Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Blesyl Sison MabanoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Blesyl Sison MabanoCopyright:
Available Formats
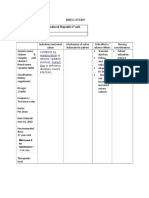
DRUG STUDY Name of Patient Diagnosis Doctor Mechanism of Action Pharmacokinetics: Onset, Duration: unknown Peak: Immediate Absorption:
Absorbed from the GI tract with peak plasma concentrations after 2-3 hr (oral); may be enhanced by the presence of food. Distribution: Pleural and synovial fluid, sputum, bone and aqueous fluids; CSF (therapeutic concentrations). Crosses the placenta and enters breast milk. Protein-binding: Up to 50%. Metabolism: Rapidly hydrolysed (intestinal mucosa and blood). Excretion: Via the urine by glomerular filtration and renal tubular secretion (as unchanged); via bile Age Sex Date of Admission Height Weight Body Build Nursing Responsibilities Before: 1. Consider 10 rights of drug administration. 2. Assess for hypersensitivity. 3. sensitivity tests 4. Obtain hepatic and renal impairment, 5. Consider dugs interaction. 6. For each 750mg vial of Zinacef, reconstitute with 8ml sterile water During: 1. Inject into tubing of free-flowing I.V. solution over 3-5 mins 2. `For intermittent infusion, add reconstituted drug to 100 ml D5W, normal saline solution for injection. Infuse over 15-60 mins. 3. Incompatible with aminoglycosides, ciprofloxacin, clarithromycin, filgrastim, fluconazole, midazolam 4. Discontinue if
Drug Data Generic Name: cefuroxime Trade name: Aeruginox, Altacef, Ambixime, Bactipoz, Cefogen,Ceftin, Cefucil, Cefuzime, Zefur, Zinacef, Zinnat Patients Dosage:
Classification Pharmacologic: secondgeneration cephalosporin Therapeutic: Antibiotic Category: B
Indication General: - Lower respiratory infections - Dermatologic infections - UTIs - Uncomplicated and disseminated gonorrhea - Septicemia - Meningitis - Bone and joint infections - Perioperative prophylaxis - Treatment of acute bacterial maxillary sinusitis in patients 3 mo12 yr Patients Indication:
Contraindications Contraindications: -hypersensitivity to drugs and its components Precautions: - renal impairment -children less than 2 years of age Drug Interactions: Diuretics: Increase risk of adverse renal reactions Probenecid: Inhibit excretion and increase level of cefuroxime
Adverse Reaction GI: abdominal cramps, anal pruritus, anorexia, diarrhea, dyspepsia, glossitis, nausea GU: genital pruritus, and candidiasis Skin: maculopapular and erythematous rashes, urticaria Hema: eosinophilia, hemolytic anemia Respiratory: dyspnea CNS: dizziness, headache, malaise, paresthesia
Availability: Infusion: 750mg, 1.fg premixed, frozen solution Injection: 750 mg, 1.5g Minimum Dosage: 75-100 mg/kg/day Maximum Dosage: 8 g/day Route of administration: IVTT
(small amounts); 70 min (elimination halflife); prolonged in neonates and renal impairment. Pharmacodynamics: binds to one or more of the penicillinbinding proteins (PBPs) which inhibits the final transpeptidation step of peptidoglycan synthesis in bacterial cell wall, thus inhibiting biosynthesis and arresting cell wall assembly resulting in bacterial cell death. Source: http://RNpedia.com- Nursing Notes and Community
hypersensitivity reaction occurs. 5. Monitor clients clinical response. After: 1. Teach patient about drugs side effect. 2. Encourage patient Comply religiously the full course of therapy. 3. Report severe diarrhea, difficulty breathing, unusual tiredness or fatigue, pain at injection site. 4. Promote comfort measures. 5. Assess patient's condition thereafter the therapy.
You might also like
- Drug Study (CELECOXIB)Document1 pageDrug Study (CELECOXIB)Angela Mae Cabajar100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyBlesyl Sison MabanoNo ratings yet
- Statutory Construction NotesDocument32 pagesStatutory Construction Notespriam gabriel d salidaga95% (102)
- Hepatic FailureDocument37 pagesHepatic FailureWinston Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Propiverine HCl Brand Name: Mictonorm Classification: Urinary AntispasmodicDocument7 pagesGeneric Name: Propiverine HCl Brand Name: Mictonorm Classification: Urinary AntispasmodicMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- DS KetosterilDocument1 pageDS KetosteriljessicamaysNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Captopril CefuroximeDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Captopril CefuroximeJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Dexamethasone (Decilone)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Dexamethasone (Decilone)mikErlhNo ratings yet
- Celecoxib CelebrexDocument1 pageCelecoxib CelebrexBeverly Ann de LeonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AspirinDocument1 pageDrug Study AspirinMaria Charis Anne Indanan100% (1)
- Drug Study - GDM - Caltrate PlusDocument2 pagesDrug Study - GDM - Caltrate PlusGAYOL BREEN IRAH A.No ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument1 pageSodium BicarbonateALbinong VelascoNo ratings yet
- Ferlin PDFDocument1 pageFerlin PDFRomeo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Voltaren@cefuroxime (Kefox)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Voltaren@cefuroxime (Kefox)Claudette CayetanoNo ratings yet
- LansoprazoleDocument3 pagesLansoprazoleJody FelizioNo ratings yet
- Opstres Maalox Benutrex-C Paracetamol Essentiale Forte BactidolDocument6 pagesOpstres Maalox Benutrex-C Paracetamol Essentiale Forte Bactidolpark nisseNo ratings yet
- Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Document1 pageLexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Famotidine: Maintenance Therapy For Duodenal Ulcer Patients at Reduced Dosage After Healing of An Active UlcerDocument2 pagesFamotidine: Maintenance Therapy For Duodenal Ulcer Patients at Reduced Dosage After Healing of An Active Ulcerangeleigh viernesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SummaryDocument7 pagesDrug Study SummaryKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesTramadol Drug StudyJust A Nsg StudentNo ratings yet
- High Risk PreschoolerDocument7 pagesHigh Risk PreschoolerAngela Del CastilloNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine CPDocument2 pagesAmlodipine CPRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- OB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesOB Drug Study - Mefenamic AcidJustin Ancog100% (1)
- Setraline Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSetraline Drug StudyOtaku MiyoNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesMechanism of Action and Nursing ResponsibilitiesMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- ILOILO DOCTORS’ COLLEGE COLLEGE OF NURSING Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesILOILO DOCTORS’ COLLEGE COLLEGE OF NURSING Ferrous SulfatePauline AnesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Vitamin C + ZincDocument2 pagesDrug Study Vitamin C + ZincKrizzia FosterNo ratings yet
- Kremil S Drug StudyDocument1 pageKremil S Drug StudyDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDrug Study CefuroximeTipey Segismundo100% (1)
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument3 pagesNifedipineNovi YulianaNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument4 pagesDischarge PlanVillanueva NiñaNo ratings yet
- MANNITOL Drug StudyDocument5 pagesMANNITOL Drug StudyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Vit K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVit K Drug StudyKrisha AristonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - IbuprofenDocument3 pagesDrug Study - IbuprofenThalia UyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Table 3Document5 pagesDrug Study Table 3Juliet De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ferrous SulfateBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug SoludexideDocument2 pagesName of Drug SoludexideSian AsadaNo ratings yet
- Impaired Urinary EliminatonDocument5 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminatonLoriejae Marie DesulocNo ratings yet
- ItoprideDocument2 pagesItoprideLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Nursing Role in Reproductive and Sexual HealthDocument10 pages3 - Nursing Role in Reproductive and Sexual HealthShanealle Athaliah Magsalay CuaNo ratings yet
- TB DrugsDocument14 pagesTB DrugsLexy CadigalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDrug Study - FurosemideryanNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin Dosage Indications Adverse Effects NursingDocument1 pageAzithromycin Dosage Indications Adverse Effects NursingGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- D50WDocument1 pageD50WElizalde Husband100% (1)
- CEFUROXIMEDocument2 pagesCEFUROXIMEMelvz BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Treatment/ Infusion d5lrDocument1 pageTreatment/ Infusion d5lrjbespirituNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudymYiE23No ratings yet
- PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesPrednisoloneKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyAldrin Ian Oraza AlpeNo ratings yet
- Drug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationDocument2 pagesDrug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationart_mutantNo ratings yet
- Drug Study IsoniazidDocument1 pageDrug Study IsoniazidEphraim MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Furosemide ChlorthalidoneDocument5 pagesFurosemide ChlorthalidoneLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Timolol MaleateDocument3 pagesTimolol MaleateAP TOROBXNo ratings yet
- DuphalacDocument2 pagesDuphalacianecunarNo ratings yet
- Tetracycline Drug StudyDocument5 pagesTetracycline Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- AldazideDocument2 pagesAldazideianecunarNo ratings yet
- Name: Sophia Angela Famor BSN12EDocument4 pagesName: Sophia Angela Famor BSN12EZumi IskakNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument8 pagesGeneric Namemel aquinoNo ratings yet
- NCP Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNCP Drug StudyArthadian De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Cefazolin AncefDocument4 pagesCefazolin AncefAmanda La SalaNo ratings yet
- LanguageDocument1 pageLanguageBlesyl Sison MabanoNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument1 pageTable of ContentsBlesyl Sison MabanoNo ratings yet
- THE PRACTICE (Season 2 Episode 13) : ST NDDocument1 pageTHE PRACTICE (Season 2 Episode 13) : ST NDBlesyl Sison MabanoNo ratings yet
- LanguageDocument1 pageLanguageBlesyl Sison MabanoNo ratings yet
- European Convention On Human RightsDocument2 pagesEuropean Convention On Human RightsBlesyl Sison MabanoNo ratings yet
- Quinto Vs ComelecDocument53 pagesQuinto Vs ComelecBlesyl Sison MabanoNo ratings yet
- Statutory ConstructionDocument11 pagesStatutory ConstructionBlesyl Sison MabanoNo ratings yet
- Statutory ConstructionDocument11 pagesStatutory ConstructionBlesyl Sison MabanoNo ratings yet
- Social Contract TheoryDocument15 pagesSocial Contract TheoryBlesyl Sison MabanoNo ratings yet
- Phil Judges Association Vs PradoDocument5 pagesPhil Judges Association Vs PradoBlesyl Sison Mabano0% (1)
- A. IntroductionDocument2 pagesA. IntroductionBlesyl Sison MabanoNo ratings yet
- List of Cases Consti I.forprintingDocument1 pageList of Cases Consti I.forprintingBlesyl Sison MabanoNo ratings yet
- Increase FBSDocument1 pageIncrease FBSBlesyl Sison MabanoNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument2 pagesParacetamolBlesyl Sison Mabano100% (1)