Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ch17 Sec2
Uploaded by
api-272720493Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ch17 Sec2
Uploaded by
api-272720493Copyright:
Available Formats
Nonrenewable Energy
Section 2: Nuclear Energy
Preview
Bellringer
Objectives
Nuclear Energy
Fission: Splitting Atoms
How Nuclear Energy Works
The Advantages of Nuclear Energy
Why Arent We Using More Nuclear Energy?
Storing Waste
Section 2
Nonrenewable Energy
Section 2: Nuclear Energy
Preview, continued
Safety Concerns
The Future of Nuclear Power
Section 2
Nonrenewable Energy
Bellringer
Section 2
Nonrenewable Energy
Section 2
Objectives
Describe nuclear fission.
Describe how a nuclear power plant works.
List three advantages and three disadvantages of
nuclear energy.
Fission: Splitting Atoms
Nonrenewable Energy
Section 2
Nuclear Energy
In the 1950s and 1960s, nuclear power plants were seen
as the power source of the future because the fuel they
use is clean and plentiful.
In the 1970s and 1980s, however, many planned nuclear
power plants were cancelled and others under
construction were abandoned.
Today, nuclear power accounts for 17% of the worlds
electricity.
Nonrenewable Energy
Section 2
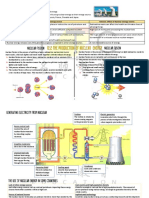
Fission: Splitting Atoms
Nuclear power plants get their power from nuclear
energy.
Nuclear energy is the energy released by a fission or
fusion reaction. It represents the binding energy of the
atomic nucleus.
The forces that hold together a nucleus of an atom are
more than 1 million times stronger than the chemical
bonds between atoms.
In nuclear power plants, atoms of the element uranium
are used as the fuel.
Nonrenewable Energy
Section 2
Fission: Splitting Atoms
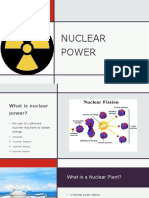
The nuclei of uranium atoms are bombarded with atomic
particles called neutrons. These collisions cause the
nuclei to split in a process called nuclear fission.
Nuclear fission is is the splitting of the nucleus of a
large atom into two or more fragments.
Nuclear fission releases a tremendous amount of energy
and more neutrons, which in turn collide with more
uranium nuclei.
Nonrenewable Energy
Fission: Splitting Atoms
Section 2
Nonrenewable Energy
Section 2
How Nuclear Energy Works
The heat released during nuclear reactions is used to
generate electricity in the same way that power plants
burn fossil fuels to generate electricity.
The energy released from the fission reactions heats a
closed loop of water that heats another body of water.
As the water boils, it produces steam that drives a
turbine, which is used to generate electricity.
Nonrenewable Energy
How Nuclear Energy Works
Section 2
Nonrenewable Energy
Section 2
The Advantages of Nuclear Energy
Nuclear fuel is a very concentrated energy source.
Nuclear power plants do not produce air-polluting gases.
Nuclear power plants release less radioactivity than coalfired power plants do, when operated properly.
Countries will limited fossil-fuel resources rely heavily on
nuclear plants to supply electricity.
Nonrenewable Energy
Section 2
Why Arent We Using More Nuclear Energy?
Building and maintaining a safe reactor is very expensive.
This makes nuclear plants no longer competitive with
other energy sources in many countries.
The actual cost of new nuclear power plants is uncertain,
so it is difficult to predict whether investors will build new
plants in the United States.
Nonrenewable Energy
Section 2
Storing Waste
The greatest disadvantage of nuclear power is the
difficulty in finding a safe place to store nuclear waste.
The fission products produced can remain dangerously
radioactive for thousands of years.
Storage sites for nuclear wastes must be located in areas
that are geologically stable for tens of thousands of years.
Scientists are researching a process called transmutation,
that would recycle the radioactive elements in nuclear
fuel.
Nonrenewable Energy
Section 2
Safety Concerns
In a poorly designed nuclear plant, the fission process
can potentially get out of control.
The Chernobyl reactor was destroyed in 1986 when an
unauthorized test caused explosions and blasted
radioactive materials into the air.
Hundreds of people in the Ukraine died from radioactive
exposure from this explosion.
Even today, parts of northern Europe and the Ukraine
remain contaminated from this disaster.
Nonrenewable Energy
Section 2
Safety Concerns
The most serious nuclear accident in the United States
occurred in 1979 at the Three Mile Island nuclear power
plant in Pennsylvania.
Human error, along with blocked valves and broken
pumps, was responsible for this accident.
Fortunately, only a small amount of radioactive gas
escaped.
Since that accident, the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory
Commission has required more than 300 safety
improvements to nuclear plants.
Nonrenewable Energy
Section 2
The Future of Nuclear Power
One possible future energy source is nuclear fusion.
Nuclear fusion is the combination of the nuclei of small
atoms to form a larger nucleus. Fusion releases
tremendous amounts of energy.
It is potentially a safer energy source than nuclear fission
is because it creates less dangerous radioactive
byproducts.
Nonrenewable Energy
The Future of Nuclear Power
Section 2
Nonrenewable Energy
Section 2
The Future of Nuclear Power
Although the potential for nuclear fusion is great, so is the
technical difficulty of achieving that potential.
For fusion to occur, three things must occur simultaneously:
Atomic nuclei must be heated to extremely high
temperatures (about 100,000,000C or 180,000,000F).
The nuclei must be maintained at very high conditions.
The nuclei must be properly confined.
The technical problems are so complex that building a
nuclear fusion plant may take decades or may never happen.
You might also like
- Everything About Nuclear EnergyDocument29 pagesEverything About Nuclear EnergygaviNo ratings yet
- Chernobyl An OverviewDocument28 pagesChernobyl An OverviewFOOTBALL AND MOVIES ZONENo ratings yet
- Nuclear EnergyDocument12 pagesNuclear Energyreemagotewala81No ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy: Spataru Liliana Grupa 2112 CDocument12 pagesNuclear Energy: Spataru Liliana Grupa 2112 CliliblondyxNo ratings yet
- NE-Traditional Energy ResourcesDocument73 pagesNE-Traditional Energy ResourcesMohamed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Sommaire: I-What Is Nuclear Energy? II - Operation of Nuclear EnergyDocument8 pagesSommaire: I-What Is Nuclear Energy? II - Operation of Nuclear Energyahmed alexisNo ratings yet
- Power PlantsDocument12 pagesPower PlantsLinda Leon TomaNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion Week 12: Debunking Myths About Nuclear PowerDocument23 pagesEnergy Conversion Week 12: Debunking Myths About Nuclear PowerSatria PanjiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Accidents and HolocaustDocument19 pagesNuclear Accidents and HolocaustSurendra RanwaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ReactionsDocument31 pagesNuclear ReactionsKrishnan JagadeesanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Vs Fossil FuelsDocument10 pagesNuclear Power Vs Fossil FuelsAYALEYDENNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant by Absharma Final PDFDocument19 pagesNuclear Power Plant by Absharma Final PDFAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- LecPPT1_Nuclear Engineering BasicsDocument41 pagesLecPPT1_Nuclear Engineering BasicsVishal MeenaNo ratings yet
- Very Simple Presentation About Nuclear Power Plants For New Beginners of The TechnologyDocument21 pagesVery Simple Presentation About Nuclear Power Plants For New Beginners of The TechnologySrinivas Reddy ParvatNo ratings yet
- GNED 1101 - Fall - 2017 - Nuclear Energy - & RadioactivityDocument26 pagesGNED 1101 - Fall - 2017 - Nuclear Energy - & RadioactivityAshleyNo ratings yet
- NuclearDocument72 pagesNuclearPrathap VuyyuruNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Operations Management - Session VIIDocument41 pagesInfrastructure Operations Management - Session VIISai Ujjwala VemuriNo ratings yet
- PPT 5 HODocument17 pagesPPT 5 HObiniamkiros09No ratings yet
- FissionDocument9 pagesFissionapi-121449898No ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy: Saswata Bag 14/CE/92 Haldia Institute of TechnologyDocument19 pagesNuclear Energy: Saswata Bag 14/CE/92 Haldia Institute of TechnologySaswata PradhanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power and Nuclear FissionDocument7 pagesNuclear Power and Nuclear Fissionapi-22931177No ratings yet
- Nuclear Power and FissionDocument7 pagesNuclear Power and Fissionapi-22931443No ratings yet
- Nuclear Power and EnergyDocument11 pagesNuclear Power and Energymitranrazvan197No ratings yet
- Production: Naturally: Some Nuclear Energy Is Produced Naturally. ForDocument5 pagesProduction: Naturally: Some Nuclear Energy Is Produced Naturally. ForSyed Tahir HassanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy BMEDocument45 pagesNuclear Energy BMEBIJETA KUNWARNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactor Document For Physics ProjectDocument12 pagesNuclear Reactor Document For Physics ProjectArshad KhanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear 2Document37 pagesNuclear 2Dan NiloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04-Nuclear EnergyDocument31 pagesChapter 04-Nuclear EnergySeab PisethNo ratings yet
- Ali MajeedDocument13 pagesAli MajeedSaad MajeedNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantsDocument8 pagesNuclear Power Plantsapi-22823300No ratings yet
- Nuclear EnergyDocument5 pagesNuclear EnergyAilen GrasaNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Understanding Nuclear Energy: Atomic Mass Unit (A.m.u)Document7 pages5.4 Understanding Nuclear Energy: Atomic Mass Unit (A.m.u)ng_jieyiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy AssingmentDocument19 pagesNuclear Energy Assingmentjameswyatt0327No ratings yet
- Understanding Nuclear Power PlantsDocument34 pagesUnderstanding Nuclear Power Plantsferdinand galut100% (1)
- Itroduction To Nuclear ChemistryDocument19 pagesItroduction To Nuclear ChemistryNickNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument12 pagesNuclear Power PlantHalifa AhmadNo ratings yet
- Nuclear-Reactor - Working and ConstructionDocument15 pagesNuclear-Reactor - Working and Constructionprince arora80% (5)
- Nuclear Energy What Is It?: David J. Diamond Energy Sciences & Technology Department February 2009Document27 pagesNuclear Energy What Is It?: David J. Diamond Energy Sciences & Technology Department February 2009Asif KhanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant Engineering: Components and Reactor TypesDocument13 pagesNuclear Power Plant Engineering: Components and Reactor TypesMehdiNo ratings yet
- F4 C12 Notes KSSMDocument3 pagesF4 C12 Notes KSSMKavilashini LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document33 pagesGroup 2poadNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Nuclear BatteriesDocument22 pagesSeminar On Nuclear BatteriesPRABATH MADHAVANNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power - A Future Prospective: Presented byDocument17 pagesNuclear Power - A Future Prospective: Presented byDev Kumar100% (1)
- Nuclear & Solar EnergyDocument36 pagesNuclear & Solar EnergyZaion ZephyrNo ratings yet
- Energy Sources & Electricity GenerationDocument23 pagesEnergy Sources & Electricity GenerationQueen BlehNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PowerDocument9 pagesNuclear Powergo goNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PowerDocument9 pagesNuclear Powergo goNo ratings yet
- What is Nuclear Energy and How Does it WorkDocument7 pagesWhat is Nuclear Energy and How Does it WorkCaryl PabasNo ratings yet
- PP1 - How Sciences Challenges SocietyDocument16 pagesPP1 - How Sciences Challenges SocietythdaleyNo ratings yet
- Fuel and Energy Utilization Ece4433: Segi UniversityDocument14 pagesFuel and Energy Utilization Ece4433: Segi Universityrock balboa100% (1)
- Nuclear PowerDocument3 pagesNuclear PowerChristian Bartl - bartlweb.netNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy: Prepared By:yee Especially For: 4 EconomyDocument53 pagesNuclear Energy: Prepared By:yee Especially For: 4 EconomyKazariyah KasaNo ratings yet
- Class 6. Nuclear Power PlantDocument25 pagesClass 6. Nuclear Power PlantsureshlalNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Nuclear ReactorsDocument34 pagesPhysics Project Nuclear ReactorssreeshagsNo ratings yet
- SpeechDocument1 pageSpeechmohameddhafer.ahmedNo ratings yet
- Hazards of Nuclear PollutionDocument18 pagesHazards of Nuclear PollutionSanktifierNo ratings yet
- 6.2 The Production of Nuclear Energy and Its UsesDocument15 pages6.2 The Production of Nuclear Energy and Its UsesAisyah Dan AnuaruddinNo ratings yet
- TAUFIA ALIYAR - Attachment: PDF: WW - Lev.1 - No.1Document7 pagesTAUFIA ALIYAR - Attachment: PDF: WW - Lev.1 - No.1TAUFIA ALIYARNo ratings yet
- Devastating Nuclear Accidents throughout History: Causes and Results - Science Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Science & Nature BooksFrom EverandDevastating Nuclear Accidents throughout History: Causes and Results - Science Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Science & Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Genetics Notes KDocument4 pagesGenetics Notes Kapi-272720493No ratings yet
- Ccpe Brownfield Article 2012Document5 pagesCcpe Brownfield Article 2012api-272720493No ratings yet
- EnvironmentallawtimelineplanDocument10 pagesEnvironmentallawtimelineplanapi-272720493No ratings yet
- Energy Resource Project 03-09-2017-074829Document2 pagesEnergy Resource Project 03-09-2017-074829api-272720493No ratings yet
- America Aljazeera Com-Worlds Largest Tax-Funded Site of Mass Graves Might Be Turned Into A ParkDocument2 pagesAmerica Aljazeera Com-Worlds Largest Tax-Funded Site of Mass Graves Might Be Turned Into A Parkapi-272720493No ratings yet
- Cell-Cycle Mitosisedit 1Document36 pagesCell-Cycle Mitosisedit 1api-272720493No ratings yet
- Dna-Transcription-Translation-Mutations Hh-After 1Document57 pagesDna-Transcription-Translation-Mutations Hh-After 1api-272720493No ratings yet
- Genetics Hh-AfterDocument63 pagesGenetics Hh-Afterapi-272720493No ratings yet
- Dna-Notes-K 1Document5 pagesDna-Notes-K 1api-272720493No ratings yet
- DBQ Scoring GuideDocument1 pageDBQ Scoring Guideapi-272720493No ratings yet
- Soil Conservation 02-15-2017-072343Document1 pageSoil Conservation 02-15-2017-072343api-272720493No ratings yet
- Crackthecodesentence 01-27-2017-034635Document2 pagesCrackthecodesentence 01-27-2017-034635api-272720493No ratings yet
- Soil Notes Key 02-15-2017-075958Document2 pagesSoil Notes Key 02-15-2017-075958api-272720493No ratings yet
- Cell-Life-Cycle-And-Reproduction PPT Notesedit-K 1Document2 pagesCell-Life-Cycle-And-Reproduction PPT Notesedit-K 1api-272720493No ratings yet
- Park DBQ: InstructionsDocument1 pagePark DBQ: Instructionsapi-272720493No ratings yet
- DbqinstructionsDocument1 pageDbqinstructionsapi-272720493No ratings yet
- Population StatisticsDocument1 pagePopulation Statisticsapi-272720493No ratings yet
- Newrepublic Com-Americas Billionaires Are Turning Public Parks Into Playgrounds For The WealthyDocument4 pagesNewrepublic Com-Americas Billionaires Are Turning Public Parks Into Playgrounds For The Wealthyapi-272720493No ratings yet
- ch08 Sec1Document26 pagesch08 Sec1api-272720493No ratings yet
- Census Population Distribution and Change 2010Document12 pagesCensus Population Distribution and Change 2010api-272720493No ratings yet
- Env Stream LabDocument3 pagesEnv Stream Labapi-272720493No ratings yet
- Air Pollution - Questions For ReadingDocument1 pageAir Pollution - Questions For Readingapi-272720493No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis-And-Respiration-Review-Questions 1Document2 pagesPhotosynthesis-And-Respiration-Review-Questions 1api-272720493No ratings yet
- Vocabulary Tic Tac ToeDocument1 pageVocabulary Tic Tac Toeapi-272720493No ratings yet
- Chemistry of Life FoldableDocument2 pagesChemistry of Life Foldableapi-272720493No ratings yet
- Travel Brochure of A CellDocument1 pageTravel Brochure of A Cellapi-272720493No ratings yet
- Macromolecule NotesDocument3 pagesMacromolecule Notesapi-272720493No ratings yet
- Measurement Conversion 08-23-2016-075606Document2 pagesMeasurement Conversion 08-23-2016-075606api-272720493No ratings yet
- Mapping AssignmentDocument12 pagesMapping Assignmentapi-272720493No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Science 08-11-2016-080057Document12 pagesCharacteristics of Science 08-11-2016-080057api-272720493No ratings yet
- Atomic Exaggeration: The Infeasibility of IND Construction by Terrorist OrganizationsDocument19 pagesAtomic Exaggeration: The Infeasibility of IND Construction by Terrorist OrganizationsNoah KerwinNo ratings yet
- KDM Proposal NuMEgen Ver02 ExecSumm 20100605 FinalDocument2 pagesKDM Proposal NuMEgen Ver02 ExecSumm 20100605 FinalKev MequetNo ratings yet
- Godfrey Boyle Chap01Document20 pagesGodfrey Boyle Chap01Vanillasky0683% (12)
- Organization Study Conducted at NTPC, KorbaDocument86 pagesOrganization Study Conducted at NTPC, KorbaMayank SainiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant Safety RulesDocument34 pagesNuclear Power Plant Safety RulesSergey AgafonovNo ratings yet
- IC4 L3 T1to8ADocument3 pagesIC4 L3 T1to8AEduardo Rodrigues Ferreira78% (9)
- SEO-Optimized Title for Vietnamese Exam Document on EnglishDocument4 pagesSEO-Optimized Title for Vietnamese Exam Document on English7C-26 Xuân MaiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactor Core ComponentsDocument4 pagesNuclear Reactor Core ComponentsdcudfhiudfiuNo ratings yet
- The EPR™ Reactor: The Reference For New BuildDocument8 pagesThe EPR™ Reactor: The Reference For New BuildklareNo ratings yet
- Xenon adsorption on GACDocument8 pagesXenon adsorption on GACfarhadzakerNo ratings yet
- Oppenheimer and Slotin Study Guide-2Document12 pagesOppenheimer and Slotin Study Guide-2Bunhong AvNo ratings yet
- Kapal OH KapalDocument20 pagesKapal OH KapalDatz leoNo ratings yet
- ML23030B894Document4 pagesML23030B894Nathan BlockNo ratings yet
- Trends in Nuclear EducationDocument28 pagesTrends in Nuclear Educationesma baharNo ratings yet
- Reg Guide 1.9 r3Document12 pagesReg Guide 1.9 r3Kg SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Achieving New Nuclear Configuration Management: Presented By: Ken Barry - EPRI Lloyd Hancock - LRH ConsultingDocument21 pagesAchieving New Nuclear Configuration Management: Presented By: Ken Barry - EPRI Lloyd Hancock - LRH ConsultingEnrique Lopez De ArroyabeNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Hasin Mussayab Ahmed, Lecturer, Dept of EEE, UU: Power Plant Engineering Lecture On Nuclear Power PlantDocument26 pagesPrepared by Hasin Mussayab Ahmed, Lecturer, Dept of EEE, UU: Power Plant Engineering Lecture On Nuclear Power Plantহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- ASME Course Catalog 2011-2012Document12 pagesASME Course Catalog 2011-2012Arju M. SularnoNo ratings yet
- Design Estimation of Rooftop Solar Plants 1670158631Document111 pagesDesign Estimation of Rooftop Solar Plants 1670158631Le Van ChauNo ratings yet
- Iaea CN 245 96Document8 pagesIaea CN 245 96Gfr AllegroNo ratings yet
- Marine Propulsion SystemDocument114 pagesMarine Propulsion SystemWajih100% (3)
- GaqtertretDocument46 pagesGaqtertretPrince HeheNo ratings yet
- TH I Gian Làm Bài: 60 Phút: (A) (B) (C) (D) (A) (B) (C) (D) (A) (B) (C) (D)Document5 pagesTH I Gian Làm Bài: 60 Phút: (A) (B) (C) (D) (A) (B) (C) (D) (A) (B) (C) (D)HIendzNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Transmission and Distribution in ScotlandDocument53 pagesA Guide To Transmission and Distribution in ScotlanddhrghamNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Nuclear Waste ManagementDocument7 pagesAssignment On Nuclear Waste ManagementPankaj GillNo ratings yet
- Application of Ion Exchange Processes For The Treatment of Radioactive Waste....Document124 pagesApplication of Ion Exchange Processes For The Treatment of Radioactive Waste....Nguyen DungNo ratings yet
- Tri-City Toxics Final ReportDocument21 pagesTri-City Toxics Final Reportapi-264276114No ratings yet
- The Electrical Worker October 2008Document16 pagesThe Electrical Worker October 2008Kathryn R. ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Npcil TrainingDocument23 pagesNpcil TrainingParikshit Sharma100% (1)
- Practicing The Pie ChartDocument8 pagesPracticing The Pie ChartPhan Phương ThuýNo ratings yet