Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4: Inventory Management BUSI2603U Fall 2015
Uploaded by
Jharr699Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4: Inventory Management BUSI2603U Fall 2015
Uploaded by
Jharr699Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 4: Inventory Management
BUSI2603U
Fall 2015
Handout 1: The Ambrosia Bakery makes cakes for freezing and subsequent sale. The bakery,
which operates five days a week, 52 weeks a year, produce cakes at the rate of 56 cakes per
day. The bakery sets up the cake-production operation and produces until a predetermined
number (Q*) have been produced. When not producing cakes, the bakery uses its personnel
and facilities for producing other bakery items. The setup cost for a production run of cakes is
$700. The cost of holding frozen cakes in storage is $10 per cake per year. The annual demand
for frozen cakes, which is constant over time, is 6500 cakes. Assume that each cake costs $15
to purchase. Determine the following:
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
f)
Optimal production run quantity (Q*)
Total annual inventory costs
Optimal number of production runs per year
Optimal cycle time (time between run starts)
Run length in working days (t)
Average inventory
Handout 2: A local artisan uses supplies purchased from an overseas supplier. The owner
believes the assumptions of the EOQ model are met reasonably well. Minimization of inventory
costs is her objective. Relevant data, from the files of the craft firm, are annual demand of 175
units, ordering cost of $35 per order, and holding cost of $3 per unit per year
a)
b)
c)
d)
How many should she order at one time?
How many times per year will she replenish her inventory of this material?
What will be the total annual inventory costs associated with this material?
If she discovered that the carrying cost had been overstated, and was in reality only $1
per unit per year, what is the corrected value of EOQ?
Chapter 4: Inventory Management
BUSI2603U
Fall 2015
Handout 3: The annual demand for an item is 11,000 units. The cost to process an order is $75
and the annual inventory holding cost is 65 per unit. Justify your responses to the following
by showing all pertinent calculations.
a) What is the optimal order quantity?
b) What price should the firm pay per unit?
c) What is the total annual cost at the optimal behavior?
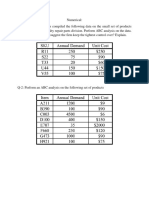
Quantity
1-9
10 999
1,000 - 4,999
5,000 or more
Price
$3.00 per unit
$2.65 per unit
$2.37 per unit
$1.95 per unit
Handout 4: County Hospital orders syringes from a hospital supply firm. The hospital expects
to use 45,000 per year. The cost to order and have the syringes delivered is $850. The annual
carrying cost is $1.50 per syringe because of security and theft. The hospital supply firm offers
the following quantity discount pricing schedule. Determine the minimum order size for the
hospital that minimizes the total cost. Justify your response by showing all pertinent
calculations.
Quantity
Price
09999
3.4
10,00019,999
3.2
20,00029,999
3.0
30,000+
2.8
Chapter 4: Inventory Management
BUSI2603U
Fall 2015
Handout 5: Nathan Manufacturing manufactures specialty car parts one of which is hubcaps.
The demand for hubcaps this year is forecasted to be 10000 units. The company produces
hubcaps at an annual production rate of 15000 hubcaps. When not producing the hubcaps, the
workers at Nathan Manufacturing produce other car parts. The workshop is open for 250 days.
The set up cost is $15 per production run and the holding cost is $0.70 per unit per year.
Assume that each hubcap costs $14 to purchase.
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
Optimal production run quantity
Total annual inventory costs
Optimal number of production runs per year
Optimal cycle time (time between run starts)
Run length in working days
Handout 6: Groundz Coffee Shop uses 4 pounds of a specialty tea weekly; each pound costs
$12. Carrying costs are $1 per pound per week because space is very scarce. It costs the firm
$13 to prepare an order. Assume the basic EOQ model with no shortages applies. Assume 52
weeks per year, closed on Mondays.
a) How many pounds should Groundz order at a time?
b) What is total annual cost (excluding item cost) of managing this item on a costminimizing basis?
c) In pursuing lowest annual total cost, how many orders should Groundz place annually?
d) How many days will there be between orders (assume 310 operating days) if Groundz
practices EOQ behavior?
Chapter 4: Inventory Management
BUSI2603U
Fall 2015
Handout 7: Holstein Computing manufactures an inexpensive audio card (Audio Max) for
assembly into several models of its microcomputers. The annual demand for this part is 90,000
units. The annual inventory carrying cost is $6.5 per unit and the cost of preparing an order and
making production setup for the order is $800. The company operates 250 days per year. The
machine used to manufacture this part has a production rate of 2000 units per day.
a)
b)
c)
d)
Calculate the optimum lot size.
How many lots are produced in a year?
What is the average inventory for Audio Max?
What is the annual cost of preparing the orders and making the setups for Audio Max?
Handout 8: A watch repair shop buys batteries for a variety of products. The most frequent
battery purchase is the K350, with a demand of 65 per week. The order cost is $25 per order,
and the annual carrying cost is $5 per unit. Given the following price schedule, determine the
optimal order quantity and its respective cost. Show all required evidence to support your
decision.
Number of Batteries
Price
1 to 249
250 to 499
500 to 999
1000 or more
$7
$6.50
$6.00
$5.75
Chapter 4: Inventory Management
BUSI2603U
Fall 2015
Handout 9:Office express sells office supplies to businesses on a membership basis i.e. walkin customers without a membership are not allowed. The company delivers supplies to the
purchaser as long as a minimum purchase of $30,000 is made. In order to encourage bulk
orders, Office Express offers the following discount schedule on purchase quantities of boxes
of paper. Larrys Lumber has annual demand of 6,000 boxes of paper, an ordering cost of
$12.50 per order, and carrying costs are $4.55 per unit annually.
Calculate the optimal order quantity, and its associated total cost. Show all required evidence to
support your decision.
Quantity Order
Price
1 to 99 boxes
100 to 249 boxes
250 to 499 boxes
500 to 999 boxes
1000 or more boxes
$6.5 per box
$6.00 per box
$5.60 per box
$5.25 per box
$5.10 per box
You might also like
- practice_problems_1Document5 pagespractice_problems_1Murtaza PoonawalaNo ratings yet
- C10 12ed Quantitative DataDocument9 pagesC10 12ed Quantitative DataAdam LoNo ratings yet
- EOQ Problems: Economic Order Quantity SolutionsDocument4 pagesEOQ Problems: Economic Order Quantity SolutionsGhilman HabibNo ratings yet
- Inventory NumericalDocument2 pagesInventory NumericaljehadNo ratings yet
- 7.0 Inventory ManagementDocument24 pages7.0 Inventory Managementrohanfyaz00No ratings yet
- MT 378 TS3Document2 pagesMT 378 TS3Mike NdalamaNo ratings yet
- InventoryDocument82 pagesInventoryKiran GadmaleNo ratings yet
- Practice of Material ManagementDocument8 pagesPractice of Material ManagementBilal AliNo ratings yet
- Week7 Case StudyDocument3 pagesWeek7 Case StudyAhmed UsaydNo ratings yet
- SCM Numerical 2011Document13 pagesSCM Numerical 2011arvindpmNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1mayen DauNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Homework Template - 13thDocument11 pagesWeek 7 Homework Template - 13thalgadilan0% (2)
- 15 ExercisesDocument3 pages15 ExercisesAravind ShankarNo ratings yet
- Inventory Models: For Independent DemandDocument22 pagesInventory Models: For Independent DemandFranklin MendozaNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management EOQ ProblemsDocument3 pagesInventory Management EOQ ProblemsTushar MehndirattaNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management 2021Document43 pagesInventory Management 2021BABY SUZYNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Basic EoqDocument6 pagesTutorial 1 - Basic EoqdikkanNo ratings yet
- Total Relevant Cost (TRC)Document7 pagesTotal Relevant Cost (TRC)LinhThùyNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Pactice QuestionsDocument8 pagesOperations Management Pactice QuestionsHumphrey OsaigbeNo ratings yet
- Take Home QUIZ and PROBLEM SET in ORDocument1 pageTake Home QUIZ and PROBLEM SET in ORRyan Jeffrey Padua CurbanoNo ratings yet
- Working CapitalDocument5 pagesWorking Capitalchanchal shahiNo ratings yet
- GROUP 4 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON OPM - Volume 2Document11 pagesGROUP 4 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON OPM - Volume 2Humphrey OsaigbeNo ratings yet
- 6310 S2 - 20 Tutorial 9 Questions PDFDocument2 pages6310 S2 - 20 Tutorial 9 Questions PDFThuraga LikhithNo ratings yet
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT Problems Only For Class Nov 2014Document2 pagesINVENTORY MANAGEMENT Problems Only For Class Nov 2014swaroop666No ratings yet
- Unit5 Part I InventoryDocument100 pagesUnit5 Part I InventoryMounisha g bNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 QuestionDocument8 pagesAssignment 2 QuestionJanarthanan Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- ACC315 Cost Accounting Test Chapters 8, 10-12Document4 pagesACC315 Cost Accounting Test Chapters 8, 10-12Jamie N Clint BrendleNo ratings yet
- EOQ Model for Speedy Wheels and Color ViewDocument1 pageEOQ Model for Speedy Wheels and Color ViewThanh Thanhh100% (1)
- Assignment 1 (BBA & BBIS) SUB: OM Inventory Management: EOQ 200 Units & ROL 40 L, L Lead TimeDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 (BBA & BBIS) SUB: OM Inventory Management: EOQ 200 Units & ROL 40 L, L Lead Timesajal koiralaNo ratings yet
- Additional Inventory & Simulation Problems: ABC Analysis, EOQ, Demand ForecastingDocument11 pagesAdditional Inventory & Simulation Problems: ABC Analysis, EOQ, Demand Forecastingproject44No ratings yet
- Inventory NumericalsDocument4 pagesInventory Numericalsalizasajid50No ratings yet
- Homework AssignmentDocument11 pagesHomework AssignmentHenny DeWillisNo ratings yet
- Bai Giang Quan Tri Kho Hang SVDocument40 pagesBai Giang Quan Tri Kho Hang SVKu SjnNo ratings yet
- Briefly Speaking IncDocument21 pagesBriefly Speaking IncdavidNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDocument14 pagesInventory ManagementAmzelle Diego LaspiñasNo ratings yet
- Inventory Decisions and Economic Order Quantity CalculationsDocument5 pagesInventory Decisions and Economic Order Quantity Calculationssbb anbwNo ratings yet
- 2 5370806713307890464 PDFDocument5 pages2 5370806713307890464 PDFMekuriawAbebawNo ratings yet
- Inventory DocumentsDocument82 pagesInventory Documentsdinugypsy123-1No ratings yet
- Nguyễn Đức Anh-chap-12-TOMDocument3 pagesNguyễn Đức Anh-chap-12-TOMĐức Anh LeoNo ratings yet
- IE 323 Study Set 2 Optimal Inventory SolutionsDocument5 pagesIE 323 Study Set 2 Optimal Inventory SolutionsMehmet ŞahinNo ratings yet
- Quiz in Operman and OpmatqmDocument2 pagesQuiz in Operman and OpmatqmzairusbasilidesNo ratings yet
- Chicagoland Sweets (Questions 3 and 4) Chicagoland Sweets, A Commercial Baker, UsesDocument5 pagesChicagoland Sweets (Questions 3 and 4) Chicagoland Sweets, A Commercial Baker, UsesIpsita RathNo ratings yet
- SeDocument2 pagesSeRajeev AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 30784rtpfinalnov2013 5Document0 pages30784rtpfinalnov2013 5kamlesh1714No ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions Operations Management (Iet204)Document3 pagesTutorial Questions Operations Management (Iet204)Jagajith Sathis Chandran NairNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2raqibapp0% (1)
- Quiz 3 QuestionsDocument1 pageQuiz 3 Questionsmahnoor javaidNo ratings yet
- 2) All Questions Carry Equal Marks: Subject: Materials Management Marks: 100Document1 page2) All Questions Carry Equal Marks: Subject: Materials Management Marks: 100Aravind 9901366442 - 9902787224No ratings yet
- EOQ QuestionDocument8 pagesEOQ QuestionSaurav ShawNo ratings yet
- Guide Questions - Inventory & Aggregate PlanningDocument3 pagesGuide Questions - Inventory & Aggregate PlanningErica SalasNo ratings yet
- 12.1 INVENTORY ITEM $ VAlUEICASEDocument5 pages12.1 INVENTORY ITEM $ VAlUEICASERonald Huanca Calle50% (4)
- Ch-05 Material Inventory Controls (Online Class)Document6 pagesCh-05 Material Inventory Controls (Online Class)shayan zamanNo ratings yet
- 01 03 2022Document6 pages01 03 2022Noor HossainNo ratings yet
- Iteb G621 275 C 2007 1Document2 pagesIteb G621 275 C 2007 1saket reddyNo ratings yet
- Managing Economies of Scale Cycle InventoryDocument33 pagesManaging Economies of Scale Cycle InventoryRohit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Inventory ModelsDocument42 pagesInventory ModelsGabby MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Mendenhall Corp Experience Curve Cost CalculationDocument10 pagesMendenhall Corp Experience Curve Cost CalculationEzgi Su KilitNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management FinalDocument32 pagesInventory Management Finaljessa rodene franciscoNo ratings yet
- A to Z Cost Accounting Dictionary: A Practical Approach - Theory to CalculationFrom EverandA to Z Cost Accounting Dictionary: A Practical Approach - Theory to CalculationNo ratings yet
- Cost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsFrom EverandCost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Paosjjd: Apokdka ApokdkaDocument5 pagesPaosjjd: Apokdka ApokdkaJharr699No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Inventory Management BUSI2603U Fall 2015Document5 pagesChapter 4: Inventory Management BUSI2603U Fall 2015Jharr699No ratings yet
- CH11-IOawf Management and Disk SchedulingDocument21 pagesCH11-IOawf Management and Disk SchedulingJharr699No ratings yet
- Constraint MGMT Tutorial MaterialDocument8 pagesConstraint MGMT Tutorial MaterialJharr699No ratings yet
- Calculus For BeginnersDocument21 pagesCalculus For BeginnersJay LawsonNo ratings yet
- A1 - Infr3600 - F15Document1 pageA1 - Infr3600 - F15Jharr699No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Inventory Management BUSI2603U Fall 2015Document5 pagesChapter 4: Inventory Management BUSI2603U Fall 2015Jharr699No ratings yet
- Cryptography: Assignment 3Document4 pagesCryptography: Assignment 3Jharr699No ratings yet
- Outline ThisDocument9 pagesOutline ThisJharr699No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - IntroductionDocument62 pagesLecture 1 - IntroductionJharr699No ratings yet
- Calculus For BeginnersDocument21 pagesCalculus For BeginnersJay LawsonNo ratings yet
- Privacy and Biometrics: Balancing Security and RightsDocument69 pagesPrivacy and Biometrics: Balancing Security and RightsJharr699No ratings yet
- Whatever MangDocument1 pageWhatever MangJharr699No ratings yet
- Whatever MangDocument1 pageWhatever MangJharr699No ratings yet
- CCNP Switch AnsDocument10 pagesCCNP Switch AnsDimitar Georgiev100% (1)
- Brochure SawmillDocument2 pagesBrochure SawmillVishal ShirsatNo ratings yet
- IIW/EWF Diploma in Welding QualificationDocument8 pagesIIW/EWF Diploma in Welding Qualificationreezman100% (1)
- Project Management of Panipat Refinery MS Quality UpgradeDocument5 pagesProject Management of Panipat Refinery MS Quality UpgradeShaunak VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Manual CODELINE PDFDocument48 pagesManual CODELINE PDF4l0h44No ratings yet
- New For Pole Line Hardware Superior Corrosion Resistant OptionsDocument1 pageNew For Pole Line Hardware Superior Corrosion Resistant OptionsWency JavateNo ratings yet
- Hardness TesterDocument16 pagesHardness TesterMohamed SameerNo ratings yet
- Rapid PrototypingDocument42 pagesRapid Prototypingmoxen100% (1)
- Jit and Lean OperationsDocument8 pagesJit and Lean OperationsIvyJoyce100% (1)
- Business-Process Integration: Supply-Chain Management 2.0 (SCM 2.0)Document8 pagesBusiness-Process Integration: Supply-Chain Management 2.0 (SCM 2.0)nidayousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Excavators 17 1Document4 pagesExcavators 17 1eunice199703150% (1)
- Brochure Impact CrusherDocument36 pagesBrochure Impact CrusherMohammad YounesNo ratings yet
- Schmidt Bretten SIGMAWIGDocument6 pagesSchmidt Bretten SIGMAWIGUroš ČampragNo ratings yet
- 25 Pdfsam Pinch Analysis and Process IntegrationDocument1 page25 Pdfsam Pinch Analysis and Process IntegrationLinh GiangNo ratings yet
- Aluminium RollingDocument5 pagesAluminium RollingChetna BarochiyakalolaNo ratings yet
- Welding Defects - Its Causes and Remedial Actions & Safety in Oxyfuel Gas CuttingDocument144 pagesWelding Defects - Its Causes and Remedial Actions & Safety in Oxyfuel Gas CuttingSuraj RawatNo ratings yet
- Welding and Inspection Techniques for MetalsDocument45 pagesWelding and Inspection Techniques for Metalsgaganesan1972100% (1)
- PrivatisationDocument17 pagesPrivatisationSandeep Kumar Yadav50% (2)
- TENGL Corporate Brochure FinalDocument12 pagesTENGL Corporate Brochure FinalRohit KaleNo ratings yet
- Group Technolog1 AssegmentDocument5 pagesGroup Technolog1 AssegmentYAKUBU ISSAHAKU SAIDNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument7 pagesArticleLu CastilloNo ratings yet
- Acronym NsDocument8 pagesAcronym Nsacere18No ratings yet
- TEConomy BIO 2018 ReportDocument68 pagesTEConomy BIO 2018 ReportAngel MendezNo ratings yet
- How To Thread PipeDocument9 pagesHow To Thread Pipenurlisa khaleedaNo ratings yet
- Dell Supply Chain Planning and Design..Document30 pagesDell Supply Chain Planning and Design..Rakshith RajendrappaNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science Pilani: Automobile Sector in IndiaDocument16 pagesBirla Institute of Technology and Science Pilani: Automobile Sector in Indiaਸਚਿਨ ਸੋਨੀNo ratings yet
- A367 Chill Method PDFDocument4 pagesA367 Chill Method PDFOziel RomeroNo ratings yet
- CRM Complex - Tata SteelDocument8 pagesCRM Complex - Tata SteelSourav DasNo ratings yet
- Warehouse Receiving & Putaway OptimizationDocument14 pagesWarehouse Receiving & Putaway OptimizationShamsa Noorallah BudhwaniNo ratings yet
- WPS, PQR 041Document21 pagesWPS, PQR 041swamykommula100% (1)
- NilkamalDocument31 pagesNilkamalAshwin GkNo ratings yet