Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Faw Worksheet 2a II Thesis I
Uploaded by
Yeni PurtikaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Faw Worksheet 2a II Thesis I
Uploaded by
Yeni PurtikaCopyright:
Available Formats
YENI PURTIKA S.
8113612087
B4-LTBI
FUNCTIONAL APPROACHES TO WRITING
FORMATIVE II
Instruction: 1) Get one thesis on a topic of your interest. 2) Work individually. 3) Choose relevant statements to put in every
structure of the genre. 4) Discuss with your partner to make sure that the statements are correct. 5) Type your work and print.
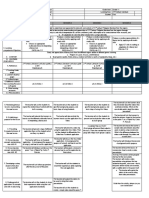
GENRE 1(REPORT)
No Generic Structure Quotation References
Position (Chapter, Page
and Paragraph)
1. General Classification Pragmatics concerns with some fields and politeness
is one of them.
Situmeang, Canra. (2013).
The politeness of 7 years
old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter I; page 1;
paragraph 2.
2. Description of Parts Not found.
3. Description of
Qualities
It is difficult to learn because it involves
understanding not only the language but also the
social and cultural values of the community,
(Brown:1987).
Brown, P. and Levinson S.
(1987) Politeness: some
universals in language
usage. Cambridge:
Cambridge University
Press. In Situmeang,
Canra. (2013). The
politeness of 7 years old
children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter I; page 1;
paragraph 2.
4. Description of Uses it is used by people in their social interactions as
in specific contexts, knowing what to say, how to
say, when to say and how to be with other people.
Situmeang, Canra. (2013).
The politeness of 7 years
old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter I; page 1;
paragraph 2.
YENI PURTIKA S.
8113612087
B4-LTBI
FUNCTIONAL APPROACHES TO WRITING
GENRE 2 (ANALYTICAL EXPOSITION)
No Generic Structure Quotation Reference
Position (Chapter, Page
and Paragraph)
1. Thesis During this stage (concrete operation stage), logical,
rational, thought processes and the ability to reason
deductively and inductively developed.
Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness
of 7 years old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter II; page 34,
paragraph 1
2. Argument 1 Children in this stage are able to think more objectively,
are willing to listen to others and will selectively use
questioning to find answers to unknown.
Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness
of 7 years old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter II; page 34,
paragraph 1
3. Argument 2 they can consider two premises and draw a logical
conclusion from them, (Elkind, 1984).
Elkind. (2004) in
Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness
of 7 years old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter II; page 34,
paragraph 1
4. Argument 3 They are also intellectually able to understand cause and
effect in a concrete way.
Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness
of 7 years old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter II; page 34,
paragraph 3
5. Reiteration Not Found.
YENI PURTIKA S.
8113612087
B4-LTBI
FUNCTIONAL APPROACHES TO WRITING
GENRE 3 (PROCEDURE)
No Generic Structure Quotation References
Position (Chapter, Page
and Paragraph)
1. Goal The technique of data collection.
Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness
of 7 years old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter III; page 44;
paragraph 2
2. Materials The researcher used some tools in collecting the data
such as pen and book when taking note.
Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness
of 7 years old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter III; page 44;
paragraph 1
3. Steps In collecting the data, the researcher used some steps.
The steps were: 1) observing the subjects both inside
and outside the class, 2) taking notes of the utterances
produced by the subjects by using a pen and a book, 3)
then, the data which were in Indonesian would be
translated into English, 4) the researcher only took the
data needed based on research problems and the data
which were not related to politeness strategies would be
reduced, it was called as data reduction (Miles and
Huberman, 1984:21), 5) finally, the researcher analyzed
the data.
Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness
of 7 years old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Miles and Huberman.
(1984).
Chapter III; page 45;
paragraph 2.
YENI PURTIKA S.
8113612087
B4-LTBI
FUNCTIONAL APPROACHES TO WRITING
GENRE 4 (DESCRIPTIVE)
No Generic Structure Quotation References
Position (Chapter, Page
and Paragraph)
1. Identification Politeness strategies are ways to convey the
utterances as polite as possible.
Situmeang, Canra. (2013).
The politeness of 7 years old
children. UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter I; page 2;
paragraph 2
2. Description of parts Brown and Levinson divided politeness
strategies into two namely 1) bald-on-record
strategy and 2) off-record strategy.
Brown, P. and Levinson S.
(1987) Politeness: some
universals in language
usage. Cambridge:
Cambridge University
Press. In Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness of 7
years old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter I; page 2;
paragraph 2
3. Description of qualities Politeness strategies are important in avoiding
or minimizing the threat of addressees face.
Situmeang, Canra. (2013).
The politeness of 7 years old
children. UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter I; page 2;
paragraph 2
4. Description of
characteristics
It also relates to the speakers and hearers age,
status and power.
Situmeang, Canra. (2013).
The politeness of 7 years old
children. UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter I; page 2;
paragraph 2
YENI PURTIKA S.
8113612087
B4-LTBI
FUNCTIONAL APPROACHES TO WRITING
GENRE 5 (HORTATORY EXPOSITION)
No Generic Structure Quotation References
Position (Chapter, Page
and Paragraph)
1. Thesis The children of seven years old sometimes are not
able to use politeness strategy in their
communication naturally
Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness
of 7 years old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter I; page 6;
paragraph 2
2. Argument Not found.
3. Argument Not found.
4. Recommendation they should be taught how to use it properly as
their psychosocial still also develops
Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness
of 7 years old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter I; page 6;
paragraph 2
YENI PURTIKA S.
8113612087
B4-LTBI
FUNCTIONAL APPROACHES TO WRITING
GENRE 6 (EXPLANATION)
No Generic Structure Quotation References
Position (Chapter,
Page and Paragraph)
1. General Statement Pinter (2006:617) also classified
stages of children cognitive
development into four stages,as
follows.
Pinter, A. (2006). Teaching young
language learners. Oxford: Oxford
University Press in Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness of 7 years old
children. UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter II; page 28;
paragraph 1
2. Explanation Sensori motor stage (from birth to two
years of age). This stage is
characterized by the interaction of a
child with the environment.
Pinter, A. (2006). Teaching young
language learners. Oxford: Oxford
University Press in Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness of 7 years old
children. UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter II; page 28;
paragraph 2
3. Explanation Pre-operational stage (from two to
seven years of age). In this stage
children are more dependent on
perception and start to be more
capable of logical thinking.
Pinter, A. (2006). Teaching young
language learners. Oxford: Oxford
University Press in Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness of 7 years old
children. UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter II; page 28;
paragraph 3
4. Explanation Concrete operational stage (from
seven to eleven years of age). When
children become 7 year old their
thinking begins to resemble, logical,
and adult-like thinking (Pinter,
2006:7).
Pinter, A. (2006). Teaching young
language learners. Oxford: Oxford
University Press in Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness of 7 years old
children. UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter II; page 28;
paragraph 4
5 Explanation Formal operation stage (from eleven
year onwards). Children are able to
think in terms that are more abstract.
Pinter, A. (2006). Teaching young
language learners. Oxford: Oxford
University Press in Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness of 7 years old
children. UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter II; page 28;
paragraph 5
YENI PURTIKA S.
8113612087
B4-LTBI
FUNCTIONAL APPROACHES TO WRITING
GENRE 7 (DISCUSSION)
No. Generic Structure Quotation References
Position (Chapter, Page
and Paragraph)
1. Issue Not found.
2. Arguments for By studying language on the basis of pragmatics, we
can get a big advantage, we can talk about peoples
intended meanings, their assumptions, their goals and
the kinds of actions (request, refusal, agreement,
disagreement, thinking, apologizing, etc.) when they
are speaking.
Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness
of 7 years old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter I; page 11;
paragraph 2
3. Arguments against On the other hand, the disadvantage is that these
human concepts are difficult to analyze in a consistent
and objective way.
Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness
of 7 years old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter I; page 11;
paragraph 2
4. Conclusion Not found.
YENI PURTIKA S.
8113612087
B4-LTBI
FUNCTIONAL APPROACHES TO WRITING
GENRE 8 (REVIEW)
No. Generic Structure Quotation References
Position (Chapter, Page
and Paragraph)
1. Orientation Not found.
2. Interpretive Recount This research was aimed at describing and
determining the positive politeness used in Harry and
the Half-Blood Prince.
Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness of
7 years old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter II; page 38;
paragraph 3
3. Evaluation Kartikas dealed only with the positive politeness
strategies used in Harry Potter and Half-Blood Prince
movie without analyzed more detail about the process
and the reasons of using the strategy.
Situmeang, Canra.
(2013). The politeness of
7 years old children.
UNIMED:Medan.
Chapter II; page 39;
paragraph 1
4. Evaluative
Summation
Not found.
You might also like
- MC Script Public SpeakingDocument3 pagesMC Script Public SpeakingHazwan StyntethNo ratings yet
- Script Host-MeidaDocument3 pagesScript Host-MeidaYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Article 1 Challenges Facing Refugee Camps in JordanDocument5 pagesArticle 1 Challenges Facing Refugee Camps in JordanYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Peer Observation SheetDocument3 pagesPeer Observation SheetYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Beginning Crossword Puzzle - AnimalsDocument1 pageBeginning Crossword Puzzle - Animalsanon_646587872No ratings yet
- Asking and Giving Opinion WorksheetDocument1 pageAsking and Giving Opinion WorksheetYeni Purtika100% (2)
- Four CornersDocument7 pagesFour CornersYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Cultural Differences in Standards of Beauty - Mauritania vs IndonesiaDocument5 pagesCultural Differences in Standards of Beauty - Mauritania vs IndonesiaYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Mid Test Malay LitDocument1 pageMid Test Malay LitYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Activity Pictures of TOEFL ClassDocument13 pagesActivity Pictures of TOEFL ClassYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Group evaluation advertising persuasive languageDocument1 pageGroup evaluation advertising persuasive languageYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Crossword Puzzle - BankingDocument1 pageAdvanced Crossword Puzzle - BankingSaidriziNo ratings yet
- REC003 Sleep Habits PDFDocument9 pagesREC003 Sleep Habits PDFRoberto Figueroa ZúñigaNo ratings yet
- Unique Culture From Ethnics in IndonesiaDocument1 pageUnique Culture From Ethnics in IndonesiaYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Review Skills 1-10Document12 pagesReview Skills 1-10Yeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- ComputationDocument1 pageComputationYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- EDCI 647 Descriptive Writing Presentation V 2Document30 pagesEDCI 647 Descriptive Writing Presentation V 2Yeni Purtika100% (1)
- Kinds of DramaDocument2 pagesKinds of DramaYeni Purtika50% (2)
- English tenses and subjectsDocument5 pagesEnglish tenses and subjectsYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Branding - FEB English ClubDocument1 pageBranding - FEB English ClubYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Business 5DDocument10 pagesBusiness 5DCristina Gabriela BNo ratings yet
- Clandfield, L. (2006) Straightforward Elementary SB, MacmillanDocument1 pageClandfield, L. (2006) Straightforward Elementary SB, MacmillanYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TOEPDocument3 pagesIntroduction To TOEPYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument2 pagesConditional SentenceYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Starting: English For Presentation Teaching Unit Pusba USUDocument10 pagesStarting: English For Presentation Teaching Unit Pusba USUYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Face2face LS Sample ScopeAndSequenceDocument4 pagesFace2face LS Sample ScopeAndSequenceYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- What Makes A Good PresentationDocument8 pagesWhat Makes A Good PresentationYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Agreement: Name: - ClassDocument1 pageAgreement: Name: - ClassYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- Agreement: Name: - ClassDocument1 pageAgreement: Name: - ClassYeni PurtikaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Glasgow Seminar-Ana Ivenicki.2017 Opt PDFDocument1 pageGlasgow Seminar-Ana Ivenicki.2017 Opt PDFCRADALLNo ratings yet
- Eduu 511 Online Course at A Glance OnlineDocument6 pagesEduu 511 Online Course at A Glance Onlineapi-268700252No ratings yet
- Rommel C. Bautista, Ceso V School Division Superintendent Division of Cavite Trece Martires City, CaviteDocument2 pagesRommel C. Bautista, Ceso V School Division Superintendent Division of Cavite Trece Martires City, CaviteChristina Aguila NavarroNo ratings yet
- DLP 15Document5 pagesDLP 15Chi-square A DamzNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 21st Century Literature Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesGrade 11 21st Century Literature Lesson PlanMlynNo ratings yet
- Get Students Into the Green with Reading PlusDocument2 pagesGet Students Into the Green with Reading PlusSyaiful RohmanNo ratings yet
- PPG Q2 Week CD - Decentralization and Local GovernanceDocument4 pagesPPG Q2 Week CD - Decentralization and Local Governancejaeson mariano100% (2)
- Pokorny Kristin ProfessionaldevelopementDocument2 pagesPokorny Kristin Professionaldevelopementapi-302769851No ratings yet
- Aug23.2015solon Proposes Magna Carta of The Out-Of-School YouthDocument2 pagesAug23.2015solon Proposes Magna Carta of The Out-Of-School Youthpribhor2No ratings yet
- Colors: Penguin Young Readers FactsheetsDocument4 pagesColors: Penguin Young Readers FactsheetsSilvia AmadoNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Guide Frankenstein SignetDocument28 pagesTeacher's Guide Frankenstein SignetEmbronte80% (5)
- ResumecDocument1 pageResumecapi-317022118No ratings yet
- Instructional Materials GuideDocument6 pagesInstructional Materials GuideLorieDaleNo ratings yet
- Close Reading Practice Sherman Alexies Superman and MeDocument4 pagesClose Reading Practice Sherman Alexies Superman and Meapi-359644173No ratings yet
- ICT Utilization and Instructional Competence of TeachersDocument29 pagesICT Utilization and Instructional Competence of TeachersLloyd MacalindolNo ratings yet
- Inside The Most Expensive Boarding School in The World - OdtDocument6 pagesInside The Most Expensive Boarding School in The World - OdtThavam RatnaNo ratings yet
- Math10 DLLDocument5 pagesMath10 DLLNoraisa MacabaasNo ratings yet
- Ielts Writing TestDocument3 pagesIelts Writing TestVõ Duy KhaNo ratings yet
- Merit or Demerit of Bilinguality in Learning English As ADocument33 pagesMerit or Demerit of Bilinguality in Learning English As AMohammad ZohrabiNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Level IDocument38 pagesSimple Present Level IJuan Daniel FelipeNo ratings yet
- Multiple Intelligences Theory: Howard GardnerDocument16 pagesMultiple Intelligences Theory: Howard GardnertenNo ratings yet
- Final Copy Animal Farm Essay ExampleDocument4 pagesFinal Copy Animal Farm Essay Exampleapi-296874431No ratings yet
- New ResumeDocument2 pagesNew Resumeapi-255583689No ratings yet
- DR Frederick W Gomez... The ABC On The Methods of Educational ResearchDocument45 pagesDR Frederick W Gomez... The ABC On The Methods of Educational ResearchFrederick W GomezNo ratings yet
- A Token Economy System Is A Type Ofreward SystemDocument14 pagesA Token Economy System Is A Type Ofreward SystemKristina De Peralta WillyNo ratings yet
- 2) - William Grabe PDFDocument11 pages2) - William Grabe PDFJalal Zbirat67% (3)
- Primary Education For Disadvantaged Children (PEDC) : Innovation Grants Operational Manual March 2007Document39 pagesPrimary Education For Disadvantaged Children (PEDC) : Innovation Grants Operational Manual March 2007edselsawyerNo ratings yet
- Global EdTech LandscDocument63 pagesGlobal EdTech LandscamberatalNo ratings yet