Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cells Unit 7 Day 2 Teacher
Uploaded by
api-280035690Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cells Unit 7 Day 2 Teacher
Uploaded by
api-280035690Copyright:
Available Formats
Unit 7 Day 2 Teacher: Cells
Name__________________________________
I can identify the two types of cells and tell at least one difference between them.
POD:
1.
Tool
Meter stick
Graduated cylinder
Triple beam balance
sieve
Use
Measure length, width, height
Measure volume
Measure the mass
Separate
Unit(s)used (if applicable)
Mm, cm, M
mL
g, mg
n/a
2. Make a graph of your choice to show the following data of the growth of a plant:
Height
2 mm
6mm
10mm
Day
3
5
7
3. What is the growth pattern on the plant above? The plant grows 4 mm every 2 days
4. What type of reactions take place in the sun and what do they produce? Nuclear reactions, light/heat
5. Draw the following fronts on the frontal line for the following descriptions below:
a. Cooler temps and clear skies will follow this front
b. Warmer temps and many days of precipitation may follow this front
6.
Evidence of a chemical reaction
Activity: Reading Comprehension, Highlighting and Notes
Teacher Directed: Teacher will model expectations for 2 sections
Partners: Students will alternate reading aloud and both will come up with the main point
Whole Class: discuss and write down main points from the text
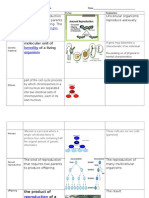
Cells are the Starting Point
All living organisms on Earth are divided into cells. The main concept of cell theory is
that cells are the basic structural unit for all organisms. Cells are small compartments
that hold the biological equipment necessary to keep an organism alive and successful.
Living things may be single-celled or they may be very complex such as a human being.
Cells make up all living things
There are smaller pieces that make up cells such as macromolecules and
organelles. A protein is an example of a macromolecule while a mitochondrion
is an example of an organelle. Cells can also connect to form larger structures.
They might group together to form the tissues of the stomach and eventually the
entire digestive system. However, in the same way that atoms are the basic unit
when you study matter, cells are the basic unit for biology and organisms.
Cells are the basic units for organisms and are made up of smaller parts
In larger organisms, the main purpose of a cell is to organize. Cells hold a variety
of pieces and each cell type has a different purpose. By dividing responsibilities
among different groups of cells, it is easier for an organism to survive and grow.
Cells are used to organize and perform different responsibilities/purpose
If you were only made of one cell, you would be very limited. You don't find single
cells that are as large as a cow. Cells have problems functioning when they get too
big. Also, if you were only one cell you couldn't have a nervous system, no
muscles for movement, and using the internet would be out of the question. The
trillions of cells in your body make your way of life possible.
Humans are not made of one cell
One Name, Many Types
There are many types of cells. In biology class, you will usually work with plant-like
cells and animal-like cells. We say "animal-like" because an animal type of cell could be
anything from a tiny microorganism to a nerve cell in your brain. Biology classes often
take out a microscope and look at single-celled microbes from pond water. You might
see hydra, amoebas, or euglena.
There are animal cells and plants cells
Plant cells are easier to identify because they have a protective structure called a
cell wall made of cellulose. Plants have the wall; animals do not. Plants also have
organelles such as the green chloroplast or large, water-filled vacuoles.
Chloroplasts are the key structure in the process of photosynthesis.
Plants have a cell wall and chloroplasts, animals do not
Cells are unique to each type of organism. If you look at very simple organisms, you will
discover cells that have no defined nucleus (prokaryotes) and other cells that have
hundreds of nuclei (multinucleated).
Cells are unique in each type of organism
Humans have hundreds of different cell types. You have red blood cells that are
used to carry oxygen (O2) through the body and other cells specific to your heart
muscle. Even though cells can be very different, they are basically compartments
surrounded by some type of membrane.
Cells are unique in each type of organism
Summary of Notes from Cells are the Starting Point
Cells make up all living things
Cells are the basic units for organisms and are made up of smaller parts
Cells are used to organize and perform different responsibilities/purpose
Humans are not made of one cell
There are animal cells and plants cells
Plants have a cell wall and chloroplasts, animals do not
Cells are unique in each type of organism
Cells are unique in each type of organism
Exit Activity: Vocabulary comprehension using context clues.
Fill in the blanks below using the correct vocabulary words from your Vocab Chart.
Highlight the context clues that helped you choose the correct vocab word.
1. Trees, humans and bacteria are all ____________ because they are living.
organism
2. An amoeba is ______________ because it is only made of 1 cell. unicellular
3. Cells group together to make connective ___________ that makes up your skin,
which is a major organ. tissue
4. The nucleus and mitochondria are all __________ of a cell. These are just 2
examples of parts within a cell. organelles
5. The human body is made up of _________ cells because we are very complex
organisms. Each cell is responsible for different jobs to make out body work.
specialized
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Legend of The Galactic Heroes, Volume 1 - DawnDocument273 pagesLegend of The Galactic Heroes, Volume 1 - DawnJon100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- English (Step Ahead)Document33 pagesEnglish (Step Ahead)ry4nek4100% (1)
- Gomez Vs PalomarDocument2 pagesGomez Vs PalomarKim Lorenzo CalatravaNo ratings yet
- Distinguish Opinion From TruthDocument12 pagesDistinguish Opinion From TruthMAR ANTERO R. CENIZA100% (2)
- Ablutophobia Fear of Bathing and HomoeopathyDocument8 pagesAblutophobia Fear of Bathing and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (1)
- Divorce Bill in The PhilippinesDocument19 pagesDivorce Bill in The PhilippinesNeiqui Aubrey Antaran CañeteNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Materials Science for NDTDocument96 pagesIntroduction to Materials Science for NDTMircea Dubenco100% (1)
- Recovering Mind and Body (Mental Health)Document24 pagesRecovering Mind and Body (Mental Health)Shivamani143100% (1)
- Reveiw TeacherDocument2 pagesReveiw Teacherapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Unit 7 Science Vocabulary Sheet TeacherDocument3 pagesUnit 7 Science Vocabulary Sheet Teacherapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Unit 9 Day 7 Student Test Study Guide RetakeDocument3 pagesUnit 9 Day 7 Student Test Study Guide Retakeapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Science Vocabulary Sheet Unit 2 Teacher 2Document3 pagesScience Vocabulary Sheet Unit 2 Teacher 2api-280035690No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Vocabulary TeacherDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Vocabulary Teacherapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Water Cycle at Home ProjectDocument4 pagesWater Cycle at Home Projectapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Day 4 StudentDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Day 4 Studentapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Sci Method Station Activity Answer KeyDocument9 pagesSci Method Station Activity Answer Keyapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Unit 8 Day 2 TeacherDocument4 pagesUnit 8 Day 2 Teacherapi-280035690No ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Sci Method Study Guide Answer KeyDocument3 pagesSci Method Study Guide Answer Keyapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Unit 8 Day 3 StudentDocument2 pagesUnit 8 Day 3 Studentapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Unit 9 Science Master Vocabulary SheetDocument4 pagesUnit 9 Science Master Vocabulary Sheetapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Scientific Method Vocabulary SheetDocument3 pagesScientific Method Vocabulary Sheetapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Where Do Cells Come FromDocument4 pagesWhere Do Cells Come Fromapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Master Vocabulary SheetDocument4 pagesMaster Vocabulary Sheetapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Unit 8 Vocabulary SheetDocument3 pagesUnit 8 Vocabulary Sheetapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Unit 7 ReviewDocument4 pagesUnit 7 Reviewapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Unit 6 Day 3 StudentDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Unit 6 Day 3 Studentapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Unit 7 Day 5 StudentDocument4 pagesUnit 7 Day 5 Studentapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Cells Unit 7 Day 1 TeacherDocument1 pageCells Unit 7 Day 1 Teacherapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Unit 6 Vocabulary With Definitions and ExplanationsDocument3 pagesUnit 6 Vocabulary With Definitions and Explanationsapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Photosynethesis PowerpointDocument8 pagesPhotosynethesis Powerpointapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Cell Project 2014 Unit 7Document3 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell Project 2014 Unit 7api-280035690No ratings yet
- Unit 6 Day 5 TeacherDocument2 pagesUnit 6 Day 5 Teacherapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Day 16 FoldableDocument2 pagesUnit 1 Day 16 Foldableapi-280035690No ratings yet
- Asfaw & Veni (2015)Document15 pagesAsfaw & Veni (2015)Jessa BeloyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document3 pagesChapter 8sasafoadjeiNo ratings yet
- Chong Co Thai Restaurant LocationsDocument19 pagesChong Co Thai Restaurant LocationsrajragavendraNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Treadmill Based and Track Based Rockport 1 Mile Walk Test For Estimating Aerobic Capacity in Healthy Adults Ages 30-50 YearsDocument4 pagesComparison of Treadmill Based and Track Based Rockport 1 Mile Walk Test For Estimating Aerobic Capacity in Healthy Adults Ages 30-50 Yearsmanjula dangeNo ratings yet
- Competitor Analysis - Taxi Service in IndiaDocument7 pagesCompetitor Analysis - Taxi Service in IndiaSachin s.p50% (2)
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1lauraNo ratings yet
- Employee Retention Plan QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesEmployee Retention Plan QuestionnaireThayyib MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law Notes SummaryDocument12 pagesCriminal Law Notes SummaryPurplaawNo ratings yet
- Philippians 1:27-2:18Document3 pagesPhilippians 1:27-2:18Buddy OvermanNo ratings yet
- GEY 102-Introduction To Geology 1-Lecture Slides - Prof. M.E. NtonDocument44 pagesGEY 102-Introduction To Geology 1-Lecture Slides - Prof. M.E. Ntonabuabdmuqseet2001No ratings yet
- NGSS Core Concepts PDFDocument1 pageNGSS Core Concepts PDFNancy Angélica LopezNo ratings yet
- At HomeDocument16 pagesAt HomesamoorewritesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16-Analyzing Qualitative DataDocument3 pagesChapter 16-Analyzing Qualitative DataLiko Pah TuafNo ratings yet
- Autonomy Vs IntegrationDocument31 pagesAutonomy Vs IntegrationWahid KhanNo ratings yet
- List of Private Schools in Batangas SY 2016-2017Document9 pagesList of Private Schools in Batangas SY 2016-2017Lucky MalihanNo ratings yet
- P - 3Y - Test Paper - Motion in 2 Dimension.Document5 pagesP - 3Y - Test Paper - Motion in 2 Dimension.sudhir_kumar_33No ratings yet
- Sic 789 ADocument19 pagesSic 789 AFlorinMacoveiNo ratings yet
- Irish Chapter 6 Causes of DeathDocument8 pagesIrish Chapter 6 Causes of DeathIrish AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Memorial On Behalf of PetitionerDocument35 pagesMemorial On Behalf of PetitionerAjitabhGoel67% (3)
- Aircrew Standards Manual FY2015 V1Document211 pagesAircrew Standards Manual FY2015 V1Anonymous Pb39klJ100% (1)
- MSO 1st Year Assignments 2017-18 (English) PDFDocument7 pagesMSO 1st Year Assignments 2017-18 (English) PDFAmritpal BhagatNo ratings yet
- Assessment: Direction: Read The Story of "Silence - A Fable" by Edgar Allan Poe. Interpret and Analyze The StoryDocument4 pagesAssessment: Direction: Read The Story of "Silence - A Fable" by Edgar Allan Poe. Interpret and Analyze The StoryElsa BorrinagaNo ratings yet