Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 12 Presentations Answer Key
Uploaded by
api-253009691Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 12 Presentations Answer Key
Uploaded by
api-253009691Copyright:
Available Formats
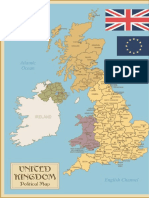
United Kingdom
Official name: United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
Often called Great Britain
Four regions: England, Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland
English Channel separates Great Britain from Europe
England:
o Fertile plains
o Thames River helps with trade in London
Scotland, Wales: rough highlands and mountains
o Poor soil and cold climate=difficulties in farming
o Herd sheep
Economy:
o industrial and trading center
o Manufactured goods and machinery
o Service industries: banking, healthcare
o Energy sources: coal, oil, and natural gas
Government: constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy
Culture:
o 60 million people
o live in cities
o Speak English, Welsh, and Scottish Gaelic
o Protestant Christians along with Islam, Sikhism, and Hinduism
o Culture spread through the British Empire into Australia, Caribbean, and South Asia
Republic of Ireland:
Island of Ireland: British control Northern Ireland (Protestants) and Republic of Ireland rules
itself after winning independence in 1922
Lowland plain with rolling hills
Coastal areas: rocky highlands, cliffs
Regular rainfall: green fields
o Called Emerald Isle
Lots of peat; dug from bogs
Raise sheep and cattle
Grow vegetables, such as potatoes and sugar beets
Manufacturing: clothing, pharmaceuticals, computer equipment
Ancestry: Celts
Languages: Irish Gaelic and English
60% live in cities with 1/3 in Dublin
Culture: music, folk dancing
Strong Catholics want to unit with Protestant neighbors in Northern Ireland
Scandinavia
Five nations: Sweden, Finland, Denmark, Iceland
High standard of living
o Agriculture, manufacturing, and service industries
o Produce food the countries need
o Fishing (especially Iceland and Norway)
Mild climate as whole
o Northern Scandinavia is cold
Plains, mountains, forests, lakes
Less densely populated
o Some parts are too cold or mountainous
Norway, Sweden, Denmark, and Iceland share many customs
Mainly Protestant Lutheran
Denmark, Norway, and Sweden are constitutional monarchies
Finland and Iceland are republics
Welfare states
Iceland:
o sits on two tectonic plates, creating hot springs and geysers
o About 200 volcanoes
o Geothermal energy
o Hydroelectric power
Norway:
o has many fjords, which provide fish
o oil, natural gas
Finland:
o Hydroelectric power
o Shipbuilding
o Wood
Sweden
o Nuclear energy, oil
o Iron ore
o Wood
Denmark
o Shipbuilding
o Center of trade
o High population density
France
Has the Northern European Plain, high mountain ranges, and the Loire and Seine Rivers
Mild climate and rich soil=good farming
o Grow grapes
o Use milk to make cheese (famous)
Industry: cars, chemicals, textiles, processed foods, computers
Tourism: Alps, castles, beaches
Ancestors: Celts, Romans, and Germanic peoples
Religions: Roman Catholic, Islam
60.7 million people
Live in urban areas, with 1o million in Paris
Culture: cooking, fashion, film, art, museums, and more
Democratic republic: president (elected by people) appoints the prime minister
Benelux Countries: Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg
Flat, low land
Densely populated
Live in cities, work in factories or businesses
High standard of living
Parliamentary democracies; monarchs are heads of state
Belgium: little resources, trade, manufacturing
o Three regions: Flanders, Wallonia, Brussels (bilingual)
o Brussels: capital of European Union
Netherlands: people are called Dutch
o 25% of country is below sea level so build banks of soil to control it
o Have rich farming soil in polders
o Amsterdam is capital
o Service industries, trade, manufacturing
Export cheese, vegetables, and flowers
Luxemburg: small
o Center of finance and trade
o Home to multinational companies
o Mixed French and German background
Germany
Flat Northern European Plain
Rocky highlands: rich coal deposits
Majestic Alps: forests threatened by acid rain
Rivers transport raw materials and manufactured goods
Danube River and Elbe River and Rhine River*
Deeply involved in Europes wars
Sparked twp. world wars in effort to dominate Europe
Federal republic
Elected president is head of state, but chancellor (chosen by parliament) is real head of
government
82.5 million people
90% live in urban areas
Berlin: largest and capital with museums ,concerts, and theaters
Bach and Beethoven are from here
Mostly native Germans
Global economic power in EU
Highly productive agriculture: fertile land, mile climate
Industry: leading producer of steel, chemicals, cars, and electrical equipment
Challenge: reunification of East and West Germany in 1990:East had less experience with
modern technology so many businesses closed
Alpine Countries: Switzerland, Austria, Liechtenstein, and more
Liechtenstein: only 62 square miles; 40,000 people
Switzerland:
o stable democratic government
o rugged mountains isolates people
Each town has unique traditions
o German, French, Italian, and Romansch are four national languages
o Few natural resources
o Lots of industry: hydroelectric power, electronics, chemicals, fine clocks and watches;
excellent chocolate and cheese
o banking
o Neutrality during wars
Austria:
o Alps cover most of it; little farmland
o Attracts skiers
o Valuable timber and iron ore
o Hydroelectric power
o Produce machinery, chemicals, metals, vehicles
o Strong banking and insurance companies
o Speak German and are mainly Catholic
o Vienna: 1/5 live there ; center of culture and learning
o Concerts, historic palaces, churches
Spain
The Meseta (dry plateau surrounded by mountain ranges) covers most of Spain
o Poor soil and scarce rain
o Use dry farming to grow wheat and vegetables
Use irrigation to grow citrus fruits, olives, and grapes
Manufacturing and service industries are important
o Foods, clothing, steel, cars, and footwear
Tourism: castles, cathedrals, beaches on the Mediterranean
Cultural traditions: bullfighting, flamenco dancing
Speak Spanish
Some distinct groups
Ruled by dictator; became democracy in late 1970s
43.5 million people
Madrid, Barcelona (seaport, industrial center)
Mainly Roman Catholic and growing number of Muslims
Portugal
Low coastal plain
Grow crops: grapes, oak trees
Live in small villages on coast near Lisbon and Porto
Fishing
Sea power
Democratic government
Economy is growing stronger with subsidies
Manufacturing and service industries are more important
Italy
The Alps, Apennine Mountains, and volcanoes are found throughout Italy
Po River valley in northern Italy: good farming
o Grow grapes and olives; raise livestock
Industrial economy: cars, clothing, appliances, and more
Southern Italy: less industrialized; mountainous; few minerals
58.7 million people
Live in urban areas
Democratic republic
Speak Italian
Mainly Roman Catholic
o Vatican City is within Romes boundaries, but is a separate country
Greece
Mainland with 2,000 islands
Has earthquakes
Mountains and poor soil=little farming
Raise sheep and goats in highlands
Grow some wheat and olives in plains and valleys
Industries: footwear, chemicals, textiles, shipping
Tourism: Parthenon and other historic sites
60% live in urban areas; 1/3 in Athens (capital)
Greek Orthodox
Democratic republic
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Written Analysis of The Film "Angela'S Ashes": TH STDocument2 pagesWritten Analysis of The Film "Angela'S Ashes": TH STMauricio Herrera CamachoNo ratings yet
- UK profile: islands, capitals, flagsDocument47 pagesUK profile: islands, capitals, flagsАнастасия ЯловаяNo ratings yet
- Gerry AdamsDocument19 pagesGerry AdamsMihai Iulian Păunescu0% (1)
- Transcript For Test 5Document8 pagesTranscript For Test 5Tố UyênNo ratings yet
- Michael Collins History 4U Major Research Essay: Jordan Khan Tuesday, June 12, 2018 Loyola S.S. Mr. SmolDocument7 pagesMichael Collins History 4U Major Research Essay: Jordan Khan Tuesday, June 12, 2018 Loyola S.S. Mr. SmolJoNo ratings yet
- Publications 15342Document16 pagesPublications 15342007003sNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris - Modul 3Document110 pagesBahasa Inggris - Modul 3atikahNo ratings yet
- (Critical Lives) Andrew Gibson-Samuel Beckett-Reaktion Books (2009)Document207 pages(Critical Lives) Andrew Gibson-Samuel Beckett-Reaktion Books (2009)JonatanMirkovic100% (2)
- Ireland Tim VicaryDocument35 pagesIreland Tim VicaryantonioNo ratings yet
- Country and PeopleDocument3 pagesCountry and PeopleTadas Varvarinas100% (1)
- Patron Saints of Great Britain and Other FactsDocument18 pagesPatron Saints of Great Britain and Other FactsPaola ArosNo ratings yet
- The UK. From Past To PresentDocument184 pagesThe UK. From Past To PresentRamin Dadasov0% (1)
- Ireland, English Colonization: British IslesDocument44 pagesIreland, English Colonization: British IslesRocio BarrioNo ratings yet
- Erekle Gozalishvili - Review - Opinion - Brexit and The Continued Troubles in Northern IrelandDocument1 pageErekle Gozalishvili - Review - Opinion - Brexit and The Continued Troubles in Northern IrelandErekle GozalishviliNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Revision Ireland Timeline 1867-1922Document7 pagesEdexcel Revision Ireland Timeline 1867-1922TommyParkerNo ratings yet
- Business Etiquette in The UKDocument15 pagesBusiness Etiquette in The UKBogdan Dendrino100% (1)
- British Early Armoured Cars from WW1-1930sDocument10 pagesBritish Early Armoured Cars from WW1-1930sJose Luis CastilloNo ratings yet
- The Good Friday AgreementDocument2 pagesThe Good Friday AgreementDeniseFrăţilăNo ratings yet
- Uk AssignmentDocument2 pagesUk Assignmentsuman parajuliNo ratings yet
- Tema 69Document44 pagesTema 69gomezin88No ratings yet
- Quizzes EL VHXHDocument15 pagesQuizzes EL VHXHRachel PhanNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ THI MÔN VĂN MINH ANH - 15g00 NGÀY 19 - 1 - 2022 - CA 2Document29 pagesĐỀ THI MÔN VĂN MINH ANH - 15g00 NGÀY 19 - 1 - 2022 - CA 2tuệ gia0% (1)
- Orange ParadesDocument27 pagesOrange Paradesapi-3709748No ratings yet
- 118549669-V Black OperationsDocument174 pages118549669-V Black Operationsandrew100% (4)
- Understanding Northern IrelandDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Northern Irelandapi-427106949No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Great Britain and The UKDocument143 pagesLecture 1 Great Britain and The UKქეთი ნოზაძეNo ratings yet
- Britain - Country and People Key FactsDocument3 pagesBritain - Country and People Key Factsalexandru_cimpean88No ratings yet
- T56C Historical Relations Between Ireland and Great BritainDocument27 pagesT56C Historical Relations Between Ireland and Great BritainknesuxNo ratings yet
- Education in Northern Ireland Since The Good Friday Agreement Kabuki Theatre Meets Danse MacabreDocument17 pagesEducation in Northern Ireland Since The Good Friday Agreement Kabuki Theatre Meets Danse Macabremrgallagher.deanNo ratings yet