Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5.1 Theory of Machines
Uploaded by
Tanuj ChauhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5.1 Theory of Machines
Uploaded by
Tanuj ChauhanCopyright:
Available Formats
102 5.1 THEORY OF MACHINES L T P 3 1 RATIONALE Diploma Holders in Mechanical Engineering come across many machines.
He must have the knowledge of various mechanisms, power transmission, balancing of masses vibrations etc. Hence, this subject is offered. DETAILED CONTENTS 1. Basic Concepts Definition of statics, kinetics, kinematics and dynamics Rigid body and resistant body Links Kinematics pairs and their types Degree of freedom Kinematics chain and their types Constrained motion and mechanisms Classification of mechanisms Equivalent mechanism Laws of inversion of mechanisms Single slider crank chain and its inversions Quick return mechanism and IC engine mechanism Double slider crank chain mechanism and its inversions like scotch yoke mechanism Indicator mechanism, pantograph Steering gear mechanism (5 hrs)
103 2. Fly Wheel Functions of fly wheel Kinetic Energy of rotating masses, turning moment diagram. Types of fly wheels Co-efficient of energy & speed Simple problems. 3. Governor Functions of governor; comparison between a fly wheel and governor. Types of governor Principle, construction and working of Watt Porter, governor, Hartnell governor. Simple problems on watt and porter Governor Terminology used in Governors: Height, equilibrium speed, Hunting, isochronism, stability, sensitiveness (No numerical problem) 4. Cams Definition of cam Classification of cams Followers and their classification Brief description of different types of cams and followers with simple line diagram Simple cam profile for uniform velocity, SHM and uniform acceleration and deceleration with Flat, knife edge and roller type follower 5. Power Transmission Devices (Belt, Rope and Chain Drive) Introduction Belt and rope drives, open and crossed belt drives, actions of belt on pulleys, velocity ratio (8 hrs) (5 hrs) governor (4 hrs) (5 hrs)
104 Material for belts and ropes Slip in belts & ropes Types of V Belt and Flat belt Types of pulleys step pulley, flat pulley Crowning in pulley Laws of belting and length of belt (open & cross belt) Ratio of tensions Power transmitted and max power transmitted by belt Centrifugal effect on belt Initial tension Chain drive, classification of chains Selection of rope based on the load to be lifted 6. Gear Drive Functions of gear Classification of gears Gear nomenclature Forms of teeth, cycloid profile and involute profile teeth Simple, compound, reverted and epicyclic gear train Simple problems on gear trains 7. Friction & Clutches Frictional torque in screws for both square and V-threads Screw jack Calculation of power required for raising a load (6 hrs) (7 hrs)
105
Friction in collars & pivots. Friction in plate clutch & conical clutch Different types of bearings & their applications Derivation of formula for torque wasted in friction bearing and torque transmission capacity of clutches 8. Balancing Need of balancing Concept of static and dynamic balancing Balancing of rotating mass by another mass in the same plane Concept of reference plane Simple problems pertaining to several masses rotating in different planes 9. Vibration Introduction Types of vibration longitudinal, transverse and torsional vibration Causes, remedial measures & harmful effects of viberations RECOMMENDED BOOKS 1. 2. 3. 4. JS Rao and Dukkipati; Mechanism and Machine Theory; Wiley Eastern, New Delhi A Ghosh and AK Malik: Theory of Mechanism and Machine; East West Press (Pvt) Ltd., New Delhi MF Spotts: Design of Machine Elements; Prentice Hall of India Ltd., New Delhi R.C Jindal; Theory of Machines & Mechanisms; Ishan Publications, Ambala City 5. S.S Rattan: Theory of Machines; Tata McGrawHill , New Delhi (2 hrs) (6 hrs)
106 5.2 RATIONALE There are different weather conditions around the year in our country. For human comfort, industrial production, safety of perishable food, storage of seasonal food, controlled temperature and humidity is required. As such the growth of refrigeration and air conditioning is expanding. This field creates opportunities for employment and entrepreneurship. DETAILED CONTENT 1. Fundamental of Refrigeration Introduction to refrigeration and air conditioning, units of refrigeration, methods of refrigeration, natural system and artificial system of refrigeration, refrigeration effect. Rating of refrigeration, co efficient of performance. Difference between COP and efficiency. Introduction to air refrigeration cycle. 2. Vapour Compression System Principle, function, parts and necessity of vapour compression system. P H charts. Dry, wet, and super heated compression. Effect of sub cooling and super heating, effect of moisture in vapour compression system. Comparison between air refrigeration and vapour compression system. 3. Refrigerants Physical, chemical, thermodynamic and commercial properties of NH3, water, CO2, R-12, R-22 and R-134 A. Properties of ideal refrigerants used in refrigeration system. 4. Vapour Absorption System Introduction, principle and working of electrolux refrigeration system, solar power refrigeration system, advantages and disadvantages of solar power refrigeration system over vapour compression system. (8 hrs) (8hrs) (8 hrs) (5 hrs) REFRIGERATION & AIR CONDITIONING L T P 3 1 2
107 5. Refrigeration Equipment (5 hrs)
Compressor Function, various types of compressor. Condenser Function, Various types of condenser. Evaporators Function, Various types of evaporators. Expansion Devices Function, Different types such as capillary tube, thermostatic expansion valve, automatic expansion valve, low side float valve and high side float valve. 6. Psychrometry Definition of dry air, moisture, saturated air, unsaturated air, specific humidity, relative humidity, degree of saturation, DBT, WBT, DPT. Psychrometric charts, heating with humidification, cooling with dehumidification, by pass factor. Air conditioning systems. Windows type air conditioner, split type air conditioner. 7. Miscellaneous (4 hrs) (10 hrs)
Study of Ice plant, cold storage, centrally air-conditioned plant, air conditioning of car. Insulating materials. Safety switches thermostat, overload protector, low pressure high pressure cut out switch, oil pressure cut out switch. LIST OF PRACTICALS 1. Identify various tools of refrigeration kit and carry out following operations. Cutting Bending Flaring Swaging and brazing of copper tubes. 2. Study the following compressors used in refrigeration system. Reciprocating compressor Reciprocating hermetically sealed compressor. 3. 4. 5. Study of thermostatic switch, LP/HP cut out switch, overload protector, filters, strainers and filter driers. Locating leaks and charging a refrigeration system. To find COP of a refrigeration system.
108 6. 7. 8. 9. Detect trouble/faults in a refrigerator and window air conditioner. Visit to a cold storage plant. Visit to a centrally air conditioned building. Dismantling of window type A.C. and testing after assembly.
RECOMMENDED BOOKS 1. 2. 3. Refrigeration and Air conditioning by A.S Sarao; Satya Prakashan, New Delhi. Refrigeration and Air conditioning by Mahohar Lal. Refrigeration and Air Conditioning by R.S Khurmi & J.K Gupta; S. Chand, New Delhi.
109 5.3 RATIONALE A diploma holder will have to conduct time and motion study to improve the methods/system. This subject impart valuable skills to plan and understand plant layout, and production planning and control. DETAILED CONTENT 1. Production and Productivity Production, production functions, productivity, factors affecting productivity, measurement of productivity, causes of decrease in productivity, difference between production and productivity. 2. Plant Location, Layout and Material Handling Plant location, factors affecting plant location, concept of plant layout, types of layout, their characteristics, factors affecting plant layout, work station design, factors considered while designing a work station, introduction, need and objective of material handling, factors considered while selecting a material handling device, safety concept of material handling equipment. 3. Work Study Definition and scope of work study; areas of application of work study in industry, Role of work study in improving productivity, Objectives, needs and methods of method study, information collection, recording techniques, process symbols, charts and diagrams, critical examination, development, installation and maintenance of improved methods, work measurement objectives, needs and methods of work measurement, time study, various allowances, calculation of time, work sampling, standard data and its use. Application of engineered time standards and work sampling Ergonomics, concept and advantages. 4. Job Evaluation and Incentives Introduction, objectives, needs of job evaluation, job definition, job analysis, data source, job evaluation methods such as ranking method, grade description method, point system and factor comparison method, (12 hrs) (12 hrs) (8 hrs) (6 hrs) INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING L T P 4 - -
110 hybrid system. Incentive-definition and concept, incentive and productivity relation, types of incentives such as financial, non financial. Individual and group incentives, pre requisites for incentives, characteristics of a good incentives plan 5. Production Planning and Control Introduction, objectives and components (functions) of P.P.C, Advantages of production planning and Production Control, stages of P.P.C, process planning, routing, scheduling, dispatching and follow up, routing purpose, route sheets, scheduling purpose, machine loading chart, Gantt chart, dispatching purpose, and procedure, follow up purpose and procedure. CPM/PERT technique, drawing of simple networks and critical time calculation. Production Control in job order, batch type and continuous type of productions. Difference between these controls. 6. Estimation and Costing Introduction, purpose/functions of estimating, costing concept, ladder and elements of cost, difference between estimation and costing. Overheads and their types, estimation of material cost, estimation of cost for machining processes, numerical problems. (12 hrs) (14 hrs)
RECOMMENDED BOOKS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Industrial Engineering by O.P. Khanna; Dhanpat Rai and Sons, New Delhi. Industrial Engineering by S.C. Sharma; Khanna Publisher. Industrial Engineering and Management by T.R. Banga. Elements of work study by Suresh Dalela. Production Management by Jain and Aggarwal.
111 5.4 RATIONALE Diploma holders are responsible for supervising production processes to achieve production targets and for optimal utilization of resources. For this purpose, knowledge about various machining processes, modern machining methods, processing of plastic, CNC machining, tool, jigs and fixtures is required to be imparted. Hence the subject of workshop technology. DETAILED CONTENTS 1. Modern Machining Processes (20 hrs) WORKSHOP TECHNOLOGY - III L TP 3 - -
Mechanical Process: Ultrasonic machining (USM): Introduction, principle, process, advantages and limitations, applications. Electro Chemical Processes: Electro chemical machining (ECM) Fundamental principle, process, applications. Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): Introduction, principle parts of EDM machine, EDM terminology. Principal, metal removing rate, dielectric fluid and properties of electric fluid, applications. Wire cut EDM. (8 hrs)
2.
Plastic Moulding Techniques -
Injection moulding working principle, advantages and limitations Blow moulding working principle, advantages and limitations Compression moulding Working principle, advantages and limitations (4 hrs)
3.
Metallic Coating Process Metal spraying Wire process, powder process, applications Electro plating, anodizing and galvanizing Organic Coatings- oil base paint, rubber base coating
4.
Gear Manufacturing and Finishing Processes Gear hobbing Gear shaping Gear shaving Gear burnishing
(4hrs)
112 5. Finishing Processes 6. Purpose of finishing surfaces Surface roughness definition & units. Honing process and its applications. Description of hones. Brief idea of honing machines. Lapping process, its applications. Description of lapping compounds & tools. Brief idea of lapping machines. Super finishing process and its applications. Use of super finishing attachment on center lathe. Polishing. Buffing. (7hrs) (5hrs)
Jigs & Fixtures -
Importance and use of jigs & fixtures. Principle of location. Locating devices. Clamping devices. Types of jigs Drilling jigs, bushes, template jigs, plate jigs, channel jig, leaf jig. Fixture for milling. Advantages of jigs & fixtures.
RECOMMENDED BOOKS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Manufacturing Technology by Rao; Tata McGraw Hill Publishers, New Delhi Workshop Technology Vol. I, II, III by Chapman; Standard Publishers Distributors, New Delhi Manufacturing Technology by M. Adithan and A.B. Gupta; New Age International (P) Ltd., New Delhi. Production Engineering and Science by Pandey and Singh; Standard Publishers Distributors, New Delhi Modern Machining Process by Pandey; Tata McGraw Publishers, New Delhi A text Book of Production Engineering by P.C. Sharma; S. Chand and Company Ltd., New Delhi
113
5.5 CNC MACHINES AND AUTOMATION 3 RATIONALE Diploma holders are required to supervise and handle specialized machines and equipment like CNC machines. For this purpose, knowledge and skills about NC machines, part programming in NC machines and tooling for CNC machines are required to be imparted for enabling them to perform above functions. This subject aims at development of knowledge and skills about CNC machines, tools, equipment and use of high tech machines for increased productivity and quality. DETAILED CONTENTS 1. Introduction 2. Basic concepts of NC, CNC & DNC, adoption controls. Advantages & Disadvantage of CNC Machines. Application of CNC Machines. Difference between conventional & CNC Machines. Profitable applications of CNC Machines. (12 hrs) (6 hrs) L T P - -
Construction of CNC Machines Machine control unit. NC control. PLC control, its advantages & disadvantages. Application aid limitations of PLC machines. Axis designate of CNC machines. Special constructional requirement of CNC machines. Slide ways, bolt screw & nut assembly. Lubrication & cooling of CNC machines. Spindle & spindle motors, axis drives motor. Swarf removal & safety provision of CNC machines. Feedback mechanism in CNC machines.
3.
Tooling of CNC Machines Introduction. Various cutting tools for CNC machines. Work holding devices. Automatic tool changer. Control System Open & close loop control system
(6 hrs)
4.
(8 hrs)
114 Fundamental problem in control: Accuracy, resolution, repeatability, instability, response & damping, Type of position control: i) Point to point ii) Straight line iii) Continuous (8 hrs)
5.
Part Programming
Part programming and basic concepts of part programming, NC words, part programming formats, simple programming for rational components, part programming using conned cycles, subroutines and do loops, tool off sets, cutter radius compensation and wear compensation 6. Common Problems in CNC Machines (4 hrs)
Common problems in mechanical, electrical, pneumatic, electronic and PC components of NC machines, diagnostic study of common problems and remedies, use of on-time fault finding diagnosis tools in CNC machines 7. Industrial Automation What is automation? Need of automation. Different types of automation. Advantages/disadvantages of automation. (4 hrs)
RECOMMENDED BOOKS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. CNC Machines Programming and Applications by M Adithan and BS Pabla; New Age International (P) Ltd., Delhi. Computer Aided Manufacturing by Rao, Kundra and Tiwari; Tata Mc Graw Hill, New Delhi. Numerical Control of Machines Tools by Yorem Korem and IB Uri; Khanna Publishers, New Delhi. CNC Machine by Bharaj; Satya Publication, New Delhi. Mechatronics by HMT, Banglore.
115 5.6 WORKSHOP PRACTICE III L T P - - 9 RATIONALE Diploma holders are responsible for supervising production processes to achieve production targets and for optimal utilization of resources. For this purpose, skills in various machining processes, modern machining methods, processing of plastic, CNC machining, tool, jigs and fixtures is required to be imparted. Hence the subject of workshop practice. LIST OF PRACTICALS CNC Machine 1. Plain turning, facing, step turning, taper turning. 2. Taper turning. 3. Concave and convex curves. 4. Threading. 5. Two surface at 90* on a square block. 6. Machine students first name on an acrylic sheet on a CNC milling machine. 7. Demonstration of FMS & Wire cut EDM machine 8. Exercise for preparation of one female & one male electrode on EDM machine. 9. Exercise on profile cutting on EDM wire cut. 10. Various types of programming like polar programming, blue print programming and profile programming. Milling & Shaper 11. Machine of a square block of 100mm*100mm. *100mm on a shaper. 12. Cutting of a slot & V-groove on opposite faces of the block on the shaper. 13. Cutting of a slot and V-groove by a milling machine on a suitable block. 14. Cutting of a T slot by milling. 15. Milling of a spur gear. 16. Flute cutting of a tap or reamer. Surface Finishing 17. Exercise on hand lapping. 18. Honing of a hole. 19. Buffing practice 20. Electroplating of copper and nickel. 21. Barrel polishing and barrel plating for small pieces.
116
Grinding 22. Grinding of surface at 45, 60, 75 on tool and cutter grinder. 23. Grinding and sharpening of lathe tool, drills. 24. Grinding of job on cylindrical grinder. 25. Grinding of job on centreless grinder. 26. Grinding of die plate on a surface grinder. 27. Grinding of a wedge shape job on a surface grinder. Project Work The students will make preparations for the project to be undertaken by them in the final semester like detailed drawing, materials, cost analysis and all other prerequisites. (A Foreman Instructor in consultation with HOD/Workshop Superintendent will handle this group. Note: The Workshop Superintendent. will finalize the specific drawings of all the jobs in the beginning of semester in consultation with the staff.
117 5.7 COMPUTER INTEGRATED MANUFACTURING L T P 2 - 4
RATIONALE
Manufacturing of this century belongs to computerized equipment & machine tools to manufacture a variety of components with high quality, high precision & low cost at a faster rate. Commuter Aided Designing (CAD), Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM), Numerical Control Machine Tools, Commuter Aided Process Planning (CAPP), Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) & Flexible Manufacturing Systems-all are the part of Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) which help to achieve the desired goals in manufacturing. After studying the subject, the students will be able to know about these integrated techniques which help a manufacturer to achieve his goal with in stipulated time. DETAILED CONTENTS
1.Introduction
(3 hrs)
Fundamental of manufacturing, CAD-CAM Meaning, Activities of a CAD/CAM system, Manufacturing components of CAD/CAM integration, system approach in manufacturing, Introduction of Automation and Computer Integrated manufacturing, Concept of CIM. 2. Automation
(5 hrs)
Automation in manufacturing, Basic concepts of automation, Hard automation, Soft automation, comparison of manual operation, hard automation and flexible (Soft) automation, Trends in manufacturing automation, composition of work force in conventional and automated manufacturing system. 3. Computer System for CAD/CAM/CIM/FMS
(3 hrs)
Selection of a computer, CAD/CAM Hardware, CAD/CAM system components, computer languages and CIM/FMS, software selection. 4. NC Production System
(5 hrs)
Introduction to Numerical Control, NC machine Tools, NC control unit, Tooling for NC machine, NC part Programming, Computer automated part programming, CNC/DNC and adaptive control, Components of a DNC system, Categories of adaptive control-adaptive control with optimization (ACO), adaptive control with constraints (ACC), Geometric adaptive control (GAC), benefits of adaptive control.
118
5. Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP)
(5 hrs)
Concepts of group Technology, approaches to process planning-manual approach, variant process planning, Generative process planning; economic regions for different process planning system, role of process planning in computer integrated manufacturing, integrated process planning system, advantages of CAPP. 6. Automated Material Handling
(6 hrs)
Introduction to material handling, Objectives of material handling, Types of materials to be moved, Integrated material handling, handling system selection, Introduction to Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV), Types of AGV-Wire Guided Vehicles, Painted Guided Vehicle, Free ranging AGVs; Different AGVs guidance system, components of an AGV, AGVs basic function, Advantages of using AGVs, Industrial application of AGVs; Automated storage/retrieval systems, Industrial applications. 7. Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS)
(5 hrs)
Introduction to FMS, manufacturing flexibility, FMS elements, FMS data Files, Software for FMS, Design aspects of flexible manufacturing, Sequencing & Scheduling in FMS, Computer aided Scheduling. PRACTICAL EXERCISES 1. Creating parts Sketching, selection of sketch plane, creating feature on work plane, extrude, dimensioning sketches, constraining sketches. - Create Rectangle, Circle, and Polygons. Extrude these to make box, cylinder & prism and dimension the above part, change size by editing dimensions & using constraints. 2. Creating Drawing Views Planning and setting of drawings, creating drawing views, Hiding extraneous dimensions. Create various drawing views of the 3-D parts.
119 3. Advanced Modeling Techniques Extrudes to face/plane, intersect, face draft, 3D rounds, 3D fillets & 3D chamfers, setting & modifying feature dimensions, history based part modification. - Use extrude commands to make holes through the above objects. Also face drafts a part on another part. - Create 3-D rounds and fillets on box corners and Use history to modify above feature and their dimensions. 4. Assembly of Parts Basic concepts, starting assembly design, creating part instances, assembling the parts, checking for interference. Make cylinder and piston and assemble them.
RECOMMENDED BOOKS
1. Computer Aided Manufacturing By Surinder Kumar, Aditya Shah; Parkashan, New Delhi Satya
2. Numerical Control & Computer Aided Manufacturing By T.K. Kundra, P.N. Rao & N.K.Tewari; Tata McGraw Hills Pub. Co. New Delhi. 3. Sysetm Apporach to Computer Integrated Design & Manufacturing By N.Singh; John Willey & Sons Inc. 4. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Hand Book By Teicholz, Orr; McGrawHill Book Co.
120
You might also like
- STR Final June 4-ModelDocument1 pageSTR Final June 4-Modelmolateam2No ratings yet
- Inspection SheetDocument1 pageInspection Sheetmolateam2No ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- BIMForum LOD 2018 Spec Part 1 and Guide 2018 09Document253 pagesBIMForum LOD 2018 Spec Part 1 and Guide 2018 09Incopi GreenNo ratings yet
- Saudi Arabia Ministry of Water & Electricity Guidelines for Excavation SafetyDocument26 pagesSaudi Arabia Ministry of Water & Electricity Guidelines for Excavation Safetymolateam2No ratings yet
- Introduction ToPrimavera PresentationDocument17 pagesIntroduction ToPrimavera Presentationmolateam2No ratings yet
- Steel A2Document1 pageSteel A2molateam2No ratings yet
- RS002 Villa MR Salih Revised RS002 Villa MR Salih RevisedDocument4 pagesRS002 Villa MR Salih Revised RS002 Villa MR Salih Revisedmolateam2No ratings yet
- KCLogDocument1 pageKCLogmolateam2No ratings yet
- C# Framework Design PDFDocument84 pagesC# Framework Design PDFmolateam2100% (1)
- Sched LogDocument3 pagesSched Logmolateam2No ratings yet
- Floow UpDocument20 pagesFloow Upmolateam2No ratings yet
- Concrete works for Djibouti embassy buildingsDocument24 pagesConcrete works for Djibouti embassy buildingsmolateam2No ratings yet
- International Supply Contract TemplateDocument6 pagesInternational Supply Contract Templatemolateam20% (2)
- Eccentric WorkoutDocument2 pagesEccentric WorkoutVolchromeNo ratings yet
- Eccentric WorkoutDocument2 pagesEccentric WorkoutVolchromeNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument1 pageNew Text Documentmolateam2No ratings yet
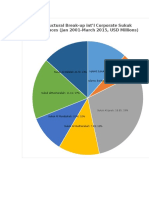
- Structural Breakdown Global Sukuk Issuances 2001-2015Document7 pagesStructural Breakdown Global Sukuk Issuances 2001-2015molateam2No ratings yet
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledmolateam2No ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument1 pageNew Text Documentmolateam2No ratings yet
- Chart of Accounts For Small Business Template V 1.0Document3 pagesChart of Accounts For Small Business Template V 1.0molateam2No ratings yet
- When Is The Critical Path Not The Critical PathDocument9 pagesWhen Is The Critical Path Not The Critical PathDWG8383No ratings yet
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Aia Cher Private RoomDocument6 pagesAia Cher Private Roommolateam2No ratings yet
- Net LogDocument6 pagesNet Logmolateam2No ratings yet
- 11Document1 page11molateam2No ratings yet
- Kasbersky LabDocument1 pageKasbersky Labmolateam2No ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument1 pageNew Text Documentmolateam2No ratings yet
- MidDocument1 pageMidDaniel J Salazar GNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- User Manual: T6DBG721N T6DBG720NDocument26 pagesUser Manual: T6DBG721N T6DBG720NViorica TrohinNo ratings yet
- 3-day CertificateDocument25 pages3-day Certificateganesh kondikire100% (8)
- Engine Fundamentals 1Document3 pagesEngine Fundamentals 1anuradhaNo ratings yet
- Pump QuotationsDocument3 pagesPump Quotationsdibyendu65No ratings yet
- MERCEDES MEDIC ACROYNMS GUIDEDocument6 pagesMERCEDES MEDIC ACROYNMS GUIDEDProkhorov100% (1)
- ATSDocument8 pagesATSserban_elNo ratings yet
- 1000 Most Common Words in English - Numbers Vocabulary For 1Document12 pages1000 Most Common Words in English - Numbers Vocabulary For 1izmitlimonNo ratings yet
- MODULE I - 10 Marks Basic Laboratory TechniquesDocument18 pagesMODULE I - 10 Marks Basic Laboratory TechniquesArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Quat KrugerDocument52 pagesQuat Krugerruby0808No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 (2nd Law of ... )Document64 pagesChapter 5 (2nd Law of ... )yohannes lemiNo ratings yet
- Toyota 2trfe Valve Stem Lash CapsDocument3 pagesToyota 2trfe Valve Stem Lash CapsJose Pichinte100% (2)
- History of Pneumatics: A 38-year EvolutionDocument2 pagesHistory of Pneumatics: A 38-year EvolutionJean Claude ArizaNo ratings yet
- Rwu90 SpecsDocument2 pagesRwu90 SpecsEduardo LuboNo ratings yet
- Mooring System Analysis of Multiple Wave Energy Converters in A Farm ConfigurationDocument10 pagesMooring System Analysis of Multiple Wave Energy Converters in A Farm ConfigurationAleix Jesus Maria ArenasNo ratings yet
- Ductable Fan Coil Unit: Product Selection DataDocument26 pagesDuctable Fan Coil Unit: Product Selection DataNelson MartinsNo ratings yet
- Catalase TestDocument2 pagesCatalase TestsekaralingamNo ratings yet
- Protection of Synchronous Machines: Application GuideDocument44 pagesProtection of Synchronous Machines: Application GuideDerouich2019No ratings yet
- FCRR19 (6) Kirkwood Matura-ShepherdDocument5 pagesFCRR19 (6) Kirkwood Matura-ShepherdRuslan ZakirovNo ratings yet
- Development of Smart Solar-Powered Waste Bin Segregation Using Image ProcessingDocument7 pagesDevelopment of Smart Solar-Powered Waste Bin Segregation Using Image ProcessingBriely BrizNo ratings yet
- Master Plan For Delhi: Dr. Mayank MathurDocument40 pagesMaster Plan For Delhi: Dr. Mayank MathurJay PrakashNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Salient Features of The Electricity Act 2003 1231332387635957 1Document14 pagesPresentation On Salient Features of The Electricity Act 2003 1231332387635957 1Anonymous m8oCtJBNo ratings yet
- Oil & Gas Financial JourneyDocument85 pagesOil & Gas Financial Journeyabsolutvacio82No ratings yet
- DC Generator: Construction and WorkingDocument7 pagesDC Generator: Construction and WorkingGlen Howell PanesNo ratings yet
- Exercise-01 Check Your Grasp: O CH HO HODocument7 pagesExercise-01 Check Your Grasp: O CH HO HOChesta MalhotraNo ratings yet
- F0358 CMM 010Document164 pagesF0358 CMM 010MJI EUWNo ratings yet
- Miroljub Todorović - ApeironDocument25 pagesMiroljub Todorović - Apeiron"Mycelium" samizdat publishersNo ratings yet
- Surge TankDocument2 pagesSurge TankBilel MarkosNo ratings yet
- Huawei PI OverviewDocument15 pagesHuawei PI OverviewHdz EdilNo ratings yet
- Station Locations in Caloocan, Malabon, Valenzuela & Nearby CitiesDocument15 pagesStation Locations in Caloocan, Malabon, Valenzuela & Nearby CitiesTricia Mae Paras WajeNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Diffusion: Lecture No. 5Document2 pagesModule 2: Diffusion: Lecture No. 5Mehwish NoorNo ratings yet