Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Screening For Down Syndrome
Uploaded by
abhagaurOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Screening For Down Syndrome
Uploaded by
abhagaurCopyright:
Available Formats
Down Syndrome
syndrome is a variable combination of congenital malformations caused by trisomy 21. It is the most commonly recognized genetic cause of mental retardation Because of the morbidity associated with Down syndrome, screening and diagnostic testing for this condition are offered as optional components of prenatal care. Prenatal diagnosis of trisomy 21 allows parents the choice of continuing or terminating an affected pregnancy.
Etiology and Clinical Manifestations
Down syndrome is usually identified soon after birth by a characteristic pattern of dysmorphic features The diagnosis is confirmed by karyotype analysis. Trisomy 21 is present in 95 percent of persons with Down syndrome. Mosaicism, a mixture of normal diploid and trisomy 21 cells, occurs in 2 percent. The remaining 3 percent have a Robertsonian translocation in which all or part of an extra chromosome 21 is fused with another chromosome. Most chromosome-21 translocations are sporadic. AGE RELATED RISK A 20 year-old woman has a 1 in 1,500 risk of having a baby with Down's syndrome. A 30 year-old woman has a 1 in 800 risk. A 35 year-old woman has a 1 in 270 risk. A 40 year-old woman has a 1 in 100 risk. A 45 year-old woman has a 1 in 50 risk or greater.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging can be used to screen for Down syndrome. Increased fetal nuchal translucency (NT) is an indicator of increased risk of Down syndrome. A 2003 systematic review of 30 studies of NT in Down syndrome found an average sensitivity of 75-80% with a false positive rate of 5.8-6% (95% confidence intervals).Therefore, while the false positive rate is too high for NT to be used alone as a screening test, it is useful as part of a combined test. Ultrasound measurement of NT is usually performed between 11 and 14 weeks gestation.
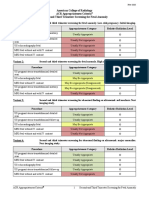
First and second trimester Down syndrome screens
Screen
When False Detection performed positive rate (weeks rate
Description
Combined test (Nuchal translucency/free beta-hCG/PAPP-A screen)
1013.5
85%
5%
Quad screen
1520
81%
5%
This test measures the maternal serum alphafetoprotein, unconjugated estriol, beta-hCG, andAlpha (INHA).
Integrated test
15-20
95
5%
The integrated test uses measurements from both the 1st trimester combined test and the 2nd trimester quad test to yield a more accurate screening result. Because all of these tests are dependent on accurate calculation of the gestational age of the fetus, the real-world false-positive rate is >5% and may be closer to 7.5%.
Incidence of Some Associated Medical Complications in Persons with Down Syndrome
DISORDER Mental retardation Growth retardation Early Alzheimer's disease INCIDENCE (%) > 95 > 95 Affects 75% by age 60 40
Congenital heart defects (atrioventricular canal defect, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus, tetralogy of Fallot) Hearing loss (related to otitis media with effusion or sensorineural) Ophthalmic disorders (congenital cataracts, glaucoma, strabismus) reased nuchal fold thickness Cystic hygromas Echogenic intracardiac foci Congenital heart defects Increased intestinal echogenicity
40 to 75
60
RECURRENCE RISK AND FAMILY HISTORY
If a patient has had a trisomy 21 pregnancy in the past, the risk of recurrence in a subsequent pregnancy increases to approximately 1 percent above the baseline risk determined by maternal age. Diagnosis of a chromosome-21 translocation in the fetus or newborn is an indication for karyotype analysis of
both parents. If both parents have normal karyotypes, the recurrence risk is 2 to 3 percent. If one parent carries a balanced translocation, the recurrence risk depends on the sex of the carrier parent and the specific chromosomes that are fused.
Recommended additional monitoring of children with Down syndrome by DSMIG and CGAAP.
Test
Age
Hearing test
6 months, 12 months, then 1/year
T4 and TSH
6 months, then 1/year
Ophthalmic evaluation
6 months, then 1/year
Dental examination
2 years, then every 6 months.
Coeliac disease screening
Between 2 and 3 years of age, or earlier if symptoms occur.
Baseline polysommography
3 to 4 years, or earlier if symptoms of obstuuctive sleep apnea occur.
Cervical neck x-rays
Between 3 and 5 years of age
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- First-Trimester Ultrasound Nuchal Translucency Screening For Fetal AneuploidyDocument37 pagesFirst-Trimester Ultrasound Nuchal Translucency Screening For Fetal AneuploidyCTAFDocumentsNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Icri Guidelines On 11-14 Weeks Obstetric Scan July 2020Document19 pagesIcri Guidelines On 11-14 Weeks Obstetric Scan July 2020hasnainpasha100% (2)
- Clinics in ObstetricsDocument770 pagesClinics in ObstetricsSAKAI69100% (3)
- Menstrual DisordersDocument17 pagesMenstrual DisordersabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Ujian Lokal MCQDocument23 pagesUjian Lokal MCQAnnissa Syaira100% (2)
- IUGRDocument6 pagesIUGRabhagaurNo ratings yet
- 1 First Trimester UltrasonographyDocument17 pages1 First Trimester UltrasonographyClaudia Paola Salazar SanchezNo ratings yet
- Obs Gynae Full Summary NotesDocument41 pagesObs Gynae Full Summary NotesJana Aldour100% (1)
- Master 2 8Document167 pagesMaster 2 8abhagaurNo ratings yet
- HospitalDocument2 pagesHospitalabhagaurNo ratings yet
- SynopsysDocument4 pagesSynopsysabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Fibre Optics BasicsDocument12 pagesFibre Optics BasicsSenthilathiban Thevarasa100% (2)
- Worker's Day Inspection - 2013: Dedicated To Make The Difference Dalla HospitalDocument42 pagesWorker's Day Inspection - 2013: Dedicated To Make The Difference Dalla HospitalabhagaurNo ratings yet
- PPHDocument4 pagesPPHabhagaurNo ratings yet
- C EssentialsDocument45 pagesC EssentialssuchitraprasannaNo ratings yet
- Pointers and MemoryDocument31 pagesPointers and MemorySivasai KumarNo ratings yet
- C EssentialsDocument45 pagesC EssentialssuchitraprasannaNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasmosis During PregnancyDocument4 pagesToxoplasmosis During PregnancyabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Colposcopy ExaminationDocument5 pagesColposcopy ExaminationabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Basic CioDocument10 pagesBasic CioabhagaurNo ratings yet
- 7 Indian Restaurants Among Asia's Top 50 - The Times of IndiaDocument7 pages7 Indian Restaurants Among Asia's Top 50 - The Times of IndiaabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Follow Up Protocol in PT On OcDocument1 pageFollow Up Protocol in PT On OcabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Disaster MitigationDocument19 pagesDisaster MitigationAbha GaurNo ratings yet
- Colposcopy ExaminationDocument5 pagesColposcopy ExaminationabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Visual ScreeningDocument35 pagesVisual ScreeningabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Food Establishment Inspection ReportDocument5 pagesFood Establishment Inspection ReportabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Worker's Day Inspection - 2013: Dedicated To Make The Difference Dalla HospitalDocument42 pagesWorker's Day Inspection - 2013: Dedicated To Make The Difference Dalla HospitalabhagaurNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Health Related Physical FitnessDocument70 pagesHealth Related Physical FitnessabhagaurNo ratings yet
- April 2009 Diabetes Communique FinalDocument6 pagesApril 2009 Diabetes Communique FinalabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Diabetes in Adults Quality StandardDocument5 pagesDiabetes in Adults Quality StandardabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Adios AmigoDocument13 pagesAdios AmigoabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasmosis: Clinical Features Investigation Management Outcome PreventionDocument4 pagesToxoplasmosis: Clinical Features Investigation Management Outcome PreventionabhagaurNo ratings yet
- BMWDocument29 pagesBMWabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Tablet: List of Medicines Required For Upcp HospitalsDocument6 pagesTablet: List of Medicines Required For Upcp HospitalsabhagaurNo ratings yet
- Screening and Diagnostic Test For Chromosomal DisordersDocument21 pagesScreening and Diagnostic Test For Chromosomal DisordersJohn Van Dave TaturoNo ratings yet
- Congenital Anomalies: Dr. Bertha Soegiarto, Sp.ADocument26 pagesCongenital Anomalies: Dr. Bertha Soegiarto, Sp.AChristine VerinaNo ratings yet
- Medical Ethics Study Guide 6-3-2010Document54 pagesMedical Ethics Study Guide 6-3-2010kachapaxxNo ratings yet
- Ecocardiografia 5 Cortes YagelDocument3 pagesEcocardiografia 5 Cortes YagelMaria Alejandra Guzmán Quijada100% (1)
- 1st TRIMESTER US SCREENING - SONOEMBRIOLOGI PDFDocument17 pages1st TRIMESTER US SCREENING - SONOEMBRIOLOGI PDFhadisejati81No ratings yet
- Chromosomal Disorder: Genetics DiseasesDocument40 pagesChromosomal Disorder: Genetics Diseaseslilik maula shobriNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Aneuploidy ScreeningDocument80 pagesPrenatal Aneuploidy ScreeningBharti Pant GahtoriNo ratings yet
- Platinum Clalit Nov 2011Document3 pagesPlatinum Clalit Nov 2011EnglishAccessibilityNo ratings yet
- Second and Third Trimester Screening For Fetal AnomalyDocument12 pagesSecond and Third Trimester Screening For Fetal AnomalyIqra NazNo ratings yet
- PRISCA PresentationDocument42 pagesPRISCA PresentationAlexandr ChuvakovNo ratings yet
- Down SyndromeDocument20 pagesDown SyndromeChristine Damayanti LumbangaolNo ratings yet
- Us ObDocument16 pagesUs ObWahyu RianiNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Human Development, Meaning, Concepts and Approaches Content OutlineDocument28 pagesModule 1: Human Development, Meaning, Concepts and Approaches Content OutlineCristine Joy CalingacionNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1028455920301753 MainDocument4 pages1 s2.0 S1028455920301753 MainAditi SoniNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care What Is Meant by Antenatal Care?Document6 pagesAntenatal Care What Is Meant by Antenatal Care?Syed Haseeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- Down's Syndrome Pada KehamilanDocument35 pagesDown's Syndrome Pada KehamilanArga AdityaNo ratings yet
- Down's Syndrome GP GuideDocument6 pagesDown's Syndrome GP GuideElison J PanggaloNo ratings yet
- Basics of First Trimester Ultrasound in ObstetricsDocument29 pagesBasics of First Trimester Ultrasound in ObstetricsGeorge LeahuNo ratings yet
- Down Syndrome - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument20 pagesDown Syndrome - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaVenkataKrishna GaddeNo ratings yet
- Down Syndrome What Is Down Syndrome?Document4 pagesDown Syndrome What Is Down Syndrome?Vanessa Rose NoelNo ratings yet
- Non-Immune Fetal Hydrops: Are We Doing The Appropriate Tests Each Time?Document3 pagesNon-Immune Fetal Hydrops: Are We Doing The Appropriate Tests Each Time?dian_067No ratings yet
- Pathology Handbook - Royal Cornwall Hospital Trust 2011Document136 pagesPathology Handbook - Royal Cornwall Hospital Trust 2011Fuzzy_Wood_PersonNo ratings yet
- Prenatal ScreeningDocument24 pagesPrenatal Screeningk_hemantNo ratings yet
- Common Tests During PregnancyDocument7 pagesCommon Tests During Pregnancyrraja2k2No ratings yet