Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nalbuphine (Nubain)
Uploaded by
Adrianne BazoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nalbuphine (Nubain)
Uploaded by
Adrianne BazoCopyright:
Available Formats
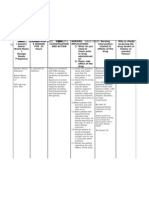
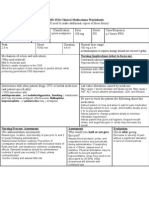
NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications Worksheets
Generic Name Trade Name Classification Dose Route Time/frequency
Nalbuphine Nubain Opioid analgesics 2mg IVP PRN
Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range
30 min 2-3 min 3-6 hr 0.3-3mg/kg over 10-15 min
Why is your patient getting this medication For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or
Pain r/t knee surgery solutions
Y-Site Incompatibility: ♦cefepime ♦methotrexate ♦nafcillin
♦piperacillin/tazobactam ♦ sargramostim ♦sodium bicarbonate
Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
(Why med ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactions
Binds to opiate receptors in the CNS, alters the Hypersensitivity, hypothyroidism,
perception of and responses to painful stimuli
while producing generalized CNS depression Common side effects
Dizziness, headache, sedation, dry mouth, nausea,
vomiting, clammy feeling, sweating
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or Lab value alterations caused by medicine
herbal medicines (ask patient specifically) May cause increased serum amylase and lipase concentrations
Be sure to teach the patient the following about this
medication
May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Advise patient to call for
assistance when ambulating and to avoid driving or other activities
requiring alertness until response to the medication is known. Caution
patient to change positions slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension.
Advise patient that frequent mouth rinses, good oral hygiene, and
sugarless gum or candy may decrease dry mouth. Encourage patient to
turn, cough, and breathe deeply every 2 hr to prevent atelectasis
Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this Check after giving
Assess type, location, and intensity of pain med? Decrease in severity of pain
before and 1 hr after IM or 30 min (peak) after Toxicity and Overdose: If an opioid without significant alteration in
IV administration. When titrating opioid antagonist is required to reverse respiratory level of consciousness or
doses, increases of 25-50% should be depression or coma, naloxone (Narcan) is the respiratory status
administered until there is either a 50% antidote.
reduction in the patient's pain rating on a
numeric or visual analogue scale or the patient
reports satisfactory pain relief. A repeat dose
can be safely administered at the time of the
peak if previous dose is ineffective and side
effects are minimal. Patients requiring doses
higher than 20 mg should be converted to an
opioid agonist.
Assess blood pressure, pulse, and
respirations before and periodically during
administration. If respiratory rate is
<10/min, assess level of sedation.
Physical stimulation may be sufficient to
prevent significant hypoventilation. Dose
may need to be decreased by 25-50%.
You might also like
- Med 3 Drug StudyDocument12 pagesMed 3 Drug StudyJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageGeneric Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesmaemalabonNo ratings yet
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToDocument2 pagesDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- IsoketDocument2 pagesIsoketJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Drug LisinoprilDocument1 pageDrug LisinoprilSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Dopamine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageDopamine HydrochlorideJoannes SanchezNo ratings yet
- Enoxaparin (Lovenox)Document1 pageEnoxaparin (Lovenox)ENo ratings yet
- Formoterol Gonzaga.Document2 pagesFormoterol Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- EsomeprazoleDocument2 pagesEsomeprazolekpanggat100% (2)
- Lowering Cholesterol with EzetimibeDocument2 pagesLowering Cholesterol with EzetimibeFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- AmilorideDocument1 pageAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- Drug Study FORTDocument3 pagesDrug Study FORTLysa Mae EleazarNo ratings yet
- Drug Stidy TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Stidy TramadolRez ApegoNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Enalapril MaleateDocument3 pagesEnalapril MaleatelichunghkNo ratings yet
- Terbutaline SulfateDocument2 pagesTerbutaline SulfateRhoellet VenzonNo ratings yet
- ChlorphenamineDocument1 pageChlorphenaminereinaNo ratings yet
- AeknilDocument2 pagesAekniljaycey24No ratings yet
- Aspirin: Generic NameDocument4 pagesAspirin: Generic NameGwww BabababaNo ratings yet
- PropranololDocument6 pagesPropranololanon_678895677No ratings yet
- Fentanyl Citrate Drug StudyDocument1 pageFentanyl Citrate Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Glipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardDocument1 pageGlipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudymichpaduaNo ratings yet
- DORMICUMDocument1 pageDORMICUMArian Rose100% (1)
- Doxazosin MesylateDocument2 pagesDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Casilan, Ynalie Drug Study (Morphine)Document5 pagesCasilan, Ynalie Drug Study (Morphine)Ynalie CasilanNo ratings yet
- OB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesOB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidJustin Ancog100% (1)
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamStephanie PeNo ratings yet
- SpironolactoneDocument2 pagesSpironolactoneKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Bicillin C-R Penicillin G: Drug StudyDocument1 pageBicillin C-R Penicillin G: Drug StudyChristine Pialan Salimbagat100% (1)
- DexmedetomidineDocument2 pagesDexmedetomidineapt48 ukwmsNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Diphenhydramine)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac and NalbuphineDocument4 pagesKetorolac and NalbuphineMaureen Campos-PineraNo ratings yet
- JM DrugDocument3 pagesJM DrugVerdie B. NgayanNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy OrsdDocument10 pagesDrugstudy OrsdRafmar A. SalundaguitNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Classification of opioid analgesicsDocument2 pagesClassification of opioid analgesicsNylia Atibi100% (1)
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinJoi Danielle Tabares IsturisNo ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument6 pagesDrugs StudyAllan MacacapagalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument5 pagesDrug Study ICUEcko MoawiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DelanDocument3 pagesDrug Study - DelanJuliana Sophia DelanNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin-Tazobactam Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesPiperacillin-Tazobactam Nursing ResponsibilitiesAnalyn SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyKristine Joy A. AniNo ratings yet
- Dextrose Injection Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDextrose Injection Nursing ResponsibilitiesSalwa ZeinNo ratings yet
- PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesPrednisoloneKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cushing's SyndromeDocument5 pagesDrug Study Cushing's SyndromeSelena MarieNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide Drug Study: Uses, Side Effects, Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesMetoclopramide Drug Study: Uses, Side Effects, Nursing ConsiderationsJohn Paolo Tamayo OrioNo ratings yet
- Arixtra Drug StudyDocument2 pagesArixtra Drug StudyEdelweiss Marie Cayetano100% (1)
- DarvacetDocument1 pageDarvacetAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Percocet Drug CardDocument1 pagePercocet Drug CardSheri490100% (4)
- Darvocet N Drug CardDocument1 pageDarvocet N Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- NURS 2516 Clinical Medications Worksheets: Opioid AnalgesicsDocument1 pageNURS 2516 Clinical Medications Worksheets: Opioid AnalgesicsENo ratings yet
- DilaudidDocument2 pagesDilaudidAdrianne Bazo100% (2)
- ZofranDocument1 pageZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- NURS 2516 Clinical Medications Worksheets: Nursing Process-AssessmentDocument1 pageNURS 2516 Clinical Medications Worksheets: Nursing Process-AssessmentAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Morphine (Astramorph)Document1 pageMorphine (Astramorph)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Morphine (Astramorph) PCADocument2 pagesMorphine (Astramorph) PCAAdrianne Bazo100% (3)
- Drug Carbidopa LevodopaDocument1 pageDrug Carbidopa LevodopaSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Zofran Drug CardDocument1 pageZofran Drug CardSheri4900% (1)
- Zocor (Simvastin)Document3 pagesZocor (Simvastin)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Zofran IVPDocument1 pageZofran IVPAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Zoloft SertralineDocument1 pageZoloft SertralineAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- TumsDocument2 pagesTumsAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Vitamin EDocument1 pageVitamin EAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Levalbuterol XopenexDocument2 pagesLevalbuterol XopenexCassie100% (1)
- ZithromycinDocument1 pageZithromycinAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Vitamin DDocument2 pagesVitamin DAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Temazepam (Restoril)Document1 pageTemazepam (Restoril)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Tim OpticDocument2 pagesTim OpticAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- ToradolDocument2 pagesToradolAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Theragran (Multiple Vitamins)Document3 pagesTheragran (Multiple Vitamins)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Preparations (Thyrar)Document1 pageThyroid Preparations (Thyrar)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- ValiumDocument2 pagesValiumAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Tamoxifen NolvadexDocument1 pageTamoxifen NolvadexAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Seroquel (Quetiapine)Document1 pageSeroquel (Quetiapine)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Promethazine (Phenergan)Document1 pagePromethazine (Phenergan)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Predacot PrednisoneDocument1 pagePredacot PrednisoneAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- SinacDocument2 pagesSinacENo ratings yet
- RisperdalDocument2 pagesRisperdalAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Pepcid IV FamotidineDocument2 pagesPepcid IV FamotidineAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Quest RanDocument2 pagesQuest RanAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Prozac FluoxetineDocument2 pagesProzac FluoxetineENo ratings yet
- Dulcolax SuppositoryDocument1 pageDulcolax SuppositoryAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Reglan Drug CardDocument4 pagesReglan Drug CardAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- ProtonixDocument1 pageProtonixAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Potassium ChlorideDocument2 pagesPotassium ChlorideAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Plavix ClopidogrelDocument2 pagesPlavix ClopidogrelAdrianne Bazo50% (2)
- Protonix IVDocument1 pageProtonix IVAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Prinivil (Lisinapril)Document2 pagesPrinivil (Lisinapril)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Commodity FuturesDocument19 pagesCommodity FuturesPrabhu G UmadiNo ratings yet
- How Time Management Impacts Working Students' Academic AchievementDocument13 pagesHow Time Management Impacts Working Students' Academic AchievementJames RayNo ratings yet
- Pdev 111 Week 1 20 1st SemesterDocument123 pagesPdev 111 Week 1 20 1st SemesterReyn TabelismaNo ratings yet
- John Taylor Case Study ENP and EPPDocument11 pagesJohn Taylor Case Study ENP and EPPAhata Sham NewazNo ratings yet
- Screening Criteria For Application of EOR Processes in Offshore FieldsDocument7 pagesScreening Criteria For Application of EOR Processes in Offshore FieldsSajad FalahNo ratings yet
- List of Job Specific Safety PPE Used On Site.Document2 pagesList of Job Specific Safety PPE Used On Site.Aejaz MujawarNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Leadership and Management in Nursing 4th Edition Mary Ellen Grohar MurrayDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Leadership and Management in Nursing 4th Edition Mary Ellen Grohar Murraywitchingmazybs7k7100% (39)
- Final National HCF WASH Guideline ETHIOPIADocument97 pagesFinal National HCF WASH Guideline ETHIOPIAEfrem TsegabuNo ratings yet
- 16-Bit UUID Numbers DocumentDocument28 pages16-Bit UUID Numbers DocumentJuan M Iñiguez RNo ratings yet
- Ate-U2 - Steam Boilers - PPT - Session 3Document13 pagesAte-U2 - Steam Boilers - PPT - Session 3MANJU R BNo ratings yet
- Flow Crete OverviewDocument1 pageFlow Crete OverviewsathiyanNo ratings yet
- Anabolic Steroids Are Easily PurchasedDocument14 pagesAnabolic Steroids Are Easily Purchasedfaqed ilzakira100% (2)
- Specifications of TES-593Document2 pagesSpecifications of TES-593symasiNo ratings yet
- Solarizer Value, Spring & UltraDocument4 pagesSolarizer Value, Spring & UltraEmmvee SolarNo ratings yet
- Letter To Judge Anita Brody From Debra PykaDocument1 pageLetter To Judge Anita Brody From Debra PykaRobert LeeNo ratings yet
- Ventilation SystemDocument13 pagesVentilation SystemSaru BashaNo ratings yet
- 01 Basic Design Structure FeaturesDocument8 pages01 Basic Design Structure FeaturesAndri AjaNo ratings yet
- The Earths Internal HeatDocument39 pagesThe Earths Internal Heatkaynechologallardo02No ratings yet
- AquaNereda Brochure 1017 WebDocument4 pagesAquaNereda Brochure 1017 WebdmnNo ratings yet
- CAPE Biology 2006 U2 P1 PDFDocument28 pagesCAPE Biology 2006 U2 P1 PDFvedant seerattanNo ratings yet
- B25 Pompe de Peinture PDFDocument98 pagesB25 Pompe de Peinture PDFchahineNo ratings yet
- Work Procedure For CCB Installation of Raised Floor 2Document13 pagesWork Procedure For CCB Installation of Raised Floor 2ResearcherNo ratings yet
- تحليل البول بالصور والشرحDocument72 pagesتحليل البول بالصور والشرحDaouai TaaouanouNo ratings yet
- Official Game GuideDocument30 pagesOfficial Game GuideHhfugNo ratings yet
- YUMMY TUMMY - Beef Biryani Recipe - Beef Dum Biryani RecipeDocument48 pagesYUMMY TUMMY - Beef Biryani Recipe - Beef Dum Biryani RecipeWilliam Cj LyngdohNo ratings yet
- CuO Based Solar Cell With V2O5 BSF Layer - Theoretical Validation of Experimental DataDocument12 pagesCuO Based Solar Cell With V2O5 BSF Layer - Theoretical Validation of Experimental DataNur Aisyah ShariNo ratings yet
- Genie Z45.25 J Internal Combustion - Service Manual - Part No. 219418Document331 pagesGenie Z45.25 J Internal Combustion - Service Manual - Part No. 219418marciogianottiNo ratings yet
- TPB - Questionnaire Sample PDFDocument10 pagesTPB - Questionnaire Sample PDFhaneena kadeejaNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Analysis: Ship Date: Port of Discharge: Carrier: Vessel: Voyage: Quantity (MT) : Us GallonsDocument1 pageCertificate of Analysis: Ship Date: Port of Discharge: Carrier: Vessel: Voyage: Quantity (MT) : Us GallonsMercadeo BelaraviNo ratings yet
- Climate and Cultural IdentityDocument2 pagesClimate and Cultural IdentityCha AbolucionNo ratings yet