Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Angles
Uploaded by
Jefferson VenturaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Angles
Uploaded by
Jefferson VenturaCopyright:
Available Formats
Straight angle >An angle whose measure is 180 degrees.Thus, a straight angle look like a straight line.
The following is a straight angle. >an angle that is 180 exactly >A straight angle changes the direction to point the opposite way.
Reflex angle: >An angle whose measure is bigger than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees.The following is a reflex angle. >an angle that is greater than 180. >A Reflex Angle is more than 180 but less than 360 >The reflex angle is the larger angle. It is more than 180 but less than 360
Adjacent angles: >Angle with a common vertex and one common side. <1 and <2, are adjacent angles. >Two angles are Adjacent if they have a common side and a common vertex (corner point) >Adjacent Angles Two Angles are Adjacent if they have a common side and a common vertex (corner point) Angle ABC is Adjacent to Angle CBD
Complementary angles: >Two angles whose measures add to 90 degrees. Angle 1 and angle 2 are complementary angles because together they form a right angle.
>Note that angle 1 and angle 2 do not have to be adjacent to be complementary as long as they add up to 90 degrees >Two Angles are Complementary if they add up to 90 degrees (a Right Angle).
Supplementary angles: >Two angles whose measures add to 180 degrees. The following are supplementary angles. >Two Angles are Supplementary if they add up to 180 degrees. >These two Angles (140 and 40) are Supplementary Angles, because they add up to 180.
Vertical angles: >Angles that have a common vertex and whose sides are formed by the same lines. The following(angle 1 and angle 2) are vertical angles. >Vertical Angles are the angles opposite each other when two lines cross >They are called "Vertical" because they share the same Vertex (or corner point) >They are also called Vertically Opposite Angles , which is just a more exact way of saying the same thing. Congruent Angles Parallel Lines and Pairs of Angles Corresponding Angles Alternate Interior Angles Alternate
POLYGONS
A polygon is a plane shape with straight sides. (n.) A plane figure having many angles, and consequently many sides; esp., one whose perimeter consists of more than four sides; any figure having many angles. A closed plane figure bounded by three or more line segments.
A). KINDS WITH DRAWINGS TRIANGLE > A draughtsmans square in the form of a right-angled triangle. > A small constellation situated between Aries and Andromeda. >An instrument of percussion, usually made of a rod of steel, bent into the form of a triangle, open at one angle, and sounded by being struck with a small metallic rod. > A kind of frame formed of three poles stuck in the ground and united at the top, to which soldiers were bound when undergoing corporal punishment, -- now disused. > A figure bounded by three lines, and containing three angles. >A small constellation near the South Pole, containing three bright stars.
QUADRILATERAL > Having four sides, and consequently four angles; quadrangular. > An area defended by four fortresses supporting each other; as, the Venetian quadrilateral, comprising Mantua, Peschiera, Verona, and Legnano. >A plane figure having four sides, and consequently four angles; a quadrangular figure; any figure formed by four lines.
PENTAGON > A plane figure having five angles, and, consequently, five sides; any figure having five angles.
HEXAGON >A plane figure of six angles.
HEPTAGON > A plane figure consisting of seven sides and having seven angles.
OCTAGON >A plane figure of eight sides and eight angles. >Any structure (as a fortification) or place with eight sides or angles.
NONAGON > A figure or polygon having nine sides and nine angles.
DECAGON >A plane figure having ten sides and ten angles; any figure having ten angles. > A regular decagon is one that has all its sides and angles equal.
DODECAGON > A figure or polygon bounded by twelve sides and containing twelve angles.
B). PERIMETER An instrument for determining the extent and shape of the field of vision. The outer boundary of a body or figure, or the sum of all the sides. Polygon Perimeter
Equilateral Triangle Length of side times three
Equilateral Quadrilateral (Square or Rhombus) Length of side times four
Equilateral Pentagon Length of side times five
Equilateral Hexagon Length of side times six
Equilateral Heptagon Length of side times seven
Equilateral Octagon Length of side times eight
Equilateral Nonagon Length of side times nine
Equilateral Decagon Length of side times ten
Equilateral Dodecagon Length of side times twelve
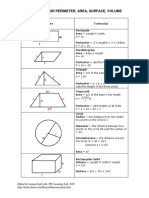
Areas of Squares
Area of a square = s2 Areas of Rectangles
Area of a rectangle = lw
Areas of Parallelograms
To get the area of a parallelogram, we first draw a perpendicular line segment from one corner of the parallelogram to the opposite side. This is the height ( h) of the parallelogram. Area of a parallelogram = lh You may notice that lh is also the area of a rectangle with dimensions l and h. The diagram below will explain why. If we cut out the triangle ABC and add it to the other side (triangle DEF), you will have a rectangle with dimensions l and h that has the same area as the original parallelogram.
Areas of Triangles
To get the area of a triangle, we first choose one of the sides to be the base ( b). Then we draw a perpendicular line segment from a vertex of the triangle to the base. This is the height ( h) of the triangle.
Areas of Rhombus
To get the area of a rhombus, we first draw a line segment from one vertex to another vertex ( b). Then we draw a perpendicular line segment from a third vertex to the base ( h). The rhombus consists of two triangles with base ( b) and height (h).
Area of a rhombus = bh Areas of Trapezoids
a is parallel to b
SPACE OR SPATIAL FIGURES A spatial figure is one that is three dimensional, it is that simple. examples of spatial figures are the cylinder, cube, and some shapes in which u think that you can put something unto it... that's all...
A). KINDS AND DRAWINGS CYLINDER >The equation for determining the volume (V) of a cylinder is V = r2h. >The cylinder is the aggregate of the same track number on every platter used for recording. >A cylinder is a three dimensional shape with two round shapes at either end and two parallel lines connecting the round ends.
CONE >A solid (3-dimensional) object that has a circular base and one vertex >A cone is made by rotating a triangle!
SPHERE >All points on the surface are the same distance from the center >It is perfectly symmetrical >A 3-dimensional object shaped like a ball. >Every point on the surface is the same distance from the center.
TORUS >It can be made by revolving a small circle along a line made by another circle. >It has no edges or vertices >It is not a polyhedron
POLIHEDRON >A polyhedron is a solid with flat faces (from Greek poly- meaning "many" and -edron meaning "face"). >A polyscope, or multiplying glass. > A body or solid contained by many sides or planes.
. RECTANGULAR SOLID >A solid (3-dimensional) object which has six faces that are rectangles. >It is a prism because it has the same cross-section along a length.
B).VOLUMES >Volume and Surface Area of a Right Circular Cylinder
Volume = Pi * r 2 * h Surface Area = 2 * Pi * r * h >Volume and Surface Area of a Right Circular Cone
Volume = (1/3)* Pi * r 2 * h Surface Area = Pi * r * sqrt (r 2 + h 2) >Volume and Surface Area of a Sphere
Volume = (4/3)* Pi * r 3 Surface Area = 4 * Pi * r 2
>Volume and Surface Area of a Rectangular Solid
Volume = L*W*H Surface Area = 2(L*W + H*W + H*L) CIRCE WITH DRAWING PARTS All points are the same distance from the center. The set of all points on a plane that are a fixed distance from a center. Indirect form of words; circumlocution. A circular group of persons; a ring. An instrument of observation, the graduated limb of which consists of an entire circle. A round body; a sphere; an orb. To move around; to revolve around. Compass; circuit; inclosure. A territorial division or district. A series ending where it begins, and repeating itself. A form of argument in which two or more unproved statements are used to prove each other; inconclusive reasoning. To encompass, as by a circle; to surround; to inclose; to encircle. To move circularly; to form a circle; to circulate. A company assembled, or conceived to assemble, about a central point of interest, or bound by a common tie; a class or division of society; a coterie; a set. The line that bounds such a figure; a circumference; a ring. A plane figure, bounded by a single curve line called its circumference, every part of which is equally distant from a point within it, called the center.
CIRCUMFERENCE >The Circumference is the distance around the edge of the circle. >The circumference is the distance around the circle. >The external surface of a sphere, or of any orbicular body. >To include in a circular space; to bound. >A circle; anything circular. >The line that goes round or encompasses a circular figure; a periphery.
AREA >The area of a circle is times the Radius squared
>The size of a surface. >The amount of space inside the boundary of a flat (2-dimensional) object such as a triangle or circle.
ELECTRIC METER READING >a meter for measuring the amount of electric power used power meter >An electricity-measuring device that totalizes with time, such as a watthour meter or amperehour meter, in contrast to an electric instrument. >An electricity meter or energy meter is a device that measures the amount of electric energy consumed by a residence, business, or an electrically powered device. >An electricity-measuring device that totalizes with time, such as a watthour meter or amperehour meter, in contrast to an electric instrument.
WATER METER READING >A contrivance for measuring a supply of water delivered or received for any purpose, as from a street main. >A contrivance for measuring a supply of water delivered or received for any purpose, as from a street main. >meter for measuring the quantity of water passing through a particular outlet meter - any of various measuring instruments for measuring a quantity >A device used to measure the flow of water. Most often used by local utilities to bill residents for water used. >an instrument that measures and records the amount of water flowing through a pipe
GRAPH >A diagram symbolizing a system of interrelations by spots, all distinguishable from one another and some connected by lines of the same kind. >A curve or surface, the locus of a point whose coordinates are the variables in the equation of the locus. CIRCLE GRAPH >A circle graph is shaped like a circle. It is divided into fractions that look like pieces of pie, so sometimes a circle graph is called a pie graph. Many times the fractional parts are different colors and a key explains the colors.
BAR GRAPH >A bar graph uses bars to show data. The bars can be vertical (up and down), or horizontal (across). The data can be in words or numbers.
PICTURE GRAPH > A picture graph uses pictures or symbols to show data. One picture often stands for more than one vote so a key is necessary to understand the symbols.
HISTOGRAM > A histogram is a special kind of bar graph. The data must be shown as numbers in order.
LINE GRAPH >A line graph shows points plotted on a graph. The points are then connected to form a line.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Seamo 2016 PaperbDocument8 pagesSeamo 2016 PaperbAgnes De Yong100% (2)
- Coordinate Geometry Booster For IIT JEE Main and Advanced PDFDocument383 pagesCoordinate Geometry Booster For IIT JEE Main and Advanced PDFUday Prakash Sahu100% (5)
- 5.lines and AnglesDocument41 pages5.lines and Anglesmary gamboa0% (2)
- Solutions of TriangleDocument16 pagesSolutions of TriangleMamta KumariNo ratings yet
- Skema Add Maths Trial SPM 2013 Penang k12 WDocument22 pagesSkema Add Maths Trial SPM 2013 Penang k12 WJessica MasonNo ratings yet
- Soh Cah Toa Performance TaskDocument3 pagesSoh Cah Toa Performance Taskapi-238109871No ratings yet
- Diy 3d Tessellation ModelDocument6 pagesDiy 3d Tessellation ModelAganNo ratings yet
- 03 Understanding Quadrilaterals TestDocument11 pages03 Understanding Quadrilaterals TestKavita DhootNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Grade 11 Pre-CalculusDocument7 pagesFirst Quarter Grade 11 Pre-CalculusGary VargasNo ratings yet
- Spherical TriangleDocument22 pagesSpherical TriangleJoseph TobsNo ratings yet
- GEOMETRY CH 5 Law of SinesDocument2 pagesGEOMETRY CH 5 Law of SinesJackson LudtkeNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Formulae: sin 2θ=2 sin θ cos θDocument2 pagesTrigonometry Formulae: sin 2θ=2 sin θ cos θMaishNo ratings yet
- 1 26 15 HW-GDocument2 pages1 26 15 HW-Gapi-233938654No ratings yet
- X Maths Mid Term Question Paper (2021-22)Document4 pagesX Maths Mid Term Question Paper (2021-22)SHUBHAM MISHRANo ratings yet
- The Olympiad Corner: No. 307 Nicolae StrungaruDocument6 pagesThe Olympiad Corner: No. 307 Nicolae StrungaruFustei BogdanNo ratings yet
- ADM SPM Formulae KBSMDocument4 pagesADM SPM Formulae KBSMJason LeeNo ratings yet
- 15.trigonometry Password RemovedDocument18 pages15.trigonometry Password RemovedfameNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFsagar sagarNo ratings yet
- Paavai Vidhyashram Senior Secondary School: Unit Test 1 ExamDocument5 pagesPaavai Vidhyashram Senior Secondary School: Unit Test 1 ExamAkash.SNo ratings yet
- Math Quiz ReviewerDocument15 pagesMath Quiz ReviewerMarvin Rinon0% (1)
- Classification of QuadrilateralDocument5 pagesClassification of QuadrilateralPatricia SamsonNo ratings yet
- Veselin RmušDocument24 pagesVeselin RmušMato KankarašNo ratings yet
- JR Maths - Ib Ipe Question Bank Locus: Short Answer QuestionsDocument16 pagesJR Maths - Ib Ipe Question Bank Locus: Short Answer QuestionsSAMUDRALA SIVA NAGA VENKATESHNo ratings yet
- DPS Indirapuram Class - VII Subject - Mathematics Final Examination Revision SheetDocument6 pagesDPS Indirapuram Class - VII Subject - Mathematics Final Examination Revision SheetnaihsaNo ratings yet
- Common Tablet ShapesDocument1 pageCommon Tablet ShapesDamar MuktiNo ratings yet
- Properties of Plane Areas: A X I I I IDocument6 pagesProperties of Plane Areas: A X I I I INovNo ratings yet
- How To Draft A Geodesic DomeDocument9 pagesHow To Draft A Geodesic DomeMaria ZachariaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Notes Class9 Maths Chapter7Document9 pagesCbse Notes Class9 Maths Chapter7LatoyaWatkinsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To Pythagoras (Twinkl)Document17 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To Pythagoras (Twinkl)8yhpxmw9j4No ratings yet
- Geometry ProofsDocument6 pagesGeometry ProofsAlfredo L. Cariaso0% (1)