Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12 Refining The Sketch
Uploaded by
athenalavegaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12 Refining The Sketch
Uploaded by
athenalavegaCopyright:
Available Formats
Refining the sketch
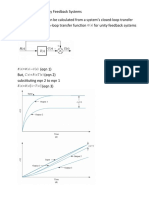
Breakaway/ break-in point, σ b- a point on the real axis where two or more
branches of the root-locus depart from or arrive at the real axis
o Breakaway point- point where the locus leaves the real axis
o Break-in point- a point where the locus returns to the real axis
m n
∑ σ +1 z =∑ σ +1 p
1 i 1 i
zi & pi- are the negative of the zero and pole values, respectively of G( s)
Departure and Arrival angles
o The departure angle of the root locus from a complex pole is given by
θ D=180 ° +argG ( s)'
Where G(s)' - phase angle of G( s) computed at the complex pole but ignoring the
contribution of that particular pole
o The angle of arrival of the root locus at a complex zero is given by
θ A =180 °−argG (s)
Where G(s) - phase angle of G(s) at the complex zero ignoring the effect of that
particular zero
NOTE:
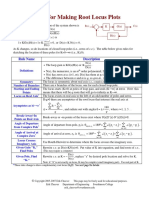
1. Real axis segments
a. Rule for k > 0- points of the root-locus on the real axis lie to the left of an
odd number of finite poles and zeroes.
b. Rule for k < 0- points of the root-locus on the real axis lie to the left of an
even number of finite poles and zeros.
2. Asymptotes
Angles between the asymptotes and the real axis are given by
(2 l+1)π
θa = , for k >0
¿ finite poles−¿ finite zeros
( 2l) π
θa = , for k <0
¿ finite poles−¿ finite zeros
l=0,1,2 , … , ¿ of finite poles−¿ of finite zeros−1
Total number of asymptotes = ¿ of finite poles−¿ of finite zeros
You might also like
- Root LocusDocument26 pagesRoot Locusaty27062004No ratings yet
- Module 3Document40 pagesModule 3AlphaBravoNo ratings yet
- Root Locus Techniques: by Nand KishoreDocument19 pagesRoot Locus Techniques: by Nand KishoreTyson LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Root Locus Analysis and Design Using Control System Poles and ZerosDocument16 pagesRoot Locus Analysis and Design Using Control System Poles and ZerosVamshidhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ee481 p10 Root - LocusDocument37 pagesEe481 p10 Root - Locusminato4thNo ratings yet
- Sketching A Root Locus PlotDocument9 pagesSketching A Root Locus PlotsajjadnedianNo ratings yet
- Root Locus:: Determine The Open Loop Poles, Zeros and A Number of Branches From Given G(S) H(S) )Document3 pagesRoot Locus:: Determine The Open Loop Poles, Zeros and A Number of Branches From Given G(S) H(S) )Vara LakshmiNo ratings yet
- 11 Root Locus 1Document6 pages11 Root Locus 1athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet II S Bs ... S As ... : M m1 N n1Document1 pageCheat Sheet II S Bs ... S As ... : M m1 N n1Ryan BlancNo ratings yet
- Root Locus Plots of Positive Feedback Systems Ongata BM ExtensionDocument8 pagesRoot Locus Plots of Positive Feedback Systems Ongata BM ExtensionOLAGO ACHOKANo ratings yet
- Fraunhoffer DiffractionDocument15 pagesFraunhoffer DiffractionLinNo ratings yet
- CE-G2 Pre-Board 1: Plane and Solid Geometry Key PointsDocument2 pagesCE-G2 Pre-Board 1: Plane and Solid Geometry Key PointsDaniela CaguioaNo ratings yet
- Exchange Interaction: Orbital SpinDocument4 pagesExchange Interaction: Orbital Spinsubhratanu_bNo ratings yet
- Qual 18 p2 SolDocument4 pagesQual 18 p2 SolKarishtain NewtonNo ratings yet
- Module 02 - Plane and Spherical Trigonometry PDFDocument3 pagesModule 02 - Plane and Spherical Trigonometry PDFNiwled UyNo ratings yet
- Basic Plane Geometry ConceptsDocument28 pagesBasic Plane Geometry Conceptsfrancis de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Design Via Root LocusDocument53 pagesDesign Via Root LocusAhmed ShareefNo ratings yet
- Rules For Making Root Locus Plots: Rule Name DescriptionDocument2 pagesRules For Making Root Locus Plots: Rule Name DescriptionJUAN DAVID BECERRA MOLANONo ratings yet
- Power Dividers and Directional CouplersDocument43 pagesPower Dividers and Directional CouplersSaraswathi AsirvathamNo ratings yet
- Robotics1 13.01.09Document5 pagesRobotics1 13.01.09asalifew belachewNo ratings yet
- Equation Sheet 13.03.2022Document6 pagesEquation Sheet 13.03.2022Nirav PatelNo ratings yet
- Time Response, Root Locus and Bode Plot AnalysisDocument12 pagesTime Response, Root Locus and Bode Plot Analysisanon_119740855No ratings yet
- Part 8Document27 pagesPart 8TwinkelsNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips The Root Locus TechniqueDocument21 pagesDokumen - Tips The Root Locus TechniqueSolid Work and Mechanical software TutorialNo ratings yet
- Prestige Institute of Engineering & Science Indore (M.P.)Document3 pagesPrestige Institute of Engineering & Science Indore (M.P.)SagarManjrekarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Part 2: Refining The Root Locus: Engineering 5821: Control Systems IDocument15 pagesUnit 7: Part 2: Refining The Root Locus: Engineering 5821: Control Systems INikhil PanikkarNo ratings yet
- RootDocument25 pagesRootTushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Root Locus TechniquesDocument24 pagesRoot Locus TechniquesNikhil PanikkarNo ratings yet
- AMP1 Q (Theo) 2021 SeriesD (Emo) en (1sidedBUNDLE) Answers enDocument4 pagesAMP1 Q (Theo) 2021 SeriesD (Emo) en (1sidedBUNDLE) Answers enDaufNo ratings yet
- Cam Follower ManualDocument13 pagesCam Follower ManualTejas RaoNo ratings yet
- A5 SolutionDocument8 pagesA5 SolutionRaja KumarNo ratings yet
- Luc CA 2018 Root LocusDocument15 pagesLuc CA 2018 Root LocusUM ZaidNo ratings yet
- Root LocusDocument64 pagesRoot Locus200110039No ratings yet
- Nyquist PlotDocument28 pagesNyquist PlotLloyds RajaNo ratings yet
- Cat Imp Qunat FormulaDocument4 pagesCat Imp Qunat FormulaMohnish IsraniNo ratings yet
- Controller Design Using Root-Locus TechniquesDocument10 pagesController Design Using Root-Locus TechniquesABDELRHMAN ALINo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Control System I - Web 2Document16 pagesChap 5 Control System I - Web 2吳晨瑋No ratings yet
- Division of Line SegmentDocument2 pagesDivision of Line Segmentprince ian cruzNo ratings yet
- Q 7 Control Fall 2015Document1 pageQ 7 Control Fall 2015Fahad SiddiqNo ratings yet
- The 180 Degree HybridDocument3 pagesThe 180 Degree HybridalfredomatiasrojoNo ratings yet
- LecttureIIRoot Locus Method 2Document57 pagesLecttureIIRoot Locus Method 2JmbernabeNo ratings yet
- Gr11-Gr12 Trigs Study SheetDocument6 pagesGr11-Gr12 Trigs Study SheetSaraNo ratings yet
- Root Locues PDFDocument32 pagesRoot Locues PDFnoor deenNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response and Bode Plot AnalysisDocument30 pagesFrequency Response and Bode Plot AnalysisSatya SuryaNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Graph The Polar Curve, Rose PDFDocument27 pages6.1 Graph The Polar Curve, Rose PDFPierre CachouNo ratings yet
- Problems On Symmetrical Parabolic Curve PDFDocument20 pagesProblems On Symmetrical Parabolic Curve PDFJoash Normie DuldulaoNo ratings yet
- Root Locus MethodDocument23 pagesRoot Locus MethodChanoxismNo ratings yet
- Groupsp 3Document5 pagesGroupsp 3Hoàng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- A6 SolutionDocument8 pagesA6 SolutionRaja KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7c Directivity IndexDocument12 pagesChapter - 7c Directivity IndexAlinaBogoiNo ratings yet
- LAB No. 10 Analysis of Linear Control System Using Root Loci TechniqueDocument7 pagesLAB No. 10 Analysis of Linear Control System Using Root Loci TechniqueSanjar BeyNo ratings yet
- Root Locus RulesDocument3 pagesRoot Locus RulesCollins EhizojieNo ratings yet
- Trig Identities & Triangle FormulasDocument3 pagesTrig Identities & Triangle FormulasAaron Rapha RosalesNo ratings yet
- Lessons 22-45Document179 pagesLessons 22-45Shakeel NawazNo ratings yet
- Real Numbers Formulas: Here You Can Check The Important Formulas Related To Class 10 Maths Real NumbersDocument7 pagesReal Numbers Formulas: Here You Can Check The Important Formulas Related To Class 10 Maths Real NumbersAryan KananiNo ratings yet
- R. R. Auelmann Stereo Imaging and GeolocationDocument19 pagesR. R. Auelmann Stereo Imaging and Geolocationleeminji.v.lNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios NyquistDocument13 pagesEjercicios Nyquistpepe gomezNo ratings yet
- Ps6sol v2 PDFDocument13 pagesPs6sol v2 PDFRahuldev MuraleedharanNo ratings yet
- Root Locus: Illustrative ExampleDocument17 pagesRoot Locus: Illustrative Examplevaibhav471995No ratings yet
- Ee 170 Final GradesDocument1 pageEe 170 Final GradesathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 6-Stability Routh Hurwitz SPECIALDocument1 page6-Stability Routh Hurwitz SPECIALathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Ee 170 Final GradesDocument2 pagesEe 170 Final GradesathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Postfinal 170Document1 pagePostfinal 170athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 6 Stability HandoutDocument3 pages6 Stability HandoutathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Signal Flow AdditionalDocument2 pages8 - Signal Flow AdditionalathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 11 Root Locus 1Document6 pages11 Root Locus 1athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Ee 170 Final GradesDocument1 pageEe 170 Final GradesathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Ee 170 Final GradesDocument1 pageEe 170 Final GradesathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Signal Flow GraphsDocument3 pages8 - Signal Flow Graphsathenalavega100% (1)
- 9 - Steady State 2Document7 pages9 - Steady State 2athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- EE 170 Problem Set 1 AY 2010-2011 2 SemDocument1 pageEE 170 Problem Set 1 AY 2010-2011 2 SemathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 9-Steady State SpecificationsDocument3 pages9-Steady State SpecificationsathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 9-Steady State ErrorDocument4 pages9-Steady State ErrorathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Ee 131 Problem SetDocument3 pagesEe 131 Problem SetathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 7-Block Diagram Reduction Notes2Document6 pages7-Block Diagram Reduction Notes2athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Handout 131Document4 pages4 - Handout 131athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 5 - Handout 131Document3 pages5 - Handout 131athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Handout 131Document4 pages4 - Handout 131athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Handout 131Document3 pages3 - Handout 131athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- 6 Stability Routh Hurwitz BasicDocument2 pages6 Stability Routh Hurwitz BasicathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Control SystemsDocument2 pagesControl SystemsathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Simplest Form of A Block DiagramDocument7 pagesSimplest Form of A Block DiagramathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Simplest Form of A Block DiagramDocument7 pagesSimplest Form of A Block DiagramathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- Introduction HandoutDocument3 pagesIntroduction Handoutathenalavega100% (1)
- Course Outline 131Document3 pagesCourse Outline 131athenalavegaNo ratings yet
- EE170-Problem Set 3Document1 pageEE170-Problem Set 3athenalavega100% (1)
- Set Elements: Lecture Notes A. Set DefinitionsDocument4 pagesSet Elements: Lecture Notes A. Set DefinitionsathenalavegaNo ratings yet
- EE170-Problem Set 3Document1 pageEE170-Problem Set 3athenalavega100% (1)