Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atomic Structure
Uploaded by
api-2645479760 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views5 pagesThe mass of an atom in atomic mass units (amu) is the combined mass of p+ and n0. Many elements have multiple isotopes. To determine the mass seen on the periodic table the weighted average is calculated: Mg-24: (23.985)(0.7870) 18.876 = 2.531 Mg-25: (24.986)(0.1013) = 2.902 Mg-26: (25.983)(0.1117) = weighted average of all
Original Description:
Original Title
atomic structure
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe mass of an atom in atomic mass units (amu) is the combined mass of p+ and n0. Many elements have multiple isotopes. To determine the mass seen on the periodic table the weighted average is calculated: Mg-24: (23.985)(0.7870) 18.876 = 2.531 Mg-25: (24.986)(0.1013) = 2.902 Mg-26: (25.983)(0.1117) = weighted average of all
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views5 pagesAtomic Structure
Uploaded by
api-264547976The mass of an atom in atomic mass units (amu) is the combined mass of p+ and n0. Many elements have multiple isotopes. To determine the mass seen on the periodic table the weighted average is calculated: Mg-24: (23.985)(0.7870) 18.876 = 2.531 Mg-25: (24.986)(0.1013) = 2.902 Mg-26: (25.983)(0.1117) = weighted average of all
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
UNIT 2 ATOMIC STRUCTURE
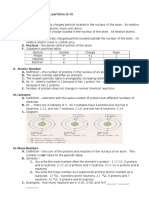
I. Basic Subatomic Particles
A. Reproduce this table in your
notes:Abb. Charge Locatio Mass (g) Mass (amu)
Particle
n
proton
neutron
electron
p+
n0
e-
+1
Neutral
-1
Nucleu
s
1.67 x10-
Nucleu
s
1.67 x10-
ecloud,
orbitals
~1 amu
24
~1 amu
24
9.11 X1028
1/1840th
B. A typical square on the periodic table
Get out your table!
1.The Atomic Number (Z)
*The whole #, the smaller of
the two numbers
*Corresponds to the # of p+
in an atom
*Determines the identity of
the atom
*In an electrically neutral
atom, #p+ = #e-
2. The Atomic Mass (A)
*The larger of the two numbers,
not usually a whole number
*The mass of an atom in atomic
mass units (amu), the combined
mass of p+ and n0.
*What is reported on the periodic
table is the weighted average of
the elements ISOTOPES.
*For an individual isotope of that
element:
#p+ + #of n0 = Atomic mass
C. ISOTOPES Atoms of the same
element (same # of p+, same atomic
number) that have a different
number of n0 and therefore a
different
atomic
mass.
+
0
Notatio Notatio
#p
#e
#n
H-1
H-2
H-3
1
2
3
D. Many elements have multiple isotopes. To
determine the mass seen on the periodic table
the weighted average is calculated:
Magnesium:
Isotope
Mass (amu) % Abundance
Mg-24
23.985
78.70%
Mg-25
24.986
10.13%
Mg-26
25.983
11.17%
Step 1:(Mass of each isotope)(% abundance as a
decimal) =
Step 2: Sum the calculations for all isotopes
Mg-24: (23.985)(0.7870)
18.876
=
2.531
Mg-25 (24.986)(0.1013)
=
2.902
Mg-26 (25.983)(0.1117) =
Weighted average is the total:
24.309 amu
You might also like
- Mse 221 Final ReviewDocument8 pagesMse 221 Final ReviewnmfreedomNo ratings yet
- Structure of An AtomDocument19 pagesStructure of An Atomgenesis_asperaNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument11 pagesAtomsapi-262604908No ratings yet
- Science G9 Q2 W1 ModDocument8 pagesScience G9 Q2 W1 ModRhia Mae AjocNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 13: Nucleus and Binding EnergyDocument39 pagesPhysics Chapter 13: Nucleus and Binding EnergyAwlas Ron HapnautNo ratings yet
- Week 1: in Search of NegativesDocument31 pagesWeek 1: in Search of NegativesMaricarGabitanNo ratings yet
- CE 112 MODULE 5 NUCLEAR CHEM UsedDocument25 pagesCE 112 MODULE 5 NUCLEAR CHEM UsedDana Clarisse M. GalutNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Chap 01 PDFDocument44 pagesChemistry Form 6 Chap 01 PDFryder1man6433No ratings yet
- Grand Canonical EnsembleDocument15 pagesGrand Canonical EnsembleRian AshariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 1 01Document44 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 1 01Stephanie Tan0% (1)
- General Chemistry 5 To 8Document26 pagesGeneral Chemistry 5 To 8AM LocaylocayNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument20 pagesStructure of AtomSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Recitation 03Document1 pageRecitation 03Casey GrenierNo ratings yet
- TD Element Atome Classification-2024-Lsll - WahaDocument2 pagesTD Element Atome Classification-2024-Lsll - WahaMame asta BoussoNo ratings yet
- Chem Form 6 Lessons 1Document3 pagesChem Form 6 Lessons 1mona lisaNo ratings yet
- Review For FinalsDocument54 pagesReview For FinalsChristianAvelinoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atoms and MoleculesDocument54 pages1.1 Atoms and MoleculesAbdullah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chem Part-2Document10 pagesChem Part-2Thun su ThawNo ratings yet
- Resonance Interactions of a Two-State SystemDocument11 pagesResonance Interactions of a Two-State SystemReza MohammadianNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Charges: Structure and CompositionDocument11 pagesAtoms and Charges: Structure and CompositionNicole MediodiaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Structure of The Atom and PTDocument4 pages3.1 Structure of The Atom and PTRoldan Delapa PachecoNo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument167 pagesAtoms and MoleculesPUTRI AMELIANo ratings yet
- Subatomic Particles 2 4 1Document2 pagesSubatomic Particles 2 4 1api-272358521No ratings yet
- AtomDocument28 pagesAtomCynthi Ramírez ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Medical Chemistry IDocument55 pagesMedical Chemistry IViolet StewardNo ratings yet
- Atom and Atomic StructureDocument8 pagesAtom and Atomic StructureAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument13 pagesBiochemLhay de OcampoNo ratings yet
- Basic Nuclear Physics: Milestones and StructureDocument48 pagesBasic Nuclear Physics: Milestones and StructureEciNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 (The Number of Subatomic Particles in Atoms, Ions and IsotopesDocument50 pagesLESSON 3 (The Number of Subatomic Particles in Atoms, Ions and IsotopesCzerina AlemonNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Hydrogen Atom in A Magnetic Field: Non-Relat Ivist Ic TreatmentDocument1 page2.1 Hydrogen Atom in A Magnetic Field: Non-Relat Ivist Ic TreatmentSandipNo ratings yet
- Chem Final ExamDocument42 pagesChem Final ExamWild RiftNo ratings yet
- Notes On Sub Atomic ParticlesDocument10 pagesNotes On Sub Atomic ParticlesBon PatiñoNo ratings yet
- Chapter8 PDFDocument11 pagesChapter8 PDFLogan BleysNo ratings yet
- General Inorganic Chemistry - Lecture NotesDocument24 pagesGeneral Inorganic Chemistry - Lecture NotesLorenz100% (2)
- Nuclear Physics: 1. NucleusDocument13 pagesNuclear Physics: 1. NucleusAditya BansalNo ratings yet
- Subatomic ParticlesDocument14 pagesSubatomic ParticlesLloydNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atoms and MoleculesDocument43 pages1.1 Atoms and MoleculesDinie BidiNo ratings yet
- Intro To Nuclear Chemistry - NewDocument68 pagesIntro To Nuclear Chemistry - NewPink WandererNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atoms and MoleculesDocument60 pages1.1 Atoms and MoleculesMOHAMAD FIRDAUS BIN HARUN KM-PensyarahNo ratings yet
- ES III - Midterm - Module 4/week 4: Objectives: at The End of This Module, You Will Be Able ToDocument3 pagesES III - Midterm - Module 4/week 4: Objectives: at The End of This Module, You Will Be Able ToOct Toberey MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasnDocument37 pagesIdeal GasnabdiiNo ratings yet
- List of Things To Know For Chem RegentsDocument9 pagesList of Things To Know For Chem RegentsRemle CetinNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Lens (10 Points) : TheoryDocument4 pagesElectrostatic Lens (10 Points) : TheoryHemendra PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument39 pagesBasic Conceptsrejie magnayeNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument3 pagesAtomsmaribel bathanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Atoms, Elements, Compounds and IsotopesDocument41 pagesBiochemistry: Atoms, Elements, Compounds and IsotopesKiryuu Shiki KagamineNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Thermochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry Chemistry AP Chapter 23: Nuclear Chemistry 23.1: The Nature of Nuclear ReactionsDocument16 pagesUnit 4: Thermochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry Chemistry AP Chapter 23: Nuclear Chemistry 23.1: The Nature of Nuclear ReactionsPankaj Kumar50% (4)
- Section 2 Atomic Structure - EditedDocument83 pagesSection 2 Atomic Structure - EditedcpliamNo ratings yet
- Wang 2017 Chinese Phys C 41 030003 PDFDocument443 pagesWang 2017 Chinese Phys C 41 030003 PDFAviteshNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics BasicsDocument16 pagesBioenergetics Basicsdwr135No ratings yet
- 1 SSA HW 12 Review For The Quarterly Assessment ANSWER KEYDocument6 pages1 SSA HW 12 Review For The Quarterly Assessment ANSWER KEYkyleighleehaadkins137No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure (Master)Document39 pagesAtomic Structure (Master)yooga palanisamyNo ratings yet
- A Level - Chemistry, George FacerDocument147 pagesA Level - Chemistry, George FacerHeba Ali100% (4)
- Electronic Structure of Molecules: Diatomic Molecules, Small Molecules, Saturated Hydrocarbons, Conjugated Molecules, Molecules of Biochemical InterestFrom EverandElectronic Structure of Molecules: Diatomic Molecules, Small Molecules, Saturated Hydrocarbons, Conjugated Molecules, Molecules of Biochemical InterestNo ratings yet
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsFrom EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckNo ratings yet
- Setting and ContextDocument5 pagesSetting and Contextapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Teacher Work SampleDocument35 pagesTeacher Work Sampleapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Education ResumeDocument3 pagesEducation Resumeapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Instruction and Management PlanDocument4 pagesInstruction and Management Planapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Extra-Curricular Activity Write-UpDocument1 pageExtra-Curricular Activity Write-Upapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Unit Topic and RationaleDocument4 pagesUnit Topic and Rationaleapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Unit Standards Goals and ObjectivesDocument3 pagesUnit Standards Goals and Objectivesapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Assessment ToolsDocument4 pagesAssessment Toolsapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Assessment Data and AnalysisDocument6 pagesAssessment Data and Analysisapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Instructional Strategies AssignmentDocument12 pagesInstructional Strategies Assignmentapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Unit PlanDocument29 pagesUnit Planapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Section 1: Setting and Context: The School Community:: STEPP Lesson Plan FormDocument24 pagesSection 1: Setting and Context: The School Community:: STEPP Lesson Plan Formapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Grand RoundsDocument6 pagesGrand Roundsapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Alternative AssessmentDocument3 pagesAlternative Assessmentapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Traditional AssessmentDocument7 pagesTraditional Assessmentapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Poudre High School MYP Chemistry: Before The Bell RingsDocument5 pagesPoudre High School MYP Chemistry: Before The Bell Ringsapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Educational AutobiographyDocument4 pagesEducational Autobiographyapi-264547976No ratings yet
- Case Study PaperDocument7 pagesCase Study Paperapi-264547976No ratings yet