Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brugada and Cocaine - Midwest Hospital Med Meeting
Uploaded by
Abdul Hamid AlraiyesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brugada and Cocaine - Midwest Hospital Med Meeting
Uploaded by
Abdul Hamid AlraiyesCopyright:
Available Formats
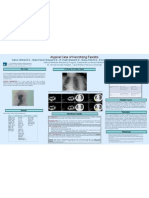
Brugada Electrocardiographic Pattern And Cardiovascular Complications Associated With Cocaine Toxicity
M. Chadi Alraies M.D., Abdul Hamid Alraiyes M.D., Samer Alhindi M.D., Richard Christie M.D.
Internal Medicine Residency Program, Department of Internal Medicine
Case Western Reserve University - St. Vincent Charity Hospital – Cleveland, Ohio
The Case Cocaine induced dysrhythmias Treatment of Cocaine Intoxication With Myocardial Complications
• The event: A previously healthy 27-year-old man ingested the content of a bag of cocaine as an impulsive • What is the diagnosis of this electrocardiogram (ECG)? • Which of the following agents considered first line for the management of cocaine induced myocardial
gesture to avoid police detection. One hour later, he developed psychomotor agitation and generalized seizures. 1. Acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction. injury?
Within seconds, patient found pulseless and the electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring showed ventricular 2. Bundle branch block (BBB) 1. Metoprolol
asystole. CPR started and ventilation with supplemental oxygen by endotracheal (ET) intubation two ampules of 3. Ventricular tachycardia 2. Lisinopril
Epinephrine and two ampules of Sodium Bicarbonate delivered by EMS immediately restored spontaneous heart 4. Accelerated AV junctional rhythm. 3. Lorazepam
beats. 4. Phentolamine
5. Brugada pattern.
5. Tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA)
• Vitals signs: Temperature of 39oC peripheral pulse of 70 bmp, blood pressure 90/70mm Hg, respiratory rate 32, • The electrocardiograms are showing accelerated idioventricular rhythm at 66 beats/min, QRS (0.44 sec), • Cocaine has no known antidote. Lorazepam supportive care and benzodiazepines such as lorazepam is the
SpO2 98% with full ventilator support (FiO2 100%), and Glasgow Coma scale of 5/15. QTc (0.533 sec) with right bundle branch block (RBBB) and left anterior hemiblock (LAHB) configuration, cornerstone of therapy. Furthermore, benzodiazepines considered first line treatment of cocaine related
and rSR' pattern with coved ST-segment elevation in V1 and more clearly in V2 mimicking Brugada myocardial injury. Review the following table for the agents recommended by AHA for treatment.
• Physical exam: Pupils were fixed, dilated and non-reactive to light bilaterally. The fundoscopic exam showed pattern. However, underlying ischemia/infraction can’t be ruled out.
arterial narrowing. His skin was warm and flushed and his oral mucosa was dry with no signs of tongue Cocaine And Sodium Bicarbonate
laceration. Bilateral crackles more on the right than the left side heard on chest examination. Heart exam was • Which of the following cardiac dysrhythmias and conductions disturbances reported with cocaine • Several reports have described the treatment of cocaine-induced wide-complex tachycardia including
significant for regular rate and rhythm with frequent escaped beats. The abdominal exam was negative. use? Brugada pattern, associated with drugs having sodium channel blocking action, such as cocaine with the
1. Bundle-branch block administration of sodium bicarbonate
• Initial work-up: Severe anion-gap metabolic acidosis with elevated lactic acid, creatinine kinase and myocardial 2. Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
Troponin I. 3. Ventricular tachycardia
4. Torsade de pointes
• Electrocardiogram: serial ECG’s done and shown below (ECG 1 and ECG 2) 5. Brugada pattern (right bundle-branch block with ST-segment elevation in leads V1, V2, and V3)
6. All of the above.
• All of the choices in previous question are correct. But the precise arrhythmogenic potential of the drug is
poorly defined. Suggested mechanisms:
• As a sympathomimetic agent, it may increase ventricular irritability and lower the threshold for
fibrillation.
• Inhibits the generation and conduction of the action potential as a result of its sodium-channel-
blocking effects.
• Increases the intracellular calcium concentration
• It reduces vagal activity, which potentiates cocaine’s sympathomimetic effects.
• Which one of the following antiarrhythmics safe in patients with cocaine induced ventricular
tachycardia or fibrillation?
1. Lidocaine
2. Quinidine
3. Procainamide
4. Disopyramide
5. Non of the above
• Lidocaine has been used safely in patients with cocaine induced ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation. Class IA
antiarrhythmic drugs, such as quinidine, procainamide, and disopyramide, should be avoided, since they may
exacerbate prolongation of the QRS and QT intervals and slow the metabolism of cocaine and its metabolites.
Cocaine And Brugada syndrome
ECG 1 on arrival to ER
The syndrome is characterized by (ECG) pattern of right bundle branch block (RBBB) with coved or occasionally
saddleback ST-segment elevation in leads V1 through V3, the absence of demonstrable structural heart disease,
and a propensity for ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and sudden cardiac death.
The arrhythmogenic potential of cocaine is extremely complex and poorly understood. Theses characteristic ECG
changes occasionally are transient and may be exposed by sodium channel blocker, such as cocaine, or
procainamide in patients with “latent” Brugada syndrome.
There is considerable debate in the literature whether an incidental finding of the Brugada pattern on the ECG of
asymptomatic individuals with no family history of sudden death warrants an electrophysiologic evaluation.
Back To The Case
The patient was treated with IV fluids boluses and continuous infusion, sodium bicarbonate and lorazepam (1
mg/h) drips. All this led to hemodynamic stabilization and almost normalization of serum bicarbonate and PH
From: N Eng J Med, Lange RA, cardiovascular Complications of Cocaine. Vol. 345 No. 5
levels. Subsequently, repeated ECG showed normal sinus rhythm. Cardiac catheterization showed normal
coronary arteries with normal LV EF of 60%. Patient discharged back to the jail and to follow up with
electrophysiology clinic.
Cocaine-Induced Myocardial Infarction Conclusion
Cocaine can unmask latent Brugada syndrome in patient with the susceptible gene. Cocaine associated seizures
Three suggested mechanisms: and severe metabolic acidosis is multifactorial. Electrocardiogram has a low sensitivity in detecting cocaine-
ECG 2. six hours after arrival to ED 1. An increased myocardial oxygen demand in the face of a limited or fixed supply. related myocardial ischemia and infarction. Sodium bicarbonate has more than one indication in the management
2. Marked vasoconstriction of the coronary arteries. of cocaine toxicity, reversal of the metabolic acidosis, treatment of rhabdomyolysis, and reversal of the sodium
3. Enhanced platelet aggregation and thrombus formation. channel blocking property of cocaine on myocardium.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Garlic - Toxic and A Brain Synchronization DestroyerDocument6 pagesGarlic - Toxic and A Brain Synchronization Destroyerxreader0No ratings yet
- Human Longevity Project Vitality Experience Guidebook 2Document42 pagesHuman Longevity Project Vitality Experience Guidebook 2Britt LangNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Pharmacotherapy DipiroDocument70 pagesPharmacotherapy DipiroSisisNo ratings yet
- Fibroid in WomenDocument13 pagesFibroid in Womentnemwill1880% (5)
- RHU Blue Book 6 - 070852 1Document14 pagesRHU Blue Book 6 - 070852 1Jm Jm100% (1)
- EEG Sleep StagesDocument18 pagesEEG Sleep StagesAbdul Hamid Alraiyes100% (1)
- Materia Medica For Students - Part-1 - by Ritu KinraDocument253 pagesMateria Medica For Students - Part-1 - by Ritu KinraAshish Pandey100% (1)
- Facts and Myths of AgingDocument50 pagesFacts and Myths of AgingangayarkanniNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentilationDocument29 pagesMechanical VentilationAbdul Hamid Alraiyes100% (8)
- Chapter 10 Dermal (Capillary) Puncture: Phlebotomy, 5e (Booth)Document30 pagesChapter 10 Dermal (Capillary) Puncture: Phlebotomy, 5e (Booth)Carol ReedNo ratings yet
- Assessment of RA 9994 implementation for senior citizensDocument12 pagesAssessment of RA 9994 implementation for senior citizenserroljohnescorial100% (1)
- History of medicine from ancient Egypt to IndiaDocument12 pagesHistory of medicine from ancient Egypt to Indiaaditya_2kNo ratings yet
- OceanofPDF - Com Undoctored - Adam KayDocument209 pagesOceanofPDF - Com Undoctored - Adam Kaykatherine grey100% (1)
- Loeys - Dietz Syndrome and Sleep Disordered BreathingDocument44 pagesLoeys - Dietz Syndrome and Sleep Disordered BreathingAbdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- Sleep & EpilepsyDocument45 pagesSleep & EpilepsyAbdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- EKG For Sleep LabDocument40 pagesEKG For Sleep LabAbdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- ICSADocument43 pagesICSAAbdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- Apnea and HypopneaDocument6 pagesApnea and HypopneaAbdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- Abdul Alraiyes MDDocument7 pagesAbdul Alraiyes MDAbdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- ICSADocument43 pagesICSAAbdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome "OHS"Document56 pagesObesity Hypoventilation Syndrome "OHS"Abdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- OSADocument59 pagesOSAAbdul Hamid Alraiyes0% (1)
- Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome "OHS"Document56 pagesObesity Hypoventilation Syndrome "OHS"Abdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- ABG Approach in 6 StepsDocument1 pageABG Approach in 6 StepsAbdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- Review of System (ROS)Document6 pagesReview of System (ROS)Abdul Hamid Alraiyes0% (1)
- CHEST CTscan ProjectDocument1 pageCHEST CTscan ProjectAbdul Hamid Alraiyes100% (1)
- Post - Traumatic Stress Disorder Abdul Alraiyes MD.Document25 pagesPost - Traumatic Stress Disorder Abdul Alraiyes MD.Abdul Hamid Alraiyes100% (1)
- Necrotizing Faciitis SGIMDocument1 pageNecrotizing Faciitis SGIMAbdul Hamid Alraiyes100% (1)
- Acid Base Disorders2Document23 pagesAcid Base Disorders2Abdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- Abdul Hamid Alraiyes CV-3Document4 pagesAbdul Hamid Alraiyes CV-3Abdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDocument16 pagesAmniotic Fluid EmbolismAbdul Hamid Alraiyes100% (4)
- Bulous PEMPHIGOID - SGIMDocument1 pageBulous PEMPHIGOID - SGIMAbdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- Esrd & Dka1Document53 pagesEsrd & Dka1Abdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Disorders1Document23 pagesAcid Base Disorders1Abdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- SpirometryDocument12 pagesSpirometryAbdul Hamid Alraiyes100% (2)
- Airway AssessmentDocument24 pagesAirway AssessmentAbdul Hamid Alraiyes100% (1)
- Review of Systems AbdulDocument1 pageReview of Systems AbdulAbdul Hamid Alraiyes100% (1)
- Pulmonary Artery Catheter ppt2Document12 pagesPulmonary Artery Catheter ppt2Abdul Hamid Alraiyes100% (3)
- ICU EquationsDocument6 pagesICU EquationsAbdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- Abdul Hamid Alraiyes Internal Medicin Case Western Reserve UniversityDocument1 pageAbdul Hamid Alraiyes Internal Medicin Case Western Reserve UniversityAbdul Hamid AlraiyesNo ratings yet
- Brochure Systeme MedilogDocument8 pagesBrochure Systeme MedilogAbrourNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology - Peripheral Blood Smear - Part 1 (Dr. Carretas)Document7 pagesClinical Pathology - Peripheral Blood Smear - Part 1 (Dr. Carretas)ashley nicholeNo ratings yet
- CSH Perspectives Rev - Apolipoprotein E and Apolipoprotein E Receptors - Normal Biology and Roles in ADDocument23 pagesCSH Perspectives Rev - Apolipoprotein E and Apolipoprotein E Receptors - Normal Biology and Roles in ADGeneziz DiazNo ratings yet
- Bsc2086 Ass. 1 SummerDocument51 pagesBsc2086 Ass. 1 SummerGeico88No ratings yet
- 2021 Henkel Nash PatonDocument31 pages2021 Henkel Nash PatonLaura Goncalves FontesNo ratings yet
- Case Report VTDocument12 pagesCase Report VTAnonymous ZbhBxeEVNo ratings yet
- Ok 466962500 Ok 7 Yds Nisan 2017Document22 pagesOk 466962500 Ok 7 Yds Nisan 2017gizemcetinNo ratings yet
- Genomics in India - Kapil Khandelwal - EquNev CapitalDocument5 pagesGenomics in India - Kapil Khandelwal - EquNev CapitalKapil KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- City of Galveston RFP Employee Health Insurance Addendum #3Document75 pagesCity of Galveston RFP Employee Health Insurance Addendum #3garbagepatchNo ratings yet
- EPT FinalDocument8 pagesEPT FinalJerry G. Gabac100% (1)
- Genetic Control of ProteinDocument43 pagesGenetic Control of ProteinGabriela ZahiuNo ratings yet
- Ptosis SurgeryDocument18 pagesPtosis Surgerysri sinagaNo ratings yet
- Risk factors of diabetic retinopathy and vision threatening diabetic retinopathy and vision threatening diabetic retinopaty based on diabetic retinopathy screening program in greater bandung, west java.astriDocument14 pagesRisk factors of diabetic retinopathy and vision threatening diabetic retinopathy and vision threatening diabetic retinopaty based on diabetic retinopathy screening program in greater bandung, west java.astriSi PuputNo ratings yet
- Managing Chronic Pancreatitis with a Multidisciplinary ApproachDocument22 pagesManaging Chronic Pancreatitis with a Multidisciplinary ApproachamhoylaiNo ratings yet
- Lectura Adn MitocondrialDocument13 pagesLectura Adn MitocondrialIvan Berrios VillegasNo ratings yet
- The Witch Trials of Finnmark, Northern NorwayDocument14 pagesThe Witch Trials of Finnmark, Northern NorwaythestylerhimselfNo ratings yet
- Leading Cause of Death by State: Allison Sandys, Graham Vogtman, Madison MannDocument10 pagesLeading Cause of Death by State: Allison Sandys, Graham Vogtman, Madison MannGrahamVogtmanNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument43 pagesQuestionnaireGracie O. Ching50% (2)
- June 2018 QP - Biology 1 (H) Edexcel Science GCSEDocument24 pagesJune 2018 QP - Biology 1 (H) Edexcel Science GCSESHOABNo ratings yet