Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sn1sn2e1e2 Summary
Uploaded by
skiprokOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sn1sn2e1e2 Summary
Uploaded by
skiprokCopyright:
Available Formats
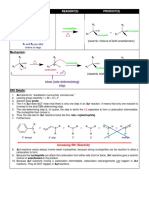
Substitution and Elimination Reactions Comparative Chart
Reaction Structure of RX Reactivity of Nu: Conc. Of Nu: Solvent Stereochemistry
SN2 1>2>3 Strong nucleophile High concentration of Aprotic polar solvent favors inversion of configuration
favors reaction nucleophile favors a SN2 reaction if either of
Only this reaction and reaction the reactants is charged
E2 will most likely ex: DMF DMSO Acetone
react with a primary
RX
E2 3>2>1 Strong Base favors High concentration of Aprotic polar solvent favors If the reactant has 2 H bonded
Major product is more reaction base favors reaction a E2 reaction if either of to the carbon from which a H is
substituted alkene the reactants is charged to be removed, both E and Z
unless ex: DMF DMSO Acetone result.
*the base is large The conformers that has the
*the alkyl halide is an bulkiest groups on opposite
alkyl flouride sides will be the major product.
*the alkyl halide Anti and syn elimination– if it
contains one or more is cyclohexane, it has to be
double bonds axial (anti)
SN1 3>2>1 Not effected by strength Not effected but low Protic polar favors a SN1 Racemization (with some
of nucleophile but a concentration disfavors a reaction if the reactant is not inversion because of ion
Forms a carbocation weak nucleophile favors SN2 reaction charged. pairing)
it by not favoring a Ex: H2O, CH3OH, etc.
SN2 reaction
E1 3>2>1 Weak base favors E1 Not effected but a low Protic polar favors a E1 Bulkiest groups on opposite
reaction by disfavoring concentration of base reaction if the reactant is not sides
Forms a carbocation E2 reaction favors E1 by disfavoring a charged.
E2 reaction Ex: H2O, CH3OH, etc.
SN Versus E
Methyl halide Primary halide Secondary halide Tertiary halide
SN2 reaction most SN2 when the main SN2 if the main reaction is with weak base or Nu: where Pka of E2 if Main reaction is with strong bases
favored reaction is with good conjugate acid is 11 or less ex: I- or Ch3CO2- like OH- and RO-
nucleophiles/weak
No Elimination bases such as I- and E2 if the main reaction is with a strong base or Nu: where Pka of SN1/E1 if main reaction is with a poor
reactions! CH3CO2- conjugate acid is 11 or greater- , high temperatures and bulky Nu: High temperatures favor E1 out of the
bases increas elimination two.
E2 if you use strong
bulky bases such as SN1/E1 are common in reactions with weak Nu: in polar protic solvents
t-butoxide steric effects like water, high temps favor E1
You might also like
- Chapter 7 - Alkyl Halides 2022Document66 pagesChapter 7 - Alkyl Halides 2022Hoài Nguyễn Phan VũNo ratings yet
- Substitution Versus Elimination Reactions: Presented By: Hina Javed Punjab Group of Colleges Rwp/IsbDocument15 pagesSubstitution Versus Elimination Reactions: Presented By: Hina Javed Punjab Group of Colleges Rwp/IsbRaja Haris JavedNo ratings yet
- SN2 RXDocument25 pagesSN2 RXGebby FebriliaNo ratings yet
- JeevanDocument26 pagesJeevanseelampadmaNo ratings yet
- WK 2-2 Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Jan 18Document54 pagesWK 2-2 Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Jan 18cerelia.dkuNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halide Reactions: SN1, SN2, E1 and E2Document60 pagesAlkyl Halide Reactions: SN1, SN2, E1 and E2Himanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Year 2 - : Organic ChemistryDocument33 pagesYear 2 - : Organic ChemistryManWol JangNo ratings yet
- Elimination ReactionsDocument19 pagesElimination ReactionsanantNo ratings yet
- Organic Reaction Mechanisms and ClassificationsDocument64 pagesOrganic Reaction Mechanisms and ClassificationsAudry YuniarNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halide PDFDocument29 pagesAlkyl Halide PDFSantosh Potdar100% (2)
- Substitution vs. Elimination: 2 Reaction, Sometimes The E2 ReactionDocument2 pagesSubstitution vs. Elimination: 2 Reaction, Sometimes The E2 ReactionFadhlih Al-zakiNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions GuideDocument10 pagesNucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions Guidesamantha davidsonNo ratings yet
- RXN Mech Otto Lect 5Document21 pagesRXN Mech Otto Lect 5P.No ratings yet
- Elimination ReactionDocument89 pagesElimination ReactionManahil FatimaNo ratings yet
- SN2 and E2 Reaction MechanismsDocument4 pagesSN2 and E2 Reaction MechanismsBagusprPrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Addition and elimination reactionsDocument11 pagesAddition and elimination reactionsmaganda akoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Elimination ReactionDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Elimination Reactionahmedmustefa773No ratings yet
- Summary of Reactions chm2120Document4 pagesSummary of Reactions chm2120sabrinasameja75No ratings yet
- Reviewer in OrgDocument18 pagesReviewer in OrgMichael Josh RamosNo ratings yet
- Elimination Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocument24 pagesElimination Reactions of Alkyl HalidesmaulidyaNo ratings yet
- Reaction MechanismDocument20 pagesReaction MechanismPalash ChawhanNo ratings yet
- 15 Nucleophilic Substituion - IIT FinalDocument14 pages15 Nucleophilic Substituion - IIT FinalEnglish words BY Utkarsh johriNo ratings yet
- Vs. E1 vs. E2 - Factors Affecting The Type of Reaction An Alkyl Halide Undergoes IncludeDocument9 pagesVs. E1 vs. E2 - Factors Affecting The Type of Reaction An Alkyl Halide Undergoes Includenikhil jalanNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides: SN2 and E2 ReactionsDocument4 pagesAlkyl Halides: SN2 and E2 ReactionsShenchu XieNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Summery of ReactionsDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry Summery of ReactionsguiamakhloufNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 PG 61 Notes Solns BLC F22Document17 pagesUnit 7 PG 61 Notes Solns BLC F22Lamees IbeidNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic substitution reactionsDocument70 pagesNucleophilic substitution reactionsBình NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Organic Reaction Mechanism-Lecture-4Document25 pagesOrganic Reaction Mechanism-Lecture-4Namrah ZakaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Chemistry of Life and Beyond ..: SynthesisDocument71 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Chemistry of Life and Beyond ..: Synthesiskrystel pyneeNo ratings yet
- Deciding SN1 - SN2 - E1 - E2 (2) - The Nucleophile - Base - Master Organic ChemistryDocument26 pagesDeciding SN1 - SN2 - E1 - E2 (2) - The Nucleophile - Base - Master Organic ChemistryKinjal Busa100% (1)
- 07 Handout 1Document2 pages07 Handout 1odrhey hernandezNo ratings yet
- Reaksi SN-1, SN-2, E-1, Dan E-2.Document64 pagesReaksi SN-1, SN-2, E-1, Dan E-2.Annik QurniawatiNo ratings yet
- MechanismsDocument1 pageMechanismsPimmada DangwibulNo ratings yet
- Guide To SN1 SN2 E1 and E2Document7 pagesGuide To SN1 SN2 E1 and E2كوفيتي رمز اصالتيNo ratings yet
- Labile or Inert?Document7 pagesLabile or Inert?veronicaNo ratings yet
- Ankyl Halogenua Phan Ung The Nucleophil Va Tach LoaiDocument103 pagesAnkyl Halogenua Phan Ung The Nucleophil Va Tach LoaiQuang Cường HoàngNo ratings yet
- Alkyl HalideDocument1 pageAlkyl HalideApurba Sarker ApuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10. Substitution Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocument49 pagesChapter 10. Substitution Reactions of Alkyl HalidesThanh NguyênNo ratings yet
- Deciding SN1SN2E1E2 2 The NucleophileBaseDocument3 pagesDeciding SN1SN2E1E2 2 The NucleophileBaseDivyanshu RawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Substitution ReactionDocument41 pagesChapter 4 Substitution Reactionahmedmustefa773No ratings yet
- Reaction Mechanism DDocument36 pagesReaction Mechanism Dprajaktac506No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry SN1 vs SN2 ReactionsDocument36 pagesOrganic Chemistry SN1 vs SN2 ReactionsExcellent KhozaNo ratings yet
- 01-01-2021 GOC2 English ADocument39 pages01-01-2021 GOC2 English APrabhakar BandaruNo ratings yet
- Substitution & Elimination Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDocument71 pagesSubstitution & Elimination Reactions of Alkyl HalidesDaniel McDermottNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Lecture on Nucleophilic Substitution and SN1 SN2 MechanismsDocument21 pagesChemical Reactions Lecture on Nucleophilic Substitution and SN1 SN2 MechanismsKalpa DihingiaNo ratings yet
- New CHY3201 Chapter 7 Nucleophilic Substitution On Saturated CarbonsDocument44 pagesNew CHY3201 Chapter 7 Nucleophilic Substitution On Saturated Carbons222418No ratings yet
- Reaction Flashcards (Substitution and Elimination) PDFDocument5 pagesReaction Flashcards (Substitution and Elimination) PDFArjun GandotraNo ratings yet
- SN1 SN2 E1 E2 Cheat SheetDocument1 pageSN1 SN2 E1 E2 Cheat SheetMyshaM099No ratings yet
- Loudon Chapter 8 & 9 Review: Substitutions and Eliminations: CL Nu CL HDocument6 pagesLoudon Chapter 8 & 9 Review: Substitutions and Eliminations: CL Nu CL HxryceuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.2Document13 pagesChapter 4.2skywalkerNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides Elimination Reactions MechanismsDocument63 pagesAlkyl Halides Elimination Reactions MechanismsFlorencia AngellicaNo ratings yet
- SN Reactions Lecture3Document21 pagesSN Reactions Lecture3Kalpa DihingiaNo ratings yet
- BhivbnmDocument8 pagesBhivbnmPrachiNo ratings yet
- Substitutuon Elimination A.M. ClassDocument34 pagesSubstitutuon Elimination A.M. ClassmalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four 221212Document24 pagesChapter Four 221212Barnabas YohannesNo ratings yet
- FlowChart NSRs and ERsDocument1 pageFlowChart NSRs and ERsChemistry Department Government City CollegeNo ratings yet
- The Stopping and Ranges of Ions in Matter: Handbook of Stopping Cross-Sections for Energetic Ions in All ElementsFrom EverandThe Stopping and Ranges of Ions in Matter: Handbook of Stopping Cross-Sections for Energetic Ions in All ElementsNo ratings yet
- Palladium Reagents and Catalysts: New Perspectives for the 21st CenturyFrom EverandPalladium Reagents and Catalysts: New Perspectives for the 21st CenturyNo ratings yet
- BackIntelligence Herniated Disc ExercisesDocument9 pagesBackIntelligence Herniated Disc Exercisesswaminathan1No ratings yet
- Research Proposal On Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties of Kiwi FruitDocument25 pagesResearch Proposal On Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties of Kiwi FruitCatherine100% (1)
- 51-11-15-001-Data Recording of Allowable Damage and Repairs-A320Document6 pages51-11-15-001-Data Recording of Allowable Damage and Repairs-A320FredNo ratings yet
- ALL-Q (Coenzyme Q10) Plus - PDSDocument3 pagesALL-Q (Coenzyme Q10) Plus - PDSMarlon2370No ratings yet
- Raúl Edgardo Macchiavelli: Raul - Macchiavelli@upr - EduDocument53 pagesRaúl Edgardo Macchiavelli: Raul - Macchiavelli@upr - EduDhaval patelNo ratings yet
- 571470-29 Linear Encoders For Numerically Controlled Machine ToolsDocument60 pages571470-29 Linear Encoders For Numerically Controlled Machine ToolsIjabiNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Management and Cathodic Protection GuideDocument52 pagesCorrosion Management and Cathodic Protection GuideErol DAĞNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document9 pagesChapter 4Aung KhantNo ratings yet
- SPE 18184 OPUS: An Expert Advisor For Artificial LiftDocument8 pagesSPE 18184 OPUS: An Expert Advisor For Artificial Liftlepro brunelNo ratings yet
- Peds Ati - VS + Lab ValuesDocument1 pagePeds Ati - VS + Lab Valuesluke jackson100% (1)
- Incepbio Project PPT - 080124Document21 pagesIncepbio Project PPT - 080124adminpuneNo ratings yet
- Cat Marine Engine ProgramDocument4 pagesCat Marine Engine ProgramRobert BeddingfieldNo ratings yet
- BX 560GDocument20 pagesBX 560Gmacanipharoldf6220No ratings yet
- Vakri Grahas - Effects of Retrograde Planets in Hindu AstrologyDocument4 pagesVakri Grahas - Effects of Retrograde Planets in Hindu AstrologyBailvan100% (1)
- The Wankel Engine Design Development AppDocument271 pagesThe Wankel Engine Design Development AppFurqanNo ratings yet
- Ashrae Handbook 2000 CHDocument32 pagesAshrae Handbook 2000 CHKazuto NakazatoNo ratings yet
- Ask Astrologer Report - Specific Answer To Major Concern of LifeDocument8 pagesAsk Astrologer Report - Specific Answer To Major Concern of LifecyberastroNo ratings yet
- Tots FaqDocument12 pagesTots FaqkbsnNo ratings yet
- The Design of Tomato Paste Plant - Problem StatementDocument3 pagesThe Design of Tomato Paste Plant - Problem StatementvictorNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication, Assignment 2Document3 pagesPurposive Communication, Assignment 2Myles Ninon LazoNo ratings yet
- 04-S-2023 Moa Water Refilling Station - OliverioDocument2 pages04-S-2023 Moa Water Refilling Station - OliveriobarangaysancarlosofficialNo ratings yet
- English 4 Q2 Weeks 1-4Document36 pagesEnglish 4 Q2 Weeks 1-4Em AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Noon Fees StructureDocument8 pagesNoon Fees StructureNithin SreekumarNo ratings yet
- Computer PackagesDocument72 pagesComputer PackagesBildad JoashNo ratings yet
- Major Practice in Swine ProductionDocument29 pagesMajor Practice in Swine ProductionMark GarciaNo ratings yet
- KS1 A Good Bubbling CauldronDocument11 pagesKS1 A Good Bubbling CauldronViktoriia PolushkoNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature of Jackfruit SeedDocument4 pagesReview of Related Literature of Jackfruit SeedPrince Martin John Villamor80% (5)
- SEISMIC LOAD ANALYSISDocument9 pagesSEISMIC LOAD ANALYSISAditya RoyNo ratings yet
- Your First ProgramDocument7 pagesYour First ProgramJosephat MugumbaNo ratings yet