Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assumed L Computed L Diff Assumed L Computed L Diff Assumed L Computed Ldiff Assumed L Computed Ldiff
Uploaded by
papilolo2008Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assumed L Computed L Diff Assumed L Computed L Diff Assumed L Computed Ldiff Assumed L Computed Ldiff
Uploaded by
papilolo2008Copyright:
Available Formats
Example 7-1: Wave Length for a given Period and Water Depth
Correct wave length is computed iteratively using deep water and shallow water starting values to check what will give correct result with
fewer iterations for a given period
Note that how quickly the convergence is achived depends on starting value
Wave Description
Period
T:
20 sec
Water Depth
50 m
Intrinsic eqn for wave length:
Accurate wave legth using Airy wave theory
2
2
=
tanh
2
Approx. Deep water wave length:
Iteration No
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
2
Initial value based on deep Water wave length =
624.52 m
See Note 1
See Note 2
Assumed L Computed L diff
Assumed L Computed L diff
624.52
290.09
1
624.52
290.09
290.09
496.06
-334
2 457.30863
372.24
-167
496.06
349.94
206
3 414.7733
399.42
-43
349.94
446.66
-146
4 407.09605
404.64
-8
446.66
378.77
97
5 405.86929
405.49
-1
378.77
424.78
-68
6 405.67786
405.62
0
424.78
392.76
46
7 405.64811
405.64
0
392.76
414.67
-32
8 405.64348
405.64
0
414.67
399.49
22
9 405.64277
405.64
0
399.49
409.91
-15
10 405.64265
405.64
0
409.91
402.71
10
11 405.64264
405.64
0
402.71
407.67
-7
12 405.64263
405.64
0
407.67
404.25
5
13 405.64263
405.64
0
404.25
406.60
-3
14 405.64263
405.64
0
406.60
404.98
2
15 405.64263
405.64
0
404.98
406.10
-2
16 405.64263
405.64
0
406.10
405.33
1
17 405.64263
405.64
0
405.33
405.86
-1
18 405.64263
405.64
0
405.86
405.49
1
19 405.64263
405.64
0
405.49
405.75
0
20 405.64263
405.64
0
Approx. Shallow water wave length:
Iteration No
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Initial value based on deep Water wave length =
442.94 m
See Note 1
See Note 2
Assumed L Computed Ldiff
Assumed L Computed Ldiff
442.94
381.09
1
442.94
381.09
381.09
423.08
-62
2
381.09
423.08
423.08
393.88
42
3
423.08
393.88
393.88
413.87
-29
4
393.88
413.87
413.87
400.03
20
5
413.87
400.03
400.03
409.54
-14
6
400.03
409.54
409.54
402.97
10
7
409.54
402.97
402.97
407.49
-7
8
402.97
407.49
407.49
404.37
5
9
407.49
404.37
404.37
406.52
-3
10
404.37
406.52
406.52
405.04
2
11
406.52
405.04
405.04
406.06
-1
12
405.04
406.06
406.06
405.36
1
13
406.06
405.36
405.36
405.84
-1
14
405.36
405.84
405.84
405.51
0
15
405.84
405.51
405.51
405.74
0
16
405.51
405.74
405.74
405.58
0
17
405.74
405.58
405.58
405.69
0
18
405.58
405.69
405.69
405.61
0
19
405.69
405.61
405.61
405.66
0
20
405.61
405.66
-62
42
-29
20
-14
10
-7
5
-3
2
-1
1
-1
0
0
0
0
0
0
Note 1: We start with a value and compute L from the intrinsic equation; the computers value is then used as the next assumed value and so until the difference between the assumed and the computed value is say les than 0.5m
Note 2: To achieve quicker convergence the starting value is the same as earlier but nest asumed value is average of previous assumed and computed values. Thus second assumed value based on deep water approximation is 0.5*(624.52+290.9)=457.31
Note 3: Converged values shown in bold letters. The above examples show that the use of average values lead to fast convergence in both cases; hence it does not matter which starting wave length is used.
You might also like
- Assumed L Computed L Diff Assumed L Computed L Diff Assumed L Computed Ldiff Assumed L Computed LdiffDocument1 pageAssumed L Computed L Diff Assumed L Computed L Diff Assumed L Computed Ldiff Assumed L Computed Ldiffpapilolo2008No ratings yet
- The Critical Depth-Derivation of The Specific Energy EquationDocument21 pagesThe Critical Depth-Derivation of The Specific Energy Equationpotato9233% (3)
- To Develop A Relationship Between Specific Energy 'E' With The Depth of Flow 'Y' in A Computerized Rectangular Flow ChannelDocument3 pagesTo Develop A Relationship Between Specific Energy 'E' With The Depth of Flow 'Y' in A Computerized Rectangular Flow ChannelAamir AwanNo ratings yet
- CD and CM of A Vertical CylinderDocument5 pagesCD and CM of A Vertical Cylinderpraveench1888No ratings yet
- PhysicsipDocument13 pagesPhysicsipRaunak AsnaniNo ratings yet
- Jia-Wei TAO, Jing-Ping WU, Tian-Long MEI, Ling XUDocument6 pagesJia-Wei TAO, Jing-Ping WU, Tian-Long MEI, Ling XUSiddhant AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Response of A U Tube ManometerDocument8 pagesDynamic Response of A U Tube ManometerRitikranjan YadavNo ratings yet
- Fluid Lab Experiment # 2: Open Channel FlowDocument5 pagesFluid Lab Experiment # 2: Open Channel FlowYahyaSheikhNo ratings yet
- FINAL Fluid Friction LabDocument6 pagesFINAL Fluid Friction LabShazeem HoseinNo ratings yet
- Charging and Discharging of CapacitorDocument22 pagesCharging and Discharging of Capacitorpratyushkarn39% (38)
- RL LabDocument4 pagesRL LabJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument7 pagesMechanical Engineering Departmentحسين عمريNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Speed of Light.Document12 pagesDetermination of The Speed of Light.mohammed1998No ratings yet
- Hot Wire Lab ReportDocument19 pagesHot Wire Lab ReportEddie BallNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project: Charging and Discharging of Capacitor in R-C CircuitDocument15 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Charging and Discharging of Capacitor in R-C CircuitSM niranjaneNo ratings yet
- Presentation DielectricDocument25 pagesPresentation Dielectricjose mirandaNo ratings yet
- RC Differentiator and IntegratorDocument5 pagesRC Differentiator and IntegratorMd. AbdullahNo ratings yet
- EdmDocument12 pagesEdmRajuRamRainNo ratings yet
- Reporte 3Document7 pagesReporte 3حسين عمريNo ratings yet
- FLuid FlowDocument13 pagesFLuid FlowDuncoh DunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document8 pagesChapter 7LTE002No ratings yet
- Bhoj Reddy Engineering College For Women: Microwave and Digital Communications Laboratory ManualDocument52 pagesBhoj Reddy Engineering College For Women: Microwave and Digital Communications Laboratory Manuallakshmipriya94No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument18 pagesPhysics ProjectSiddhi MirajkarNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Maximization of Filter LengthDocument6 pagesDynamic Maximization of Filter LengthGica JoeNo ratings yet
- Astroparticle Physics: Detectors For Cosmic Rays: Humberto Salazar and Luis VillaseñorDocument13 pagesAstroparticle Physics: Detectors For Cosmic Rays: Humberto Salazar and Luis Villaseñorh shekarlabNo ratings yet
- Velocity of sound in air determined using resonance columnDocument8 pagesVelocity of sound in air determined using resonance columnKaran TejwaniNo ratings yet
- TDR Paper OnlineDocument8 pagesTDR Paper OnlinegarycatlinNo ratings yet
- Microwave Communication Lab ExperimentDocument5 pagesMicrowave Communication Lab ExperimentSreejit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Frequency Measurement ExperimentDocument4 pagesFrequency Measurement ExperimentKEDARISETTY SAISREENo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Measurement of Frequency and WavelengthDocument3 pagesExperiment 1 Measurement of Frequency and WavelengthengrkskNo ratings yet
- Charing RCDocument6 pagesCharing RCRajdev KapletiaNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project 2017-18Document21 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project 2017-18Ashok Kumar69% (54)
- Practice Midterm 03Document7 pagesPractice Midterm 03Ha ViNo ratings yet
- Charging and Discharging of CapacitorDocument19 pagesCharging and Discharging of CapacitorRitik NandanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics & HydrologyDocument4 pagesHydraulics & Hydrologyamitkap00rNo ratings yet
- Forced Convection Lab Report AnalysisDocument10 pagesForced Convection Lab Report AnalysisEugene100% (1)
- Chapter20pp181 190Document10 pagesChapter20pp181 190InderMaheshNo ratings yet
- Broad Crested WeirDocument7 pagesBroad Crested Weirrancid100% (1)
- Electrical Type Flow MetersDocument22 pagesElectrical Type Flow MetersAnuNarayan R0% (1)
- Phy InvestigatoryDocument20 pagesPhy InvestigatoryAbhipsita SarkarNo ratings yet
- Answer For Question Module No:2 200: Wave Length (CM)Document1 pageAnswer For Question Module No:2 200: Wave Length (CM)Rosaimi Abd WahabNo ratings yet
- Ramalan Paper 3 SPM 2012 EditDocument10 pagesRamalan Paper 3 SPM 2012 EditA. SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis - Federico GaggiottiDocument212 pagesPHD Thesis - Federico GaggiottiadeshinexxNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument22 pagesPhysics Projectmokey420op100% (1)
- Assignment #9 2008Document1 pageAssignment #9 2008Ahmed AmerNo ratings yet
- HVE Lab PDFDocument39 pagesHVE Lab PDFhassanNo ratings yet
- Seakeeping Extract High BoatDocument4 pagesSeakeeping Extract High BoatJesse Garcia OlmosNo ratings yet
- Liquid Diffusion CoefficientDocument7 pagesLiquid Diffusion CoefficientFoo He Xuan67% (3)
- Charging and Discharging of RC CircuitDocument16 pagesCharging and Discharging of RC CircuitSahil GautamNo ratings yet
- Report EDDocument11 pagesReport EDLong NguyenNo ratings yet
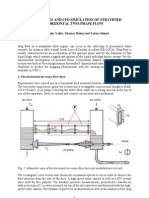
- Experiments and CFD Simulation of Stratified Horizontal Two-Phase FlowDocument7 pagesExperiments and CFD Simulation of Stratified Horizontal Two-Phase Flowsmmousavi1363No ratings yet
- Sin Sin: Btech/5 Year Dual Degree Mtech/RsDocument1 pageSin Sin: Btech/5 Year Dual Degree Mtech/Rsprateek amrawanshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Microwave DevicesDocument18 pagesChapter 10 Microwave DevicesAghna Tiyas MandalNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1.1Document8 pagesProblem Set 1.1meenuraj979100% (3)
- RC Circuit Transients ExperimentDocument12 pagesRC Circuit Transients Experimentaguinaga9No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Jump ExperimentDocument5 pagesHydraulic Jump Experiment1man1book50% (2)
- Hydraulic Jump Experiment Results and AnalysisDocument12 pagesHydraulic Jump Experiment Results and AnalysisWho_cares2No ratings yet
- USP Lab 4 SFEE Blower DuctDocument4 pagesUSP Lab 4 SFEE Blower DuctRoshiv Sharma0% (1)
- Enhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsFrom EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pipeline Tow Cuts Installation Costs Offshore TunisiaDocument9 pagesPipeline Tow Cuts Installation Costs Offshore Tunisiapapilolo2008100% (1)
- Typical Pipeline Installation Engineering DeliverablesDocument1 pageTypical Pipeline Installation Engineering Deliverablespapilolo2008No ratings yet
- CALCULATE WIND LOAD PER BS 6399-2Document1 pageCALCULATE WIND LOAD PER BS 6399-2papilolo2008No ratings yet
- Plate Bending Machine Installation View2Document1 pagePlate Bending Machine Installation View2papilolo2008No ratings yet
- TouchdownDocument1 pageTouchdownpapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Wind CalcDocument1 pageWind Calcpapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Seting Up Grid Data in SAP 2000Document7 pagesSeting Up Grid Data in SAP 2000papilolo2008No ratings yet
- FootingDocument22 pagesFootingpapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Implementation Report CobieDocument106 pagesImplementation Report Cobiepapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Touchdown PDFDocument1 pageTouchdown PDFpapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Autocad To Staad DXF ImportDocument6 pagesAutocad To Staad DXF ImportAlok DixitNo ratings yet
- Plate Bending Machine Installation-ViewDocument1 pagePlate Bending Machine Installation-Viewpapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Bend RadiusDocument1 pageBend Radiuspapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Environmental ForcesDocument1 pageEnvironmental Forcespapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Insert Draft Watermark MS WordDocument4 pagesInsert Draft Watermark MS Wordpapilolo2008No ratings yet
- EC8 Seismic Design of Buildings-Worked ExamplesDocument522 pagesEC8 Seismic Design of Buildings-Worked Examples0BALSENo ratings yet
- Offshore CP Design CalculationDocument1 pageOffshore CP Design Calculationpapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Wave ValidityDocument1 pageWave Validitypapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Offshore Pipeline Systems OverviewDocument71 pagesOffshore Pipeline Systems Overviewpapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Environmental ForcesDocument1 pageEnvironmental Forcespapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Stress Analysis BucklingDocument1 pageStress Analysis Bucklingpapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Wall Thickness CalculationDocument1 pageWall Thickness Calculationpapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Offshore Pipeline Systems OverviewDocument71 pagesOffshore Pipeline Systems Overviewpapilolo2008No ratings yet
- Behavior of A Reinforced Concrete BeamDocument13 pagesBehavior of A Reinforced Concrete BeamRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Paper09 Zamriahmad Petronas PmuDocument28 pagesPaper09 Zamriahmad Petronas PmugengiskahnNo ratings yet
- The Numerical Simulation of Pipe/Soil Interaction Under Wave LoadingsDocument6 pagesThe Numerical Simulation of Pipe/Soil Interaction Under Wave LoadingszenislerNo ratings yet
- Paper09 Zamriahmad Petronas PmuDocument28 pagesPaper09 Zamriahmad Petronas PmugengiskahnNo ratings yet
- Cpm322e Ch5 Time-CostDocument18 pagesCpm322e Ch5 Time-Costpapilolo2008No ratings yet