Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 1 Review Answers
Uploaded by
helloblargOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 1 Review Answers
Uploaded by
helloblargCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 1 Issue Analysis
Current Issues Related to Organic Chemistry
Student Textbook pages 110111 This performance task provides an excellent opportunity for students to examine the economic and social issues surrounding organic chemistry. Several of the issues listed are current, and students may be able to find relevant information in newspapers and magazines. You may also want to direct the class towards issues involving organic chemistry that are important in your community. When researching information on the Internet, warn students to watch out for web sites containing information that is slanted very strongly towards a certain point of view. Many of these web sites contain inaccurate and incorrect information. Encourage students to form their own opinions using books and web sites that are produced by reputable organizations, and that contain balanced viewpoints.
Assessment and Evaluation
Performance Task Unit 1 Issue: Current Issues Related to Organic Chemistry Curriculum Expectations
I
Assessment Achievement Tools/Techniques Chart Categories
I
Learning Skills
I I I
[OC 3.02] describe the variety and importance of organic compounds in our lives [OC 3.03] analyze the risks and benets of the development and application of synthetic products [OC 3.04] provide examples of the use of organic chemistry to improve technical solutions to existing or newly identied health, safety, and environmental problems
Rubric for Unit 1 Issue (see Assessment Rubrics in the Teachers Resource CD-ROM)
Making Connections
Teamwork Initiative Organization
Unit 1 Review Answers
Student Textbook, pages 112115
Answers to Knowledge/ Understanding Questions
Multiple Choice
1. (d) 2. (c) 3. (a) 4. (a) 5. (d) 6. (c) 7. (d) 8. (e) 9. (a) 10. (c) 11. (d) 12. (e) 13. (b) 14. (c) 15. (d) 16. (c)
Short Answer
17. The term chemical does not necessarily mean harmful
chemical, as implied by this statement. Many healthy foods contain harmless and benecial additives. In any case, food itself is composed of chemicals.
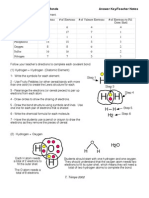
18. An amide contains a C O group joined to a nitrogen
atom, while an amine contains only the nitrogen atom. Examples of the two include ethanamide, CH2CONH2, and ethanamine, CH2CH2NH2.
19. The double bond in an alkene, the triple bond in an
alkyne, and the benzene group in an aromatic hydrocarbon are functional groups.
Chapter 2 Reactions of Organic Compounds MHR
73
UNIT 1 Chapter 2 REACTIONS OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
20. The boiling point of a carboxylic acid will be higher than
(c) 6-ethyl-5-methyl-2-octyne (d) butanamide (e) 6-ethyl-7-methyl-4-decanone (f) 2-ethyl-3-methylcyclohexanol (g) 4,4,6,6-tetramethyl-1-heptanal (h) 4-ethyl-3,5-dimethyl-1-cyclopentene (i) N-ethyl-N-methylethanamide (j) 3,6,7-trimethylcyclononanone 32 (a)
the boiling point of a similarly sized alcohol, due to the particularly strong hydrogen bonding between carboxylic acid molecules.
21. A primary amine has two NH bonds, while a tertiary
amine has none. To form hydrogen bonds, a compound must have an NH, OH, or FH bond.
22. No reaction occurs when an oxidizing agent is added to a
tertiary alcohol. Tertiary alcohols do not have a CH bond to be broken at the oxidizing site.
23. When an oxidizing agent is added to a secondary alcohol,
the alcohol is oxidized to form a ketone. 24. Ethanol is also called grain alcohol.
25. The IUPAC name for acetic acid is ethanoic acid. 26. The carbonyl group of an aldehyde is always located on (b)
The correct name is 4-methyl-2-heptanone.
the rst carbon atom of the chain, so no position number is necessary.
27. The rst product is 3-ethyl-4-methylhexanal, and the
Tthe correct name is 3,3-dimethylhexane.
(c)
OH
second is 3-ethyl-4-methyl hexanoic acid.
O OH The correct name is 2,5-octanediol.
33. The nger dipped into the 2-propanol (rubbing alcohol) 3-ethyl-4-methylhexanal
O OH
3-ethyl-4-methylhexanoic acid
will feel cooler. Both 2-propanol and water form hydrogen bonds. A water molecule has two OH bonds, while a 2-propanol molecule has one. Therefore, 2-propanol has weaker hydrogen bonding and a lower boiling point than water, and will evaporate faster, making your nger feel cooler.
34. The 1-pentanol will undergo an oxidation reaction with
Answers to Inquiry Questions
28. (a) butanoic acid (b) methanol (c) methyl pentanoate (d) 2-butanone (e) N-methylethanamine (f) 4,5-dimethylheptanal 29. (a) wood alcohol (b) rubbing alcohol (c) diethyl ether 30. (a) 3-ethyl-4-methyl-1-hexene (b) methoxypropane (c) 3-methyl-1-pentanamine (d) 5-ethyl-3,7,9-trimethyl-2-decanol (e) butyl propanoate 31. (a) 5-methyloctanoic acid (b) N-ethyl-1-butanamine
acidied potassium permanganate, but the pentanoic acid will not. Also, the boiling point of pentanoic acid will be higher than that of 1-pentanol. 34. Ethanol is miscible with water, while the other two are non-polar and will not dissolve. Use this fact to identify the ethanol. Next, react the two hydrocarbons with bromine. 2,4-hexadiene will react with the bromine, so that the bromine colour disappears. Benzene requires a catalyst to react. 36. (a) 2,3-diiodopentane, CH3CH2CH(I)CH(I)CH3
(b) 1-chloropropane, CH3CH2CH2Cl water, H2O (c) 2-methylpropanoic acid, CH3CH(CH3)COOH
(d) propyl methanoate, HCOOCH2CH2CH3 water, H2O (e) 1-heptene, CH2 CHCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 water, H2O
37. (a) 2-propanol (major), CH3CH(OH)CH3
1-propanol
(minor), CH3CH2CH2OH
(b) 1-propanol, CH3CH2CH2OH
decanoic acid, CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COOH (c) 3-methyl-1-butanol, CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2OH hydrobromic acid, HBr
74
MHR Unit 1 Organic Chemistry
(d) propanone, CH3COCH3 (e) 1,3-dichlorobutane (major), CH3CH(Cl)CH2CH2Cl
40. (a)
O O
1,4-dichlorobutane (minor), ClCH2CH2CH2CH2Cl water, H2O
CH3
(b)
38. (a) ethyne, HCCH (b)
O CH3 CH2 CH2 CH CH2 Cl
(c) 1-chloro-2-methylpentane (c)
OH O O OH
(d)
CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
1-butanol (d)
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2C
heptanoic acid
O N
O CH3 CH CH3
2-methylpropanoic acid
(e)
OH
41. Nylon-6 is made from the polymerization of a single
(e)
molecule, caprolactam, as shown below.
O CH3 n NH NH (CH2)5 O C NH (CH2)5 O C
OH CH3 CH CH3 CH CH2
CH3 C CH3
3-ethyl-4,4-dimethyl-2-pentanol
caprolactam
Nylon6
Answers to Communication Questions
39. (a) CH3NH2 (b)
OH
(c)
Nylon was intended as a substitute for silk. When Nylon6,6 was invented in the 1930s, it was used for toothbrush bristles and stockings, among other uses. (Nylon-6 was invented shortly afterwards.) During the war, nylon was used to make parachutes. (Note: Useful Internet search words include nylon 6 polymerization caprolactam and nylon invention Carothers.)
Cl
(d)
Cl NH2
(e)
O O
Chapter 2 Reactions of Organic Compounds MHR
75
You might also like
- Tutorial 8Document11 pagesTutorial 8Ahmad WahideeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8: Determination of An Equilibrium Constant: PurposeDocument10 pagesExperiment 8: Determination of An Equilibrium Constant: PurposeJohn Joseph0% (1)
- CAIE Chemistry A-Level: 24: ElectrochemistryDocument8 pagesCAIE Chemistry A-Level: 24: ElectrochemistryahumanbeinginearthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2helloblargNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry Qs: Fischer, R/S, ID pairs, Optical ActivityDocument2 pagesStereochemistry Qs: Fischer, R/S, ID pairs, Optical ActivityShilajit BaruaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols LabDocument7 pagesAlcohols Lab7sky7harveyNo ratings yet
- SCH4C Organic Chem Test Cheat SheetDocument1 pageSCH4C Organic Chem Test Cheat SheetSteve M Hall50% (2)
- Acid Base Titration ExperimentDocument2 pagesAcid Base Titration ExperimentDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Practice Test Answers 4u1Document1 pageChapter 8 Practice Test Answers 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- 19.2 Acid-Base Titration CurvesDocument9 pages19.2 Acid-Base Titration CurvesYuyun Sri IriantiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Practice Test 4u1Document1 pageChapter 8 Practice Test 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- T10 QuestionsDocument20 pagesT10 Questionsleafar96100% (4)
- Organic Reactions and MechanismsDocument38 pagesOrganic Reactions and Mechanismszarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- EsterificationDocument7 pagesEsterificationsushmakumari009No ratings yet
- F325 Acids and PHDocument19 pagesF325 Acids and PHDoc_CrocNo ratings yet
- Alcohols-Phenols and EthersDocument16 pagesAlcohols-Phenols and EthersTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- H2 Equilibrium and Ideal GasDocument9 pagesH2 Equilibrium and Ideal GaskitoniumNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases NotesDocument10 pagesAcids and Bases NotesThaarvena RetinaNo ratings yet
- Aromaticity CompleteDocument104 pagesAromaticity Completewahidalwahdi100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Practice TestDocument2 pagesChapter 7 Practice TesthelloblargNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8: Reduction of 4-T-Butylcyclohexanone With Sodium BorohydrideDocument7 pagesExperiment 8: Reduction of 4-T-Butylcyclohexanone With Sodium BorohydrideNorazma ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- McMurry Chapter 2: Polar Covalent Bonds and Acid-Base ConceptsDocument44 pagesMcMurry Chapter 2: Polar Covalent Bonds and Acid-Base ConceptsKirilKocevskiNo ratings yet
- Hydroxy CompoundsDocument9 pagesHydroxy Compoundschong56No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document30 pagesChapter 4helloblargNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Containing Organic CompoundsDocument9 pagesOxygen Containing Organic CompoundsmNo ratings yet
- Aromaticity NotesDocument6 pagesAromaticity NotesSLIMBOI OpNo ratings yet
- Alcohols & Phenols:: GeneralizationsDocument27 pagesAlcohols & Phenols:: GeneralizationsdoudoudoudouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Acid and BaseDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Acid and BaseKelsi Kyla PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry: Chapter OutlineDocument68 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry: Chapter OutlineMaden betoNo ratings yet
- F325 Redox Equations and TitrationsDocument9 pagesF325 Redox Equations and TitrationsDoc_Croc100% (1)
- Chapter 8Document31 pagesChapter 8helloblarg100% (4)
- Identification of Ketones and Aldehydes Using Chemical TestsDocument10 pagesIdentification of Ketones and Aldehydes Using Chemical TestsManjeeta Mandlik0% (1)
- Cape Chemistry Unit Ii Module I Alcohols and Phenol and Alkenes Worksheet and Revision GuideDocument10 pagesCape Chemistry Unit Ii Module I Alcohols and Phenol and Alkenes Worksheet and Revision GuideAshli GrantNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Reactive Intermediate FinalDocument38 pagesChemistry of Reactive Intermediate FinalTefera100% (1)
- Kineticsss Notes PDFDocument73 pagesKineticsss Notes PDFArun SharmaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Answers: Functional Groups, Isomerism and Physical PropertiesDocument26 pagesOrganic Chemistry Answers: Functional Groups, Isomerism and Physical PropertiesVictor HuangNo ratings yet
- Molecular Polarity: AP ChemistryDocument13 pagesMolecular Polarity: AP ChemistryArvie Guevarra ToqueroNo ratings yet
- Chem 350 Jasperse Ch. 6 SummaryDocument29 pagesChem 350 Jasperse Ch. 6 SummaryAhmed SideegNo ratings yet
- CH2.2 - AlkeneDocument48 pagesCH2.2 - AlkeneNur Ain SyuhadaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formulae and Equations Part 2Document18 pagesChemical Formulae and Equations Part 2Mohd NorihwanNo ratings yet
- Day 2 - Introduction To Stoichiometry Guided Notes AssignmentDocument15 pagesDay 2 - Introduction To Stoichiometry Guided Notes AssignmentDaveNo ratings yet
- Constitution of AlloysDocument4 pagesConstitution of AlloysKancharla KiranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Further Aspects of EquilibriaDocument6 pagesChapter 21 Further Aspects of EquilibriaAndrea MelissaNo ratings yet
- Chem Extra Grade11Document4 pagesChem Extra Grade11Lakshmi DesikanNo ratings yet
- 1.6 BondingDocument17 pages1.6 BondingMahmoud TahaNo ratings yet
- Bonding Basics CovalentDocument2 pagesBonding Basics Covalentwosli350% (2)
- Lab Polymer - SlimeDocument4 pagesLab Polymer - SlimeThats Gone WrongNo ratings yet
- Chem12 SM 01 4Document4 pagesChem12 SM 01 4Firdausia Rahma PutriNo ratings yet
- Chemitry NotesDocument6 pagesChemitry NotesRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Alkanes McqsDocument2 pagesAlkanes McqsMuhammad Ahtisham AsifNo ratings yet
- 03 Organic Chemistry Introduction 2Document126 pages03 Organic Chemistry Introduction 2Hamid Hussain HamidNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Notes IiDocument9 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Notes IiJabez MatigaNo ratings yet
- Grade9 Alcohols & Carboxylic Acids NotesDocument8 pagesGrade9 Alcohols & Carboxylic Acids Notesnobody impNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base TitrationDocument16 pagesAcid-Base TitrationChloe KittyNo ratings yet
- Resonance Structure WorksheetDocument3 pagesResonance Structure WorksheethbjvghcgNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Ncert Ch09 Coordination Compounds Part 01 QuesDocument43 pages12 Chemistry Ncert Ch09 Coordination Compounds Part 01 Queshumayun khalidNo ratings yet
- 02 - Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument48 pages02 - Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingAyulia Annisa100% (1)
- AP Chemistry - Rate Law Determination of Crystal Violet ReactionDocument13 pagesAP Chemistry - Rate Law Determination of Crystal Violet ReactionRyan PanNo ratings yet
- Post16organicsynthesisquizv1 322597Document19 pagesPost16organicsynthesisquizv1 322597diceplayaaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Lesson 1 AnswersDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Lesson 1 AnswersShazara MohammedNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Number Balancing 4u1Document1 pageOxidation Number Balancing 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Net Ionic and Half Reactions 4u1Document2 pagesNet Ionic and Half Reactions 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Half Reactions Balancing 4u1Document1 pageHalf Reactions Balancing 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Practice TestDocument2 pagesChapter 7 Practice TesthelloblargNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Practice Test AnswersDocument1 pageCH 7 Practice Test AnswershelloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Practice Test 4u1Document3 pagesChapter 10 Practice Test 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Practice Test 4u1Document3 pagesChapter 10 Practice Test 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Practice Test 4u1Document1 pageChapter 8 Practice Test 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Solution Chemistry Basics Ch8 4u1Document2 pagesSolution Chemistry Basics Ch8 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Illustrating EquilibriumDocument1 pageIllustrating EquilibriumhelloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Practice Test Answers 4u1Document1 pageChapter 8 Practice Test Answers 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 Review Problem AnswersDocument4 pagesChapter7 Review Problem AnswershelloblargNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy of NeutralizationDocument2 pagesEnthalpy of NeutralizationhelloblargNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Review SolutionsDocument5 pagesUnit 3 Review SolutionshelloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 Equilibrium PP AnswersDocument15 pagesChapter7 Equilibrium PP Answershelloblarg50% (2)
- Molecular Shape and Polarity Ch4 4u1Document1 pageMolecular Shape and Polarity Ch4 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Theories Ch8 4u1Document1 pageAcid Base Theories Ch8 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Rate Law QuestionsDocument3 pagesRate Law QuestionshelloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 Review ProblemsDocument3 pagesChapter5 Review ProblemshelloblargNo ratings yet
- Heat Equations and StoichiometryDocument3 pagesHeat Equations and StoichiometryhelloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 TestDocument5 pagesChapter 6 TesthelloblargNo ratings yet
- Potential Energy QuestionsDocument3 pagesPotential Energy QuestionshelloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Review SolutionsDocument3 pagesChapter 6 Review SolutionshelloblargNo ratings yet
- Ch6 Sheets AnswersDocument2 pagesCh6 Sheets Answershelloblarg100% (2)
- Chapter 5 TestDocument4 pagesChapter 5 TesthelloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Practice Test Answers 4u1Document2 pagesChapter 3 Practice Test Answers 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Sheets AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter 5 Sheets AnswershelloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Practice Test 4u1Document5 pagesChapter 3 Practice Test 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Practice Test 4u1Document4 pagesChapter 4 Practice Test 4u1helloblargNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Review AnswersDocument5 pagesChapter4 Review AnswershelloblargNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Synthesis and Analytical TechniquesDocument32 pagesQuestion Paper Synthesis and Analytical TechniquesrajksdNo ratings yet
- Uop Teuop-Tech-And-More-Air-Separation-Adsorbents-Articlech and More Air Separation Adsorbents ArticleDocument8 pagesUop Teuop-Tech-And-More-Air-Separation-Adsorbents-Articlech and More Air Separation Adsorbents ArticleRoo FaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of LipidDocument6 pagesAnalysis of LipidanaNo ratings yet
- Formulae, Equations, Amounts of Substance (Multiple Choice) 1 QPDocument19 pagesFormulae, Equations, Amounts of Substance (Multiple Choice) 1 QPveronica burlacuNo ratings yet
- Dyeing Wool and Cotton with Malachite GreenDocument7 pagesDyeing Wool and Cotton with Malachite GreenpeeyushNo ratings yet
- A. Continuous vs. Semi-Continuous vs. Discontinuous Solvent ExtractionDocument2 pagesA. Continuous vs. Semi-Continuous vs. Discontinuous Solvent ExtractionHayleyNo ratings yet
- UPS Chemical Table - ICAO/IATA Version (U.S. Air PackagesDocument146 pagesUPS Chemical Table - ICAO/IATA Version (U.S. Air PackagesgeorgevoommenNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of CoumarinDocument2 pagesSynthesis of CoumarinMilan VadodariaNo ratings yet
- Aim To Prepare A Sample of Cuprammonium Rayon Threads From Filter Paper Apparatus Required ADocument11 pagesAim To Prepare A Sample of Cuprammonium Rayon Threads From Filter Paper Apparatus Required ANitinAgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Chem. Imp. QuestionsDocument16 pagesChem. Imp. QuestionsHimanshu NikhurpaNo ratings yet
- Directed C H Functionalization of C3-Aldehyde, Ketone, and Acid/ Ester-Substituted Free (NH) Indoles With Iodoarenes Via A Palladium Catalyst SystemDocument20 pagesDirected C H Functionalization of C3-Aldehyde, Ketone, and Acid/ Ester-Substituted Free (NH) Indoles With Iodoarenes Via A Palladium Catalyst SystemMutiva YyNo ratings yet
- Preparation of An EsterDocument5 pagesPreparation of An EsterKojo Eghan100% (1)
- Reactions of Copper (Edited, 10 Sept 2023)Document5 pagesReactions of Copper (Edited, 10 Sept 2023)Rose-AnnMirambilNo ratings yet
- Valency Table PDFDocument1 pageValency Table PDFrkrishna4467% (15)
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry I Lab ManualDocument57 pagesPharmaceutical Organic Chemistry I Lab ManualDeep Mali100% (1)
- BayabasDocument5 pagesBayabasBTS ARMYNo ratings yet
- Amount of Substance Worksheet SolutionsDocument5 pagesAmount of Substance Worksheet SolutionsTai PanNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers For Chemistry STPM Section ADocument8 pagesSuggested Answers For Chemistry STPM Section ASong Sing LikNo ratings yet
- Reactivity Series WorksheetDocument6 pagesReactivity Series WorksheetjanithaNo ratings yet
- Tub & Tile Cleaners - 031Document2 pagesTub & Tile Cleaners - 031mndmattNo ratings yet
- AFCONA - Universal Pigment Concentrate ConceptDocument13 pagesAFCONA - Universal Pigment Concentrate ConceptAelya SanNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.xphs.2017.02.006Document52 pagesAccepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.xphs.2017.02.006Cristhian Javier YarceNo ratings yet
- AlkaloidsDocument15 pagesAlkaloidsAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions Detailed Worksheet Extra EditedDocument5 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions Detailed Worksheet Extra EditedBayot KuhNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Polymers-03 - Assignments (New)Document11 pagesBiomolecules and Polymers-03 - Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Desalting OverviewDocument9 pagesDesalting OverviewSampat100% (1)
- Fe HbedDocument6 pagesFe HbedMuhammad Iqbal ChandioNo ratings yet
- Catálogo Llaberia Plàstics PE - C - EN 2010 PDFDocument67 pagesCatálogo Llaberia Plàstics PE - C - EN 2010 PDFmeka_nathNo ratings yet
- Corbonyl CompOUND AND Corboxilic AcidDocument12 pagesCorbonyl CompOUND AND Corboxilic AcidApex InstituteNo ratings yet
- Organometallic Reagents: Carbon-Metal BondsDocument41 pagesOrganometallic Reagents: Carbon-Metal BondsAldi JonataNo ratings yet