Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brain - Effects of Stroke: E-Mail Story Print Story
Uploaded by
Alexandru VeliciOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brain - Effects of Stroke: E-Mail Story Print Story
Uploaded by
Alexandru VeliciCopyright:
Available Formats
Brain -- Effects of Stroke
e-mail story | print story
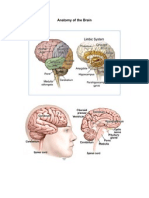
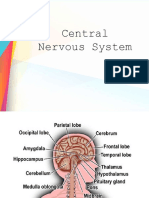
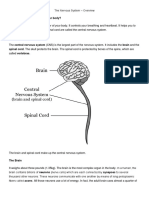
Your brain has three main components - the cerebrum (which consists of the left and right cerebral hemispheres), the cerebellum, and the brain stem. The cerebral hemispheres of the brain make up the largest part of your brain. The cerebellum is the structure located behind the brain stem, and the brain stem is the lowest section of the brain and is connected to the spinal cord.
Illustration pro ided by! "eslie "aurien, #$#I
Region of the Cerebrum Damaged by Stroke
Signs and Symptoms
%ernicke&s area (central language 'ifficulty speaking understandably and comprehending speech( area) confusion between left and right( difficulty reading, writing, naming ob)ects, and calculating *roca&s area (speech) 'ifficulty speaking and, sometimes, writing
+arietal lobe on the left side of the "oss of coordination of the right arm and leg brain ,acial and limb areas of the motor +aralysis of the right arm and leg and the right side of the face corte- on the left side of the brain ,acial and arm areas of the sensory corte.bsence of sensation in the right arm and the right side of the face /ptic radiation "oss of the right half of the isual field of both eyes
Glossary Brain stem #ainly controls unconscious ital functions such as blood pressure and breathing
Broca's area 0ontrols speech Cerebellum #aintains posture, balance and coordination of mo ement Gustatory area 0ontrols the sense of taste Left cerebral hemisphere Together with right cerebral hemisphere, controls most conscious and mental acti ities Left middle cerebral artery . ma)or source of blood supply to the brain otor corte! $ends instructions to muscles to cause oluntary mo ements "ptic radiation Tract of ner e fibers in ol ed in ision #arietal lobe In ol ed in sensations of pain and touch, spatial orientation, and speech #refrontal corte! +ro ides ability to plan, reason, concentrate, and ad)ust beha ior #remotor corte! 0oordinates series of mo ements or intricate, comple- mo ements #rimary auditory corte! 'istinguishes sound 1ualities (eg, loudness and tones) #rimary somatic sensory corte! 2ecei es information from skin receptors, distinguishing different types of sensations #rimary $isual corte! 'etects basic parts of a isual scene (eg, outlines and light or dark) %ernicke's area Interprets sensory information
Brain -- Lobes
e-mail story | print story
The cerebrum (the portion of your brain that performs motor and sensory functions and a ariety of mental acti ities) is di ided into four lobes - the frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobes. $ome of these lobes are separated by deep groo es called fissures.
Source& .#.&s Current Procedural Terminology, 2e ised 3445 6dition. 0+T is a trademark of the .merican #edical .ssociation.
Brain -- Side 'ie(
e-mail story | print story
Your brain has three main components! the cerebrum (which consists of the left and right cerebral hemispheres), the cerebellum and the brain stem. The cerebral hemispheres of the brain make up the largest part of your brain. The cerebellum is the structure located behind the brain stem, and the brain stem is the lowest section of the brain and is connected to the spinal cord. The central structures of the brain are the thalamus, hypothalamus, and pituitary gland. The thalamus relays sensory information to the cerebrum( the hypothalamus helps regulate body functions such as thirst and appetite, as well as sleep, aggression, and se-ual beha ior( and the pituitary gland produces hormones that play a role in growth, de elopment, and arious other physiological ariables. The pons, medulla, and midbrain are the three structures that compose the brain stem. The entricles are natural ca ities inside the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Source& .#.&s Current Procedural Terminology, 2e ised 3445 6dition. 0+T is a trademark of the .merican #edical .ssociation.
You might also like
- Brain Parts and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesBrain Parts and Their FunctionsSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Principles of Transactional Analysis - by Eric BerneDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Transactional Analysis - by Eric BernecornelpcNo ratings yet
- Mini Question Bank - Vety Sci - For Students PDFDocument106 pagesMini Question Bank - Vety Sci - For Students PDFRakesh Prajapati100% (3)
- Microsoft Word Document جديدDocument3 pagesMicrosoft Word Document جديدHisham EssamNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy, Anatomy of The Human BrainDocument12 pagesBrain Anatomy, Anatomy of The Human BrainElmir ƏzimovNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy and FunctionsDocument9 pagesBrain Anatomy and FunctionsAbdelmar SusulanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Pathophy2Document3 pagesAnatomy and Pathophy2Ernie P. BrizuelaNo ratings yet
- Most popular types of Fonts and their usesDocument17 pagesMost popular types of Fonts and their usesameliaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes 2Document5 pagesBiology Notes 2Vanessa SantosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BRAINDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BRAING FernandezNo ratings yet
- Brain Structures and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesBrain Structures and Their FunctionsvijushaaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Biological Basis of Behavior 2: Central Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesLecture 4: Biological Basis of Behavior 2: Central Nervous SystemT-Bone02135No ratings yet
- Trixie - Anatomy and Physiology (Brain Tumor)Document4 pagesTrixie - Anatomy and Physiology (Brain Tumor)Trixie Marie Sabile AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Brain and FunctionsDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Brain and FunctionsGopinadh GanjiNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy (Reading Topic 1)Document6 pagesNeuroanatomy (Reading Topic 1)Fernanda LópezNo ratings yet
- โท the BrainDocument39 pagesโท the BrainFadil Wanna-mart100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BrainLhyn BagunuNo ratings yet
- CNS Guide: Brain and Spinal Cord Control Body FunctionsDocument18 pagesCNS Guide: Brain and Spinal Cord Control Body FunctionsMeg ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Cerebrum: Gross Appearance DR - Aiza Nasir PTDocument25 pagesCerebrum: Gross Appearance DR - Aiza Nasir PTWaqar YounasNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Structure and Functions of the BrainDocument18 pagesUnderstanding the Structure and Functions of the BrainAbu GNo ratings yet
- Function of The BrainDocument16 pagesFunction of The BrainJohn Matthew CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument13 pagesHuman BrainAaniya AsadNo ratings yet
- Brain: Figure 1. The Brain Has Three Main Parts: The Cerebrum, Cerebellum and BrainstemDocument7 pagesBrain: Figure 1. The Brain Has Three Main Parts: The Cerebrum, Cerebellum and BrainstemsukhleenNo ratings yet
- Brain Physiology PDFDocument36 pagesBrain Physiology PDFAnonymous bTl1daBVB1No ratings yet
- About BrainDocument4 pagesAbout Brainanand sahuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the BrainDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the BrainEnna PaulaNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument6 pagesHuman AnatomyJanel TamNo ratings yet
- The Brain Is Composed of The,, andDocument23 pagesThe Brain Is Composed of The,, andMohd NizamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Brain and Spinal CordDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Brain and Spinal CordKate Nucum Fernandez100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesNervous SystemJoyce NieveraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiologymhel03_chickmagnetNo ratings yet
- The Human Brain Regions and Their FunctionsDocument35 pagesThe Human Brain Regions and Their FunctionsRonaleen mislang100% (1)
- Introduction To NeuropsychologyDocument15 pagesIntroduction To NeuropsychologyPsychology Department Ilahia Arts CollegeNo ratings yet
- Health Psychology - The BrainDocument3 pagesHealth Psychology - The BrainSaerah ParkNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyMaquirang Cris JaisonNo ratings yet
- The nervous system controls every part of your daily lifeDocument1 pageThe nervous system controls every part of your daily lifeTimothy Van Emil LopezNo ratings yet
- General Brain Structure N FunctionDocument6 pagesGeneral Brain Structure N Function'Niq Hdyn100% (1)
- Parts of The Brain and FunctionsDocument3 pagesParts of The Brain and FunctionsLee Ayn PoncardasNo ratings yet
- Brain Structures and Their Functions in 40 CharactersDocument6 pagesBrain Structures and Their Functions in 40 CharactersVasudha RohatgiNo ratings yet
- Dia GridDocument7 pagesDia GridMark Ross CanaoayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BraineriannajNo ratings yet
- Science ReportDocument3 pagesScience ReportAna Miadel Mojica MartalNo ratings yet
- 0301a AllDocument3 pages0301a AllWiendha LiendriasariNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nervous System Conduction: B. Pathophysiology 1.) Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument27 pagesFundamentals of Nervous System Conduction: B. Pathophysiology 1.) Anatomy and PhysiologyJanine P. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- HNP- Predisposing FDocument42 pagesHNP- Predisposing FLady Jean Milan ColataNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System – An OverviewDocument3 pagesThe Nervous System – An Overviewcaoimhin54No ratings yet
- Anatomia e Sistema NerosoDocument8 pagesAnatomia e Sistema NerosoChloe BujuoirNo ratings yet
- Brain & Limbic SystemDocument63 pagesBrain & Limbic Systemgopscharan100% (1)
- Brain and Structute(1)Document10 pagesBrain and Structute(1)dhatreyi.g.gubbalaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System (2015 - 06 - 09 22 - 21 - 55 Utc)Document60 pagesNervous System (2015 - 06 - 09 22 - 21 - 55 Utc)DiazNo ratings yet
- Reavin Opera - OdtDocument26 pagesReavin Opera - OdtReavin FuentesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BrainkazelleNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Nueroscience - NotesDocument8 pagesCognitive Nueroscience - NotesEirrah AcenasNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy, Anatomy of The Human Brain - Mayfield Brain & Spine Cincinnati, Ohio 2 PDFDocument20 pagesBrain Anatomy, Anatomy of The Human Brain - Mayfield Brain & Spine Cincinnati, Ohio 2 PDFRitika KishoreNo ratings yet
- How The Brain WorksDocument12 pagesHow The Brain WorksAbdullah B.No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Human BrainDocument2 pagesAnatomy of Human BrainIan Rhadel RaganasNo ratings yet
- CNS Structure and FunctionDocument12 pagesCNS Structure and FunctionsheinelleNo ratings yet
- Discuss Action Potential of The Axon and Nerve ImpulseDocument3 pagesDiscuss Action Potential of The Axon and Nerve ImpulsePink PastaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous Systemkitkat22phNo ratings yet
- Constitution of The Argentine NationDocument21 pagesConstitution of The Argentine Nationjual76No ratings yet
- Petrografie Sedimentara: An Ii Inginerie Geologica Si GeofizicaDocument36 pagesPetrografie Sedimentara: An Ii Inginerie Geologica Si GeofizicaAlexandru VeliciNo ratings yet
- Climate UruguayWeb PDFDocument12 pagesClimate UruguayWeb PDFAlexandru VeliciNo ratings yet
- Petrografie Sedimentara: An Ii Inginerie Geologica Si GeofizicaDocument36 pagesPetrografie Sedimentara: An Ii Inginerie Geologica Si GeofizicaAlexandru VeliciNo ratings yet
- Roy Hodgson Claims England Squad Is Shaping Up For World Cup in BrazilDocument10 pagesRoy Hodgson Claims England Squad Is Shaping Up For World Cup in BrazilAlexandru VeliciNo ratings yet
- Roy Hodgson Claims England Squad Is Shaping Up For World Cup in BrazilDocument10 pagesRoy Hodgson Claims England Squad Is Shaping Up For World Cup in BrazilAlexandru VeliciNo ratings yet
- Roy Hodgson Claims England Squad Is Shaping Up For World Cup in BrazilDocument10 pagesRoy Hodgson Claims England Squad Is Shaping Up For World Cup in BrazilAlexandru VeliciNo ratings yet
- Procedimento Implante AmbicorDocument12 pagesProcedimento Implante Ambicorapi-3762376No ratings yet
- XxssDocument13 pagesXxssfkhunc07No ratings yet
- Wiki Apgar Score01Document3 pagesWiki Apgar Score01Leevon ThomasNo ratings yet
- Q4 Health 6 Week3Document4 pagesQ4 Health 6 Week3Ethelyn Joy FarquerabaoNo ratings yet
- Punjab Healthcare Commission: CG-09RM-Ed2Document168 pagesPunjab Healthcare Commission: CG-09RM-Ed2saimaNo ratings yet
- Use of Anticoagulants During Pregnancy and Postpartum - UpToDateDocument38 pagesUse of Anticoagulants During Pregnancy and Postpartum - UpToDateCristinaCaprosNo ratings yet
- Emergency Welfare FormDocument2 pagesEmergency Welfare FormKristopher HarperNo ratings yet
- PCRL 627: Clinical Microbiology and Immunology 2016: Email: Shilling@uic - EduDocument45 pagesPCRL 627: Clinical Microbiology and Immunology 2016: Email: Shilling@uic - Edui24youNo ratings yet
- Vit KDocument22 pagesVit KKimbek BuangkeNo ratings yet
- Goblet CellDocument4 pagesGoblet CellMuhammad ZairulfikriNo ratings yet
- Aos 94 10Document11 pagesAos 94 10Andi Tiara S. AdamNo ratings yet
- Treponema Pallidum: Human PathogensDocument27 pagesTreponema Pallidum: Human PathogensGeorgeNecoarăNo ratings yet
- Intraoperative Fluid ManagementDocument15 pagesIntraoperative Fluid ManagementMirela Marina BlajNo ratings yet
- Akf Stok 13Document67 pagesAkf Stok 13Grace Riani Pongsipulung TariganNo ratings yet
- 53 Vol. 6 Issue 7 IJPSR 2015 RA 4953Document9 pages53 Vol. 6 Issue 7 IJPSR 2015 RA 4953Dina AyupnNo ratings yet
- Carlson DS - Transverse Development of The Human Jaws Between The Ages of 8.5 and 15.5 Years Studied Longitudinally With Use of ImplantsDocument11 pagesCarlson DS - Transverse Development of The Human Jaws Between The Ages of 8.5 and 15.5 Years Studied Longitudinally With Use of Implantscruzjulio480No ratings yet
- 01 M039 43754Document16 pages01 M039 43754DrDeepak PawarNo ratings yet
- 12-Lead ECG Placement GuideDocument9 pages12-Lead ECG Placement GuideFalusi Blessing OlaideNo ratings yet
- IMSS Nursing Knowledge ExamDocument11 pagesIMSS Nursing Knowledge ExamScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- CLONE - Chinoike Clan - The HomebreweryDocument7 pagesCLONE - Chinoike Clan - The Homebreweryrashid jones100% (1)
- Advances in Psychological and Social Support After DisastersDocument149 pagesAdvances in Psychological and Social Support After DisastersjprewittdiazNo ratings yet
- Fissural CystsDocument17 pagesFissural CystssailalithaNo ratings yet
- The Sacred Mushroom "Reishi"-A ReviewDocument4 pagesThe Sacred Mushroom "Reishi"-A ReviewDinesh Babu PugalenthiNo ratings yet
- Register Now for the 3rd Hematology Forum 2023Document1 pageRegister Now for the 3rd Hematology Forum 2023modather sanosiNo ratings yet
- American Society For Biochemistry and Molecular BiologyDocument23 pagesAmerican Society For Biochemistry and Molecular BiologyShishui UchihaNo ratings yet
- HTC Intake Form - September 4 - Final - Doc 7.9.13Document10 pagesHTC Intake Form - September 4 - Final - Doc 7.9.13Kealeboga Duece ThoboloNo ratings yet
- Sing With Distortion - 10 TipsDocument10 pagesSing With Distortion - 10 TipstjoodleNo ratings yet