Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Algebra Rules
Uploaded by
Kirti ChhayaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Algebra Rules
Uploaded by
Kirti ChhayaCopyright:
Available Formats
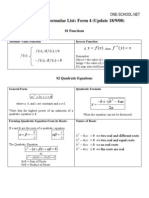
Basic Rules for Algebra & Logarithmic Functions
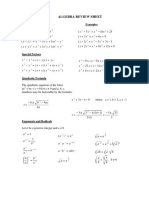
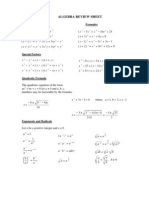
Quadratic Formula: If p( x) = ax 2 + bx + c , a 0 and 0 b 2 4ac ,
b b 2 4ac . 2a
Example:
If p( x) = x 2 + 3x 1 =0, with a=1, b=3, and c=-1, then p(x) =0 if x =
3 13 2 Examples: x 2 9 = ( x 3)( x + 3) x 3 8 = ( x 2)( x 2 + 2 x + 4) x 3 + 27 = ( x + 3)( x 2 3x + 9) Examples: ( x + 3) 2 = x 2 + 2( x)(3) + 32 = x 2 + 6 x + 9 ( x 5) 2 = x 2 2( x)(5) + 52 = x 2 10 x + 25 ( x + 2)3 = x 3 + 3( x) 2 (2) + 3( x)(2) 2 + 23 = x 3 + 6 x 2 + 12 x + 8 ( x 1)3 = x 3 3( x) 2 (1) + 3( x)(1) 2 13 = x 3 3 x 2 + 3 x 1 Example: 3x 3 2 x 2 6 x + 4 = x 2 (3 x 2) 2(3x 2) = ( x 2 2)(3x 2)
then the real zeroes of p are x =
Special Factors:
x 2 a 2 = ( x a)( x + a) x 3 a 3 = ( x a)( x 2 + ax + a 2 ) x 3 + a 3 = ( x + a)( x 2 ax + a 2 ) Binomial Theorem ( x + a) 2 = x 2 + 2ax + a 2 ( x a) 2 = x 2 2ax + a 2 ( x + a)3 = x 3 + 3ax 2 + 3a 2 x + a 3 ( x a)3 = x 3 3ax 2 + 3a 2 x a 3 Factoring by Grouping acx 3 + adx 2 + bcx + bd = ax 2 (cx + d ) + b(cx + d ) = (ax 2 + b)(cx + d )
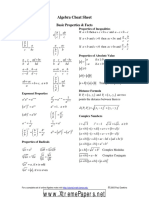
Arithmetic Operations:
a b = a c = a d = ad c b d b c bc d
ab + ac = a(b + c)
a c ad + bc + = b d bd
a+b a b = + c c c
b a b ab a = = c c 1 c
a a b a c ac = = = b 1 c 1 b b c
a b 1 a b b a = = c d 1 c d d c
ab + ac a(b + c) = =b+c, a a a0
a b = a c = a1 = a c b 1 b c bc
The Math Center
Valle Verde
Tutorial Support Services
EPCC
Exponents and Radicals
a0 = 1 , a 0
ax = a x y y a
ax a = bx b
am = a
n
( a)
n
a x =
x y
1 ax
x+ y
(a )
(ab )
x y
= a xy
a =a
x
n
ab = n a n b
n
a a =a
=ab
x
a =a
a = b
n n
a b
Algebraic Errors to Avoid:
a a a + x+b x b
x2 + a2 x + a a b( x 1) a bx b
To see this error, let a, b, and, x all equal to 1. Then, To see this error, let x = 3 and a = 4. Then, 5 7 .
1 2. 2
x a bx b a
x2 + a2 x2 a2 a + bx 1 + bx a
Remember to distribute the negative signs. The equation should be a b( x 1) = a bx + b To divide fractions, invert and multiply. The equation should be x x x 1 x a = a = = b b a b ab 1 We cant factor a negative sign outside of the square root.
This is one of many examples of incorrect cancellation. By applying a + bx a bx bx the properties above, the equation should be = + = 1+ . a a a a In this case we multiply the exponents, then the correct equation is ( x 2 )3 = x 2 x 2 x 2 = x 2 + 2 + 2 = x 6
LOGARITHMIC RULES
(x )
2 3
x5
Logarithmic function Common logarithm Natural logarithm Log Properties
y = log a x , defined by x = a y log x = log10 x ln x = log e x
log a (MN ) = log a M + log a N
log a (M ) = N (log a M )
N
log a a x = x ; a log a x = x
log a (M / N ) = log a M log a N
Change of base formulas
log x log b ln x logb x = ln b log b x =
Valle Verde Tutorial Support Services EPCC
The Math Center
You might also like
- Algebra Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesAlgebra Cheat SheetSophieSzhangNo ratings yet
- Algebra and Geometry FormulasDocument2 pagesAlgebra and Geometry FormulasKhanNo ratings yet
- Halliday-Resnick-Walker Fundamentals of Physics 9th EditionDocument3 pagesHalliday-Resnick-Walker Fundamentals of Physics 9th EditionJose Garcia100% (1)
- MATH-FORMULAE1 mEquation of normal: y − y1 = − 1 ( x − x1 ) mmDocument16 pagesMATH-FORMULAE1 mEquation of normal: y − y1 = − 1 ( x − x1 ) mmNicholas Rogers80% (5)
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Algebra Cheat Sheet: Basic Properties & FactsDocument4 pagesAlgebra Cheat Sheet: Basic Properties & FactsmacgyverNo ratings yet
- Algebra Review 05Document2 pagesAlgebra Review 05lmlNo ratings yet
- Algebra Review SheetDocument2 pagesAlgebra Review SheetGiulio CNo ratings yet
- Math Resources Algebra FormulasDocument4 pagesMath Resources Algebra FormulasSanjiv GautamNo ratings yet
- Fórmulas de Cálculo Diferencial e Integral: Jesús Rubí MirandaDocument3 pagesFórmulas de Cálculo Diferencial e Integral: Jesús Rubí MirandaAnthony GuaniloNo ratings yet
- Mathematical RelationshipsDocument5 pagesMathematical RelationshipsJuan A RaposoNo ratings yet
- Formulario de Cálculo Diferencial e Integral: Jesús Rubí Miranda (Document2 pagesFormulario de Cálculo Diferencial e Integral: Jesús Rubí Miranda (lagarto27No ratings yet
- F C D I: Ormulario de Álculo Iferencial E NtegralDocument2 pagesF C D I: Ormulario de Álculo Iferencial E Ntegralpaz_aranibarNo ratings yet
- Essential FormulasDocument7 pagesEssential FormulasShinigami01001No ratings yet
- A-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047) Updated 6th Apr 2015 PDFDocument12 pagesA-Math Formula List - Additional Math (4047) Updated 6th Apr 2015 PDFilluminatehNo ratings yet
- Formulario Calculo Dif - IntegralDocument4 pagesFormulario Calculo Dif - IntegralRocki R SebastiánNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics 4Document15 pagesPure Mathematics 4toney lukaNo ratings yet
- Integration Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesIntegration Cheat Sheetjiebo100% (1)
- Fracciones Exponentes Ecuaciones: ResumenDocument1 pageFracciones Exponentes Ecuaciones: ResumenYomira Burgos FernándezNo ratings yet
- Lecture Week 1Document16 pagesLecture Week 1Fiona Ann Marie GagucasNo ratings yet
- Rules of Differentiation and IntegrationDocument10 pagesRules of Differentiation and IntegrationKitchanan KosalathipNo ratings yet
- m30-1 Formula SheetDocument1 pagem30-1 Formula Sheetapi-289565679No ratings yet
- Calculus and Differential Integral Formulas GuideDocument2 pagesCalculus and Differential Integral Formulas GuideSergio Jimenez ZarzaNo ratings yet
- Partial Fractions: Harvey Mudd College Math TutorialDocument3 pagesPartial Fractions: Harvey Mudd College Math TutorialArtist RecordingNo ratings yet
- Desigualdades e Inecuaciones: A A A B A B A A B ADocument2 pagesDesigualdades e Inecuaciones: A A A B A B A A B AjpazmNo ratings yet
- Wang07 PDFDocument6 pagesWang07 PDFNandang Arif SaefulohNo ratings yet
- Integration by Partial FractionDocument23 pagesIntegration by Partial FractionMisa KurobaneNo ratings yet
- Essential formulae for Number and AlgebraDocument16 pagesEssential formulae for Number and AlgebraMaruthappan Sundaram100% (1)
- Polynomial functions and factoring techniquesDocument43 pagesPolynomial functions and factoring techniquesAnonymous na314kKjOANo ratings yet
- Algebra, Equations and Functions Solved ExamplesDocument6 pagesAlgebra, Equations and Functions Solved ExamplesBiswajeet PandaNo ratings yet
- A2 Reference Sheet 01Document5 pagesA2 Reference Sheet 01rajbmohanNo ratings yet
- Formula RioDocument6 pagesFormula RioJorge Laura GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Formule Trigonometrice Derivarea Si Integrarea Functiilor CompuseDocument2 pagesFormule Trigonometrice Derivarea Si Integrarea Functiilor Compusekissu_diana281No ratings yet
- Formule Puteri Radicali Si LogaritmiDocument3 pagesFormule Puteri Radicali Si LogaritmiAdrian CocosNo ratings yet
- Emcet Bits PDFDocument7 pagesEmcet Bits PDFPaladugurevanth40% (5)
- Exponential Function NotesDocument14 pagesExponential Function NoteswelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- Math Stats Booklet 1Document20 pagesMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoNo ratings yet
- Ah FormulaeDocument5 pagesAh FormulaeVijay RajuNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)Document4 pagesFormula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)naedkcinNo ratings yet
- Zavrsni Rjesenja 2806Document2 pagesZavrsni Rjesenja 2806AdnanKapetanovicDadoNo ratings yet
- Other Inequalities Exercise Solution PDFDocument4 pagesOther Inequalities Exercise Solution PDFChai Usajai UsajaiNo ratings yet
- Exponent, Square and Cube RootDocument8 pagesExponent, Square and Cube RootAyesha AfzalNo ratings yet
- Online Lecture Week 2 - Morning ClassDocument24 pagesOnline Lecture Week 2 - Morning ClasszamkNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Cambridge Mathematics AS and A Level Course: Second EditionFrom EverandCambridge Mathematics AS and A Level Course: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"From EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)