Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHAPTER 8 Hazop Study
Uploaded by
NethiyaaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 8 Hazop Study
Uploaded by
NethiyaaCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 8
HAZOP STUDY OF STRIPPER
SUMMARY
In this chapter, it reviews about the hazop study of stripper. It describes the parameters need to be used and control during the process begins. HAZOP is a formal procedure that offers a great potential to improve the safety, reliability and operability of process plants by recognizing and eliminating potential problems at the design stage. It is not limited to the design stage, however. It can be applied anywhere that a design intention (Perrys Handbook, 1998). When using the operability study technique to vet a process design, the action to be taken to deal with a potential hazard will often be modification to the control system and instrumentation, the inclusion of additional alarms, trips or interlock. If major hazard are identified, major design changes may be necessary, alternatives processes, material and equipment. In order to have a safe process successfully producing to specification to the required product, a sound control system is necessary but not sufficient(Coulson & Richardsons, 1999).
8.1 INTRODUCTION In this project, the safety procedure will be used to study the safety of the plant designed. HAZOP study is a structured and systematic examination of a planned or existing process or operation in order to identify and evaluate problems that may represent risks to personnel or equipment, or prevent efficient operation. This procedure is preferred since it is a formal systematic examination of a processing plant for identifying hazards, failure and operability problems and assessing the consequences. This leads to fewer lapses in safety, quality and production provided that the plant is installed according to the design and maintained in appropriate condition. A HAZOP is carried out as a team activity. The HAZOP can also be used as a check on the operability of an existing plant. The procedure for a HAZOP study is to apply a number of guide words to various parts of the process design intention, which tells us what, the process is, expected to do. The advantages of HAZOP study to the design application: Early identification of problems areas when conceptual design stage. Identifies need for emergency procedures to mitigate. Provide essential information for safety case, such as on the hazards identified and effectiveness of safety systems. Through examination of hazard and operability problems when applied at detailed stage. Meets legislative requirements. Identifies need for commissioning, operating and maintenance procedures for safe and reliable operations.
8.2 Parameters and guide words The key feature is to select appropriate parameters which apply to the design intention. These are general words such as flow, temperature, pressure, level, time, concentration and reaction. It can be seen that variations in these parameters could constitute deviations from the design Intention. A set of guide words to each parameter for each section of the process was applied in order to identify deviations. These guide words are given below and are applied to the stripper unit operations to be considered. Guide Word Meaning The complete negation of these intentions Comment No part of the intentions is achieved but nothing else happens. These refer to quantities More or Less Quantitative increases or and properties such as flow decreases rate and temperature as well activity likes HEAT All As well as A qualitative increases the design intentions together and are with
No or Not
operating achieved
some additional activity. Part of A qualitative decrease Only some of the attention achieved; some are not.
The following words are used in a special way, and have the precise meanings given below: i. Intention: the intention defines how the particular part of the process was intended to operate and the intention of the designer. ii. Deviations: these are departures from the designers intention which are detected by the systematic application of the guide words.
iii. Causes: reasons why, and how, the deviations could occur. Only if a deviation can be shown to have a realistic cause is it treated as meaningful. iv. Consequences: the results that follow the occurrence of a meaningful deviation.
The table below shows the typical HAZOP process parameter that could be considered during the measurement of the HAZOP study.
Typical Hazop Process Parameter Pressure Temperature Flow Level Time Composition pH Reaction Heating Cooling Mixing Addition Data Information Separation Viscosity Voltage Frequency Speed Density Solubility
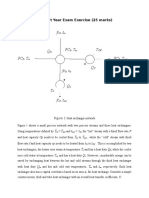
Type of vessel: Stripper Temperature: 180C Pressure: 2.75Pa Guide Word None No Flow No flow in stream coming to the column Line fracture Quality amount and of Deviation Possible Causes Consequences Actions Required Install low level alarm
product will suffer. Accidental discharge to the environment (aromatics are flammable material). -
Plant shut down.
More of
Flow
LCV fails open error in
Overfills Incomplete separation of nonaromatics from solvent + aromatics
Install high level alarm and check sizing.
Pressure
Isolation valve close in error
Full delivery
pump
Isolation valve close error in
Temperatu re
Higher pressure in transfer
Degradation of the solvent quality will
High Temperat ure Alarm
5
line
become significant ms.
(HTA).
Less of
Flow
Leaking flange valve of
Material discharge to the environment
Isolate that of plant part the
Others
Maintenan ce
Equipment Failure
Line be
cannot
Install alarms.
completely drained purged or
REFERENCES Charles A.Wentz, Safety, Health, And Environmental Protection, McGraw Hill, 1998 Coulson and Richardsons. Chemical Engineering Design, Volume 6. Butterworth Heinemann. 2000. Green W. Don & Perry Robert H. Perrys Chemical Engineers Handbook. Seventh Edition Kansas. McGraw Hill, 1997.
You might also like
- HazopDocument8 pagesHazopferrari.indiaNo ratings yet
- HAZOP - Grinding SystemDocument9 pagesHAZOP - Grinding SystemNothando ShanduNo ratings yet
- Example: HAZOP Analysis of A Fueling Terminal For A BargeDocument4 pagesExample: HAZOP Analysis of A Fueling Terminal For A BargeBharat LalNo ratings yet
- Useful tips for successful HAZOP studiesDocument10 pagesUseful tips for successful HAZOP studiesDesiree MolinaNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Investigation On High-Pressure LDPE Manufacturing: Dynamic Modelling of Compressor, Reactor and Separation UnitsDocument6 pagesA Comprehensive Investigation On High-Pressure LDPE Manufacturing: Dynamic Modelling of Compressor, Reactor and Separation UnitsAbdul SamadNo ratings yet
- Inherently Safer DesignDocument64 pagesInherently Safer Designsepideh_entezari100% (1)
- Atul LTD Risk AssessmentDocument108 pagesAtul LTD Risk AssessmentdevangNo ratings yet
- Production of Acetone from IsopropanolDocument93 pagesProduction of Acetone from IsopropanolSanjeevNo ratings yet
- En Analysis of Thermal Efficiency Limit of Steam Methane Reforming ProcessDocument8 pagesEn Analysis of Thermal Efficiency Limit of Steam Methane Reforming ProcessAgam HanasichulaNo ratings yet
- HAZOP Training290620Document93 pagesHAZOP Training290620NasrulNo ratings yet
- Process Safety Seminar SummaryDocument5 pagesProcess Safety Seminar SummaryBrijesh100% (1)
- Application of Extended HazopDocument10 pagesApplication of Extended HazopTonga ProjectNo ratings yet
- Reactor OperationDocument8 pagesReactor OperationBerlianiNo ratings yet
- Suggestions For The Optimum Process Conditions That Should Be Adopted To Improve The Process DesignDocument2 pagesSuggestions For The Optimum Process Conditions That Should Be Adopted To Improve The Process DesignAddison JuttieNo ratings yet
- Fta Oil+gasdistilcolumn PDFDocument7 pagesFta Oil+gasdistilcolumn PDFPrasanna GNo ratings yet
- Feedback Control Tuning in Chemical ProcessesDocument22 pagesFeedback Control Tuning in Chemical ProcessesTaniadi SuriaNo ratings yet
- 1 PB PDFDocument19 pages1 PB PDFBalint Simon EmanuelNo ratings yet
- Vinyl Chloride MSDSDocument8 pagesVinyl Chloride MSDSHoshiNo ratings yet
- TA Chemicals Guide en LRDocument24 pagesTA Chemicals Guide en LRYehor HorbatkoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Inherently Safer Design: Prepared For Safety and Chemical Engineering Education (SACHE) byDocument71 pagesIntroduction To Inherently Safer Design: Prepared For Safety and Chemical Engineering Education (SACHE) bySebastian iacopiNo ratings yet
- Hazop Study: 11.1.1 BackgroundDocument14 pagesHazop Study: 11.1.1 BackgroundMuhammad100% (1)
- Distillation Columns Risk Assessment When The Regular Hazop Evaluation Is Not EnoughDocument7 pagesDistillation Columns Risk Assessment When The Regular Hazop Evaluation Is Not Enoughmyusuf_engineerNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument33 pagesCase StudyMir Hasib Ul LatifNo ratings yet
- 434-1 Process Release Freq 2020Document62 pages434-1 Process Release Freq 2020Aiman LatifNo ratings yet
- Contoh PDFDocument270 pagesContoh PDFwan100% (1)
- HASILT Software for HAZOP, LOPA, SRS and SILDocument9 pagesHASILT Software for HAZOP, LOPA, SRS and SILRonyNo ratings yet
- Hazard and Operability Study (Hazop) : Dr. M. Azam SaeedDocument39 pagesHazard and Operability Study (Hazop) : Dr. M. Azam SaeedMuhammad Bilal100% (1)
- Polymer Handbook 4th EditionDocument1 pagePolymer Handbook 4th EditionJanika KetratnkulNo ratings yet
- Cricondentherm & Cricondenbar PressuresDocument7 pagesCricondentherm & Cricondenbar PressuresdesertflowNo ratings yet
- Viva Master SlideDocument36 pagesViva Master Slidethivya keasavanNo ratings yet
- KQD7005 ALOHA Mini Project-Group 8Document9 pagesKQD7005 ALOHA Mini Project-Group 8taned8787No ratings yet
- CHEN 4460 - Process Synthesis, Simulation and OptimizationDocument40 pagesCHEN 4460 - Process Synthesis, Simulation and Optimizationmppatilmayur1679No ratings yet
- NCERT Solution For CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions PDFDocument50 pagesNCERT Solution For CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions PDFneetaNo ratings yet
- CFSP Membership - WWW - CfseDocument3 pagesCFSP Membership - WWW - CfseSARFRAZ ALINo ratings yet
- Safety: Table 1: Safe Equipment. Authors: Cango. P, Espinoza. A, Lopez. C. (2019)Document4 pagesSafety: Table 1: Safe Equipment. Authors: Cango. P, Espinoza. A, Lopez. C. (2019)Alexander EspinozaNo ratings yet
- ALOHA Final Techdoc and QADocument51 pagesALOHA Final Techdoc and QAAubrey WessonNo ratings yet
- ChE 534 - Module 3Document34 pagesChE 534 - Module 3Precious JamesNo ratings yet
- Production of Sodium DithioniteDocument10 pagesProduction of Sodium DithioniteDhaval PadaliaNo ratings yet
- Lec5 PDFDocument15 pagesLec5 PDFRaviNo ratings yet
- REACTOR DESIGNDocument9 pagesREACTOR DESIGNKhalil LasferNo ratings yet
- ON Overview of Ongc C2-C3 Plant, Dahej, Gujarat: Winter Training ProgramDocument46 pagesON Overview of Ongc C2-C3 Plant, Dahej, Gujarat: Winter Training ProgramU19CH076 ZEELKUMAR PATEL SVNITNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution - Plume RiseDocument15 pagesAir Pollution - Plume RiseAmrut RajkarneNo ratings yet
- Efficient PHA of Non-Continuous Operating ModesDocument25 pagesEfficient PHA of Non-Continuous Operating ModesShakirNo ratings yet
- Optimise Heat Exchanger Network DesignDocument2 pagesOptimise Heat Exchanger Network DesignAmirul AfiqNo ratings yet
- CHE F418 Modelling and Simulation in Chemical Engineering 3 0 3Document5 pagesCHE F418 Modelling and Simulation in Chemical Engineering 3 0 3Narayani KelkarNo ratings yet
- Hse Uitm - Chapter 3Document90 pagesHse Uitm - Chapter 3MasrulIsmailNo ratings yet
- PHA Training - Day 1Document50 pagesPHA Training - Day 1ahmad jamalNo ratings yet
- Rate Equation of Polymarization ReactionDocument334 pagesRate Equation of Polymarization ReactionSherif Nour100% (1)
- Hazop Analysis Worksheet (Ammonia High Level)Document2 pagesHazop Analysis Worksheet (Ammonia High Level)Kenneth Teow100% (1)
- HSE - Loss Prevention in The Petrochemical and Chemical-Process High-Tech Industries in TaiwanDocument8 pagesHSE - Loss Prevention in The Petrochemical and Chemical-Process High-Tech Industries in TaiwanLandryNo ratings yet
- Oims Framework BrochureDocument20 pagesOims Framework BrochureJorge Rodríguez100% (1)
- Hazop - Net PDFDocument9 pagesHazop - Net PDFPalash DeyNo ratings yet
- OPITO and Other CoursesDocument17 pagesOPITO and Other Coursesrony_lesbtNo ratings yet
- Steam Methane Reforming Reaction Process Intensification by Using A ReactorDocument14 pagesSteam Methane Reforming Reaction Process Intensification by Using A ReactorserchNo ratings yet
- Materials Selection in Oil and Gas-An OverviewDocument15 pagesMaterials Selection in Oil and Gas-An OverviewAli AliNo ratings yet
- European Nickel PLCDocument24 pagesEuropean Nickel PLCewin basokeNo ratings yet
- 73 220 Lecture14 SolnDocument13 pages73 220 Lecture14 Solnapi-26315128No ratings yet
- Retake Form of GBIF ExaminationDocument1 pageRetake Form of GBIF ExaminationNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Brosur Env Tech MNGMT - Compressed.compressedDocument4 pagesBrosur Env Tech MNGMT - Compressed.compressedNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Signature Tower QAQC RecordsDocument18 pagesSignature Tower QAQC RecordsNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- 7days Kunming Dali Lijiang Muslim Tour (May.2018 2paxs)Document1 page7days Kunming Dali Lijiang Muslim Tour (May.2018 2paxs)NethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Vegetarian Men2 PDFDocument1 pageVegetarian Men2 PDFNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Secrets of Success PDFDocument7 pagesSecrets of Success PDFNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Communicating Risk Government DefinitionDocument80 pagesCommunicating Risk Government DefinitionlifeinthemixNo ratings yet
- Health, Safety and Environment (HSE) Monthly Report: Please Refer Calculation of LTI in Safety StatisticDocument4 pagesHealth, Safety and Environment (HSE) Monthly Report: Please Refer Calculation of LTI in Safety StatisticNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Hierarchy of ControlsDocument1 pageHierarchy of ControlsNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Chinese Phrase Dictation SheetDocument2 pagesChinese Phrase Dictation SheetNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Properties of DieselDocument7 pagesProperties of DieselNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Vegetarian Men2Document1 pageVegetarian Men2NethiyaaNo ratings yet
- CPWD Handbook Office BuildingDocument91 pagesCPWD Handbook Office Buildingexecutive engineer1No ratings yet
- Qlassic MinutesDocument2 pagesQlassic MinutesNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- UPSR SJKC English Paper 2 Section ADocument47 pagesUPSR SJKC English Paper 2 Section Ajklim100% (1)
- 2017060612325420170503164659brochure Master of EnvironmentDocument2 pages2017060612325420170503164659brochure Master of EnvironmentNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Colin Coa Peng Project Manager: Safety, Health & Environment Committee Chart Signature TowerDocument1 pageColin Coa Peng Project Manager: Safety, Health & Environment Committee Chart Signature TowerNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- AMCONDocument1 pageAMCONNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- SKMBT C35316120816230Document17 pagesSKMBT C35316120816230NethiyaaNo ratings yet
- China State Construction EngineeringDocument2 pagesChina State Construction EngineeringNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- AMCONDocument1 pageAMCONNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Client Client Client: Rfa/ Submittal Rfa/ Submittal Rfa/ SubmittalDocument17 pagesClient Client Client: Rfa/ Submittal Rfa/ Submittal Rfa/ SubmittalNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Velocity Head Method: P F Length, M Diameter, M K Volume, L/S Gravitational Force, N/M2 P, KpaDocument4 pagesEquivalent Velocity Head Method: P F Length, M Diameter, M K Volume, L/S Gravitational Force, N/M2 P, KpaNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Selecting The Right Speed Reducer For MixersDocument12 pagesSelecting The Right Speed Reducer For MixersNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Ratio of Impeller Diameter To Tank DiameterDocument2 pagesRatio of Impeller Diameter To Tank DiameterNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste ManagementDocument75 pagesSolid Waste ManagementNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- HRDocument7 pagesHRNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Rankine CycleDocument2 pagesOptimization of Rankine CycleNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- References UreaDocument2 pagesReferences UreaNethiyaaNo ratings yet
- JLG Lighting Tower 6308AN Series II 20150907Document2 pagesJLG Lighting Tower 6308AN Series II 20150907DwiSulistyo09No ratings yet
- Modeling of SO2 Scrubbing in Spray TowersDocument16 pagesModeling of SO2 Scrubbing in Spray Towersrebelde96100% (1)
- TV Compatibility with Verbatim HDDsDocument2 pagesTV Compatibility with Verbatim HDDsmirciulicacatyNo ratings yet
- Filter DesignDocument4 pagesFilter Designhassan11783No ratings yet
- 2 Interference in Spur GearsDocument2 pages2 Interference in Spur Gearschris100% (1)
- Applied Fluid Mechanics: Viscosity of FluidsDocument22 pagesApplied Fluid Mechanics: Viscosity of FluidsMaggie HepditchNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0038080612000790 Main PDFDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S0038080612000790 Main PDFJuanSebastianGamezNo ratings yet
- Odv-065r18ejj-G DS 2-0-3Document1 pageOdv-065r18ejj-G DS 2-0-3Евгений Переверзев0% (1)
- Magnum 3904 DatasheetDocument3 pagesMagnum 3904 DatasheetbobNo ratings yet
- Civil 3 8sem PDFDocument43 pagesCivil 3 8sem PDFG0utham100% (1)
- Leica 307 ManualDocument4 pagesLeica 307 ManualRaluca Sandu100% (2)
- CFS50 motor feedback installation instructionsDocument1 pageCFS50 motor feedback installation instructionsJavier AlzateNo ratings yet
- January2016page1to36 Layout 1Document36 pagesJanuary2016page1to36 Layout 1c737No ratings yet
- Testing Machines For TextilesDocument35 pagesTesting Machines For TextilesAmarech YigezuNo ratings yet
- GENG 8000 Final Project Memo - W19 FinalDocument2 pagesGENG 8000 Final Project Memo - W19 Finalஇலக்கியா ராஜாNo ratings yet
- Zener DataDocument2 pagesZener Dataapi-27149887No ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements LabDocument40 pagesElectrical Measurements Labmdayyub100% (4)
- EGIG - 10th - Report - Final - 09-03-2018 - v1Document50 pagesEGIG - 10th - Report - Final - 09-03-2018 - v1Paulo Marcos Cabral JuniorNo ratings yet
- Smart Access 1105Document12 pagesSmart Access 1105Gerson Freire De Amorim FilhoNo ratings yet
- Please Note That This Form Details Exploration and Production Api Titles Available For OrderDocument8 pagesPlease Note That This Form Details Exploration and Production Api Titles Available For Orderhaotran68No ratings yet
- SW-TS40T Sub-Miniature Toggle SwitchesDocument4 pagesSW-TS40T Sub-Miniature Toggle SwitchesVALTERNo ratings yet
- Deventer04 MACDocument201 pagesDeventer04 MACFrancisco Solano Reyes EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Stress-Strain Behaviour of Steel-Fibre-Reinforced Recycled Aggregate Concrete Under Axial TensionDocument16 pagesStress-Strain Behaviour of Steel-Fibre-Reinforced Recycled Aggregate Concrete Under Axial TensionAndrucruz CruzNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Research Proposal - SandboxingDocument23 pagesCyber Security Research Proposal - SandboxingAnonymous Sa6jc83D100% (4)
- Unit Conversion Heat TransferDocument5 pagesUnit Conversion Heat TransferFamela GadNo ratings yet
- Dewatering SystemDocument124 pagesDewatering SystemSpyros NannosNo ratings yet
- Wireless Mouse m325 Quick Start GuideDocument2 pagesWireless Mouse m325 Quick Start GuideFabolos 9No ratings yet
- Manual Servicio SubaruDocument5,963 pagesManual Servicio SubaruCristian Mauricio Alarcon RojasNo ratings yet
- Murray Loop Test To Locate Ground Fault PDFDocument2 pagesMurray Loop Test To Locate Ground Fault PDFmohdNo ratings yet
- Carestream DryView 5700 PDFDocument44 pagesCarestream DryView 5700 PDFJose Quisca100% (1)