Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mechanisms T 2
Uploaded by
Alfonso Allister SmithOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mechanisms T 2
Uploaded by
Alfonso Allister SmithCopyright:
Available Formats
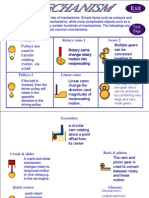
Mechanisms:
1. 2. 3. Mechanisms are simple devices (machines). It makes work easier. Mechanisms have an input and an output. P !"#$$ !UTPUT
INPUT
Input%& The input is a chan'e in condition that will in(luence the output. #)ample% Turning a key in the keyhole. Process%& Process takes place when there is a trans(er at the input. #)ample% Movement o( the ke* is transmitted throu'h the lock mechanisms (levers). !utput%& The output can take man* (orms. It is usuall* a predicta+le end result. #)ample% ,oor can +e locked and unlocked. TYPES OF MOVEMENT: -inear Movement% This is movement on a strai'ht line. #'. !penin' a door. otar* Movement% Movement in a circular direction. #'. .heels on a vehicle.
!scillatin' movement% This is semi&circular movement. #'. $win'in' on a swin'. eciprocatin' Movement% This is up&down/ le(t&ri'ht/ (orwards&+ackwards movement. #'. $awin' wood0 openin' and closin' +linds.
Cam systems: 1 cam s*stem is a mechanism that can +e used to chan'e one t*pe o( movement into another. 1 cam s*stem consists o( a cam and a (ollower. 1 cam is similar to a wheel/ +ut the a)le or sha(t is not in the middle o( the wheel. The shape o( the cam is not round either. The shape o( a cam is called a pro(ile. Cam shapes: "ams can have di((erent shapes dependin' on the movement that *ou want to create. .e (ind cam s*stems in to*s/ car en'ines/ etc. Types of cam shapes: Pear shape
2eart shape
#ccentric shape
#lliptical shape
$nail shape
Follower: 1 (ollower is a rod that rests on the ed'e o( the cam and it moves up and down as the cam moves around. The rotar* movement o( the cam creates a linear 3 reciprocatin' movement o( the (ollower. Cranks:
1 crank is a mechanism which turns rotar* movement into reciprocatin' movement. .e (ind cranks in pedals o( +ic*cles/ (ishin' rods/ windows o( cars/ hand operated sewin' machines/ to*s/ etc.
You might also like
- Kom 16 MarksDocument55 pagesKom 16 MarksnazeerabiaNo ratings yet
- ESC&AWK Operation&Maintenance ManualDocument21 pagesESC&AWK Operation&Maintenance ManualWander GomesNo ratings yet
- Cams and Followers Lecture - 2Document13 pagesCams and Followers Lecture - 2niaz kilamNo ratings yet
- 12simple MachineDocument29 pages12simple MachineuaragieNo ratings yet
- CAMS: Classification and TerminologyDocument16 pagesCAMS: Classification and TerminologySurya RSNo ratings yet
- Cam and Follower PDFDocument17 pagesCam and Follower PDFKlucifer XinNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowerDocument17 pagesCam and Followerniaz kilamNo ratings yet
- Cam and Follower: Definition, Types, Working Principle, and ApplicationsDocument17 pagesCam and Follower: Definition, Types, Working Principle, and Applicationsniaz kilamNo ratings yet
- 3 MechanismsDocument35 pages3 Mechanismsesham2100% (1)
- End Term EotDocument22 pagesEnd Term Eotishika SHANDILYANo ratings yet
- Presentation w4 LD Tran Le NhuDocument41 pagesPresentation w4 LD Tran Le NhuTài Nguyễn Văn ThànhNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowerDocument6 pagesCam and FollowerMUHAMMAD UMAR KAMRANNo ratings yet
- 1.1 A Simple Experiment: What Is A Cam?Document14 pages1.1 A Simple Experiment: What Is A Cam?Mohamed AwadNo ratings yet
- Types of MechanismsDocument19 pagesTypes of Mechanismstesfaye alebachewNo ratings yet
- UD 6 Mechanisms - Gears and Pulleys.Document10 pagesUD 6 Mechanisms - Gears and Pulleys.Sergio Ruiz ArranzNo ratings yet
- CamsDocument22 pagesCamsFelagot SisayNo ratings yet
- Blog - Oscarliang - Net - Build A Quadcopter Beginners Tutorial 1Document23 pagesBlog - Oscarliang - Net - Build A Quadcopter Beginners Tutorial 1Number ButNo ratings yet
- Towers of Hanoi: Team C Team C - ¡Los Murcielagos! Travis Brier Cristian Guajardo Gavin KangaDocument17 pagesTowers of Hanoi: Team C Team C - ¡Los Murcielagos! Travis Brier Cristian Guajardo Gavin KangatestiranjeNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowerDocument38 pagesCam and Follower1blank100% (4)
- Mechanics of Machine Lab ReportDocument22 pagesMechanics of Machine Lab ReportFaisal MehrbanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Systems - What You Need To KnowDocument19 pagesMechanical Systems - What You Need To KnowCool5150No ratings yet
- Escalator drive systems and components explainedDocument24 pagesEscalator drive systems and components explainedWawan AriessandiNo ratings yet
- Cam and FollowersDocument18 pagesCam and Followersnandkishore_singh100% (1)
- Design of Escalators ExplainedDocument32 pagesDesign of Escalators ExplainedRonalyn CalleleroNo ratings yet
- Automatic TransmissionDocument19 pagesAutomatic TransmissionFadh Zil IkramNo ratings yet
- MechanismDocument17 pagesMechanismm_er100No ratings yet
- CAMDocument27 pagesCAMVishal Oza100% (1)
- Cam Gate Notes 761686837008983Document8 pagesCam Gate Notes 761686837008983Somu SinghNo ratings yet
- CamsDocument19 pagesCamsfmgk7yjcncNo ratings yet
- Cam and Cam FollowersDocument13 pagesCam and Cam Followersm_er100No ratings yet
- What is a CAM and FOLLOWERDocument49 pagesWhat is a CAM and FOLLOWERMark Angelo Uy0% (1)
- Mesin Sekrap Pengolahan Permukaan RataDocument12 pagesMesin Sekrap Pengolahan Permukaan RataAripin SahruliNo ratings yet
- Escalators Basic ComponentsDocument37 pagesEscalators Basic Componentsnoedita100% (3)
- Mecanismos de TransmisionDocument94 pagesMecanismos de TransmisionFelipe EscobarNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Unit II: Pneumatic, Hydraulic, and Mechanical Actuation SystemsDocument20 pagesMechatronics Unit II: Pneumatic, Hydraulic, and Mechanical Actuation SystemsalagarsmeNo ratings yet
- MTD m1 NotesDocument43 pagesMTD m1 NotesAyush RajNo ratings yet
- DD 0 PT 2 N 0 Su 4 Isn 7Document13 pagesDD 0 PT 2 N 0 Su 4 Isn 7sumitsheokands57No ratings yet
- Igure: 1 (A) Fork Lever Roller Yoke Limit Switch. (B) Roller Arm Limit Switch. (C) Top Roller LimitDocument1 pageIgure: 1 (A) Fork Lever Roller Yoke Limit Switch. (B) Roller Arm Limit Switch. (C) Top Roller LimitJeffery YipNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Lab Procedure TheoryDocument10 pagesMachine Design Lab Procedure TheoryMuhammad Taufiq YusofNo ratings yet
- Unit 3. Simple MachinesDocument38 pagesUnit 3. Simple MachinesffergallNo ratings yet
- CamshaftDocument5 pagesCamshaftPrabha KaranNo ratings yet
- Btm... How Escalator WorksDocument9 pagesBtm... How Escalator WorksNiranjan KhambeteNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms Notes 2012Document12 pagesMechanisms Notes 2012kookwfNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Toy Booklet AltDocument11 pagesMechanical Toy Booklet AltPranav BISUMBHER100% (1)
- Roller Conveyor Operation ManualDocument3 pagesRoller Conveyor Operation Manualroberto_perraciniNo ratings yet
- In A Sliding Pair Minimum Number of Degree of FreedomDocument15 pagesIn A Sliding Pair Minimum Number of Degree of FreedomanuanwarNo ratings yet
- Conversion Gate02Document29 pagesConversion Gate02Ananta Kumar NandiNo ratings yet
- Everything about escalatorsDocument8 pagesEverything about escalatorsEstiven GierNo ratings yet
- ME 7 - Activity 5Document5 pagesME 7 - Activity 5Rygen Faye Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- 02P - Group 3 - Lab 3 PDFDocument18 pages02P - Group 3 - Lab 3 PDFadidas tempoNo ratings yet
- KOM MechanismsDocument20 pagesKOM MechanismsRamanathan DuraiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Robots Manipulator StructuresDocument18 pagesIndustrial Robots Manipulator StructuresTharindu Eranga FernandoNo ratings yet
- Lathe MachineDocument25 pagesLathe MachineAbhimanyu SinghNo ratings yet
- Manuel Minivator 2000Document46 pagesManuel Minivator 2000TUPET81100% (1)
- Chapter:-3 Cam and Cam ProfileDocument19 pagesChapter:-3 Cam and Cam ProfileParesh BhuvaNo ratings yet
- Abstract Eccentric CamsDocument2 pagesAbstract Eccentric CamsEnrique RuizNo ratings yet
- Oil Hydraulics and Pneumatics ApplicationsDocument25 pagesOil Hydraulics and Pneumatics ApplicationsAdeoti OladapoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 MTDocument18 pagesUnit 4 MTMuthuvel M100% (1)
- Singer Quantum Stylist 9960: Pocket Guide: Buttons, Dials, Settings, Stitches, and FeetFrom EverandSinger Quantum Stylist 9960: Pocket Guide: Buttons, Dials, Settings, Stitches, and FeetNo ratings yet
- Planning Calendar 2017Document4 pagesPlanning Calendar 2017Alfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- GRADE 5 MATHS Assessment GudelinesDocument10 pagesGRADE 5 MATHS Assessment GudelinesAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- New Pilir Annexures ADocument10 pagesNew Pilir Annexures AAlfonso Allister Smith100% (1)
- Abuse No More Protocol of The Western Cape Education DepartmentDocument36 pagesAbuse No More Protocol of The Western Cape Education DepartmentAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- 2 San Hunter GatherersDocument5 pages2 San Hunter GatherersAlfonso Allister Smith100% (1)
- 2014 Workbook2 Gr5 English NumDocument138 pages2014 Workbook2 Gr5 English NumAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- School Rules Code of ConductDocument2 pagesSchool Rules Code of ConductAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- Efal Grade 6 NovDocument10 pagesEfal Grade 6 NovAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- 2015 Released Items Ela g6Document46 pages2015 Released Items Ela g6Alfonso Allister Smith50% (4)
- Barriers To LearningDocument11 pagesBarriers To LearningAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- Thematic MapsDocument1 pageThematic MapsAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- 1 Finding Out About HunterDocument3 pages1 Finding Out About HunterAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- Thematic MapsDocument1 pageThematic MapsAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- Ehl Focus Challenge 1Document7 pagesEhl Focus Challenge 1Alfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- San Rock Art Reflects Spiritual Beliefs of Hunter-GatherersDocument2 pagesSan Rock Art Reflects Spiritual Beliefs of Hunter-GatherersAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- Positive NoteDocument1 pagePositive NoteAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- Programme of Assessment - Grade 7 TERM 2 - 2013: SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: June ExaminationDocument1 pageProgramme of Assessment - Grade 7 TERM 2 - 2013: SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: June ExaminationAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- Food Chains and WebsDocument13 pagesFood Chains and WebsGlenn Valentin MendozaNo ratings yet
- Direkte en Indirekte RedeDocument13 pagesDirekte en Indirekte RedeAlfonso Allister Smith0% (2)
- Assess Hist t2 2013Document6 pagesAssess Hist t2 2013Alfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- PST312M Assign02 2014Document5 pagesPST312M Assign02 2014Alfonso Allister Smith100% (8)
- Imperial Primary Intermediate Phase Mathematics Lesson Plan: Grade Educator Content Area: Topic Duration Date Year TermDocument2 pagesImperial Primary Intermediate Phase Mathematics Lesson Plan: Grade Educator Content Area: Topic Duration Date Year TermAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- English Revision Test 2nd TermDocument1 pageEnglish Revision Test 2nd TermAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- History Question Nov 2013Document3 pagesHistory Question Nov 2013Alfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- Programme of Assessment - Grade 7 TERM 2 - 2013: SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: June ExaminationDocument1 pageProgramme of Assessment - Grade 7 TERM 2 - 2013: SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT: June ExaminationAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- Take Home Task Feedback: Cape Teaching and Leadership InstituteDocument31 pagesTake Home Task Feedback: Cape Teaching and Leadership InstituteAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- Working With Number PatternsDocument3 pagesWorking With Number PatternsAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms T 2Document4 pagesMechanisms T 2Alfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet
- Lesson PatternsDocument2 pagesLesson PatternsAlfonso Allister SmithNo ratings yet