Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ASME B46.1 2009 Standard: Introduction To ASME B46.1-2009 Donald K. Cohen, Ph.D. 3/17/2011
Uploaded by
Sowmen ChakrobortyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ASME B46.1 2009 Standard: Introduction To ASME B46.1-2009 Donald K. Cohen, Ph.D. 3/17/2011
Uploaded by
Sowmen ChakrobortyCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To ASME B46.
1-2009
Donald K. Cohen, Ph.D.
3/17/2011
ASME B46.1 2009 Standard
The first B46.1 Standard was issued March 1940..
since 1940 --- 9 revisions
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Introduction To ASME B46.1-2009
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Introduction to ASME B46.1-2009
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Surface Texture..Why Is It Important?
Surface: The boundary that separates an object from another object,
substance, or space
Texture: The composite of certain deviations that are typical
of the real surface. It includes roughness and waviness
Surface Roughness, Ra is the average of the absolute
value of profile heights over a given length (area).
2D
1
Ra
L
Z ( x ) dx
Z
X
3D
Ly Lx
1
Sa
A0
Z(x, y)dxdy
0
ASME B46.1 2009
Z
X
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Surface Texture..Why Is It Important?
Functional / Performance Point of View........
Rolling... Sliding....Sealing....Load Bearing....Cosmetic
Electrical Contact..Metal Forming...Lubricant Retention
Friction .... Wear .... Adhesion
Typical Applications
Mechanical:
Engine cylinder bore, rings, pistons, seals, shafts, gear,
clutches, brakes, fuel delivery components, sensors
ABS components, cutting tools, coatings, bearings......
Electronics:
Disk drive components, tape drive components,
MEMS, solder bumps,.......
Misc:
Materials (Polymer..),Printing (rolls/lithoplates/paper), Medical(Implants),
Optical (contact lens)....
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Surface Texture..Why Is It Important?
Key Discrete Parts -Value of U.S. Shipments
52% of all U.S. Manufacturing 10% of GDP
2009/$15,000,000,000,000 (GDP)
Relative Time
Typical Relationship of Ra to Production Time($)
What Texture do you need?
How much does it cost?
NIST 1992
Ra m /
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Classification of Instruments for Surface Metrology
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Instruments for Texture Measurement
Range and Resolution of Major Techniques
Surface
Amplitude
Surface Wavelength
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Filtering --- Form, Waviness and ROUGHNESS
Form
Waviness
Roughness
Remove Form
Remove Form & Waviness
Roughness Profile
Remove Form & Waviness
Traversing Length
Evaluation Length
Sampling Length
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Filtering of Surface Texture Measurements - Gaussian
s = Short Wave Cutoff..... 50% Transmission....Ao/Ai = 0.50
c =Long Wave Cutoff...... 50% Transmission....Ao/Ai = 0.50
s = 2.5 m , 8 m, 25 m
c = 0.08mm, 0.25mm, 0.8mm, 2.5mm, 8mm
c/ s = 30, 100, 300
...... Gaussian filters have minimal phase distortion ......
1 um
0.50 um
0.8 mm
Gaussian Filter
c = 0.8mm
0.8 mm
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Filtering of Surface Texture Measurements
c = 2.5 mm, s =0 mm, 2 cutoffs
Ra = 11.8um
c = 0.8 mm, s =0 mm, 6 cutoffs
Ra = 8.0 um
c = 0.25 mm, s =0 mm, 20 cutoffs
Ra = 4.3um
40um
c = 0.08 mm, s =0 mm, 60 cutoffs
Ra = 1.4um
-40um
6 mm
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Filtering of Surface Texture Measurements
ASME B46.1 2009 Key Concepts
The cutoffs, c and s should be chosen by the designer in light of the intended
function of the surface. When choosing c and s, one must be cognizant that the surface
features not measured within the roughness cutoff bandwidth may be quite large and
may affect the intended function of the surface. Thus in some cases it may be necessary
to specify both surface roughness and waviness.
On all surface texture specifications as of January 1997, c and s must be stated .
When c and s are not specified, guidelines are given in section 3.3.20.1 and 3.3.20.2 of
ASME B46.1 2009 for the metrologist to establish c and s.
These guidelines are intended to include the dominant features of the
surface in the measurement whether these surface features are relevant to the
function of the surface or not.
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Surface Texture Parameters
ASME B46.1 2009 Standard
PDF/Hardcopy
Michigan Metrology, LLC
2D Surface Texture Parameters
Once the surface is measured, need to develop parameters for control etc.
Probably >100, 2D parameters introduced in the literature / standards over the years
Beginning ~1993, 3D work (Stout etal.), Identify 14+ key 3D parameters
Standard ISO/DIS 25178-2 (3D Areal parameters) out for review/2010
The parameters quantify information
Height ----- Amplitude parameters (e.g. Ra)
Spatial ----- Spacing parameters (e.g. Sm)
Height & Spatial ----- Hybrid parameters (e.g. q)
Function Bearing Area (e.g. Rpk..)
Traversing Length
Evaluation Length
Sampling Length
Michigan Metrology, LLC
2D Surface Texture Parameters
Ra ...Average Roughness..(e.g. WYKO Stylus X Ra)
Why Ra?...Standard ......Limits of technology..circa 1930...
Ra
www.ptb.de
Z
X
Ra
1
L
Z ( x ) dx
Why Not Ra?.....
No spatial structure information
No difference between peaks/valleys
L
Same
Ra!!
Z
X
Same
Ra!!
Michigan Metrology, LLC
2D Surface Texture Parameters
Amplitude Parameters .. Rq, Rsk, Rku
Rq=3, Rsk = 0, Rku=3, Gaussian Surface
Rq=12, Rsk = -1, Rku=8, Negatively Skewed
Rq=12, Rsk = 1, Rku=8, Positively Skewed
Rq=4, Rsk = 0, Rku=1.5, Slowly Varying
Rq=4, Rsk = 0, Rku=10, Extreme Peak/Valley
Michigan Metrology, LLC
2D Surface Texture Parameters
Peaks/Valleys .. Rp,Rv, Rt, Rz, Pc.... (e.g. WYKO Stylus X Rp)
Rp
Rp = Highest Point From Mean Line
Rv=Lowest Point from Mean Line
Rt = Rp - Rv = Peak to Valley
Rv
Rpi = Highest Peak from mean line in ith sampling length
Rpm= Average of all Rpi
Rti = Highest - Lowest points from mean line in ith Sampling length Peak to Valley
Rmax = Maximum Rti over evaluation length
Rz (ASME B46.1) = Average of all Rti (i.e. over all sample lengths)
Rp
1
Rp
3
Rz (DIN) =Average Rti over 5 sample lengths
Rz (ISO) = Rti (Thats right - peak to valley in one cutoff!)
For ISO must specify number of sample lengths
ISO Default 5 cutoffs for Rz Rz5
Rt1
Rt2
Rt3
Evaluation Length
Sample Length
Michigan Metrology, LLC
2D Surface Texture Parameters
Spacing Parameters Rsm, PCL (e.g. WYKO Stylus Rsm)
Sm1
Sm2
Sm3
Sm4
Rsm = The Average of all Smi
Height Threshold -10% of Rz
Spacing > 1% of sampling length
Peak 1
Peak 2
Peak 3
PCL
PCL= Peak Count Level...Threshold
Peak = When profile intersects lower and upper PCL
Rpc = Peak Density....peaks/unit length
Why Sm, Pc...?
Sealing, Appearance, Adhesion
Sheet Steel...Forming release v.s. appearance
Why Not Sm, Pc...?.
No height information
PCL-via B46
Check your software...
factors of 2 exist!
Michigan Metrology, LLC
2D Surface Texture Parameters
Hybrid Parameters...Slope, q, q (e.g. WYKO Stylus X q)
Slope 2D Profile
1
L
Low q
dZ ( x ) / dx dx
2
High q
Average Wavelength Weighted By Amplitude
q = 2Rq/q
q=2
q=4
Michigan Metrology, LLC
2D Surface Texture Parameters
Functional Parameters ..
Bearing Area Rpk, Rk Rvk....
DIN 4776 ISO 13565-2
Max Ht
Rpk
40%
Rk
Rvk
Min Ht
0%
Mr1
50%
Mr2
100%
Rpk = Peak Height .. First Region of contact
Rk = Core Height... working Region ..Base
Rvk = Valley Depth ... Lubricant Retention Region
Rpk/Rk, Rvk/Rk and Rpk/Rvk Normalized parameters
Mr1 = 1st Material Ratio... Peak Material
Mr2 = 2nd Material Ratio ... Valley Material
V0 = Rvk(100-Mr2)/200......Retention Volume
Michigan Metrology, LLC
10
2D Surface Texture Parameters
Functional Parameters ..
Bearing Area Rpk, Rk Rvk....
Rpk
Talk about Bearing area Offsets
Bearing Ratio Curve
Rk
Rvk
Mr1
Mr2
Michigan Metrology, LLC
3D Surface Texture Metrology
History.
1930s
1960s
1968
1979
1990s
2000s
First 2D instruments for texture analogue, charts etc.
Digital Computers parameter development 3D machines
The Properties and Metrology of Engineering Surfaces U. of Oxford.
1st of Triennial International Conferences
Workshops indicating a need to standardize 3D parameters
SurfStand, AutoSurf, CalStandNew ISO standard WG16ISO/DIS 25178-2
Michigan Metrology, LLC
11
Dr. David Whitehouse
Dr. Tom Thomas
Dr. Ken Stout
Dr. Liam Blunt
Dr. Thomas Mathia
Dr. Paul Scott
Dr. Xianqqian Jiang
Dr. Chris Brown
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Sa: Roughness average
Sq: Root-mean-square deviation of the surface
Sp: Maximum peak height
Sv: Maximum valley depth
Sz: Maximum height of the surface
Ssk: Skewness of surface height distribution
Sku: Kurtosis of surface height distribution
Sal: Fastest Decay Autocorrelation Length
Str: Texture Aspect Ratio
Std: Texture Direction of Surface
Sdq: Root-Mean_Square Surface Slope
Sdr: Developed Surface Area Ratio
Sds: Density of Summits*
Ssc: Mean Summit Curvature*
Smr(c): Areal Material Ratio
Sdc(mr): Inverse Areal Material Ratio
Sxp(p.q),Spk,Sk, Svk, SMr1,SMr2, Spk/Sk, Svk/Sk,Spk/Svk Bearing Area Related Parameters
Vv(mr),Vvv(p),Vvc(p,q): Areal Material Ratio Void Volume Parameters
Vm(mr), Vmp(p), Vmc(p,q): Areal Material Ration Material Volume Parameters
Sbi, Sci, Svi: Functional Index Parameters*
*not in ISO 25178-2
Michigan Metrology, LLC
12
Future Texture Analysis
Y
Future Direction
Features .. Wolf Pruning, Fractals
New Tribology parameters reservoirs- flow connectibility
Contact Mechanics asperity shape unloaded/loaded
saddle points, ridges, valleys, peaks etc.
If you flatten Vermont
will it be larger than Texas?
Chris Brown
http://www.me.wpi.edu/research/SurfMet/
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Surface Texture Parameters
From Ra....
to amplitude parameters (Rq, Rsk.....)
to bearing area (Rpk, Rvk....)
spacing (Sm....)
Hybrid.... (q.....)
S parameters........
Which one(s) do I use?
Guided by physics (e.g. bearing? Sealing? Appearance?)....choose a set of parameters..
Functional Correlation?
Is measurement Gage Capable?
Michigan Metrology, LLC
13
Specifying Surface Finish
ASME -Y14.36 - 1996
ISO 1302 - 2002
http://catalog.asme.org/Codes/PrintBook/Y1436M_1996_Surface_Texture.cfm
http://webstore.ansi.org/ansidocstore/product.asp?sku=ISO+1302%3A2002
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Specifying Surface Finish
Y14.36 1996 / ISO 3102-2002
Basic Symbology
Material Removal Constraints
Michigan Metrology, LLC
14
Specifying Surface Finish
Y14.36 - 1996
Key Measurement Concepts
Texture parameter specified is max value along the direction that gives the max value
(i.e. across the lay) .. must locate at region of expected max roughness. Can also indicate
bilateral spec.
Cutoff Length MUST be specified after 1995
Unless specified, parameters are averaged over 5 cutoff lengths
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Specifying Surface Finish
Y14.36 - 1996
Surface Finish Orientation
Michigan Metrology, LLC
15
Specifying Surface Finish
ISO 1302-2002
a Single parameter spec and bandwidth (e.g. 0.008mm 0.8mm / Ra 3.2)
b Second parameter spec and bandwidth (e.g. 0.025mm-0.2.5mm / Rz 5.0)
c Manufacturing Method (e.g. turned)
d Lay orientation (e.g. )
e Machining allowance (e.g. 2 mm)
Key Measurement Concepts
Texture parameter may be unilateral max, min, 16% or bilateral (see next slides)
Cutoff Length/ bandwidth MUST BE SPECIFIED
Unless specified, parameter are averaged over 5 cutoff lengths.
Michigan Metrology, LLC
Future Webinar Topics:
ASME B46.1-2009
Instrumentation?
Filtering?
Parameters 2D/3D?
Functional Correlation?
Advanced Analysis Fractals, Pruning, etc.
Gage Calibration/Capability?
ISO Harmonization?
Surface Metrology Friction?
Surface Metrology Wear?
Surface Metrology Application Case Studies
..
..
Michigan Metrology, LLC
16
You might also like
- Surface RoughnessDocument35 pagesSurface Roughnessds_srinivasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Surface Roughness I IDocument23 pagesLecture 6 Surface Roughness I IilincastNo ratings yet
- Presented For CMA Analytical Workshop 2012 Neal LeddyDocument55 pagesPresented For CMA Analytical Workshop 2012 Neal LeddygprjesNo ratings yet
- Surface Roughness TestDocument12 pagesSurface Roughness TestSusheel PetleNo ratings yet
- Surfaceb Finish Meterology TutorialDocument162 pagesSurfaceb Finish Meterology TutorialChristian Barnard100% (1)
- Surface RoughnessDocument9 pagesSurface RoughnessKarthick DuraiNo ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument10 pagesSurface RoughnessBa TollohNo ratings yet
- Measuring and Characterizing Surface TopographyDocument58 pagesMeasuring and Characterizing Surface TopographyPradeepa KNo ratings yet
- Surface Roughness ParametersDocument2 pagesSurface Roughness Parametersamit02mech100% (1)
- SRT NotesDocument34 pagesSRT NotesBhoopathy JNo ratings yet
- Nature and Properties of Materials: Lab Report ME-222 Experiment No.: 6 Studies On Surface RoughnessDocument13 pagesNature and Properties of Materials: Lab Report ME-222 Experiment No.: 6 Studies On Surface Roughnessrahul kumarrNo ratings yet
- Surface Roughness Parameters - ENDocument14 pagesSurface Roughness Parameters - ENNarcisDanielPetreaNo ratings yet
- 4-Surface Metrology-14-11-2022Document58 pages4-Surface Metrology-14-11-2022Prathamesh Balsingrao Adhav 4-Year B.Tech. Mechanical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Exp 5 Surface RoughnessDocument14 pagesExp 5 Surface RoughnessAshrafNamamuTeratasNo ratings yet
- ME6623D Industrial Tribology: Course Faculty: Dr. P.K. Rajendrakumar Professor Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument26 pagesME6623D Industrial Tribology: Course Faculty: Dr. P.K. Rajendrakumar Professor Department of Mechanical EngineeringAbenesh KumaresanNo ratings yet
- QuickGuide SurftestDocument2 pagesQuickGuide SurftestHeineken Ya PraneetpongrungNo ratings yet
- Katarina MONKOVA, Peter MONKA and Dusan MANDULAKDocument5 pagesKatarina MONKOVA, Peter MONKA and Dusan MANDULAKZvonimir OpicNo ratings yet
- Surface Finish NotesDocument8 pagesSurface Finish NotesSuhailshah1234No ratings yet
- Statistical Assessment of Surface Quality Using 3DDocument11 pagesStatistical Assessment of Surface Quality Using 3Dstranger3333No ratings yet
- Surface Roughness: Surface Roughness Often Shortened To Roughness, Is A Component ofDocument7 pagesSurface Roughness: Surface Roughness Often Shortened To Roughness, Is A Component ofcal2_uniNo ratings yet
- Surtronic 25 User Guide EngDocument60 pagesSurtronic 25 User Guide EngŞafak DoğruNo ratings yet
- AASHTO Design Examples NewDocument26 pagesAASHTO Design Examples NewAbhishek Banerjee100% (1)
- Explanation of Surface RoughnessDocument8 pagesExplanation of Surface RoughnessN.Palaniappan100% (6)
- Tutorial - Choosing Cut-offs and Filters for Surface Roughness MeasurementDocument2 pagesTutorial - Choosing Cut-offs and Filters for Surface Roughness MeasurementAnichitoaei Ionel0% (1)
- An experimental investigation on surface quality and dimensional accuracy of FDM componentsDocument7 pagesAn experimental investigation on surface quality and dimensional accuracy of FDM componentsnewkid2202No ratings yet
- Predictive Modeling of Tool Wear in Hard TurningDocument20 pagesPredictive Modeling of Tool Wear in Hard Turningirinuca12No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S221201731630041X MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S221201731630041X MainTrupti bagalNo ratings yet
- Metrology of Surface FinishDocument38 pagesMetrology of Surface FinishEmmanuel Thomas100% (1)
- Complete Guide To Surface Finish Symbols, Charts, RA, RZ, Measurements, and Callouts Definition of Surface FinishDocument15 pagesComplete Guide To Surface Finish Symbols, Charts, RA, RZ, Measurements, and Callouts Definition of Surface Finishbhavin178No ratings yet
- LAB. No. 3 Metal Cutting Theory Surface FinishDocument8 pagesLAB. No. 3 Metal Cutting Theory Surface FinishAbdelhay Mohamed HassanNo ratings yet
- SurfaceFinish ReportDocument8 pagesSurfaceFinish ReportsourabhdhimanNo ratings yet
- Deep Drawing Analysis by Using Explicit Dynamics in Ansys WorkbenchDocument8 pagesDeep Drawing Analysis by Using Explicit Dynamics in Ansys Workbenchsunhell1611No ratings yet
- The Use of Response Surface Methodology For Prediction and Analysis of Surface Roughness of Aisi 4140 SteelDocument4 pagesThe Use of Response Surface Methodology For Prediction and Analysis of Surface Roughness of Aisi 4140 SteelShahnewaz BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- Reliability Analysis and Design of The RCC Beam by FOSM MethodDocument5 pagesReliability Analysis and Design of The RCC Beam by FOSM MethodtruenotesrakeshNo ratings yet
- 74948-Article Text-169595-1-10-20120319Document10 pages74948-Article Text-169595-1-10-20120319Santosh PatelNo ratings yet
- Multi-Parameter IdentiicationDocument11 pagesMulti-Parameter IdentiicationmunirajNo ratings yet
- Influence of HSM Cutting Parameters On The Surface Integrity Characteristics of Hardened Aisi H13 Steel - Artigo 2013Document18 pagesInfluence of HSM Cutting Parameters On The Surface Integrity Characteristics of Hardened Aisi H13 Steel - Artigo 2013binhocleuberrezinNo ratings yet
- Dimensional and Surface Texture Characterization in Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) With ABS PlusDocument8 pagesDimensional and Surface Texture Characterization in Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) With ABS PlusChris BurgerNo ratings yet
- 2 67 1588140711 16ijmperdjun202016Document10 pages2 67 1588140711 16ijmperdjun202016TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument10 pagesSurface RoughnessMarco AsensioNo ratings yet
- Parameters Mahr Roughness PDFDocument19 pagesParameters Mahr Roughness PDFCarlos RamirezNo ratings yet
- 05 Leoni MDocument37 pages05 Leoni Msujit_sekharNo ratings yet
- Pavement DesignDocument43 pagesPavement DesignAshok NarisettiNo ratings yet
- Curtain Wall With HZ & VL Louvers Structural Calculation For Building a-PART (6) at AXIS (34-42) - A'Document59 pagesCurtain Wall With HZ & VL Louvers Structural Calculation For Building a-PART (6) at AXIS (34-42) - A'نصر عبدالسلامNo ratings yet
- Surface FinishDocument38 pagesSurface FinishSunilNo ratings yet
- Measure Surface Roughness Using ProfilometerDocument7 pagesMeasure Surface Roughness Using ProfilometerMalith MadushanNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Surface Roughness in Turning of Duplex Stainless Steel (DSS)Document8 pagesPrediction of Surface Roughness in Turning of Duplex Stainless Steel (DSS)Dr. Mahesh GopalNo ratings yet
- Email:, ,: Amel - Chabbi@yahoo - FR Belhadi23@Document34 pagesEmail:, ,: Amel - Chabbi@yahoo - FR Belhadi23@Is Lem ChaouiNo ratings yet
- Materials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationFrom EverandMaterials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationNo ratings yet
- Manual of Engineering Drawing: British and International StandardsFrom EverandManual of Engineering Drawing: British and International StandardsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- The Art of Timing Closure: Advanced ASIC Design ImplementationFrom EverandThe Art of Timing Closure: Advanced ASIC Design ImplementationNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationFrom EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertNo ratings yet
- From Microstructure Investigations to Multiscale Modeling: Bridging the GapFrom EverandFrom Microstructure Investigations to Multiscale Modeling: Bridging the GapDelphine BrancherieNo ratings yet
- Reverberation Chambers: Theory and Applications to EMC and Antenna MeasurementsFrom EverandReverberation Chambers: Theory and Applications to EMC and Antenna MeasurementsNo ratings yet
- PDS - Duco PU Universal Epoxy Primer SurfacerDocument2 pagesPDS - Duco PU Universal Epoxy Primer SurfacerSowmen ChakrobortyNo ratings yet
- Surface Texture SymbolDocument1 pageSurface Texture SymbolSrinivas RaoNo ratings yet
- Test Block No. 2 Acc. To EN ISO 3452-3 (Order No. 9992.100) : Description, Application and Handling of TheDocument1 pageTest Block No. 2 Acc. To EN ISO 3452-3 (Order No. 9992.100) : Description, Application and Handling of TheSowmen ChakrobortyNo ratings yet
- ME 216: Engineering Metrology: Fundamentals of Geometric Tolerances Fundamentals of Geometric TolerancesDocument23 pagesME 216: Engineering Metrology: Fundamentals of Geometric Tolerances Fundamentals of Geometric TolerancesLakshya MaletiNo ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument23 pagesSurface Roughnesswawawa1No ratings yet
- GPS For Supplier - English PDFDocument7 pagesGPS For Supplier - English PDFSowmen ChakrobortyNo ratings yet
- Singapore Calendar 2020Document28 pagesSingapore Calendar 2020Kps JauraNo ratings yet
- Is 3658Document12 pagesIs 3658Bhanu Pratap Choudhury100% (1)
- Shot Peening Manual PDFDocument48 pagesShot Peening Manual PDFSowmen Chakroborty100% (1)
- D1654Document4 pagesD1654manox007No ratings yet
- E164-97 UT Contact Examination of WeldmentsDocument23 pagesE164-97 UT Contact Examination of WeldmentsALP69No ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument23 pagesSurface Roughnesswawawa1No ratings yet
- Planets and Their EffectsDocument479 pagesPlanets and Their Effectsggajendranath86% (86)
- Astm A106 - 2004 PDFDocument10 pagesAstm A106 - 2004 PDFIuliana ChilăNo ratings yet
- Astm D610 PDFDocument6 pagesAstm D610 PDFAmbarNo ratings yet
- Iso 8503-1 - 8503-2 - Surface Roughness Comprator PDFDocument4 pagesIso 8503-1 - 8503-2 - Surface Roughness Comprator PDFSowmen ChakrobortyNo ratings yet
- Steel - Equivalent Grades PDFDocument23 pagesSteel - Equivalent Grades PDFSowmen Chakroborty100% (2)
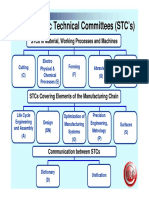
- The Scientific Technical Committees (STC'S)Document8 pagesThe Scientific Technical Committees (STC'S)Sowmen ChakrobortyNo ratings yet
- SP10Document16 pagesSP10Sumit Thakur100% (1)
- Steel - Equivalent Grades PDFDocument23 pagesSteel - Equivalent Grades PDFSowmen Chakroborty100% (2)
- En 1090Document47 pagesEn 1090Darren Thoon100% (5)
- En 1355 K Ed3Document2 pagesEn 1355 K Ed3Sowmen Chakroborty100% (1)
- Is 1852 1985Document31 pagesIs 1852 1985pavan_03No ratings yet
- Cross-Cut Adhesion TestDocument3 pagesCross-Cut Adhesion TestdcevipinNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard: Colours FOR Ready Mixed Paints and EnamelsDocument20 pagesIndian Standard: Colours FOR Ready Mixed Paints and EnamelsSam JoseNo ratings yet
- IS: 73 - 1992 Paving Bitumen - SpecificationDocument7 pagesIS: 73 - 1992 Paving Bitumen - SpecificationKarthikeyan Vedi83% (6)
- Aws D1.1 D1.1M-2010Document569 pagesAws D1.1 D1.1M-2010Abraham Aby100% (4)
- Astm A325m (2005)Document7 pagesAstm A325m (2005)THUFAIL RASHEEDNo ratings yet
- Astm B695 PDFDocument6 pagesAstm B695 PDFSowmen ChakrobortyNo ratings yet
- Serviplem StandardsDocument15 pagesServiplem StandardsSowmen ChakrobortyNo ratings yet