Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practical 11
Uploaded by
Piyush JainOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Practical 11
Uploaded by
Piyush JainCopyright:
Available Formats
PRACTICAL 11 Object:- To convert a galvanometer into ammeter of a given range and to calibrate it.
Apparatus:- given galvanometer, lead accumulator, high resistance box, low resistance box, rheostat, two keys etc. Formula:- the value of shunt required to be connected in parallel to galvanometer coil is given byi. S = ig/(i-ig)G
Thus, with a shunt S of above value, the galvanometer will become an Ammeter of range I ampere. If I is the required length of the shunt wire of radius r and specific resistance , then S= l/r
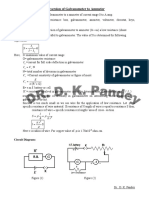
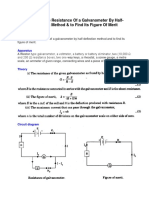
Procedure:Determination of Galvanometer Resistance (G) and the value of ig 1. Make the circuit connection in order to determine the resistance of the galvanometer by half deflection method. 2. Introduce some high resistance Rh in the high resistance box H.R.B. close to key K1 and observe deflection in the galvanometer. If the deflection goes out of the scale bring it within the scale by increasing the value of Rh. Adjust the deflection for even number of division on the scale. In this adjustment the key K2 should remain open. 3. Now close key K2. Increase the value of R in the low resistance box. Adjust the value of R such that the deflection in galvanometer becomes half of its previous value. 4. Now change the value of deflection in the galvanometer by changing the value of Rh. For each value of Rh adjust the value of R for half deflection in the galvanometer. In this way take about five sets of reading. 5. Determine the value of G from each set and determine mean G. 6. Calculate the value of ig for each set from its formula and determine mean ig. Determination of Shunt Resistance (S) and its desired length (l) 1. Determine the value of Shunt resistance(S) from EQ. using the values of galvanometer resistance(G). ig and the given range of ammeter.
2. Knowing the values of radius of shunt wire and its respectively, the desired length of shunt wire can be calculated
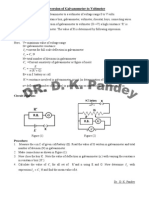
Calibration of converted Ammeter 1. Take the shunt wire of desired length and connect it across the terminals of the galvanometer. By doing so, the galvanometer is converted into the ammeter of range i. 2. Make circuit as shown in fig. in order to calibrate the converted ammeter.
3. Close the key K. Adjust the rheostat Rh to get some current in the circuit. Note this value of current in the ammeter A. simultaneously note the deflection of the converted ammeter in number of divisions of the ammeter. 4. Now change the position of the rheostat and again note the readings of the ammeter. In this way take sufficient number of readings up to the full range of the ammeter. 5. If the readings of the ammeter for a particular value of current in the circuit is I and the number of division in the converted ammeter is n for the Same value of current ,then the value of current in the converted ammeter will be i^n = (n/N) I ampere. 6. Determine the value of I and I for various readings taken. This difference will be error in the reading of converted ammeter. 7. The graph plotted between I and the error (I-I) will be the calibration graph. OBSERVATION |A| to determine the galvanometer resistance (G), current for full scale deflection in the galvanometer (ig) and shunt resistance (S): 1. No. of divisions on the galvanometer scale N=. 2. E.M.F. of the battery=volt
S.No.
High resistanc e Rh(ohm)
Deflection in galvanome ter =n divisions
Resistan ce for half deflectio n R=G(oh m)
Mean G (ohm)
Ig=(E/(R+G)) (N/n) Ampere
Mean ig (Ampere )
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
|B|
to determine the radius of wire (r ) and its desired length(l): 1. Specific resistance of material of wire()=. Ohm-cm 2. Measurement of radius of wire Pitch of screw gauge=cm Least count of screw gauge=..cm
S.No.
Diameter in one direction(cm)
Diameter in perpendicular direction(cm)
Mean diameter(cm)
Mean radius(cm)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
|C| S.No.
calibration of converted ammeter Ammeter reading I No. of deflection on galvanometer scale(n) Current measured by converted ammeter Error=(I-I) (amp)
I =(n/N)I (amp) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.
Calculations Range of converted galvanometer as ammeter(i)=..Amp Resistance of galvanometer=.Amp 1. Ig=(E/(Rh+G))(N/n)Amp=.Amp 2. Shunt resistance S=igG/(i-ig)=.ohm 3. Desired length of shunt wire l=sr^2/=..amp
You might also like
- High Level Cyber Security Assessment - Detailed ReportDocument57 pagesHigh Level Cyber Security Assessment - Detailed Reportdobie_e_martinNo ratings yet
- Mastercam Book 5 Axis Bai 1Document31 pagesMastercam Book 5 Axis Bai 1tuanvn76100% (3)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- 1SM6 2015Document63 pages1SM6 2015chikoo499No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project 1Document9 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project 1subham singh86% (7)
- BS en 12583 - 2014 - Gas Infrastructure. Compressor Stations. Functional Requirements.Document56 pagesBS en 12583 - 2014 - Gas Infrastructure. Compressor Stations. Functional Requirements.SDP02No ratings yet
- Flutter Layout Cheat SheetDocument11 pagesFlutter Layout Cheat SheetJarrett Yew0% (1)
- Eco Schools Action PlanDocument1 pageEco Schools Action PlanJohnty GreentoesNo ratings yet
- Ventilation Plan For Confined Space EntryDocument9 pagesVentilation Plan For Confined Space EntryMohamad Nazmi Mohamad Rafian100% (1)
- Physics Project On Convertion of Gslvanometer To AmmeterDocument19 pagesPhysics Project On Convertion of Gslvanometer To AmmeterSHIWANI MOHAN88% (8)
- Galvanometer To Ammeter PDFDocument2 pagesGalvanometer To Ammeter PDFMegha SaranNo ratings yet
- Vigilance MattersDocument6 pagesVigilance MattersAnonymous CVKDY65OGNo ratings yet
- Galvanometer To VoltmeterDocument2 pagesGalvanometer To Voltmeterfaizmustafa67No ratings yet
- Sensitivity TestDocument12 pagesSensitivity Testratnaraj_kanungoeNo ratings yet
- GALVANOMTER DEMONSTRATIONDocument14 pagesGALVANOMTER DEMONSTRATIONRose ytNo ratings yet
- Conversion of GalvanometerDocument13 pagesConversion of GalvanometerSimar Kaur100% (1)
- S.Y. Resistance of A Galvanometer G by Shunting GR - IIDocument2 pagesS.Y. Resistance of A Galvanometer G by Shunting GR - IINeelam KapoorNo ratings yet
- Convert Galvanometer into AmmeterDocument4 pagesConvert Galvanometer into AmmeterSulman Abbasi0% (2)
- Physics Practical March 2022-1Document20 pagesPhysics Practical March 2022-1deepakrambhakt07No ratings yet
- 07 Galvanometer - 2Document2 pages07 Galvanometer - 2Muhammad SufyanNo ratings yet
- 1082-LAB 10 Voltmeters and AmmetersDocument9 pages1082-LAB 10 Voltmeters and AmmetersNghi TranNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document4 pagesExperiment 3Kabir AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Convertion of Gslvanometer To AmmeterDocument15 pagesPhysics Project On Convertion of Gslvanometer To Ammeterharshilsapariya501No ratings yet
- ConversionDocument2 pagesConversionmurugeshkasthuri786No ratings yet
- Physics Project On Convertion of Gslvanometer To AmmeterDocument19 pagesPhysics Project On Convertion of Gslvanometer To AmmeterAbhi SableNo ratings yet
- Measure Small Currents Using a GalvanometerDocument8 pagesMeasure Small Currents Using a GalvanometerAnkit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 2022-23 Phy Lab Manual Class 12Document32 pages2022-23 Phy Lab Manual Class 12Rasu 789No ratings yet
- Conversion of Galvanometer To Ammeter PracticalDocument4 pagesConversion of Galvanometer To Ammeter Practicaldipu21250% (2)
- Expt 4 PhysicDocument1 pageExpt 4 Physic•Mr Ravi•No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument12 pagesPhysicsshuvanita2006dasNo ratings yet
- Expt No 05Document3 pagesExpt No 05rajasmitabal781No ratings yet
- Determine Galvanometer Resistance & Figure of MeritDocument4 pagesDetermine Galvanometer Resistance & Figure of MeritPriyanshu Kumar100% (4)
- Physics Practical Notes: Determining Resistance of GalvanometerDocument13 pagesPhysics Practical Notes: Determining Resistance of GalvanometerSivaRamaKrishnan R.No ratings yet
- Analog Measuring InstrumentsDocument43 pagesAnalog Measuring Instrumentsmuvvala charithaNo ratings yet
- Physics KabaDocument24 pagesPhysics KabaPrahlad ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- GalvanometerDocument4 pagesGalvanometersemabayNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Report #3Document6 pagesPhysics Lab Report #3231152No ratings yet
- Physics Lab Report 3Document5 pagesPhysics Lab Report 3usmanNo ratings yet
- AIR UIVERSITY AneesDocument7 pagesAIR UIVERSITY AneesAnees Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Phy 4th PracDocument3 pagesPhy 4th Pracahensandyn01No ratings yet
- Measure Inductance Using AC Hay's BridgeDocument53 pagesMeasure Inductance Using AC Hay's BridgeKeshav Kumar Pushpam100% (1)
- To Determine Resistance of A Galvanometer by Half-Deflection Method and To Find Its Figure of MeritDocument3 pagesTo Determine Resistance of A Galvanometer by Half-Deflection Method and To Find Its Figure of Meritatikshpro3004No ratings yet
- Delhi RepDocument2 pagesDelhi RepvinayakNo ratings yet
- II PUC ManualDocument31 pagesII PUC Manuals2263001No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument11 pagesDocumenths907757No ratings yet
- Physics Record Book 2023 24Document62 pagesPhysics Record Book 2023 24easedaeNo ratings yet
- Physics Journal 2023-24Document65 pagesPhysics Journal 2023-24vihaanshrivastaavNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Galvanometer Into Voltmeter by Mr. Charis Israel AnchaDocument6 pagesConversion of Galvanometer Into Voltmeter by Mr. Charis Israel AnchaCharis Israel Ancha50% (2)
- Experiment 4Document4 pagesExperiment 4Krish YadavNo ratings yet
- G12 Physics Experiment 23-24Document43 pagesG12 Physics Experiment 23-24anonymous3256tNo ratings yet
- Determine Resistance and Resistivity Using Metre BridgeDocument42 pagesDetermine Resistance and Resistivity Using Metre BridgeShasvat JainNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Edited Labmanual 1 8 1683724296Document24 pagesClass 12 Physics Edited Labmanual 1 8 1683724296Pratibaa LNo ratings yet
- Measurements and Instrumentation LABORATORY - 131353Document145 pagesMeasurements and Instrumentation LABORATORY - 131353NishaKamarajNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Manual - eDocument30 pagesPhysics Lab Manual - eMurukeshwari S SaravananNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual BS&TDocument28 pagesLab Manual BS&TARIVOLI SUNDARAMURTHYNo ratings yet
- To Determine Resistance of A Galvanometer by Half DeflectionDocument4 pagesTo Determine Resistance of A Galvanometer by Half DeflectionPriyojit MondalNo ratings yet
- Class XII Physics Experiment GuideDocument43 pagesClass XII Physics Experiment GuideTvara PatelNo ratings yet
- Practical Journal PhysicsDocument39 pagesPractical Journal Physicsarish ahmedNo ratings yet
- Physics PracticalDocument24 pagesPhysics PracticalPeddini Pradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Convert Ion of Galvanometer Into VoltmeterDocument3 pagesConvert Ion of Galvanometer Into Voltmeterhrpatel31No ratings yet
- Galvanometer ConversionDocument7 pagesGalvanometer Conversionashwin_airNo ratings yet
- Ace Ahead .Physics Vol 2. Student. Practical GuideDocument15 pagesAce Ahead .Physics Vol 2. Student. Practical GuideJolyn May LingNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Manual Part 01Document37 pagesPhysics Lab Manual Part 01Dr U S MirdhaNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 5Document7 pagesExperiment # 5Abdullah TahirNo ratings yet
- Physics Presentation: Resistance of Ballistic Galvanometer by Half-Deflection Method and Find Current SensitivityDocument16 pagesPhysics Presentation: Resistance of Ballistic Galvanometer by Half-Deflection Method and Find Current SensitivityNikita SangalNo ratings yet
- Resume PiyushJain Exp 1yr Linux Unix Admin CSE BTechDocument3 pagesResume PiyushJain Exp 1yr Linux Unix Admin CSE BTechPiyush JainNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming With CDocument4 pagesObject Oriented Programming With CPiyush JainNo ratings yet
- Piyush Jain: Career ObjectiveDocument2 pagesPiyush Jain: Career ObjectivePiyush JainNo ratings yet
- CmosDocument1 pageCmosPiyush JainNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorDocument1 pageSemiconductorPiyush JainNo ratings yet
- Nokia 5233Document1 pageNokia 5233Piyush JainNo ratings yet
- What Is VIDocument1 pageWhat Is VIPiyush JainNo ratings yet
- A Project Report ON: 2G Spectrum ScamDocument20 pagesA Project Report ON: 2G Spectrum ScamPiyush JainNo ratings yet
- Kamran Afzal ResumeDocument2 pagesKamran Afzal ResumeChelsea ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Trade ReportDocument6 pagesTrade ReportIKEOKOLIE HOMEPCNo ratings yet
- Dinosaur Bones - American Museum of Natural HistoryDocument7 pagesDinosaur Bones - American Museum of Natural HistoryNicholas FeatherstonNo ratings yet
- 3 To 8 Decoder in NGSPICEDocument14 pages3 To 8 Decoder in NGSPICEJaydip FadaduNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems Engineering John G Proakis Masoud Salehi PDFDocument2 pagesCommunication Systems Engineering John G Proakis Masoud Salehi PDFKatie0% (2)
- Dav Public School, Berhampur, Odisha Summer Holiday HomeworkDocument3 pagesDav Public School, Berhampur, Odisha Summer Holiday HomeworkOmNo ratings yet
- Meinrad 2018 All Symbols With NumbersDocument4 pagesMeinrad 2018 All Symbols With NumbersXer N. AcostaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 TestDocument7 pagesChapter 10 Testapi-348969276No ratings yet
- Safety and Arming Device Timer 6-7-1976Document5 pagesSafety and Arming Device Timer 6-7-1976nguyenhNo ratings yet
- Channel Line Up 2018 Manual TVDocument1 pageChannel Line Up 2018 Manual TVVher Christopher DucayNo ratings yet
- Jda Connects The Dots at Its 209821Document5 pagesJda Connects The Dots at Its 209821Gerardo LujanNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1c Bridge Profiles Allan TrussesDocument43 pagesAppendix 1c Bridge Profiles Allan TrussesJosue LewandowskiNo ratings yet
- Phy433 Lab Report 1Document9 pagesPhy433 Lab Report 1rabbani abdul rahimNo ratings yet
- MrsDocument8 pagesMrsalien888No ratings yet
- Hwids - 2012 05 22 - 19 04 00Document9 pagesHwids - 2012 05 22 - 19 04 00RONAL DAMIANO PAREJANo ratings yet
- New Membership Application GemsDocument5 pagesNew Membership Application Gemslaguila18No ratings yet
- WHLP in Reading and Writing Week 8Document4 pagesWHLP in Reading and Writing Week 8Manuel Despabiladeras0% (2)
- Product PlanningDocument23 pagesProduct PlanningGrechen CabusaoNo ratings yet
- 2017 NEC Table of ContentsDocument124 pages2017 NEC Table of ContentsFaheem PP13No ratings yet
- VSP BrochureDocument33 pagesVSP BrochuresudhakarrrrrrNo ratings yet
- Causal Inference For The Brave and True - Causal Inference For The Brave and TrueDocument2 pagesCausal Inference For The Brave and True - Causal Inference For The Brave and TrueVkook ForeverNo ratings yet
- Duration of LTMDocument3 pagesDuration of LTMsamueldaNo ratings yet
- Rexroth HABDocument20 pagesRexroth HABeleceng1979No ratings yet