Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chicken Pox 2
Uploaded by
Kristine Verana Coronacion0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views1 pageCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views1 pageChicken Pox 2
Uploaded by
Kristine Verana CoronacionCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
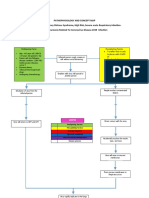
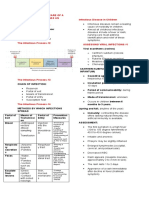
Pathophysiology
Chicken pox and Herpes Zoster (Shingles)
(A COMMUNICABLE Diagnostic
DISEASES)Test:
Inhalation of airborne respiratory droplets Determination of V-Z virus
from an infected host though Complement Fixation Test
CHICKEN POX Incubation Period:
Determination of V-Z virus
Is highly contagious disease caused by through Electron days
From10-21 Microscopic
with a mean
herpes virus varicella, characterized by vesicular examination
of 14 days or 2ofweek.
vesicular fluid
eruptions on the skin and mucous membranes Medical Management
usually with mild constitutional manifestations Clinical Manifestation
Zoverax 500mg/tablet, 1 tab 2x a
The virus infects the conjunctivae or the day for seven days must be
1. Prodromal symptoms
administered are mild
mucosa of the upper respiratory tract
andOralconsist of fever
acyclovir 800 mgand3x amalaise
day for
2. days
five Rashmust also be given
Oral Start from
antihistamine trunk
can andto
be taken
Viral proliferation
symptomatic pruritusto other parts of
then spread
Calamine lotion will ease itchiness
the body
Salicylates must not be given
Viral replication In bigger children, the
Antipyretics for fever.
lesions may be more
Synonyms and Keywords widespread and severe
Nursing Management:
Secondary viremia (14-16 days post Rapid progressions so
1. Prevention of secondary
infection.)
varicella, shingles, herpes zoster, varicella- that transitions is completed
infection of the skin lesions
zoster virus, VZV, chicken pox, chickenpox, skin in 6-8 hours
Chickenpox is usually acquired by the inhalation of airborne
through hygienic care of the
rashes in children, chickenpox vaccine, All stages are present
respiratory droplets from an infected host. The highly patient
chickenpox in pregnancy, neonatal VZV simultaneously before all are
contagious nature of VZV explains the epidemics of 2. Attention should be given to
infection, VZV immune globulin, treatment of covered scabs
chickenpox that spread through schools as one child who is nasopharyngeal discharges and
chickenpox
infected quickly spreads the virus to many classmates. High disinfection of cloths and linen by
viral titers are found in the characteristic vesicles of
Complications:
sunlight or boiling
Causative Agent:
chickenpox; thus, viral transmission may also occur through
Secondary
Cut
3. infection
fingernails of wash
short and the
“varicella” virus with these vesicles, although the risk is lower.
direct contact
lesionsmore
– furuncles, cellulites, skin
hands often in order to
abscess, erysipelas
minimize bacterial infections; may
Mode of initial
After transmission
inhalation of contaminated respiratory droplets,
Meningoencephalitis
the virus infects the conjunctivae or the mucosae of the upper be introduced by scratching
Pneumonia
respiratory tract. Viral proliferation occurs in regional lymph 4. Calamine lotion over rashes
1. Direct Contact – with patient who sheds Sepsis
nodes of the upper respiratory tract 2-4 days after initial 5. Antipyretics for fever
the virus from vesicles
infection and is followed by primary viremia on postinfection
6. Isolation of patient; cannot be
days 4-6. A second round of viral replication occurs in the
2. Indirect Contact – through articles fresh confined in general hospital;
body's internal organs, most notably the liver and the spleen,
soiled by discharges of infected persons isolated until all lesions have
followed by a secondary viremia 14-16 days postinfection.
3. Airborne – or spread by droplet become encrusted.
This secondary viremia is characterized by diffuse viral
infection
invasion of capillary endothelial cells and the epidermis. VZV
infection of cells of the malpighian layer produces both
intercellular edema and intracellular edema, resulting in the
characteristic vesicle.
You might also like
- Communicable Diseases of Childhoo1Document3 pagesCommunicable Diseases of Childhoo1esmirikNo ratings yet
- Concept Map CovidDocument7 pagesConcept Map CovidMaieca Demecillo100% (3)
- Chapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious Disorder The Infectious Process #1 Infectious Disease in ChildrenDocument20 pagesChapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious Disorder The Infectious Process #1 Infectious Disease in ChildrenMark oliver Gonzales100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Name of Patient: Attending Physician: Age: Impression/DiagnosisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Name of Patient: Attending Physician: Age: Impression/DiagnosisMelody B. Miguel0% (1)
- Chicken Pox: BSN 1A Aquino, Cadaoas, Edic, Elegino, Dela Cruz, NepomucenoDocument20 pagesChicken Pox: BSN 1A Aquino, Cadaoas, Edic, Elegino, Dela Cruz, NepomucenoRayza MaglaqueNo ratings yet
- Assessment Summary / Cover Sheet: Student Assessment HLTWHS002 Follow Safe Work Practices For Direct Client CareDocument24 pagesAssessment Summary / Cover Sheet: Student Assessment HLTWHS002 Follow Safe Work Practices For Direct Client CareGurpreet Singh WirringNo ratings yet
- English Grade 6 3RD QuarterDocument9 pagesEnglish Grade 6 3RD Quartersarah ubaNo ratings yet
- DopplerDocument1 pageDopplerKristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- Deformity Around KneeDocument94 pagesDeformity Around KneeVarun Vijay100% (3)
- Chapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious DisorderDocument12 pagesChapter 43: Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Infectious DisorderAlyssaGrandeMontimorNo ratings yet
- Viral Exanthem in PregnancyDocument3 pagesViral Exanthem in PregnancyCatherine Blanche LeeNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument4 pagesAnalysisfortuneayaNo ratings yet
- The Epi Target DiseasesDocument7 pagesThe Epi Target DiseasesElizabeth Ivory ChuaNo ratings yet
- ChickenpoxDocument13 pagesChickenpoxJoanne LagusadNo ratings yet
- CHN HandiesDocument23 pagesCHN HandiesFreeNursingNotesNo ratings yet
- 8 Childhood Viral Skin Rashes: Chickenpox, Measles and MoreDocument9 pages8 Childhood Viral Skin Rashes: Chickenpox, Measles and MoreErik OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary Disoder: Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesIntegumentary Disoder: Nursing Care PlanFrancise Elyn OcubilloNo ratings yet
- Varicella Vaccine EffectivenessDocument21 pagesVaricella Vaccine EffectivenessSul FadlyNo ratings yet
- Table of Communicable Diseases: Disease Signs & Symptoms Incubation Prevention Chicken PoxDocument10 pagesTable of Communicable Diseases: Disease Signs & Symptoms Incubation Prevention Chicken PoxJohn DamianNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument15 pagesCommunicable Diseasemaria erikaNo ratings yet
- Name of DiseaseDocument2 pagesName of DiseaseNur DiyanaNo ratings yet
- Name of DiseaseDocument2 pagesName of DiseaseNur DiyanaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever: Symptoms, Transmission and ControlDocument2 pagesDengue Fever: Symptoms, Transmission and ControlNur DiyanaNo ratings yet
- Name of DiseaseDocument2 pagesName of DiseaseNur DiyanaNo ratings yet
- Viral Exanthems ReviewerDocument4 pagesViral Exanthems ReviewerNicole TorralbaNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderDocument3 pagesPrelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderjuiceNo ratings yet
- Leocadio CD Outline RevisedDocument15 pagesLeocadio CD Outline RevisedJingle Domingo CanonizadoNo ratings yet
- ChickenpoxDocument2 pagesChickenpoxyai19100% (2)
- VaricellaDocument4 pagesVaricellasingcojericho11No ratings yet
- 22 Varicella Pink BookDocument24 pages22 Varicella Pink BookMohamad Syaikhul IslamNo ratings yet
- Insignis Pedia MMRV LopezDocument7 pagesInsignis Pedia MMRV LopezChrisfernan MondragonNo ratings yet
- Microbio Report (Dellava and Mamae)Document3 pagesMicrobio Report (Dellava and Mamae)JamesBuensalidoDellavaNo ratings yet
- FlipchartDocument24 pagesFlipchartSamantha Ishi LimNo ratings yet
- Lucid Chart ManuscriptDocument11 pagesLucid Chart ManuscriptCyrill Alexandria TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Rabies: Lyssa Virus. Genus Name of RhabdoviridaeDocument3 pagesRabies: Lyssa Virus. Genus Name of RhabdoviridaeFhaye LitucoNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 LEC Alterations With Infectious Inflammatory and Immunologic Responses PDFDocument18 pagesNCM 109 LEC Alterations With Infectious Inflammatory and Immunologic Responses PDFcalliemozartNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Preventable Diseases (Chicken Pox)Document7 pagesVaccine Preventable Diseases (Chicken Pox)Sadia Akter EmaNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseaseDocument14 pagesInfectious Diseasebiancamee100% (1)
- General Medicine 3Document60 pagesGeneral Medicine 3Zeyad AlhaimiNo ratings yet
- Patient Care Pathogen Reservoir Mode of Transmission: Viral Infections of HumansDocument21 pagesPatient Care Pathogen Reservoir Mode of Transmission: Viral Infections of HumansMark Vincent JanoyogNo ratings yet
- Fwd. Epi 8Document40 pagesFwd. Epi 8Sumayya ChughtaiNo ratings yet
- CD Learning Material 2 AirborneDocument36 pagesCD Learning Material 2 Airborne2C1 - YABES, JenniferNo ratings yet
- Del Rosario Ryan D. BSN 4C1-7 Mr. Daniel Mon Mamanao: Measles Pre-Eruptive StageDocument5 pagesDel Rosario Ryan D. BSN 4C1-7 Mr. Daniel Mon Mamanao: Measles Pre-Eruptive Stageryandelrosario9yahooNo ratings yet
- Chap4 UpdatedDocument35 pagesChap4 UpdatedROZZANE LOVELY RODNEY MoeNo ratings yet
- NCP Case Scenario Group 6Document5 pagesNCP Case Scenario Group 6Sean SeanNo ratings yet
- Chicken PoxDocument27 pagesChicken PoxLakshmiprabha KalyanaramanNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument9 pagesMalariaAliza April TyNo ratings yet
- NameDocument2 pagesNamekorikonglibatNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus-19: 5 Steps to Avoid COVID and Types of VaccinesDocument1 pageCoronavirus-19: 5 Steps to Avoid COVID and Types of VaccinesDexiel Kay RomiscalNo ratings yet
- Ananthanarayan and Paniker S Textbook of Microbiology 10th Edition 2017 PDF RemovedDocument4 pagesAnanthanarayan and Paniker S Textbook of Microbiology 10th Edition 2017 PDF RemovedjenishNo ratings yet
- Vaccine (Infant, Child)Document5 pagesVaccine (Infant, Child)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Varicella/Herpes Zoster: Communicable Disease Management ProtocolDocument5 pagesVaricella/Herpes Zoster: Communicable Disease Management Protocolyuliyanto.efendiNo ratings yet
- 7.2 - Medical Virology Part 2Document39 pages7.2 - Medical Virology Part 2Kaela Beatrice Sy LatoNo ratings yet
- 5drug StudyDocument7 pages5drug StudyPALEN, DONNA GRACE B.No ratings yet
- Rach15 - Infection Control and Asepsis NuDocument1 pageRach15 - Infection Control and Asepsis NuFalqueza JanelleNo ratings yet
- The Newborn at Risk of A Maternal Infection Opthalmia NeonatorumDocument2 pagesThe Newborn at Risk of A Maternal Infection Opthalmia NeonatorumIren Rose PañaNo ratings yet
- Virology: Herpesviruses II: Herpes SimplexDocument4 pagesVirology: Herpesviruses II: Herpes SimplexJaz CNo ratings yet
- Labels according to color: Risk Factors and Clinical Manifestations of PneumoniaDocument1 pageLabels according to color: Risk Factors and Clinical Manifestations of PneumoniaSebastianNo ratings yet
- Mayores. Chicken Pox - Concept MapDocument3 pagesMayores. Chicken Pox - Concept MapAlvic Dy KowNo ratings yet
- 2018 Varicella-Zoster Virus InfectionDocument11 pages2018 Varicella-Zoster Virus Infectioneva yustianaNo ratings yet
- Varicella, Meningitis and DHFDocument7 pagesVaricella, Meningitis and DHFdebaynNo ratings yet
- Radford 2009Document9 pagesRadford 2009JuniClaudia13No ratings yet
- Human Papilloma Virus: Incubation PeriodDocument4 pagesHuman Papilloma Virus: Incubation PeriodArabelle GONo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning for Lung Recovery: Medication, Exercise, Diet, and Follow Up CareDocument1 pageDischarge Planning for Lung Recovery: Medication, Exercise, Diet, and Follow Up CareKristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- LaborDocument1 pageLaborKristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- 8 W-S Booklet Wound MGMTDocument2 pages8 W-S Booklet Wound MGMTKhairul MustafaNo ratings yet
- ParacentesisDocument2 pagesParacentesisKristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- LaborDocument1 pageLaborKristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- AsessmentDocument1 pageAsessmentKristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument1 pagePulmonary TuberculosisKristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- Chicken Pox 2Document1 pageChicken Pox 2Kristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- Sleep Deprivation FractureDocument2 pagesSleep Deprivation FractureKristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument1 pagePulmonary TuberculosisKristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- Bone FracturesDocument8 pagesBone FracturesKristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument1 pagePulmonary TuberculosisKristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning LatestDocument3 pagesDischarge Planning LatestKristine Verana CoronacionNo ratings yet
- Dr Cabrera's Contributions to ParasitologyDocument11 pagesDr Cabrera's Contributions to ParasitologyElle CruzNo ratings yet
- ENT HAQs 1st EDDocument34 pagesENT HAQs 1st EDranjanavnish142No ratings yet
- Signal Assessment Report Embolic Thrombotic Events SMQ Covid 19 Vaccine Chadox1 S Recombinant Covid - enDocument50 pagesSignal Assessment Report Embolic Thrombotic Events SMQ Covid 19 Vaccine Chadox1 S Recombinant Covid - enFlorinelNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Lymphatic System PDFDocument4 pagesTutorial 3 - Lymphatic System PDFpizzaNo ratings yet
- PULMODocument3 pagesPULMOGianna Louisse Marie Dacalos DiazNo ratings yet
- Helpful Questions For Oral RevalidaDocument6 pagesHelpful Questions For Oral RevalidaMomo CanNo ratings yet
- HSIS DR Kishor1Document39 pagesHSIS DR Kishor1Kishor Adhikari100% (1)
- Materia Medica Viva Volume 1 George Vithoulkas.06646 2sample ABIES CANADENSISDocument7 pagesMateria Medica Viva Volume 1 George Vithoulkas.06646 2sample ABIES CANADENSISjaishnavpstorageNo ratings yet
- GIT Cont 071628Document51 pagesGIT Cont 071628Olatomide OlaniranNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Inflection 2Document33 pagesSexually Transmitted Inflection 2Daphne Ongbit-Jarito ArintocNo ratings yet
- Siberia's Lifeline Medical TrainDocument3 pagesSiberia's Lifeline Medical TrainQuan LeNo ratings yet
- Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kejadian Dermatitis Atopik Di Puskesmas Bangkinang KotaDocument10 pagesFaktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kejadian Dermatitis Atopik Di Puskesmas Bangkinang KotaAsha NopatiNo ratings yet
- MedulloblastomaDocument67 pagesMedulloblastomaAmira YasmineNo ratings yet
- Lee Chee Kwong v. Kutiandy Thanniamalay & AnorDocument16 pagesLee Chee Kwong v. Kutiandy Thanniamalay & AnorC.Y. Ong & Co. - Adv. & Sol.No ratings yet
- Hand Therapy: Evaluative GuidelinesDocument19 pagesHand Therapy: Evaluative GuidelinesPatrick MuljonoNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Nipple Hypertrophy by A Simplified Reduction TechniqueDocument7 pagesTreatment of Nipple Hypertrophy by A Simplified Reduction TechniqueАндрей ПетровNo ratings yet
- Industrial Hazard PDFDocument27 pagesIndustrial Hazard PDFMehul PatelNo ratings yet
- Icd-9-Cm RizDocument33 pagesIcd-9-Cm RizJude Had a FarmNo ratings yet
- Case Study RespiDocument3 pagesCase Study RespiMark Jheran AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris Kelas 5Document2 pagesBahasa Inggris Kelas 5effa prastiyaNo ratings yet
- Executive Function, Attention, and Memory Deficits in Antisocial PersonalityDocument11 pagesExecutive Function, Attention, and Memory Deficits in Antisocial PersonalitydendhyNo ratings yet
- Inflammation TASK 1. Briefly Discuss The Three Divisions of Immunity and Its Relationship To One AnotherDocument5 pagesInflammation TASK 1. Briefly Discuss The Three Divisions of Immunity and Its Relationship To One Anotherkristine keen buanNo ratings yet
- EMPLOYEES' COMPENSATION CLAIMDocument4 pagesEMPLOYEES' COMPENSATION CLAIMmuthuswamy77No ratings yet
- Midterm - Examination in Musculoskeletal Physical Therapy For Third Year Students First Semester 2020-2021Document6 pagesMidterm - Examination in Musculoskeletal Physical Therapy For Third Year Students First Semester 2020-2021Dena AliNo ratings yet
- Cardiac EmergenciesDocument29 pagesCardiac EmergenciesAhmad MohamadNo ratings yet
- Urinary CalculiDocument15 pagesUrinary CalculiEvita DewiNo ratings yet