Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ncp&drugstud
Uploaded by
Sarah Mae Billano BermudezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ncp&drugstud
Uploaded by
Sarah Mae Billano BermudezCopyright:
Available Formats
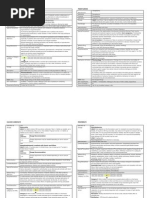
NURSING CARE PLAN # 1 (ACTUAL) ASSESSMENT Actual/Abnormal cues: nakabalo na na siya ganimag sulat gamit ang wala ya nga
kamot kay tungod may dextrose siya sa pihak.. as Definition: verbalized by the patients mother Limitation in independent, purposeful Able to physical perform limited hand movement of the body or of activities. one or more Limited extremities Range of motion. Source: NURSING DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE DESIRED OUTCOME After 5 days of nursing intervention, the client will be able to: Demonstrate techniques/beha viors that enable resumption of activities. Participate in ADLs and desired activities. INTERVENTIONS INDEPENDENT: Observe movement when client is unaware of observation Assist with treatment of underlying condition(s) Assist/have client reposition self on a regular schedule as dictated by individual situation Identify/enco -to note any incongruency with reports of abilities. JUSTIFICATIONS EVALUATION After 5 days of nursing intervention, the client:
-to maximize potential for mobility and optimal function.
-to enhance circulation to tissues, reduce risk of tissue ischemia
Verbalize
understanding of situation and individual treatment
-Limits fatigue,
Strength: Good emotional and family support Positive attitude towards recovery Risk: Prolonged bedrest Long term IVF infection
Nurses Pocket Guide 9th edition By Doenges et al
regimen and safety measures. Maintain or increase strength and function of affected or compensatory body part.
urage energyconserving techniques for ADLs.
maximizing participation.
COLLABORATIVE: Collaborate with physical medicine specialist and occupational/physical therapists in providing range-of-motion exercise (active or passive). -These techniques can be helpful in rehabilitating the client
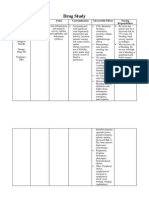
DRUG STUDY #1 Drug Generic Name: Paracetamol Brand Name: Dosage/ Frequency/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Hematologic: thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, neutropenia, leukopenia, pancytopenia Hepatic: jaundice, hepatotoxicity Metabolic: hypoglycemic coma Skin: rash, urticaria Nursing Responsibilty Observe for acute toxicity and overdose. Signs and symptoms of acute toxicity are as follows: Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, malaise, diaphoresis. Tell patient, parents, or other caregivers not to use drug concurrently with other acetaminophencontaining products. Advise patient, parents, or other caregivers to contact
Classification: Synthetic nonopioid aminophenol derivative Therapeutic class: Analgesic, antipyretic
Unclear. Pain relief may result from inhibition Mild to moderate of prostaglandin pain caused by synthesis in CNS, headache,muscle with subsequent ache, backache blockage of pain impulses. Fever reduction may result from vasodilation and increased peripheral blood flow in hypothalamus, which dissipates heat and lowers body
Hypersensitivity to drug
Use cautiously in: anemia, hepatic or renal disease elderly patients pregnant or breastfeeding patients children younger than age 2.
temperature.
Other: hypersensitivity reactions (such as fever)
prescriber if fever or other symptoms persist despite taking recommended amount of drug.
As appropriate, review all other significant and life-threatening adverse reactions and interactions.
DRUG STUDY # 2 Drug Generic Name: 10 g/ sachet Esomeprazole Magnesium Brand Name: Nexium Classification: *Proton pump inhibitor *anti-ulcer drugs PO OD Dosage/ Frequency/ Route Mechanism of Action Reduces gastric acid production by inhibiting enzyme activity in gastric parietal cells, preventing transport of hydrogen ions into gastric lumen Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilty Monitor neurologic status, especially for dizziness, headache, paresthesia, and asthenia. Watch for signs and symptoms of EENT and respiratory infections. Assess nutritional and hydration status in light of adverse GI effects. Check for rash
Treatment of
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD); healing of erosive esophagitis
Helicobacter pylori
Hypersensitivity to drug or its components Use cautiously in: severe hepatic impairment children younger than age 18 (safety not established).
CNS: headache, dizziness, asthenia, vertigo, apathy, anxiety,paresthesia, insomnia, abnormal dreams EENT: sinusitis, epistaxis GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, flatulence, dry mouth Respiratory: upper respiratory tract infection, cough Skin: rash,
eradication to decrease risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence
Treatment of
pathological hypersecretory conditions
inflammation, urticaria, pruritus, alopecia, dry skin
and other signs of hypersensitivity.
DRUG STUDY # 3 Drug Generic Name: Furosemide Brand Name: Lasix Classification: Sulfonamide loop diuretic 16 mg IVTT Stat Dosage/ Frequency/ Route Mechanism of Action inhibit sodium and chloride reabsorption from ascending loop of Henle and distal renal tubules. Increases potassium excretion and plasma volume, promoting renal excretion Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilty Watch for signs and symptoms of ototoxicity. Assess for other evidence of drug toxicity (arrhythmias, renal dysfunction, abdominal pain, sore throat, fever). Monitor CBC, BUN, and electrolyte, uric acid, and CO2 levels. Monitor blood
Acute pulmonary edema Hypertension
Edema caused
Hypersensitivity to drug or other sulfonamides Anuria Use cautiously in: diabetes mellitus, severe hepatic disease elderly patients pregnant or breastfeeding patients neonates.
by heart failure, hepatic cirrhosis, or renal disease
CNS: dizziness, headache, weakness, lethargy, paresthesia, drowsiness, restlessness, lightheadedness CV: hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, Tachycardia, arrhythmias EENT: blurred vision, hearing loss, tinnitus GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation,
of water, sodium, chloride, magnesium, hydrogen, and calcium. Reactions
dyspepsia, oral and gastric irritation, cramping, anorexia, dry mouth, acute pancreatitis GU: excessive and frequent urination, nocturia, glycosuria, oliguria Hematologic: anemia, purpura, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia Hepatic: jaundice Metabolic: hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, dehydration, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia Musculoskeletal: muscle pain,muscle cramps Skin: photosensitivity, rash, diaphoresis, urticaria, pruritus, exfoliative dermatitis, Other: fever, transient
pressure, pulse, fluid intake and output, and weight. Monitor dietary potassium intake. Watch for signs and symptoms of hypokalemia.
pain at I.M. injection site
DRUG STUDY # 4 Drug Dosage/ Frequency/ Route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilty
Generic Name: Hydroxyzine diHCl Brand Name: Iterax Classification: Antihistamin es & Antiallergics , Anxiolytics
2mg/ml 4ml BID PRN
Hydroxyzin e diHCl is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointes tinal tract and its clinical effects are usually noted within 1530 mins after oral administrat ion. A suppressio n of activity in certain key regions of the subcortical area of the central nervous system.
Symptomatic
treatment of anxiety. Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). As premedication to general anesthesia. Symptomatic treatment of pruritus of allergic origin.
Hypersensitivity to cetirizine & other piperazine derivatives. Intermittent acute porphyria. Pregnancy & lactation. Use cautiously on patients with Glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy, intestinal or urinary obstruction, myasthenia, dementia, convulsions. Predisposition to cardiac arrhythmia. May impair ability to drive or operate machinery.
Anticholinergic Effects: Dry mouth.
CNS Effects: Drowsiness is usually transitory and may disappear in a few days of continued therapy or upon reduction of the dose. Involuntary motor activities including rare instances of tremor and convulsions have been reported, usually with doses considerably higher than those recommended.
Name of Drug
Dosage, Frequency, Route
Mechanism of Action
Indications
Contraindication s
Adverse Effects
Nursing Responsibility
Trade Name:
10mg/tab
Cetirizine hydrochloride
1tab OD
A long-acting, nonsedating antihistamine that selectively inhibits peripheral H1 receptors.
Contraindicated in patients Seasonal allergic hypersensitive rhinitis to drug or to hydroxyzine and in breast-feeding women.
CNS: somnolence, fatigue, dizziness, headache
Per orem Perrenial allergic rhinitis, chronic
EENT: pharyngitis Use cautiously in
Stop drug 4 days before diagnostic skin testing because antihistamines can prevent, reduce, or mask positive skin test response.
urticaria
patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
Brand Name:
GI: dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, abdominal distress
Ainix
Classification:
Antihistamine
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Drug analysis guide for trimetazidine and phenytoinDocument9 pagesDrug analysis guide for trimetazidine and phenytoinJoannalyn Libo-on0% (1)
- Isolation Aids and Gingival Management in DentistryDocument125 pagesIsolation Aids and Gingival Management in DentistryOmanakuttan KrNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Drugs GuideDocument56 pagesRespiratory Drugs GuideIra G. Delos Santos100% (1)
- Empr Prescriber's EditionDocument420 pagesEmpr Prescriber's EditionPatel Pratyk100% (1)
- NCM105 13th PsychopharmacologyDocument17 pagesNCM105 13th PsychopharmacologyKamx MohammedNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyFelecidario TaerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Anxiety: Review ArticleDocument11 pagesAnxiety: Review ArticlePaula Vergara MenesesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 pagesClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Nursing Exam Cram Sheet For The NCLEX-RN: 1. Test Information 5. ABG ValuesDocument8 pagesNursing Exam Cram Sheet For The NCLEX-RN: 1. Test Information 5. ABG ValuesManuela GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyMariCris CaronanNo ratings yet
- Bisoprolol FumarateDocument3 pagesBisoprolol Fumarateapi-37979410% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studykcbabee0333% (3)
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyMaye HerbitoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Related To Psychiatric Nursing PDFDocument14 pagesPharmacology Related To Psychiatric Nursing PDFAnonymous nEQNlgbYQCNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System DrugsDocument64 pagesRespiratory System DrugsArlyn MendenillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies PsychDocument12 pagesDrug Studies PsychAnna Mendiola-BasbasNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac Drug StudyDocument2 pagesKetorolac Drug StudyTimothyMangrobangNo ratings yet
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Omeprazole Mechanism Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing AlertDocument19 pagesOmeprazole Mechanism Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing AlertCzarinah Ela MesiasNo ratings yet
- C C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentDocument12 pagesC C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentEarl Tony TrinidadNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument5 pagesKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyGenny Lou Lumacang OriasNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Antipyretic and Analgesic GuideDocument7 pagesParacetamol Antipyretic and Analgesic GuideAnne Monique Moran OngjocoNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac NSAID Drug StudyDocument5 pagesKetorolac NSAID Drug StudyMary Grace IlaganNo ratings yet
- ANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Document5 pagesANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Rhanne BolanteNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy Last DutyDocument5 pagesDrugstudy Last DutyJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Medication Nurse)Document42 pagesDrug Study (Medication Nurse)Ellen Grace CalayNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Anti-Bacterial CephalosporinDocument9 pagesCefuroxime Anti-Bacterial CephalosporinDustin JohnNo ratings yet
- Pentazine, Phenazine, Phencen,, Phenoject-50, Prometh, Prorex, Prothazine, V-GanDocument34 pagesPentazine, Phenazine, Phencen,, Phenoject-50, Prometh, Prorex, Prothazine, V-GankotonashiNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study For PneumoniaDocument5 pagesDrugs Study For PneumoniaLucelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- 1ST Drug StudyDocument10 pages1ST Drug Study황춘히No ratings yet
- Ampicillin Sulbactam 1.5 gm, Clindamycin Hydrochloride, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg tab, Furosemide 40mg IV, Ipratropium Bromide, Paracetamol 500mg, Tramadol Hydrochloride 500mg IV drug infoDocument10 pagesAmpicillin Sulbactam 1.5 gm, Clindamycin Hydrochloride, Clopidogrel Bisulfate 75 mg tab, Furosemide 40mg IV, Ipratropium Bromide, Paracetamol 500mg, Tramadol Hydrochloride 500mg IV drug infoVictor BiñasNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31No ratings yet
- Acetaminophen and Naproxen Study for ArthritisDocument9 pagesAcetaminophen and Naproxen Study for ArthritisIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Cortex Where Spread of SeizureDocument11 pagesCortex Where Spread of SeizureDustin JohnNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug: Gabapentin: Drug Class Therapeutic ActionsDocument2 pagesName of Drug: Gabapentin: Drug Class Therapeutic ActionsCecile EstebanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY AND SOAPIE SUBMITTEDDocument17 pagesDRUG STUDY AND SOAPIE SUBMITTEDYasi EcheniqueNo ratings yet
- All Kinds of DrugsDocument11 pagesAll Kinds of DrugsRene John Francisco100% (1)
- Ditropan Drug CardDocument2 pagesDitropan Drug CardBenNo ratings yet
- Gabapentin medication guideDocument15 pagesGabapentin medication guideTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug StudyJehannah Dayanara Berdan HayudiniNo ratings yet
- Albuterol sulfate for asthma reliefDocument19 pagesAlbuterol sulfate for asthma reliefCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Mefenamic Acid, Beetab, Esomeprazole Aspirin, Citicoline Plavix)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Mefenamic Acid, Beetab, Esomeprazole Aspirin, Citicoline Plavix)Patricia LuceroNo ratings yet
- Centrally Acting Alpha Agonist Lowers BP & HRDocument4 pagesCentrally Acting Alpha Agonist Lowers BP & HRAriadne MangondatoNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug AnaDocument4 pagesCefuroxime Drug AnaCarpz DarpzNo ratings yet
- Cavite State University drug study on mefenamic acidDocument3 pagesCavite State University drug study on mefenamic acidAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- LM, KLDocument5 pagesLM, KLVictor CondeNo ratings yet
- 5 MG Iv BidDocument17 pages5 MG Iv BidhanzreinherNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- HyosDocument8 pagesHyosAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsnurse_nurseNo ratings yet
- NalbuphineDocument5 pagesNalbuphineGab PagalilauanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument32 pagesDrug StudiesKelly ChanNo ratings yet
- Ventolin Nebulizer for Bronchospasm ReliefDocument10 pagesVentolin Nebulizer for Bronchospasm ReliefmidskiescreamzNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicDocument37 pagesTherapeutic: Urinary Tract Stimulants Pharmacologic: CholinergicApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Relief of gas and bloatingDocument6 pagesRelief of gas and bloatingMichael John Gambong SalaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument4 pagesDrug Study ICUArthadian De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyKynaWeeNo ratings yet
- Drug OrderDocument3 pagesDrug OrderSaima BataloNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Methods of Behaviour Management PedoDocument29 pagesPharmacological Methods of Behaviour Management PedoFourthMolar.com0% (2)
- Pediatric CalculationsDocument43 pagesPediatric CalculationsEros SmithNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity Anaphylaxis Treatment After ReceivingDocument3 pagesHypersensitivity Anaphylaxis Treatment After ReceivingDiah Rahayu SetiawatiNo ratings yet
- Nurdr Practice QuestionsDocument6 pagesNurdr Practice QuestionsSHEENA MAE DE LOS REYESNo ratings yet
- CredibleMeds Filtered QTDrug ListDocument13 pagesCredibleMeds Filtered QTDrug ListJavier Discórides Fernández AbadNo ratings yet
- Part XVIDocument17 pagesPart XVIphp_czarina04421No ratings yet
- Introduction To Biopharmaceutics and PharmacokineticsDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Biopharmaceutics and PharmacokineticsSyeda Eshaal JavaidNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Rationale For The Treatment of Chronic UrticariaDocument10 pagesPharmacological Rationale For The Treatment of Chronic Urticariaseptian88_cahyoNo ratings yet
- PMH Nursing Care Plan 01112017Document19 pagesPMH Nursing Care Plan 01112017api-371817203No ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Disease ED Vasocclusive Crises Pain Management GuidelineDocument1 pageSickle Cell Disease ED Vasocclusive Crises Pain Management GuidelineLakshmanan KrishnamurtiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ko ToDocument4 pagesDrug Study Ko ToGian Carlo FernandezNo ratings yet
- IteraxDocument2 pagesIteraxianecunar100% (2)
- Ortho HypoCase Drug StudyDocument10 pagesOrtho HypoCase Drug StudySolsona Natl HS MaanantengNo ratings yet
- Chronic Neuro Rx: Antiepileptics, Antidepressants & MoreDocument15 pagesChronic Neuro Rx: Antiepileptics, Antidepressants & MoreLarry TenhoffNo ratings yet
- Autacoids and their Antagonists ChapterDocument37 pagesAutacoids and their Antagonists ChapterJayaNo ratings yet
- Medical Dosage Calculations 9th Edition Olsen Test BankDocument38 pagesMedical Dosage Calculations 9th Edition Olsen Test Bankyzaaathib100% (11)
- Dick PharmaDocument10 pagesDick PharmaMaverick LimNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies RationalesDocument10 pagesPharmacological and Parenteral Therapies Rationalesrhymes2u83% (6)
- Chapter 20: Drugs & Drug InteractionsDocument18 pagesChapter 20: Drugs & Drug InteractionspoddataNo ratings yet
- STOP ANTIHISTAMINES 7 DAYS BEFORE ALLERGY SKIN TESTDocument1 pageSTOP ANTIHISTAMINES 7 DAYS BEFORE ALLERGY SKIN TESTCora GougeNo ratings yet
- AutacoidsDocument8 pagesAutacoidsDeity CelleNo ratings yet