Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Er Drugs
Uploaded by
Meriam Angelita Robles AlfaroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Er Drugs
Uploaded by
Meriam Angelita Robles AlfaroCopyright:
Available Formats
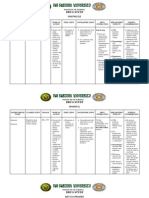
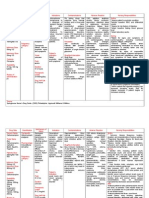
GENERIC NAME
(BRAND NAME)
CLASSIFICATION
INDICATIONS Vertigo/Meniere 's disease Vertiginous syndromes, other disorders of vestibular system Hypotension Ventricular Fibrillation (Cardiac Arrest) & Unstable Ventricular Tachycardia
SIDE EFFECTS Headache. Upset stomach / Dyspepsia Insomnia Nausea fatigue, eye deposits, tremor, unsteady gait, nausea, vomiting, constipation, weight loss, dizziness, visual changes constipation heartburn dizziness headache
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES 1. Avoid contact of oral solution or injection with skin 2. Raise bed rails 3. Safety measures 4. Supervise ambulation 1. Monitor ECG, HR, BP 2. Use a 0.22 micron filter 3. Use glass bottle for continuous infusion. A bag may be used for the bolus as long as it is given within one hour of mixing. 1. Closely monitor BP during first 2weeks of drug therapy or when dosage is adjusted esp. in patients with heart failure and hyponatremia. 2. Be alert for s/sx of angioedema. 3. Assess patient for bradycardia and hypotension w/c may indicate AV block. 4. Take the drug with food. 5. Encourage patient to increase dietary fiber intake to prevent constipation. 1.Monitor vital signs , and ECG during infusion, 2. Watch for dsyarrythmias and ischemia also monitor, PCWP,CVP, CO2, and urinary output
Betahistine HCL (Serc)
Antivertigo
Amiodarone (Cordarone)
Antiarrhythmic Agent
Verapamil (Calan)
Anti-Anginal Drugs Calcium Antagonists
Angina pectoris Hypertension AF and tachycardias to bring down HR Mania and Hypomania Migraine and cluster headaches
Dopamine (Intropin)
Adrenergic and Dopaminergic Cardiac Stimulants Sympathomime tic
Acute heart failure Hypotension Low cardiac output states
Nausea and vomiting Heartburn Sedation/ Daytime sleepiness Leg swelling
Dizziness Impulsive or compulsive behaviors e.g gambling, overeating, hypersexualit y problems
3.Monitor for possible adverse reaction 4. Assess for heart failure: dsypnea ,neck vein distention, 5. Assess for oxygenation and perfusion deficit.
You might also like
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine BesylateDocument7 pagesAmlodipine BesylatebabuagoodboyNo ratings yet
- GENERIC/BRAND MECHANISM OF CLASSIFICATION ACTIONDocument3 pagesGENERIC/BRAND MECHANISM OF CLASSIFICATION ACTIONEmJay Balansag100% (5)
- 5 MG Iv BidDocument17 pages5 MG Iv BidhanzreinherNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- IV antibiotic phlebitis signsDocument67 pagesIV antibiotic phlebitis signsjanet roosevelt94% (65)
- Drug Study: OmeprazoleDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Omeprazoleclau_latojaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyreanne_davidNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNephrolithiasis - Drug StudyAia JavierNo ratings yet
- IV antibiotics post-infusion phlebitis signsDocument124 pagesIV antibiotics post-infusion phlebitis signsD and D Educators and Associates100% (2)
- Trandate (Labetalol)Document3 pagesTrandate (Labetalol)ENo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Drug Name Adverse EffectsDocument3 pagesDrug Classification Drug Name Adverse EffectsninapotNo ratings yet
- Potassium-Sparing Diuretic Aldacton GuideDocument8 pagesPotassium-Sparing Diuretic Aldacton GuideJoy CalmerinNo ratings yet
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Document4 pagesChlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Nurginayah RusliNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Crash CartDocument14 pagesEmergency Drugs Crash CartEricson SomeraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesCardiovascular SystemRegineCuasSulibNo ratings yet
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: Aminophylline, Amiodarone, Atropine, BumetanideDocument33 pagesEMERGENCY DRUGS: Aminophylline, Amiodarone, Atropine, BumetanideNicole GarciaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument14 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyDocument8 pagesEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyShaine WolfeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN EtcDocument6 pagesDrug Study - HYDROCORTISONE, DIAZEPAM, DIGOXIN Etc'jmark FranciaNo ratings yet
- Lascuna-Drug StudyDocument8 pagesLascuna-Drug StudyAiza Pearl LascuñaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmias Drug AmiodaroneDocument7 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias Drug AmiodaroneMarie Angeline ManzanoNo ratings yet
- CARDIAC DRUGS ATROPINE SULFATE Isopto Atropine Classification Anticholinergics Dosage Bradycardi1Document11 pagesCARDIAC DRUGS ATROPINE SULFATE Isopto Atropine Classification Anticholinergics Dosage Bradycardi1Angeley SabutananNo ratings yet
- Uriarte, Kate Cybel SiaDocument11 pagesUriarte, Kate Cybel SiaChresia Schae MondejarNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin-Tazobactam AntibioticDocument9 pagesPiperacillin-Tazobactam Antibiotic배기숭No ratings yet
- Felodipine Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument22 pagesFelodipine Nursing ResponsibilitiesPaula Xavier AlfalahiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyQueenie Gail Duarte RodrigoNo ratings yet
- RNSG 1533 Raising The Bar For Success Concept: Metabolism: Diabetes Type 1/diabetes Type 2Document4 pagesRNSG 1533 Raising The Bar For Success Concept: Metabolism: Diabetes Type 1/diabetes Type 2katrinasdNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Urinary Tract Infection with CefuroximeDocument5 pagesTreatment of Urinary Tract Infection with CefuroximeOamaga NajlaNo ratings yet
- Drugprofiledobutamine 140507094836 Phpapp02Document42 pagesDrugprofiledobutamine 140507094836 Phpapp02Balaji BscRTNo ratings yet
- COPD Drug Study: Ipratropium Bromide and Albuterol SulfateDocument9 pagesCOPD Drug Study: Ipratropium Bromide and Albuterol SulfateShane Arroyo100% (1)
- Drug Mechanism of Action, Indications, Contraindications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument31 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action, Indications, Contraindications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesiamjenivicNo ratings yet
- The 10 Most Common Emergency DrugsDocument28 pagesThe 10 Most Common Emergency DrugsKrishna BalsarzaNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyAllyne GavinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument34 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsMei-mei ZhuangNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyFelecidario TaerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyIrveen Joy RamirezNo ratings yet
- C C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentDocument12 pagesC C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentEarl Tony TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Classification Mode of Action Indications Contra-Indications Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument11 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Classification Mode of Action Indications Contra-Indications Adverse Reactions Nursing ResponsibilitiesChristine AlavazoNo ratings yet
- Drug Indication Action Side Effects and Adverse Reaction Nursing ConsiderationDocument8 pagesDrug Indication Action Side Effects and Adverse Reaction Nursing Considerationkier khierNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Medications ReviewDocument4 pagesRespiratory Medications ReviewKevin VillaranteNo ratings yet
- Drug Profile Dobutamine 2Document42 pagesDrug Profile Dobutamine 2Emily MccarthyNo ratings yet
- RX - Citicoline, Kalium, Ketosteril, Methycobal, Myonal, Lipolin GelDocument6 pagesRX - Citicoline, Kalium, Ketosteril, Methycobal, Myonal, Lipolin GelntootNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineDocument8 pagesDrug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineAiryn CanonNo ratings yet
- Emergency Room Drugs Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument20 pagesEmergency Room Drugs Nursing ResponsibilitiestsikiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 pagesClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Risperidone Drug Study GuideDocument7 pagesRisperidone Drug Study GuideKristine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument12 pagesDrug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- SeroquelDocument1 pageSeroquelE100% (1)
- Daftar Obat Anti Hipertensi PDFDocument7 pagesDaftar Obat Anti Hipertensi PDFPietra Jaya100% (1)
- Drug Study For Syntocinon Potassium Chloride, and BuscopanDocument4 pagesDrug Study For Syntocinon Potassium Chloride, and BuscopanRj AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument40 pagesEmergency Drugsmattheus101No ratings yet
- Ampicillin Sulbactam 1.5 gm, Clindamycin Hydrochloride, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg tab, Furosemide 40mg IV, Ipratropium Bromide, Paracetamol 500mg, Tramadol Hydrochloride 500mg IV drug infoDocument10 pagesAmpicillin Sulbactam 1.5 gm, Clindamycin Hydrochloride, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg tab, Furosemide 40mg IV, Ipratropium Bromide, Paracetamol 500mg, Tramadol Hydrochloride 500mg IV drug infoVictor BiñasNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHyperthyroidism, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- Syncope, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandSyncope, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Functional Health PatternsDocument7 pagesFunctional Health PatternsMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Family StructureDocument92 pagesFamily StructureMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- 2013 Deadline Dates 2 PDFDocument1 page2013 Deadline Dates 2 PDFMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study. AbagonDocument4 pagesDrug Study. AbagonMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Feu ErDocument5 pagesDrug Study-Feu ErMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FurtonDocument6 pagesDrug Study FurtonMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument17 pagesPDFMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- 100 DrugsDocument3 pages100 DrugsMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- (Brand Name) : Generic Name Classificati ON Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pages(Brand Name) : Generic Name Classificati ON Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- The Despicable Guy Book 1 PDFDocument428 pagesThe Despicable Guy Book 1 PDFMeriam Angelita Robles Alfaro60% (15)
- TerrorismDocument14 pagesTerrorismMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PoDocument2 pagesDrug Study PoMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Complicated Love PDFDocument199 pagesComplicated Love PDFMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- TerrorismDocument14 pagesTerrorismMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Chronic Bone Infection AssessmentDocument2 pagesChronic Bone Infection AssessmentMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- ExamplesDocument3 pagesExamplesMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Healthy Smoothie RecipesDocument1 pageHealthy Smoothie RecipesMeriam Angelita Robles AlfaroNo ratings yet