Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Function: Voluntary and Involuntary Responses - Aviva
Uploaded by
BrendaJooYee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views6 pagesThere are two types of involuntary response, autonomic and reflex. Autonomic nervous system controls body's internal environment without conscious intervention. Reflexes mainly affect those muscles that are normally under voluntary control.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere are two types of involuntary response, autonomic and reflex. Autonomic nervous system controls body's internal environment without conscious intervention. Reflexes mainly affect those muscles that are normally under voluntary control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views6 pagesFunction: Voluntary and Involuntary Responses - Aviva
Uploaded by
BrendaJooYeeThere are two types of involuntary response, autonomic and reflex. Autonomic nervous system controls body's internal environment without conscious intervention. Reflexes mainly affect those muscles that are normally under voluntary control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Aviva
Function: Voluntary and Involuntary
Responses
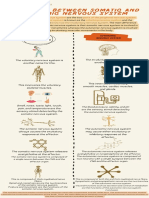
The responses of the nervous system to stimuli may be voluntary or involuntary. Voluntary
responses are mainly under conscious control, but some voluntary movements, such as
walking, require less conscious attention. There are two types of involuntary response,
autonomic and reflex. Autonomic responses regulate the bodys internal environment. Reflexes
mainly affect those muscles that are normally under voluntary control.
Voluntary responses
All voluntary activities involve the brain, which sends out the motor impulses that control
movement. These motor signals are initiated by thought and most also involve a response to
sensory stimuli. For example, people use sight and sense of position to help them coordinate
the action of walking.
Voluntary pathways
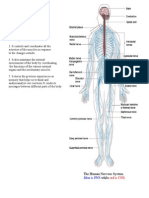
The sensory impulses that trigger voluntary responses are dealt with in many parts of the brain.
Nervemuscle junction
At this junction, a nerve fibre transmits signals to produce a response from muscle fibres.
Autonomic responses
The autonomic nervous system controls the bodys internal environment without conscious
intervention and helps to regulate vital functions, such as blood pressure. The two types of
autonomic nerves, sympathetic and parasympathetic, have opposing effects but balance each
other most of the time. At certain times, such as during stress or exercise, one system
dominates.
Autonomic pathways
Information collected by internal receptors travels along sensory nerves to the spinal cord and
the brain stem for processing. Sympathetic and parasympathetic response signals have
separate pathways.
Two types of responses
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves each produce different responses in a particular
organ. The sympathetic responses prepare the body to cope at times of stress. Parasympathetic
responses help conserve or restore energy.
Divisions of the autonomic system
Organ
Affected
Sympathetic response Parasympathetic response
Eyes Pupils dilate Pupils constrict
Lungs Bronchial tubes dilate Bronchial tubes constrict
Heart
Rate and strength of heartbeat
increase
Rate and strength of heartbeat
decrease
Stomach Enzymes decrease Enzymes increase
Liver Releases glucose Stores glucose
Reflexes
A reflex is an involuntary response to a stimulus, such as withdrawing your hand from a hot
surface before you become aware of the heat. Most reflexes are processed in the spine,
although some, such as blinking, are processed in the brain. In a spinal reflex, the stimulus
signal travels along a sensory nerve to the spinal cord, and a response signal travels back by
means of a motor nerve.
Spinal reflex pathway
Spinal reflexes involve the simplest nerve pathways: the sensory and motor neurons are directly
linked together in the spinal cord.
From the 2010 revision of the Complete Home Medical Guide Dorling Kindersley Limited.
The subjects, conditions and treatments covered in this encyclopaedia are for information only and may not be
covered by your insurance product should you make a claim.
Search the Medical Encyclopedia
Enter search word:
Enter search word...
Search
Find article by first letter
A (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/A/)
B (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/B/)
C (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/C/)
D (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/D/)
E (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/E/)
F (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/F/)
G (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/G/)
H (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/H/)
I (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/I/)
J (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/J/)
K (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/K/)
L (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/L/)
M (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/M/)
N (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/N/)
O (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/O/)
P (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/P/)
Q (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/Q/)
R (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/R/)
S (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/S/)
T (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/T/)
U (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/U/)
V (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/V/)
W (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/W/)
X (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/X/)
Y (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/Y/)
Z (http://www.aviva.co.uk/health-insurance/home-of-health/medical-centre/medical-encyclopedia/Z/)
Related Topics
You might also like
- Autonomic Nervous System - Basic and Clinical AspectsDocument393 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - Basic and Clinical AspectsGrossl Schorr Fernando100% (1)
- Difference Between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous SystemsDocument2 pagesDifference Between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous SystemsSanggetha Gal100% (1)
- Autonominen Hermosto ART Autonomic Response Testing, Englanti LopullinenDocument11 pagesAutonominen Hermosto ART Autonomic Response Testing, Englanti LopullinenGustavo RamirezNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Science NotesDocument45 pagesYear 10 Science NotesAmal VivekNo ratings yet
- Functional anatomy of cerebral cortex (40Document33 pagesFunctional anatomy of cerebral cortex (40BrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Quick ReferenceDocument12 pagesNervous System Quick ReferenceElena FlegkaNo ratings yet
- Ayurveda and Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesAyurveda and Nervous SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Physiological PsychDocument19 pagesPhysiological PsychMar Yu100% (1)
- Parasympathetic Vs Sympathetic Nervous System - Difference and ComparisonDocument4 pagesParasympathetic Vs Sympathetic Nervous System - Difference and ComparisoniwennieNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument110 pagesThe Nervous System: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- Daily Vagus Nerve Exercises For Self-Healing (2 in 1): Natural Techniques & Habits To Help With Anxiety, Overthinking, Depression, Stress-Relief, Brain Fog, Inflammation & MoreFrom EverandDaily Vagus Nerve Exercises For Self-Healing (2 in 1): Natural Techniques & Habits To Help With Anxiety, Overthinking, Depression, Stress-Relief, Brain Fog, Inflammation & MoreNo ratings yet
- Nerve Tissue & the Nervous System IntroductionDocument21 pagesNerve Tissue & the Nervous System IntroductionDan UvarovNo ratings yet
- Corporate Wellness ManualDocument353 pagesCorporate Wellness ManualAppasaheb MalagaudanavarNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine and Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesCoordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine and Reproductive SystemMaribel Membrado GreciaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesDocument6 pagesNotes On Coordination - Response - Nervous System, Reflex Arc, Type of NeuronesamberNo ratings yet
- Yoga and The Autonomic Nervous System: Re-Educating The MindDocument3 pagesYoga and The Autonomic Nervous System: Re-Educating The MindSlezák JózsefNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination Class NotesDocument13 pagesControl and Coordination Class NotesTripura Neelima100% (2)
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemFiza KhanNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination - Class XDocument5 pagesControl and Coordination - Class XMonika Mehan89% (19)
- Chapter 12 Coordination and ControlDocument22 pagesChapter 12 Coordination and ControlXaundrae McDonaldNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2-Voluntary and Involuntary ActionsDocument3 pagesLesson 2-Voluntary and Involuntary ActionskreativekerelleNo ratings yet
- Assignment Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesAssignment Autonomic Nervous Systemahmad72 raza72No ratings yet
- Science 10 Handout - Nervous and EndocrineDocument2 pagesScience 10 Handout - Nervous and EndocrineAngelica MartinNo ratings yet
- Nervous System GuideDocument22 pagesNervous System GuideSo TemptedNo ratings yet
- Influence of Nervous System On BehaviorDocument2 pagesInfluence of Nervous System On BehaviorcynthiasenNo ratings yet
- 7.reflex Regulation of Physiological Function PDFDocument2 pages7.reflex Regulation of Physiological Function PDFNektarios TsakalosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document35 pagesChapter 2Amiey SehokNo ratings yet
- Bio PsychDocument2 pagesBio PsychMichaela Jeanyvieve L. TabanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document109 pagesChapter 3amala raviNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous SystemJhunelynNo ratings yet
- Reflexes - What? How?: BiologyDocument9 pagesReflexes - What? How?: BiologysamsungloverNo ratings yet
- The Receiving Mechanism: Sense Organs Are Sensitive Nerve Endings Located in Certain Body Parts. They Are Receptors ofDocument5 pagesThe Receiving Mechanism: Sense Organs Are Sensitive Nerve Endings Located in Certain Body Parts. They Are Receptors ofArlene Cerdeña SalcedaNo ratings yet
- SPM Science Notes - Body CoordinationDocument12 pagesSPM Science Notes - Body CoordinationSPM98% (50)
- Lecture 4Document26 pagesLecture 4samrasaeedNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 07 Control and Coordination 1Document9 pages10 Science Notes 07 Control and Coordination 1Rishu KaulNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument29 pagesScience NotesADITYA KUMARNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument34 pagesNervous SystemHANNA ANGELA LEJANONo ratings yet
- 4A Notes Coordination and ResponseDocument15 pages4A Notes Coordination and ResponsenatashamautsiNo ratings yet
- Lab 03 Reflexes Referred PainDocument14 pagesLab 03 Reflexes Referred PainViraj TatikondaNo ratings yet
- ReflexDocument2 pagesReflexSarah LewisNo ratings yet
- Nerves and ReflexesDocument14 pagesNerves and ReflexesjtNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument32 pagesNervous SystemMahadi Hasan KhanNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Nervous Systemzainab umerNo ratings yet
- Coordination, Response and HomeostasisDocument31 pagesCoordination, Response and HomeostasisVenusCrazy 550No ratings yet
- Samina Ahmad Senior Lecturer Audiology BIAHSDocument28 pagesSamina Ahmad Senior Lecturer Audiology BIAHSMuhammad bilalNo ratings yet
- The Nervous Sysytem and The Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesThe Nervous Sysytem and The Endocrine SystemlaracanacarNo ratings yet
- Protection of the Eye: How the Eyeball, Eyelids, Tears and Other Structures Safeguard VisionDocument19 pagesProtection of the Eye: How the Eyeball, Eyelids, Tears and Other Structures Safeguard VisionReynaldo ThomasNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument50 pagesNervous SystemRaven Axel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Control and CordinateDocument12 pagesControl and CordinateHarsh RathoreNo ratings yet
- The Biological Perspective 2Document11 pagesThe Biological Perspective 2Radhey SurveNo ratings yet
- Vagus Nerve: A Complete Guide to Activate the Healing power of Your Vagus Nerve – Reduce with Self-Help Exercises Anxiety, PTSD, Chronic Illness, Depression, Inflammation, Anger and TraumaFrom EverandVagus Nerve: A Complete Guide to Activate the Healing power of Your Vagus Nerve – Reduce with Self-Help Exercises Anxiety, PTSD, Chronic Illness, Depression, Inflammation, Anger and TraumaNo ratings yet
- Physiological Basis of Psychology: Neurons Serve To Receive and Transmit Impulses FromDocument4 pagesPhysiological Basis of Psychology: Neurons Serve To Receive and Transmit Impulses FromPatrick RilleraNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesHuman Nervous SystemSridevi NadipalliNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous System: Sherwyn Hatab RNDocument14 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous System: Sherwyn Hatab RNSherwyn Uy HatabNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ReviewDocument18 pagesNervous System Reviewtherenam825No ratings yet
- 1. Body Control and ResponseDocument51 pages1. Body Control and ResponseAngelyn AbuevaNo ratings yet
- Pns and CnsDocument3 pagesPns and Cnsjlcanja5No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous Systemjanssen.azagra.basalloteNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesThe Nervous SystemAyan AtifNo ratings yet
- Kepy 01 09 37 EtextDocument9 pagesKepy 01 09 37 Etextmradul guptaNo ratings yet
- In Text Questions: NCERT Solutions For Class 10th: CH 7 Control and Coordination ScienceDocument8 pagesIn Text Questions: NCERT Solutions For Class 10th: CH 7 Control and Coordination ScienceJignesh KiriNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument45 pagesHomeostasisNazrene FuaNo ratings yet
- Psychology Week 3 NotesDocument9 pagesPsychology Week 3 Notes01234No ratings yet
- Nervous System and Coordination of Nervous and Endocrine System to achieve homeostasisDocument65 pagesNervous System and Coordination of Nervous and Endocrine System to achieve homeostasisJoseph yvannNo ratings yet
- Brainthe ControllerDocument4 pagesBrainthe ControllerJacklynlim LkcNo ratings yet
- Fall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC190408115Document4 pagesFall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC190408115Misbah NoreenNo ratings yet
- MyPastest 3Document1 pageMyPastest 3BrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Ischemia InjuriesDocument7 pagesIschemia InjuriesBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Houseman Paed Note 2020 2Document1 pageHouseman Paed Note 2020 2BrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid Paralysis and Enteroviral InfectionsDocument15 pagesAcute Flaccid Paralysis and Enteroviral InfectionsBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Electric Chair Haunts US Former Executions ChiefDocument4 pagesElectric Chair Haunts US Former Executions ChiefBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- DiabetesDocument17 pagesDiabetesBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- My PastestDocument1 pageMy PastestBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- MyPastest 2Document1 pageMyPastest 2BrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Phototherapy and exchange transfusion levels for neonates 35 weeks gestationDocument1 pagePhototherapy and exchange transfusion levels for neonates 35 weeks gestationBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Function in Thyroid DiseaseDocument10 pagesRespiratory Function in Thyroid DiseaseBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- PBL 30 Management of DiabetesDocument14 pagesPBL 30 Management of DiabetesBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Korea-Watchers Fear Backlash From North Over US Drills PDFDocument5 pagesKorea-Watchers Fear Backlash From North Over US Drills PDFBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- LeptospirosisDocument7 pagesLeptospirosisMichael UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- PBL DM2 BrendaPDocument18 pagesPBL DM2 BrendaPBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Tentative Quiz ProgrammeDocument1 pageTentative Quiz ProgrammeBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Nausea and Vomiting Secondary To Hydronephrosis in Palliative PatientsDocument2 pagesNausea and Vomiting Secondary To Hydronephrosis in Palliative PatientsBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Quizlet Vessels and CirculationDocument2 pagesQuizlet Vessels and CirculationBrendaJooYee100% (2)
- Cultural and Spiritual Awareness PDFDocument20 pagesCultural and Spiritual Awareness PDFBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Quizlet CVSDocument2 pagesQuizlet CVSBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- SLCC Anatomy CH 26-Digestive System: Study Online atDocument3 pagesSLCC Anatomy CH 26-Digestive System: Study Online atBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Cosmetic Surgery Past, Present, and Future: Plastic, Reconstructive, and Cosmetic SurgeryDocument5 pagesCosmetic Surgery Past, Present, and Future: Plastic, Reconstructive, and Cosmetic SurgeryBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Care of Bedridden PatientDocument2 pagesCare of Bedridden PatientBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- SLCC Anatomy CH 27: Urinary System: Study Online atDocument2 pagesSLCC Anatomy CH 27: Urinary System: Study Online atBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Quizlet Vessels and CirculationDocument2 pagesQuizlet Vessels and CirculationBrendaJooYee100% (2)
- BiochemistryDocument9 pagesBiochemistryBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- 1) Effect of HemodialysisDocument7 pages1) Effect of HemodialysisBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- 2167 0390 SR 413Document9 pages2167 0390 SR 413BrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- MCQ Selanjar 1Document4 pagesMCQ Selanjar 1BrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Chapter QuizDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Chapter QuizBrendaJooYeeNo ratings yet
- Review Notes On Lie DetectionDocument17 pagesReview Notes On Lie DetectionChristine Escobal SenganeNo ratings yet
- Polygraphy ReviewerDocument25 pagesPolygraphy ReviewerChienette MedranoNo ratings yet
- Asarudheen Final ThesisDocument62 pagesAsarudheen Final ThesisMohamed Asarudheen sNo ratings yet
- Capacitive Aspects of Diagnosis by Oriental Traditional Medicine. Regard On Electrography Through ElectroluminiscenceDocument6 pagesCapacitive Aspects of Diagnosis by Oriental Traditional Medicine. Regard On Electrography Through Electroluminiscencemamulasioan9675No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Biopsychology and NeurologyDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Biopsychology and NeurologyDeva ChiruNo ratings yet
- FullDocument81 pagesFullRade GrbicNo ratings yet
- Biopsychology Course Assignment 1Document4 pagesBiopsychology Course Assignment 1pragatiNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Support Cells and Peripheral Nervous System FunctionsDocument5 pagesNervous System Support Cells and Peripheral Nervous System FunctionsBrent ValdespinaNo ratings yet
- A new view of pain as a homeostatic emotionDocument5 pagesA new view of pain as a homeostatic emotionJulian GorositoNo ratings yet
- Human Body in Health and Disease 7th Edition Thibodeau Test BankDocument22 pagesHuman Body in Health and Disease 7th Edition Thibodeau Test Banklaeliacaixpoyf100% (30)
- Science 10 - Learning Module 3QDocument86 pagesScience 10 - Learning Module 3QJovanni SimbulanNo ratings yet
- Autonomic NotesDocument4 pagesAutonomic NotesYeyeth Jabaybay TabolongNo ratings yet
- 4 4 1 P Rs RaceresoursesheetDocument3 pages4 4 1 P Rs Raceresoursesheetapi-343748577No ratings yet
- Naval StudiesDocument106 pagesNaval StudiesPhil InkleyNo ratings yet
- Updates On The Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Autonomic NeuropathiesDocument16 pagesUpdates On The Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Autonomic Neuropathiesdeepam kapoorNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Discovering Behavioral Neuroscience An Introduction To Biological Psychology 4th Edition Freberg Test Bank PDFDocument21 pagesDwnload Full Discovering Behavioral Neuroscience An Introduction To Biological Psychology 4th Edition Freberg Test Bank PDFjapitserre5100% (10)
- Biology and BehaviorDocument72 pagesBiology and BehaviorCarlee MayesNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument75 pagesReviewerKurt SecretarioNo ratings yet
- (2022) Anxiety N Four Techniques Incomporating Sensory ModulationDocument9 pages(2022) Anxiety N Four Techniques Incomporating Sensory ModulationDummy MummyNo ratings yet
- Tisu Neural Neurofisiologi Neuron Neuroglia Terminologi SarafDocument141 pagesTisu Neural Neurofisiologi Neuron Neuroglia Terminologi SarafRainne LeeNo ratings yet
- Lie Detection Course OverviewDocument27 pagesLie Detection Course OverviewJOYDIA PILARNo ratings yet
- Semester Reflection Paper-1Document7 pagesSemester Reflection Paper-1Nasir Ali RiazNo ratings yet
- BIOS5130 Week 10 Lecture Part 1 SlidesDocument37 pagesBIOS5130 Week 10 Lecture Part 1 SlidesOkikiola JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Physiological Psychology ReviewerDocument13 pagesPhysiological Psychology ReviewerLeopando Rod CyrenzNo ratings yet