Professional Documents
Culture Documents
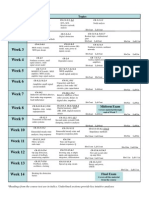
10BG501 Rev
Uploaded by
Bhaumik BhandariOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
10BG501 Rev
Uploaded by
Bhaumik BhandariCopyright:
Available Formats
NANOMATERIALS, PROCESS AND APPLICATIONS (Subject Code: 10BG501) Offered by Department of Bio Technology
The objective of this course is to educate the students about materials, process and applications of nanotechnology. Nanomaterials are of grain sizes of the order of a billionth of a meter. It is a known fact that nanomaterial outperform their conventional counterparts because of their superior chemical, physical and mechanical properties. Particles, complexes, tubes, coatings, active surfaces and devices are being explored on the nanoscale. Assembly of natures building blocks (e.g. carbon, nucleic acids, lipids and peptides) along with the combination of different materials (e.g. CdSe/ZnS, Au, Ag, Si(n)OH(n)), light harvesting dendrimers and thin films) are resulting in newer applications. Since nanomaterials possess unique chemical, physical and mechanical properties, they can be used for a wide variety of applications such as next-generation computer chips, kinetic energy penetrators with enhanced lethality, better insulation materials, phosphors for high-definition tv, low-cost flat-panel displays, tougher and harder cutting tools, elimination of pollutants, high energy density batteries, high-power magnets, highsensitivity sensors, automobiles, aerospace components, medical implants, ductile etc. The course is designed to make the student learn:
Fundamentals of Quantum concepts. Structures and properties of Carbon based, metal based and bionanomaterials: Fullerenes, Bucky Ball, Nanotubes, Graphene, Quantum Dots, Nano Shells, Dendrimers, Nanocarriers, Nanocrystals, Nanowires, Nanomembranes, hybrid biological/inorganic, protein & DNA based nanostructures. Characterizing nanomaterials using UV-Visible spectroscopy, Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR); Xray spectroscopy, Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Transmission electron microscopy (TEM),Atomic Force microscopy (AFM) and Scanning tunnel microscopy (STM). Nano Synthesis and Fabrication, bottom up-self assembly and top down approaches using processes like Ball milling, Sol-gel Process, Chemical Vapour deposition (CVD). Plasma or flame spraying synthesis, Ion-Bean sculpting, electrodeposition and various lithography techniques. Nanolithography & Soft lithography.
Overview of nanosensors: Nanosensors in industry, medicine and defense. Market for nanosensors. Various types of nanosensors Magnetic, Electromagnetic , Mechanical and Biosensors. Construction and applications of nanosensors. Micro & Nano-Electromechanical systems - Magnetic, Chemical and Mechanical Transducers Sensing and Actuators. Application of Nanotechnology: Medical Nano biotechnology in Diagnostics, therapeutics, drug delivery, Nano Surgery and Tissue Engineering. Molecular electronics, Molecular switches Mechanical: Cutting tools, Machine components, Magnets, DLC coated grinding wheels. Electrical/Electronics: Solar cells, UV/IR Sensors, Batteries/Fuel cells, Filters. Nano Safety Issues: Toxicology health effects caused by Nanoparticles. Reference Books: 1. Richard Booker and Earl Boyse., Nanotechnology. Wiley dreamtech edition 2005. 2. Chapman & Hall. Nanotechnology Basic Science & Emerging Technologies. CRC 2002 3. Gregory Timp., Nanotechnology. Spring 1st edition; 1998. 4. Teik Cheng Lim., Nanosensors. Taylor and Francis edition; 2010. 5. J Rosenthal Sandra and W Wright David; Nanobiotechnology Protocols. Humana Press, 1st edition; 2005
You might also like
- 2.2.10 Atwater Web Public 2009Document6 pages2.2.10 Atwater Web Public 2009Bhaumik BhandariNo ratings yet
- CalendarDocument1 pageCalendargsaptarshi1No ratings yet
- Greentelligent: Made by Abhishek Arora - 1RV10CS005 Abhishek Jain - 1RV10CS006Document18 pagesGreentelligent: Made by Abhishek Arora - 1RV10CS005 Abhishek Jain - 1RV10CS006Bhaumik BhandariNo ratings yet
- Designing and Manufacturing of Formula Hybrid IeeeDocument6 pagesDesigning and Manufacturing of Formula Hybrid IeeeBhaumik BhandariNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Chapter 3Document12 pagesChapter 3DRate17No ratings yet
- Lab 7 DensityisaperiodicpropertyDocument3 pagesLab 7 Densityisaperiodicpropertyapi-2999230730% (1)
- Pengertian Buah ApelDocument8 pagesPengertian Buah ApelzulfikarNo ratings yet
- STP1290 Eb.1415051 1 PDFDocument206 pagesSTP1290 Eb.1415051 1 PDFpaolaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Waterproof Breathable Membrane TechnologyDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Waterproof Breathable Membrane TechnologyIrmantas Saulius100% (3)
- PIT AND FISSURE SEALANT GUIDEDocument2 pagesPIT AND FISSURE SEALANT GUIDEAhmed FoudaNo ratings yet
- NFPA 820 Wastewater Treatment Facility Area ClassificationsDocument36 pagesNFPA 820 Wastewater Treatment Facility Area ClassificationsKarim El ShamashergyNo ratings yet
- E1219-10 Standard Practice For Fluorescent Liquid Penetrant Testing Using The Solvent - Removable Process PDFDocument6 pagesE1219-10 Standard Practice For Fluorescent Liquid Penetrant Testing Using The Solvent - Removable Process PDFManuel Andres Mantilla DuranNo ratings yet
- Sizing Pulsation Dampeners Is Critical To Effectiveness P47E11 010Document6 pagesSizing Pulsation Dampeners Is Critical To Effectiveness P47E11 010Othoniel KanoNo ratings yet
- Waste Management: Fabio Dal Magro, Haoxin Xu, Gioacchino Nardin, Alessandro RomagnoliDocument10 pagesWaste Management: Fabio Dal Magro, Haoxin Xu, Gioacchino Nardin, Alessandro RomagnoliKARAN KHANNANo ratings yet
- 2017-01-01 Bohn Water-Cooled Condensing UnitsDocument32 pages2017-01-01 Bohn Water-Cooled Condensing UnitsCrystal VenomNo ratings yet
- RNA Extraction From YeastDocument3 pagesRNA Extraction From YeastCecelia Dot DotNo ratings yet
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationDocument8 pagesDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationIndira MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Bombas Gorman RuppDocument12 pagesBombas Gorman RuppRafael Hernández RcrewNo ratings yet
- Acetic AnhydrideDocument1 pageAcetic AnhydrideCarlos Vargas de MontoyaNo ratings yet
- WCH06 01 Que 20180125Document16 pagesWCH06 01 Que 20180125Yuan XintongNo ratings yet
- Tugas Parafrase Jurnal MIPKI RevisiDocument2 pagesTugas Parafrase Jurnal MIPKI RevisiAl-aminNo ratings yet
- Sanitary FittingsDocument58 pagesSanitary FittingsMherlieNo ratings yet
- McCabe-Thiele Method Distillation DesignDocument9 pagesMcCabe-Thiele Method Distillation DesignIndra KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Pyrolysis-GC/MS/IR Analysis of PolyethyleneDocument6 pagesPyrolysis-GC/MS/IR Analysis of PolyethyleneKung KleeNo ratings yet
- Detect Concrete Corrosion with Hammer TestsDocument50 pagesDetect Concrete Corrosion with Hammer TestsSumit Singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Wesea An Experimental Study On Durability Properties of ConcreteDocument9 pagesWesea An Experimental Study On Durability Properties of ConcreteA A AdedejiNo ratings yet
- Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical AnalysisDocument16 pagesJournal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical AnalysisFania dora AslamyNo ratings yet
- FT TANQUE VERTICAL ROTOPLAS - Es.enDocument5 pagesFT TANQUE VERTICAL ROTOPLAS - Es.enEdgar MartinezNo ratings yet
- ASTM D 890 - 98 Water in Liquid Naval StoresDocument3 pagesASTM D 890 - 98 Water in Liquid Naval Storesalin2005No ratings yet
- Basf Masterbrace Fib 300 TdsDocument3 pagesBasf Masterbrace Fib 300 TdsNolosaurusNo ratings yet
- Naming and Writing Formulae of Coordination Compounds - HandoutsDocument11 pagesNaming and Writing Formulae of Coordination Compounds - HandoutsJayr SibayanNo ratings yet
- ASTM D 1413 - 99 Wood Preservatives by Laboratory Soil-Block CulturesDocument7 pagesASTM D 1413 - 99 Wood Preservatives by Laboratory Soil-Block Culturesalin2005100% (1)
- Lab Manual Power Plants PDFDocument46 pagesLab Manual Power Plants PDFKhushnoodNo ratings yet