Professional Documents
Culture Documents
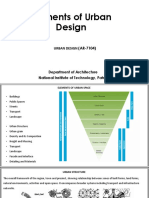
Section 7.0 - Glossary of Urban Desing and Site Planning Terms
Uploaded by
Wazir SeyedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Section 7.0 - Glossary of Urban Desing and Site Planning Terms
Uploaded by
Wazir SeyedCopyright:
Available Formats
SECTION 7.
0 | GLOSSARY OF URBAN DESING AND SITE PLANNING TERMS
7.0
Glossary of Urban Design and Site Planning Terms
Adaptive Re-Use: conversion of a building into a use other than that for which it was designed, such as changing a warehouse into a gallery space or housing. Animation: a quality of the built environment which supports sustained activity through the architectural and artistic embellishment of materials and details, the visual and physical accessibility of interior activities from the exterior, and the introduction of supportive public facilities and amenities. Areas of Archaeological Potential: Areas favourble with medium or high potential for the discovery of archaeological resources. This potential is based on the presence of a wide range of geographic and historical features which influenced past settlement. Archaeological potential is confirmed through archaeological assessment. Awning: an adjustable, roof-like covering fitted over windows, doors, etc. to provide shelter from the sun, rain and wind, and for its decorative and advertising potential. Barrier-Free Design: building and site design which is accessible to all people, regardless of age and abilities. Bay: a vertical division of a faade or a structure division of a building, marked by column spacing, roof compartments, windows or similar measures. Boulevard: the portion of land on either side of a street, between the curb and the property line, and may include sidewalk. Buffer: a strip of land established to provide separation between land uses and typically developed as a landscaped area. Building Envelope: the volume of space that may be occupied by a building, usually defined by a series of dimensional requirements such as setback, stepback, permitted maximum height, maximum permitted lot coverage. Built Heritage Resource: One or more buildings, structures, monuments, installations, or remains associated with architectural, cultural, social, political, economic, or military history, and identified as being important to a community.
Glossary of Urban Design Terms & Site Planning Terms | 7.1
SECTION 7.0 | GLOSSARY OF URBAN DESIGN AND SITE PLANNING TERMS
Canopy: a permanent fixture designed to shelter pedestrians and display goods from adverse weather conditions; a fixed awning. Circulation: movement patterns of pedestrian and vehicular traffic. Compatibility: the characteristics of different designs which, despite their differences allow them to be located near each other in harmony, such as scale, height, materials, fencing, landscaping and location of service areas. Cornice: an ornamental moulding along the top of a wall. Cultural Heritage Landscape: A defined geographical area of heritage significance which has been modified by human activities. Such an area is valued by a community, and is of significance to the understanding of the history of a people or place. Design Guidelines: criteria established to guide development toward a desired level of quality through the design of the physical environment, and which are applied on a discretionary basis relative to the context of development. Districts: geographic areas of relatively consistent character, such as exhibited in many residential neighbourhoods and the downtowns. Drip Line: The outer boundary of an area on the surface of the ground that corresponds to the outer edge of the crown of the tree (By-law No. 92-155). Elevation: a drawing showing an external face of a building. Enclosure (sense of): an experience in which a pedestrian feels sheltered with a semi-private realm. Buildings, trees, landscaping and street widths are all factors in creating a sense of enclosure. Facades: the exterior wall of a building exposed to public view or that wall viewed by persons not within the building. Fenestration: the arrangement of windows in a building. Focal Point: a prominent structure, feature or area of interest or activity.
Glossary of Urban Design Terms & Site Planning Terms | 7.2
SECTION 7.0 | GLOSSARY OF URBAN DESIGN AND SITE PLANNING TERMS
Gable: any basically triangular-shaped, upper part of a building wall, usually under a pitched roof; sometimes upper walls topped with stepped parapets are referred to as gables or stepped gables. Gateway: the design of a building, site or landscape to symbolize an entrance or arrival to a special district. Heritage Conservation: the activity undertaken to protect, safeguard, pass on or enhance heritage resources. Heritage Conservation District: a geographic area primarily made up of groups of buildings, streets and open spaces which collectively give the area a special character. Typically, the Heritage Conservation District would be subject to a By-law designed to protect and retain the character and spirit of the area and to ensure that development is sympathetic to and fits into the fabric of the neighbourhood. Heritage Designation: a measure of protection enacted by By-law under the authority of the Ontario Heritage Act for the purpose of conserving and enhancing heritage resources. Human Scale: the quality of the physical environment which reflects a sympathetic proportional relationship to human dimensions and which contributes to the citizens perception and comprehension of the size, scale, height, bulk and/or massing of buildings or other features of the built environment. Infill: the placement of new buildings into established built-up urban areas, which usually results in an increase in the existing building stock. Landmarks: buildings, structures and spaces which create distinct visual orientation points that provide a sense of location to the observer within the neighbourhood or district, such as that created by a significant natural feature or by an architectural form which is highly distinctive relative to its surrounding environment. Mass: the combination of the three dimensions of length, height, and depth which give a building its overall shape; a building is often composed of many masses, hence the term massing, which is often used to describe the form or shape of structures.
Glossary of Urban Design Terms & Site Planning Terms | 7.3
SECTION 7.0 | GLOSSARY OF URBAN DESIGN AND SITE PLANNING TERMS
Microclimate: outdoor conditions around buildings and the impact of buildings on site conditions, pedestrian spaces and adjacent buildings; conditions include amount of sunlight/shade, wind levels and snow loads are influenced by building placement, height, design, orientation and massing. Mixed Use: a development or area comprised of mixed land uses either in the same building or in separate buildings on either the same lot or on separate lots or, at a larger scale, in nodes. Modulation: variation in the plane of a building wall, often used to provide visual interest. Official Plan: a document adopted by the City Council, which contains a formal set of principles and policies, land use maps concerning the nature, pattern, extent and scheduling of future growth and change within the municipality for a specified period. Parapet: a portion of a wall that projects above a roof. Pedestrian: all people on foot or moving at walking speed, including those who use mobility aids (wheelchairs, scooters, etc.), persons with strollers and buggies, and frail elderly persons. Pedestrian-oriented: an environment designed to make movement by pedestrians fast, attractive and comfortable for various ages and abilities; considerations include separation of pedestrian and auto circulation, street furniture, clear directional and informational signage, safety, visibility, shade, lighting, surface materials, trees, sidewalk width, intersection treatment, curb cuts, ramps and landscaping. Pedestrian-oriented Uses: uses which rely on pedestrian traffic for the majority of their business such as retail stores, restaurants, service and repair shops. Podium: a base to building or structure Preservation: providing for the continued use of deteriorated old and historic buildings, sites and structure through such means as restoration, rehabilitation and adaptive re-use.
Glossary of Urban Design Terms & Site Planning Terms | 7.4
SECTION 7.0 | GLOSSARY OF URBAN DESIGN AND SITE PLANNING TERMS
Public Art: site specific artwork created to enhance and animate publicly accessible spaces through artistic interpretations that range from individual sculpture to integrated architectural and landscape features and treatments. Public Realm: the public and semi-public spaces of the city, especially the street spaces of the city from building face to the opposite building face (including the faade, front yard, sidewalk and streets) and open space such as parks and squares. Publicly Accessible Spaces: buildings, streets and exterior areas, which may be privately-owned, but to which the public has access. Renovation: modernization of an old or historic structure which unlike restoration may not be consistent with the original design. Restoration: accurately recovering the form and details of a building and site as it appeared at a particular period of time by means of the removal of later work or by the replacement of missing earlier work. Reverse Lotting: lots located adjacent to an arterial or collector road which front onto an internal street, while the rear yard faces onto the arterial or collector road. Rhythm and Pattern: relating to materials, styles, shapes an spacing of building elements and the buildings themselves, the predominance of one material or shape, and its patterns of recurrence. Right-of-Way: that part of the street space that is publicly owned and lies between the property lines. Roads, Arterial: major traffic and transit routes, intended to carry large volumes of vehicular traffic and provide continuous routes across urban areas. Roads, Collector: traffic and transit routes designed to carry lower volumes of traffic than arterial roads, and providing continuous access across neighbourhoods. Scale: the sense of proportion or apparent size of a building or building element as crated by the placement and size of the building in its setting; scale usually applies to how the sense is perceived in relation to the size of a human being and refers to the apparent size, not actual size, since it is always viewed in relationship to another building or element.
Glossary of Urban Design Terms & Site Planning Terms | 7.5
SECTION 7.0 | GLOSSARY OF URBAN DESIGN AND SITE PLANNING TERMS
Significant: in regard to wetlands and areas of natural and scientific interest, an area identified as provincially or regionally significant by the Ministry of Natural Resources using evaluation procedures established by the Province, as amended from time to time. In regard to other features and areas in policy 2.3 of the Provincial Policy Statement, ecologically important in terms of features, functions, representation or amount, and contributing to the quality and diversity of an identifiable geographic areas or natural heritage system. Criteria for determining significance may be recommended by the Province, but municipal approaches that achieve the same objective may be used. In regard to other matters, important in terms of amount, content, representation or effect. Site Plan: a plan prepared to scale, showing accurately with dimensions the boundaries of the site and the location of all buildings, structures, natural features, uses and principal site design features proposed for a parcel of land. Stepback: a setback of the upper floors of a building which is greater than the setback of the lower floors. Stormwater Management (SWM): plans and facilities designed to control the quality and quantity of storm water flows on a site. Street Furniture: municipal equipment placed along streets, including light fixtures, fire hydrants, telephones, trash receptacles, signs, benches, mailboxes, newspaper boxes and kiosks. Sense of place: the feeling associated with a location, based on a unique identity and other memorable qualities. Setback: the horizontal distance from the property line to the face of a building or from natural features to a building. Sensitive Land Use: means buildings, amenity areas, or outdoor spaces where routine or normal activities occurring at reasonably expected times would experience one or more adverse effects from contaminant discharges generated by a nearby major facility. Sensitive land uses may be a part of the natural or built environment. Examples include: residences, day care centres, and educational and health facilities.
Glossary of Urban Design Terms & Site Planning Terms | 7.6
SECTION 7.0 | GLOSSARY OF URBAN DESIGN AND SITE PLANNING TERMS
Street-line: the outside line of a required right-of-way or road allowance; the same as the property line. Streetscape: the distinguishing elements and character of a particular street as created by its width, degree of curvature, paving materials, design of the street furniture, pedestrian amenities and setback and form of surrounding buildings. Street wall: the condition of enclosure along a street created by the fronts of buildings, and enhanced by the continuity and height of the enclosing buildings. Stationary Noise Source: Source of sound which does not normally move from place to place such as noise associated with industrial or commercial establishments. Subdivision Plan: a plan for the design and division of a large property into individual building lots and blocks, streets, parks, schools and other neighbourhood facilities and uses. Subwatershed Management Plan or Study: an integrated resource management plan for a particular subwatershed whose primary focus is to develop detailed targets and objectives for resource management, environmental protection and urban development. Transit: public transportation services, particularly bus service. Transit-oriented or Transit-supportive: the elements of urban form and design which make transit more accessible and efficient, these ranging from land use elements (i.e. locating higher density housing and commercial uses along transit routes) to design (i.e. street layout which allows efficient bus routing) and encompassing pedestrian-oriented features as most transit riders begin and end their rides as pedestrians. Transit Route: the route of public transit vehicle. Tree: Includes all woody vegetation (By-law No. 92-155). Tree, Public: A tree which has more than 50 percent of its trunk diameter at breast height on public property (By-law N0. 92-155). Urban Design: the planning and design of cities focusing on the three dimension form and function of public and publicly accessible space.
Glossary of Urban Design Terms & Site Planning Terms | 7.7
SECTION 7.0 | GLOSSARY OF URBAN DESIGN AND SITE PLANNING TERMS
Utilities: facilities for gas, electricity, telephone, cable television, water and waste water. Overhead and underground power and telephone lines, all fire hydrants, watermains, storm and sanitary sewers (Town of Ancaster, Site Plan). Vehicles: all motorized conveyances for street travel, and includes automobiles, vans, trucks, motorcycles, recreational vehicles, emergency vehicles, buses and tractor trailers. Vernacular: landscape or architectural style common to, or representative of, an area. Views: that which can be seen from an observation point to an object(s), particularly a landscape or building. Vistas: a line of vision, contained by buildings of landscaping, to a building or other feature which terminates the view. Wayfinding: the information available to people which they need to find their way around the city and can be verbal, graphic, architectural and spatial. Zoning By-law: a document dividing the municipality into smaller areas called zones, employed by the municipality to regulate the use of land stating exactly what land uses are permitted and providing regulations, among other matters, regarding permitted locations for buildings; and standards for lot size, parking requirements, building height, side yard dimensions and setback from the street.
Glossary of Urban Design Terms & Site Planning Terms | 7.8
You might also like
- PLANNING 2 FUNDAMENTALSDocument29 pagesPLANNING 2 FUNDAMENTALSnads aldoverNo ratings yet
- MICD City-Design-Glossary August2017Document11 pagesMICD City-Design-Glossary August2017Sampat PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Elements in Urban DesignDocument11 pagesElements in Urban DesignAanchalNo ratings yet
- Urban Design PresentationDocument18 pagesUrban Design PresentationAuroraJanusNo ratings yet
- UDDocument14 pagesUDNancy TessNo ratings yet
- New Structures GUIDELINESDocument16 pagesNew Structures GUIDELINESanaNo ratings yet
- 1a GlossaryDocument18 pages1a GlossaryYashikaNo ratings yet
- Facade AnalysisDocument3 pagesFacade Analysis1No ratings yet
- Plaza: Access To Features: The Design Team Must Ensure That Landscaping, Level Changes, or OtherDocument9 pagesPlaza: Access To Features: The Design Team Must Ensure That Landscaping, Level Changes, or OtherJavier PereiraNo ratings yet
- Research Work No. 1Document13 pagesResearch Work No. 1Dikens 15No ratings yet
- Planning TermsDocument12 pagesPlanning TermsReese AndreaNo ratings yet
- Urban Design ControlsDocument9 pagesUrban Design ControlsMerich Jane Barlas100% (1)
- Standards For Urban DesignDocument4 pagesStandards For Urban DesignLeelaNo ratings yet
- Elements of UrbanDocument6 pagesElements of Urban1No ratings yet
- Urban Design TermsDocument27 pagesUrban Design TermsPriya PatelNo ratings yet
- Urban Design VocabularyDocument37 pagesUrban Design VocabularyPriyanka RamanNo ratings yet
- Architectural Jargon: Railing. Staircases and Porches Often Have BalustradesDocument3 pagesArchitectural Jargon: Railing. Staircases and Porches Often Have BalustradesKarishma PrasadNo ratings yet
- Urban StudyDocument6 pagesUrban StudyNagaraja Prasanna RassNo ratings yet
- Maritime School: Brief BackgroundDocument16 pagesMaritime School: Brief BackgroundMark Dela Cruz MaggayNo ratings yet
- Public PlazaDocument13 pagesPublic PlazaIslam Mostafa Ali AliNo ratings yet
- Making Better Places HandbookDocument19 pagesMaking Better Places HandbookPaulo VillasanNo ratings yet
- Building Livable Filipino CommunitiesDocument73 pagesBuilding Livable Filipino CommunitiesMark Jonathan Sacatani100% (1)
- Mixed Use Building LiteratureDocument64 pagesMixed Use Building LiteraturePaulos kasuNo ratings yet
- Design Requirements for Government Plaza ComplexDocument7 pagesDesign Requirements for Government Plaza ComplexAdrian Emmanuel ValeNo ratings yet
- Urban Design GlossaryDocument8 pagesUrban Design GlossaryashimaNo ratings yet
- Fred J Container City TheoryDocument6 pagesFred J Container City TheoryFakultativno FejzbukNo ratings yet
- Legal Consideration in Urban DesignDocument4 pagesLegal Consideration in Urban DesignJohn Fetiza ObispadoNo ratings yet
- G. Urban Design/Visual Resources: 100. DefinitionsDocument8 pagesG. Urban Design/Visual Resources: 100. DefinitionsNorman OderNo ratings yet
- PLAZA InsightsDocument4 pagesPLAZA InsightsRAMOS RON CARLOS T.No ratings yet
- Architecture Firm Business Plan by SlidesgoDocument20 pagesArchitecture Firm Business Plan by SlidesgoWenna Dale PasquinNo ratings yet
- Examples and Terminologies PDFDocument6 pagesExamples and Terminologies PDFFrancisFerrerKinomesJr.No ratings yet
- Urban IssuesDocument147 pagesUrban IssuesAvantika100% (1)
- Skyscraper & Intelligent BuildingsDocument21 pagesSkyscraper & Intelligent BuildingsMariel Paz MartinoNo ratings yet
- Landscape Arch.Document9 pagesLandscape Arch.manglicmotabigail11No ratings yet
- Planning GuidelinesDocument7 pagesPlanning GuidelinesEmy Jane ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Urban Design ObjectivesDocument13 pagesUrban Design ObjectivesFaz ShamsuddinNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument16 pagesReviewerjosephsatimbre86No ratings yet
- Urban DesignDocument15 pagesUrban DesignAr Kajal GangilNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Building Planning & Architectural - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument20 pagesUnit 4 - Building Planning & Architectural - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inMohammed Juned100% (1)
- Compact mixed-use neighborhoodsDocument10 pagesCompact mixed-use neighborhoodsAtiqah IsNo ratings yet
- Elements of Urban DesignDocument14 pagesElements of Urban DesignRajveer GuptaNo ratings yet
- Context and Connecting With The Surroundings and Wider CommunityDocument5 pagesContext and Connecting With The Surroundings and Wider CommunityMark EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Elements of A CommunityDocument20 pagesElements of A CommunityJOHN CLEMILSON FRANCISCONo ratings yet
- Construction of Pervious PavementDocument37 pagesConstruction of Pervious PavementJessa Dynn Agraviador VelardeNo ratings yet
- Urban Public Spaces and InfrastructureDocument9 pagesUrban Public Spaces and InfrastructureShivam ShanuNo ratings yet
- the-Urban-Design-Process-Documenting-the-CityDocument26 pagesthe-Urban-Design-Process-Documenting-the-CityGwendolane SilvioNo ratings yet
- Module 7 The Urban Design Process Documenting The CityDocument26 pagesModule 7 The Urban Design Process Documenting The CityMaria Fhebie Kate Alsaybar57% (7)
- Functional DimensionDocument34 pagesFunctional DimensionKhalandar BangaruNo ratings yet
- Principal of Urban DesignDocument15 pagesPrincipal of Urban DesignRajveer GuptaNo ratings yet
- Expect high quality design in Broward CountyDocument34 pagesExpect high quality design in Broward CountyErika Jehoram100% (1)
- Spatial Design of Built EnvironmentDocument23 pagesSpatial Design of Built EnvironmentOom KomariahNo ratings yet
- Urban DesignDocument14 pagesUrban DesignppayonggNo ratings yet
- 195 418 6 4 Ud PoliciesDocument35 pages195 418 6 4 Ud PoliciesVarna R anandNo ratings yet
- UD Tools and TechniquesDocument9 pagesUD Tools and TechniquesElisha K.No ratings yet
- Poster2 GuidelinesDocument1 pagePoster2 Guidelinesapi-280162730No ratings yet
- Glossary of Urban Planning Terms Flashcards - QuizletDocument60 pagesGlossary of Urban Planning Terms Flashcards - QuizletEma AhmedNo ratings yet
- Urban Design ElementsDocument1 pageUrban Design ElementsppayonggNo ratings yet
- 1 LiteratureDocument48 pages1 LiteratureSeid AbdulefetahNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document89 pagesLec 1Fayaz JerovNo ratings yet
- Traditional Music of East Asia: Japan, China and KoreaDocument10 pagesTraditional Music of East Asia: Japan, China and Koreaivy macalaladNo ratings yet
- Sva Mfa Thesis 2015Document6 pagesSva Mfa Thesis 2015Rick Vogel100% (2)
- Tony Zito's ResumeDocument3 pagesTony Zito's ResumeTony Zito100% (1)
- Calamba school integrative art lessonDocument31 pagesCalamba school integrative art lessonErly De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Alexander Pope's Life and Literary AchievementsDocument2 pagesAlexander Pope's Life and Literary AchievementsEdwin ValdésNo ratings yet
- Color by Numbers: Oh Yeah: ARTIST: Norman RockwellDocument1 pageColor by Numbers: Oh Yeah: ARTIST: Norman RockwellEVELYN DEYANIRA ARELLANO HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- 'NewsPrints' by Ru XuDocument34 pages'NewsPrints' by Ru XuI Read YA68% (37)
- John Mayer PresentationDocument19 pagesJohn Mayer PresentationJess KastelerNo ratings yet
- F4 Mid-Year Examinations Syllabus (Tentative)Document2 pagesF4 Mid-Year Examinations Syllabus (Tentative)JessieNo ratings yet
- The Importance, Meaning, Nature and Assumption of ArtDocument6 pagesThe Importance, Meaning, Nature and Assumption of ArtVic Angelo RiveraNo ratings yet
- Walking Wave Double BassDocument2 pagesWalking Wave Double BassAnonymous 1fJtzSUINo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Theory Model Answer Paper: For November 2013Document10 pagesGrade 5 Theory Model Answer Paper: For November 2013Sonalika ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- (msv-966) VP Niko Luona-Jasper JohnsDocument114 pages(msv-966) VP Niko Luona-Jasper JohnsManuel Susarte RogelNo ratings yet
- Mark SheetDocument1 pageMark SheetCesar Jr. CentenoNo ratings yet
- Realism and Symbolism in Seventeenth-Century Dutch PaintingDocument33 pagesRealism and Symbolism in Seventeenth-Century Dutch PaintingnnazolgacNo ratings yet
- Sanskrit DramaDocument4 pagesSanskrit DramaTR119No ratings yet
- Oalla Mohololi: Sotho Song From South AfricaDocument5 pagesOalla Mohololi: Sotho Song From South AfricaP.BrüggemannNo ratings yet
- Book Review StructureDocument5 pagesBook Review StructureSuban IbraimovNo ratings yet
- Afro Asian LiteratureDocument30 pagesAfro Asian LiteratureRodelyn Barroga100% (1)
- Regulation 16th Padova International Music Competition Premio Citta Di PadovaDocument6 pagesRegulation 16th Padova International Music Competition Premio Citta Di PadovaJelena FilipovićNo ratings yet
- Variations On Blues (Jamey Aebersold) .Document1 pageVariations On Blues (Jamey Aebersold) .Willem TreurNo ratings yet
- Final Carpet PPT 2003Document45 pagesFinal Carpet PPT 2003Vishal Sahitia100% (2)
- Ghosts of Chances For Redemption in Wilson Harris's PALACE of The PEACOCK and OthersDocument102 pagesGhosts of Chances For Redemption in Wilson Harris's PALACE of The PEACOCK and OthersE. Ann PowellNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Concept of TragedyDocument9 pagesAristotle Concept of Tragedykamran khanNo ratings yet
- Georgia O'KeeffeDocument17 pagesGeorgia O'KeeffeDavid BriceñoNo ratings yet
- A Monument Fragment in The Tonina Site MDocument7 pagesA Monument Fragment in The Tonina Site MAngel SánchezNo ratings yet
- Ozu's Anti-Cinenia: Yoshida KijuDocument195 pagesOzu's Anti-Cinenia: Yoshida KijuJet PNo ratings yet
- Week 016-Module Reading and Writing Creative NonfictionDocument3 pagesWeek 016-Module Reading and Writing Creative NonfictionDrei VidadNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Test: Listening Language FocusDocument2 pagesUnit 8 Test: Listening Language FocusZzz Nem tomNo ratings yet
- Manifesto: EXPOSURE - Elevating CulturalsDocument2 pagesManifesto: EXPOSURE - Elevating CulturalsAnishish SharanNo ratings yet