 16, 64,....
Solution :-
Sn =
a 1 rn
(1 r )
Sn =
a r n 1
( r 1)
When r<1
When r>1
a=1
N=12
r= 4
Sn =
1 412 1
4 1
S n =5592405
Check:-
1 2 3 4 5
6
1 4 16 64 256 102
4
7
8
9
10
11
12
4096 16384 65536 262144 1048576 4194304
1 + 4 +16 + 64 + 256 +1024 + 4096 +16384
=5592405
34
+ 65536
+ 262144
+1048576
+ 4194304
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
3.6 Find the sum to infinity of the series 4, 2, 1, 1/2, 1/4,.....
Solution :S =
a
1 r
When -1 < r < 1.
a= 4
r=
1
2
S =
4
1 0.5
S =8
35
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
3.7 Use the Binomial Series to expand (1 + x )6
Solution :The binomial expansion of ( q + p ) n is:
q n +nq n 1 p +
n( n 1) n 2 2 n( n 1)( n 2 ) n 3 3
q
p +
q
p +...
2 1
3 2 1
Therefore the binomial expansion of (1 + x ) 6 is:
(1 + x ) 6
((
((6 1 ) x ) + ( x )
1
(1 +x )6
) ((
) ((
) ((
(1) + 6 15 x + 15 14 x 2 + 20 13 x 3 + 15 12 x 4 +
5
1 +6 x +
15 x 2 +20 x 3 +
15 x 4 +6 x 5 +x 6
Check:Let x = 4 :
(1 + 4) 6 =15625
1 + ( 6 4 ) + (15 4 2 ) + (20 4 3 ) + (15 4 4 ) + (6 4 5 ) + (4 6 ) =15625
36
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
3.8 (a) Expand the following in ascending powers of x as far as the term in
3
x using the Binomial Series.
1
(4 + x)
Solution (a) :1
4+ x
1
x
2 1 +
4
1
4+x
1
x
1 +
2
4
1
2
x2
2 1 +
4
1
x
1 +
2
4
1
2
Therefore expanding 1 1 + x
2
4
1
2
in terms of (1 + x ) n gives:
1 1
1
1
1
1
2
1
x
x
2
2
2
2
1 2 + 1
+
1
+
4
2
2 1
4
1
1
4 + x 2 1 1 1
1 2 1
3
2 2 2
2 3 x
1
+ ...
4
3 2 1
1
4+ x
1 1 1
3 1
5 1
1 x + x 2 x 3 ...
2 2 4
8 16
16 64
37
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Brendan Burr
Algebraic Methods
1
4 +x
1
2
1 3
5
2
3
1 8 x + 128 x 1024 x ...
Check:Let x = 3 :
1
4+3
= 0.377964473
1 1
3
5
1 3 +
32
3 3 ... = 0.3520507813
2 8
128
1024
There is a difference of 0.02591369175.
With the additional terms of x N the 0.02591369175 will gradually
decrease and eventually equal 0.
The discrepancy comes from the expansion only being to x 3 .
(b) State the limits for which the expansion is valid.
Solution (b) :The expansion in (a) is valid provided
x <4
OR
4 < x < +4
38
x
< 1 . i.e.
4
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
Task 4
Please refer to Assignment 3 (Calculus).
39
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
Evaluation
During this assignment I found that the notes taken from classes helped
considerably.
Beginning with the Polynomial Division, I found confusing at first. This is
simply because today we very rarely use long division, and the method used
to confuse me at school so I have very easily forgotten how to use it! To
resolve the problem I decided to recap on the long division method by using
the Higher Engineering Mathematics Book by John Bird. I could then move
onto inserting letters in the place of numbers using the same methods and all
soon became clear.
With the Factor Theorem I quickly understood that the key part of the theory is
to guess a suitable number to use. Fortunately I was able to determine the
required factors quite quickly.
The Remainder Theorem question was also straight forward as it simply
involved inserting numbers for letters in a predetermined equation.
I had a bit of difficulty with 1.5a as for some reason I was getting the
denominators on the RHS around the wrong way, this meant after getting
values for A,B and C I was getting dissimilar matches between the two sides.
Using my notes from class I was able to complete and check 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4,
2.5 and 2.6, but I struggled a little bit on 2.7.
When I came to check 2.7, I found that when replacing x with my answer, I did
not get 5.32. I went back over the work a couple of times before reaching the
0.20 answer required to get the 5.32.
We had touched on Arithmetic and Geometric Progressions in previous years
so this was fairly straight forward.
I had learned to do the Binomial Series from the Statistics Assignment,
however expanding a reciprocal square root term was new to me. I
completed this before the going through this in class and then used my notes
from class to double check my workings, which seem to be accurate.
Conclusion
I am very pleased with this assignment and believe it is one of the best I have
handed in. My consistency in the presentation has taken a lot of time and
effort.
Due to the amount of work already completed I decided to leave Task 4 until
the Calculus Assignment.
I feel I understand the use of checking my answers by simply using a different
method. This also helps relieves the pressure when handing the assignment
in as the answers are unlikely to be incorrect if they have also been checked.
I will continue to check my answers by using multiple methods, as this is a
similar approach to what happens on site at work.
40
Brendan Burr
BTEC Higher National Certificate in Electronics
Algebraic Methods
Bibliography
Through guidance from my lecturer, the following text books, catalogues and
websites I was able to complete this assignment:
Books
Higher Engineering Mathematics (John Bird)
ISBN: 0-7506-8152-7
Catalogues
N/A
Websites
N/A
41
You might also like
- BTEC HNC - Analytical Methods - Statistics and ProbabilityDocument20 pagesBTEC HNC - Analytical Methods - Statistics and ProbabilityBrendan Burr50% (2)
- BTEC HNC - Control Systems and Automation - Use Laplace Transforms To Determine System ParametersDocument24 pagesBTEC HNC - Control Systems and Automation - Use Laplace Transforms To Determine System ParametersBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Analytical Methods - CalculusDocument43 pagesBTEC HNC - Analytical Methods - CalculusBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- Applied CalculasDocument15 pagesApplied Calculasmohammad rashid tkNo ratings yet
- BTEC NC - Further Mathematics For Technicians - Applied CalculusDocument15 pagesBTEC NC - Further Mathematics For Technicians - Applied CalculusBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Systems Analysis and DesignDocument5 pagesUnit 9 Systems Analysis and DesignPrakash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Selected HNC in Computing and Systems Development Units Unit 6 Management in Information TechnologyDocument7 pagesSelected HNC in Computing and Systems Development Units Unit 6 Management in Information TechnologyETClondonNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Science - Analyse Dynamic Engineering SystemsDocument15 pagesBTEC HNC - Science - Analyse Dynamic Engineering SystemsBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- Module: CP1234: The School of Computing and Information TechnologyDocument23 pagesModule: CP1234: The School of Computing and Information TechnologySteve AnddrewNo ratings yet
- AP Macro Problem Set 3 StudentDocument2 pagesAP Macro Problem Set 3 Studentspfitz11No ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Science - Analyse Static Engineering SystemsDocument23 pagesBTEC HNC - Science - Analyse Static Engineering SystemsBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- Travel Time Data Collection Handbook GuideDocument341 pagesTravel Time Data Collection Handbook GuiderasheamNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Electrical and Electronic Principles - Investigate Two Port NetworksDocument26 pagesBTEC HNC - Electrical and Electronic Principles - Investigate Two Port NetworksBrendan Burr100% (2)
- Coulomb's Law MC Questions PDFDocument7 pagesCoulomb's Law MC Questions PDFLynn Hollenbeck BreindelNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Microprocessor Systems - Investigate Microprocessor Based SystemsDocument16 pagesBTEC HNC - Microprocessor Systems - Investigate Microprocessor Based SystemsBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Analytical Methods - Trigonometric MethodsDocument34 pagesBTEC HNC - Analytical Methods - Trigonometric MethodsBrendan Burr100% (1)
- Taguchi Matrix-Worked Out ExampleDocument3 pagesTaguchi Matrix-Worked Out ExampleshekarthimmappaNo ratings yet
- SAAD AssignmentDocument115 pagesSAAD AssignmentParvinder McCartneyNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio AnalysisDocument19 pagesFinancial Ratio Analysisssophal100% (2)
- Heatpump ApplicationDocument2 pagesHeatpump ApplicationsandyolkowskiNo ratings yet
- Control (Management) : Navigation SearchDocument4 pagesControl (Management) : Navigation SearchnishejprakashNo ratings yet
- Understanding Heat PumpsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Heat PumpsSyamim HamizanNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Combinational and Sequential Logic - Design and Build Circuits Using Combinational LogicDocument16 pagesBTEC HNC - Combinational and Sequential Logic - Design and Build Circuits Using Combinational LogicBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- Very Most Basic Things You Should Know About Six SigmaDocument6 pagesVery Most Basic Things You Should Know About Six Sigmatcalhoun1285100% (1)
- Memory map for Canon DSLRsDocument42 pagesMemory map for Canon DSLRsa5OolNo ratings yet
- Industrial Engineering: Faculty - Er. Ruchita JoshiDocument71 pagesIndustrial Engineering: Faculty - Er. Ruchita Joshiaqsa imranNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information Systems ArchitectureDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Information Systems Architecturevicrattlehead2013No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture Notes on Ideal FlowDocument22 pagesFluid Mechanics Lecture Notes on Ideal FlowAlsharksi AviationNo ratings yet
- LP III Lab ManualDocument8 pagesLP III Lab Manualsaket bharati100% (1)
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentHaziq KhaliquzzamanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 TrigonometryDocument36 pagesUnit 3 TrigonometryHanif AshranNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic MechinesDocument24 pagesHydraulic Mechinesdr hs govardhana swamyNo ratings yet
- Structured Systems Analysis and Design Method, A Set of Standards Developed in The Early 1980sDocument3 pagesStructured Systems Analysis and Design Method, A Set of Standards Developed in The Early 1980sNidhiNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Engineering Project - AllDocument155 pagesBTEC HNC - Engineering Project - AllBrendan Burr100% (5)
- Tom's TEFL - Teacher's Easter Egg Hunt KeyDocument2 pagesTom's TEFL - Teacher's Easter Egg Hunt KeyTom's TEFLNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Game TheoryDocument8 pagesGlossary of Game TheoryK Krishna RaoNo ratings yet
- Carpenters' Tools: Steel Squares and Electrical TapeDocument2 pagesCarpenters' Tools: Steel Squares and Electrical TapeToy AquinoNo ratings yet
- Teaching English As A Foreign / Second Language - A HandoutsDocument34 pagesTeaching English As A Foreign / Second Language - A HandoutsAsma Haseeb QaziNo ratings yet
- Unit 16 Engineering Drawing For TechniciansDocument13 pagesUnit 16 Engineering Drawing For TechniciansMugaya Kevin Francis100% (1)
- SCHEDULEDocument35 pagesSCHEDULEVictor SampaNo ratings yet
- Inequalities Made EasyDocument17 pagesInequalities Made EasysamiNo ratings yet
- Work Study Definition, Techniques, and ToolsDocument15 pagesWork Study Definition, Techniques, and ToolsSuken ShahNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Tray ManualDocument6 pagesRectangular Tray ManualAbhishek MouryaNo ratings yet
- Gantt Chart FormatDocument1 pageGantt Chart FormatamanNo ratings yet
- BTEC Student Handbook: Pearson BTEC Level 3 National Extended Diploma in Engineering (NQF)Document12 pagesBTEC Student Handbook: Pearson BTEC Level 3 National Extended Diploma in Engineering (NQF)Brill brianNo ratings yet
- Stepwise Multiple Testing Procedure: Emmanuel D. Kpeglo April 27, 2019Document1 pageStepwise Multiple Testing Procedure: Emmanuel D. Kpeglo April 27, 2019Emmanuel kpegloNo ratings yet
- XII Linear Programming AssignmentDocument2 pagesXII Linear Programming AssignmentCRPF SchoolNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Engineering Maths SyllabusDocument6 pagesUnit 2 Engineering Maths SyllabusmikeNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory NPTEL CourseDocument289 pagesGraph Theory NPTEL CourseLalita snigdhaNo ratings yet
- DOE Course Part 13 - Dimensional AnalysisDocument47 pagesDOE Course Part 13 - Dimensional AnalysisNicolasNo ratings yet
- Time Study WorksheetDocument1 pageTime Study WorksheetAjibola H. MartinsNo ratings yet
- (Please The Slide Show To Begin) : StartDocument32 pages(Please The Slide Show To Begin) : StartSatish RaoNo ratings yet
- Course Code ME-325: Engineering EconomicsDocument36 pagesCourse Code ME-325: Engineering EconomicsGet-Set-GoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 MAT183 AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignment 2 MAT183 AssignmentFarid Danial100% (1)
- The Dot and Cross ProductDocument9 pagesThe Dot and Cross ProductallovidNo ratings yet
- Math Connections, Course 2 PDFDocument205 pagesMath Connections, Course 2 PDFLori Longo100% (1)
- Math Connects Course 2Document104 pagesMath Connects Course 2Carlos Calderon100% (3)
- Introduction to SAT/SMT Solvers and Symbolic ExecutionDocument85 pagesIntroduction to SAT/SMT Solvers and Symbolic ExecutionqdwqdNo ratings yet
- Study Guide and Intervention and Practice Workbook: PDF ProofDocument205 pagesStudy Guide and Intervention and Practice Workbook: PDF ProofAuthor academics100% (1)
- The Hitchhiker S Guide To The Programming ContestsDocument81 pagesThe Hitchhiker S Guide To The Programming ContestsAadheeshwar VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Microprocessor Systems - Investigate Microprocessor Based SystemsDocument16 pagesBTEC HNC - Microprocessor Systems - Investigate Microprocessor Based SystemsBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Engineering Project - AllDocument155 pagesBTEC HNC - Engineering Project - AllBrendan Burr100% (5)
- BTEC HNC - Engineering Design - Prepare A Design SpecificationDocument12 pagesBTEC HNC - Engineering Design - Prepare A Design SpecificationBrendan Burr100% (10)
- BTEC HNC - Business Systems - Manage Work Activities To Achieve Organisational ObjectivesDocument19 pagesBTEC HNC - Business Systems - Manage Work Activities To Achieve Organisational ObjectivesBrendan Burr50% (2)
- BTEC HNC - Science - Investigate Information and Energy Control SystemsDocument28 pagesBTEC HNC - Science - Investigate Information and Energy Control SystemsBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Control Systems and Automation - Use Analytical Techniques To Form Models of Systems and ProcessesDocument43 pagesBTEC HNC - Control Systems and Automation - Use Analytical Techniques To Form Models of Systems and ProcessesBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Business Systems - Select and Apply Costing Systems and TechniquesDocument11 pagesBTEC HNC - Business Systems - Select and Apply Costing Systems and TechniquesBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Control Systems and Automation - Examine Process Controllers Using Control PhilosophiesDocument13 pagesBTEC HNC - Control Systems and Automation - Examine Process Controllers Using Control PhilosophiesBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Control Systems and Automation - Equations To Determine System ParametersDocument37 pagesBTEC HNC - Control Systems and Automation - Equations To Determine System ParametersBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Business Systems - Applied Project Planning and Scheduling Methods For A ProjectDocument13 pagesBTEC HNC - Business Systems - Applied Project Planning and Scheduling Methods For A ProjectBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Business Systems - Financial Planning and ControlDocument13 pagesBTEC HNC - Business Systems - Financial Planning and ControlBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Electrical and Electronic Principles - Investigate Two Port NetworksDocument26 pagesBTEC HNC - Electrical and Electronic Principles - Investigate Two Port NetworksBrendan Burr100% (2)
- BTEC HNC - Science - Analyse Dynamic Engineering SystemsDocument15 pagesBTEC HNC - Science - Analyse Dynamic Engineering SystemsBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Science - Application of DC and AC TheoryDocument36 pagesBTEC HNC - Science - Application of DC and AC TheoryBrendan Burr100% (1)
- BTEC HNC - Science - Analyse Static Engineering SystemsDocument23 pagesBTEC HNC - Science - Analyse Static Engineering SystemsBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Electronics - Investigate Types of AmplifierDocument19 pagesBTEC HNC - Electronics - Investigate Types of AmplifierBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Analytical Methods - Trigonometric MethodsDocument34 pagesBTEC HNC - Analytical Methods - Trigonometric MethodsBrendan Burr100% (1)
- BTEC HNC - Electronics - Investigate Circuits With FeedbackDocument23 pagesBTEC HNC - Electronics - Investigate Circuits With FeedbackBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Electrical and Electronic Principles - Investigate Transients in RLC CircuitsDocument20 pagesBTEC HNC - Electrical and Electronic Principles - Investigate Transients in RLC CircuitsBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Electronics - Investigate Signals and NoiseDocument21 pagesBTEC HNC - Electronics - Investigate Signals and NoiseBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Electrical and Electronic Principles - Investigate Complex WavesDocument21 pagesBTEC HNC - Electrical and Electronic Principles - Investigate Complex WavesBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Electrical and Electronic Principles - Investigate Circuit TheoryDocument38 pagesBTEC HNC - Electrical and Electronic Principles - Investigate Circuit TheoryBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC NC - Further Maths For Technicians - Applied Trigonometric TechniquesDocument5 pagesBTEC NC - Further Maths For Technicians - Applied Trigonometric TechniquesBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC HNC - Combinational and Sequential Logic - Design and Build Circuits Using Combinational LogicDocument16 pagesBTEC HNC - Combinational and Sequential Logic - Design and Build Circuits Using Combinational LogicBrendan BurrNo ratings yet
- BTEC NC - Further Mathematics For Technicians - Applied Algebraic and Graphical TechniquesDocument14 pagesBTEC NC - Further Mathematics For Technicians - Applied Algebraic and Graphical TechniquesBrendan Burr100% (1)
- VHDL ExperimentsDocument55 pagesVHDL Experimentssandeepsingh93No ratings yet
- Equipment DetailsDocument10 pagesEquipment Detailsimranjani.skNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planning Product-Based Performance TaskDocument8 pagesLesson Planning Product-Based Performance TaskMaricarElizagaFontanilla-LeeNo ratings yet
- Sumitomo Catalog1Document17 pagesSumitomo Catalog1metalartbielskoNo ratings yet
- CT Selection RequirementsDocument35 pagesCT Selection RequirementsRam Shan100% (1)
- Assembly Procedure For The 793C Off-Highway Truck (7000, 7006, 7960) CaterpillarDocument129 pagesAssembly Procedure For The 793C Off-Highway Truck (7000, 7006, 7960) Caterpillarcapacitacion aapNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Experimental Design Energy Transfer (Mug Experiment)Document3 pagesWeek 3: Experimental Design Energy Transfer (Mug Experiment)Kuhoo UNo ratings yet
- Application Research of MRAC in Fault-Tolerant Flight ControllerDocument1 pageApplication Research of MRAC in Fault-Tolerant Flight ControlleradcadNo ratings yet
- AOAC BAX Assay Listeria Monocytogenes RT 121402Document18 pagesAOAC BAX Assay Listeria Monocytogenes RT 121402Yesenia Borja ArroyoNo ratings yet
- EO and EO-2 Metric Bite Type Fittings: The Fitting AuthorityDocument62 pagesEO and EO-2 Metric Bite Type Fittings: The Fitting AuthorityZahir KhiraNo ratings yet
- Selection of Dryers I - IndiaDocument38 pagesSelection of Dryers I - Indiasilvership2291100% (1)
- Certificate: Shear MachineDocument3 pagesCertificate: Shear MachinegilbertoNo ratings yet
- Quizlet-Philippine Electrical CodeDocument2 pagesQuizlet-Philippine Electrical Codena zafira0% (1)
- Ring Spinning MachineDocument25 pagesRing Spinning Machinemahmuda chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 3D Reinforcement of Stiffener-To-Skin T-Joints by Z-Pinning and TuftingDocument9 pages3D Reinforcement of Stiffener-To-Skin T-Joints by Z-Pinning and TuftingLouis GrouNo ratings yet
- Seamless Steel Tubes and Pipes For BoilersDocument20 pagesSeamless Steel Tubes and Pipes For BoilersABChungBANo ratings yet
- Effect of SR, Na, Ca & P On The Castability of Foundry Alloy A356.2Document10 pagesEffect of SR, Na, Ca & P On The Castability of Foundry Alloy A356.2jose.figueroa@foseco.comNo ratings yet
- Section 3 - Vibration MeasurementDocument24 pagesSection 3 - Vibration MeasurementAbbas AkbarNo ratings yet
- Drum RudimentsDocument4 pagesDrum Rudimentsmaame nyarkoaNo ratings yet
- POWER Nav1 - MIDTERM - Topic 1 & 2Document31 pagesPOWER Nav1 - MIDTERM - Topic 1 & 2CLIJOHN PABLO FORD100% (1)
- Experiment03 PCM-DecodingDocument10 pagesExperiment03 PCM-DecodingMary Rose P Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Business Calculus NotesDocument38 pagesBusiness Calculus NotesTom KowalskiNo ratings yet
- 10th Geometrical ConstructionDocument2 pages10th Geometrical Constructionapi-242227794100% (1)
- Steel Design 6 April 2023 PDFDocument2 pagesSteel Design 6 April 2023 PDFTristan CatapangNo ratings yet
- Profit Signals How Evidence Based Decisions Power Six Sigma BreakthroughsDocument262 pagesProfit Signals How Evidence Based Decisions Power Six Sigma BreakthroughsM. Daniel SloanNo ratings yet
- TOS in PRE-CALCULUSDocument2 pagesTOS in PRE-CALCULUSSerjohnRapsingNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Modelling & Simulation GuideDocument96 pagesReservoir Modelling & Simulation GuideyouungNo ratings yet
- LED Linear Highbay LightingDocument7 pagesLED Linear Highbay LightingMohammed YasarNo ratings yet
- Mole Conversions Extra Practice Answer KeyDocument1 pageMole Conversions Extra Practice Answer Keyapi-376281962No ratings yet
- QNX Neutrino RTOS Building Embedded SystemsDocument248 pagesQNX Neutrino RTOS Building Embedded SystemsLarken BradynNo ratings yet