Professional Documents
Culture Documents
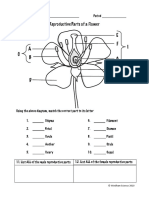
No Brain Too Small : 1 - Petal, 2 - Anther, 3 - Stigma, 4 - Ovary, 5 - Sepal
Uploaded by
Victoria LowmanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
No Brain Too Small : 1 - Petal, 2 - Anther, 3 - Stigma, 4 - Ovary, 5 - Sepal
Uploaded by
Victoria LowmanCopyright:
Available Formats
No Brain Too Small
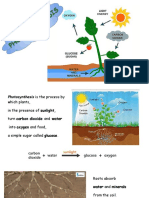
Photosynthesis
Carried by an
animal
Eaten & excreted
Carried by the
wind
Thrown by
explosion
Carried by an
animal
A flower, B
stem, C leaf, D
- roots
1 petal, 2
anther, 3 stigma,
4 ovary, 5 - sepal
Stamen (male
part of flower)
Carpel/pistil
(female part of
flower)
Less competition
for light, water,
nutrients etc
Chloroplast
No Brain Too Small
Chlorophyll
Cross pollination
Hold the plant in
the soil & absorb
minerals
Petal colour,
scent, nectar
Stamens
Self pollination
Why do we boil
the leaf when
testing for
starch?
Why do we boil
the leaf in ethanol
when testing for
starch?
To soften the leaf,
break open the cells &
remove the waxy
surface
To remove the
green chlorophyll
What is osmosis?
Where does
osmosis occur?
Why do plants
transpire?
The diffusion of water
from a high concentration
to a low concentration
through a semi permeable
membrane
In the roots of a
plant
1. To keep plants cool
2. To keep nutrients
and water moving
through the plant
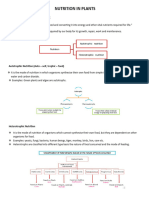
Iodine
What chemical do
plants store
glucose as?
Stem
Leaf
Starch
Chlorophyll
No Brain Too Small
Water + CO2
Glucose + ?
Plants need
sunlight and what
in order to
complete
photosynthesis?
What are the
reproductive part
of a plant?
Blue/black
Oxygen
(photosynthesis)
Chlorophyll
Flower
How is the
presence of
starch in a leaf
evidence for
photosynthesis?
What are the two
gases that diffuse
into and out of a
leaf?
What is carbon
dioxide a byproduct of?
How does gases
move into and out
of the leaf?
Photosynthesis produces
glucose which plants store in
their leaves as starch. Therefore
the presence of starch is
evidence of photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide &
oxygen
Photosynthesis
Via diffusion (moving
from high conc. to
low conc.)
What is this?
What are phloem
for?
This is a stomata
surrounded by two
bean-shaped guard
cells
Vein-like system
for transporting
glucose and starch
What is the job of
guard cells that
surround the
stomata on the
bottom of a leaf?
Stomata prevent
water loss by
opening and closing
What are xylem
for?
Gases entering &
exiting the leaf
via the stomata
No Brain Too Small
Transporting water
and nutrients from
roots to leaves
No Brain Too Small
No Brain Too Small
No Brain Too Small
You might also like
- OIPDocument74 pagesOIPFrancis TerradoNo ratings yet
- Green Algae and Land Plants LabDocument21 pagesGreen Algae and Land Plants Lab13ucciNo ratings yet
- AP Biology - 7.9 - PhylogenyDocument27 pagesAP Biology - 7.9 - PhylogenyVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- AP Biology - Worksheet - Pedigrees 2 PDFDocument3 pagesAP Biology - Worksheet - Pedigrees 2 PDFVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Science Stage 5Document20 pagesScience Stage 5Fan Asigo33% (3)
- The meaning of de-starching plants and testing with iodineDocument5 pagesThe meaning of de-starching plants and testing with iodineHend HamedNo ratings yet
- Gardening Notes (English)Document49 pagesGardening Notes (English)abhijitakadamNo ratings yet
- Biology SQ3RDocument68 pagesBiology SQ3RJay JustNo ratings yet
- Biology 1 - Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument79 pagesBiology 1 - Characteristics of Living OrganismsSaket GudimellaNo ratings yet
- How green plants feed through photosynthesisDocument41 pagesHow green plants feed through photosynthesisAnonymous s5veYTCyWHNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology:: How Plants WorkDocument70 pagesPlant Physiology:: How Plants WorkSusana DiazNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionDocument14 pagesIGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionsarNo ratings yet
- Intro To PlantsDocument33 pagesIntro To PlantsBALQIS NURAZIZAHNo ratings yet
- Guide to Plant Structure and FunctionsDocument20 pagesGuide to Plant Structure and FunctionsAariz KhanNo ratings yet
- How Plants Photosynthesize and Make FoodDocument5 pagesHow Plants Photosynthesize and Make FoodGiuseppe CondelloNo ratings yet
- Prodigious PlantsDocument9 pagesProdigious PlantsJuan CollaoNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition: Photosynthesis and Nutrient UptakeDocument31 pagesPlant Nutrition: Photosynthesis and Nutrient UptakeAbhay BhingradiaNo ratings yet
- 1 Botany BasicsDocument34 pages1 Botany BasicsAnonymous RY91UFyQNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument6 pagesNutrition in PlantsSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Structure of A LeafDocument82 pagesStructure of A Leaflevie agacerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document4 pagesChapter 10Mahir ShahriyarNo ratings yet
- All About PhotossynthesisDocument7 pagesAll About Photossynthesisapi-341032878No ratings yet
- The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesThe Process of Photosynthesisnelia mae laroyaNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy Physiology SAT REVEIWDocument35 pagesPlant Anatomy Physiology SAT REVEIWFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Is For Master Gardeners: Dan Culbert, Extension Agent III - Environmental HorticultureDocument76 pagesIs For Master Gardeners: Dan Culbert, Extension Agent III - Environmental HorticultureJemuel FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition.Document16 pagesPlant Nutrition.zena mohamedNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Plants ExplainedDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis in Plants ExplainedAedeni MirandaNo ratings yet
- 2023 Y3 Bio NotesDocument27 pages2023 Y3 Bio NotesJX35No ratings yet
- Plant and Their Systems, Gr-7, AdyalaDocument15 pagesPlant and Their Systems, Gr-7, AdyalaSidra UsmanNo ratings yet
- Power Point Science 30Document10 pagesPower Point Science 30Jerome TamayaoNo ratings yet
- PLANTS - Power PointDocument33 pagesPLANTS - Power PointChris MaxilomNo ratings yet
- How Plants Adapt to Life on LandDocument6 pagesHow Plants Adapt to Life on LandLuis Ureña HurtadoNo ratings yet
- The Food Factory of PlantsDocument15 pagesThe Food Factory of PlantsFathima Abdul AzeezNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition NoteDocument5 pagesPlant Nutrition NoteYolanda JesslinaNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument35 pagesTransport in PlantsChantae JulienNo ratings yet
- Crop 1Document6 pagesCrop 1Cynel DelaNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure and Photosynthesis - EditedDocument17 pagesPlant Structure and Photosynthesis - Editedchloe.phamNo ratings yet
- Activity 5Document2 pagesActivity 5Rigor Ruiz SuguitaoNo ratings yet
- Seed GerminationDocument3 pagesSeed GerminationfileksNo ratings yet
- Fun Facts of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesFun Facts of PhotosynthesisPinkpink ChiuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 L-1.1 1.2 1.3 Science Grade 8Document24 pagesUnit 1 L-1.1 1.2 1.3 Science Grade 8andeepthiNo ratings yet
- Cluster Biology of PlantsDocument48 pagesCluster Biology of Plantsapi-452104023100% (1)
- Seed Report OutlineDocument2 pagesSeed Report OutlineAshlee JornadalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Vascular Plant BodyDocument15 pagesIntroduction To The Vascular Plant BodyEula Trixie DenulanNo ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesDocument50 pagesAlwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- W7 - Internal Structures and Functions of PlantsDocument35 pagesW7 - Internal Structures and Functions of PlantsSally Bustillo DiscuaNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Revision - Photosynthesis and TranspirationDocument1 pageGCSE Biology Revision - Photosynthesis and TranspirationHusen Ibn IsmailNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition & TransportDocument21 pagesPlant Nutrition & TransportKim-Elaine Pohatu100% (1)
- AP Kingdom PlantaeDocument79 pagesAP Kingdom PlantaeDaniel LeeNo ratings yet
- Basic BotanyDocument47 pagesBasic Botanyartadiel28No ratings yet
- Plant Photosynthesis GuideDocument24 pagesPlant Photosynthesis GuideTomy LoustauNo ratings yet
- Plants and PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesPlants and PhotosynthesisUpeka WeerasinghaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes SummaryDocument12 pagesBiology Notes Summaryrobin.kipchumbaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 201, Task BDocument3 pagesAssignment 201, Task BroyhattersleyNo ratings yet
- How Plants SurviveDocument34 pagesHow Plants SurviveAlyzza Joy Albay100% (2)
- Plant Parts and Functions: By: Alisa Kowalski Jessi Spry Alyson WilsonDocument26 pagesPlant Parts and Functions: By: Alisa Kowalski Jessi Spry Alyson WilsonAlfie BurbosNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY II NotesDocument8 pagesBIOLOGY II NotesDarwin SawalNo ratings yet
- Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series Plant and Animal ClassificationDocument11 pagesDr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test Series Plant and Animal ClassificationHarshaWakodkar100% (1)
- Photosynthesis: How Plants Turn Sunlight Into FoodDocument26 pagesPhotosynthesis: How Plants Turn Sunlight Into FoodRocio Navas ManjavacasNo ratings yet
- Seed Germination MechanismsDocument3 pagesSeed Germination MechanismsfileksNo ratings yet
- Hydroponic Gardening: A Beginner Guide to Learn How to Design and Build Your Own Sustainable Hydroponics System, for Growing Plants and Vegetables at HomeFrom EverandHydroponic Gardening: A Beginner Guide to Learn How to Design and Build Your Own Sustainable Hydroponics System, for Growing Plants and Vegetables at HomeNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz #1 - Exothermic ReactionsDocument1 pageQuick Quiz #1 - Exothermic ReactionsVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange INB Lesson (Key Included)Document11 pagesGas Exchange INB Lesson (Key Included)Victoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Chemical Reactions SoWDocument3 pagesTopic 8 Chemical Reactions SoWVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions PresentationDocument45 pagesChemical Reactions PresentationVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Bill Nye - S2E20 Respiration (Breathing)Document3 pagesBill Nye - S2E20 Respiration (Breathing)Victoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Color Coding The Periodic Table - InstructionsDocument2 pagesColor Coding The Periodic Table - InstructionsVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions SLOsDocument1 pageChemical Reactions SLOsVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Magnesium and Acid Worksheet - Answer KeyDocument3 pagesMagnesium and Acid Worksheet - Answer KeyVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Exothermic Vs Endothermic Lab SheetDocument3 pagesExothermic Vs Endothermic Lab SheetVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Metals and WaterDocument5 pagesMetals and WaterVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Metals and WaterDocument5 pagesMetals and WaterVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- 4 Elaboration - Respiratory System - Student Project W RubricDocument2 pages4 Elaboration - Respiratory System - Student Project W RubricVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Worksheet - Answer KeyDocument3 pagesChemical Reactions Worksheet - Answer KeyVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure WorksheetDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure WorksheetAryan AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Endothermic and Exothermic ReactionsDocument6 pagesEndothermic and Exothermic ReactionsVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- 4 Elaboration - Respiratory System - Student Project W RubricDocument2 pages4 Elaboration - Respiratory System - Student Project W RubricVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- AP Biology - Ecological Pyramids - Worksheet PDFDocument6 pagesAP Biology - Ecological Pyramids - Worksheet PDFVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Activities PresentationDocument15 pagesActivities PresentationVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Lizard Evolution Virtual Lab Student WorksheetDocument5 pagesLizard Evolution Virtual Lab Student WorksheetNadia Suquillo0% (1)
- AP Biology - Ecology - PracticeDocument8 pagesAP Biology - Ecology - PracticeVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Read It! Specialised CellsDocument6 pagesRead It! Specialised CellsVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- AP Biology - Ecological Pyramids - Worksheet PDFDocument6 pagesAP Biology - Ecological Pyramids - Worksheet PDFVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Organisms Respond to Environmental Changes Through Behavioral and Physiological MechanismsDocument37 pagesOrganisms Respond to Environmental Changes Through Behavioral and Physiological MechanismsVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- 10HS - Stoichiometry - Mole and Mass Worksheet 2Document7 pages10HS - Stoichiometry - Mole and Mass Worksheet 2Victoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- 10HS Stoichiometry Concept Review Answer KeyDocument1 page10HS Stoichiometry Concept Review Answer KeyVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- 10HS Stoichiometry 2017-2018Document77 pages10HS Stoichiometry 2017-2018Victoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Worksheet Pedigrees 2Document2 pagesAP Biology Worksheet Pedigrees 2Victoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- As 1.4 l02 Standard Enthalpy Changes and Hess Law Updated 2010Document16 pagesAs 1.4 l02 Standard Enthalpy Changes and Hess Law Updated 2010Victoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Notes On Vietnamese Begonia (Begoniaceae)Document10 pagesNotes On Vietnamese Begonia (Begoniaceae)Thảo PhạmNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Pock BookDocument53 pagesClass 12 Biology Pock Bookbs.3136 VVS.No ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Chapter-7: Class-Vi ScienceDocument11 pagesNcert Solutions Chapter-7: Class-Vi ScienceAghradeep Dhar class 9 A 19100% (1)
- Glossary of Botanical Terms - WikipediaDocument412 pagesGlossary of Botanical Terms - WikipediaJanani SankarNo ratings yet
- Anthurium Breeding PPT by S Y ChandrashekarDocument30 pagesAnthurium Breeding PPT by S Y ChandrashekarDr-Chandrashekar S Y100% (20)
- SUKULENTEDocument26 pagesSUKULENTEDragana MuncanNo ratings yet
- Bisexual & Male Flower PDFDocument10 pagesBisexual & Male Flower PDFIcsNo ratings yet
- G7 - First Term Examination (2019) - Royal College, Colombo 07Document9 pagesG7 - First Term Examination (2019) - Royal College, Colombo 07Xiao ShadowlordNo ratings yet
- Wind-pollinated flowers quizDocument8 pagesWind-pollinated flowers quizmohad adeel100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 5Document10 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 5Mountain Drew100% (1)
- 8 Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Answers: Plant of The Same SpeciesDocument3 pages8 Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Answers: Plant of The Same SpeciesKiandokht KhosraviNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument3 pagesConcept Mapapi-375479875No ratings yet
- Vol. XIDocument333 pagesVol. XICamila AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- South African Flora GlossaryDocument47 pagesSouth African Flora Glossarymr.bryceNo ratings yet
- 1989 JC Science Syllabus (Revised)Document40 pages1989 JC Science Syllabus (Revised)James MontgomeryNo ratings yet
- Plant Breeding Practices in Rice (Oryza Sativa 2n 2x 24)Document3 pagesPlant Breeding Practices in Rice (Oryza Sativa 2n 2x 24)muhammadrizwanaNo ratings yet
- Solanaceae: Nightshade FamilyDocument36 pagesSolanaceae: Nightshade FamilyAnantha Krishna K SNo ratings yet
- USDA Forest Service Tree Seed ManualDocument162 pagesUSDA Forest Service Tree Seed ManualJulio Mora CastilloNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument9 pagesModule 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsMorgan BrownNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Parts of A Flower: © Windham Science 2019Document2 pagesReproductive Parts of A Flower: © Windham Science 2019api-524919792No ratings yet
- Organismal Biology ConceptsDocument97 pagesOrganismal Biology ConceptsDaryl PansoyNo ratings yet
- Taxonomic Evidence: Structural and Biochemical Characters: MorphologyDocument48 pagesTaxonomic Evidence: Structural and Biochemical Characters: MorphologyGhulamJelaniNo ratings yet
- Vii Science Student Study Material - Final New 1Document101 pagesVii Science Student Study Material - Final New 1YASHVI MODINo ratings yet
- Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 - 1Document21 pagesLife Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 - 1Shyamal AryalNo ratings yet
- grade-11-life-sciences-revision-material-term-1-2024Document31 pagesgrade-11-life-sciences-revision-material-term-1-2024youngmarley457No ratings yet
- Points to Remember: Plant Morphology and StructuresDocument9 pagesPoints to Remember: Plant Morphology and StructuresArthav KumarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 4 Social Studies Worksheet PDFDocument35 pagesCBSE Class 4 Social Studies Worksheet PDFRakesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab ManualDocument14 pagesBiology Lab ManualAkshatha NayakNo ratings yet