Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem Set On Enzyme Kinetics - FS - 2012 - 2013
Uploaded by
Chay AlcantaraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem Set On Enzyme Kinetics - FS - 2012 - 2013
Uploaded by
Chay AlcantaraCopyright:
Available Formats
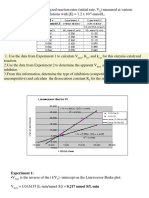
Problem Set on Binding Equilibrium and Enzyme Kinetics 1. Cytochrome f operates as a redox agent in chloroplast photosynthesis.
The standard reduction potential, , of cytochrome f at pH 7.0 is determined by coupling it to an agent of known such as ferricyanide ferrocyanide. In a typical experiment carried out spectrophotometrically, a solution at 25C and pH 7.0 containing a ratio, [Fe(CN)64 ] / [Fe(CN)63 ] equal to 2.0 is found to have a ratio [Cyt f reduced]/[Cyt f oxidized] of 0.10 at equilibrium. a. Calculate the reduction potential for Cyt f. b. On the basis of the standard reduction potential, , for the reduction of O2 to H2O at pH 7 and 25C, is oxidized Cyt f a good enough oxidant to cause the formation of O2 from H2O at 25C and pH 7? The enzyme nucleoside diphosphokinase catalyzes the reaction: Mg2+ GTP + dGDP GDP + dGTP In an experiment with the ezyme isolated from erythrocytes, the following results were obtained: [GTP] (M) 30 50 Velocity (katal kg 1) 20 0.095 0.112 0.141 25 0.102 0.120 0.155 40 0.112 0.136 0.180 100 0.125 0.156 0.218 What can you deduce from these data regarding a likely mechanism for the catalyzed reaction? How could you check your conclusion? [dGDP] (M) 3. 22 200 0.196 0.223 0.284 0.385 enzyme
2.
The binding of a ligand A to a macromolecule was studied by equilibrium dialysis. In each measurement a 1 M solution of the macromolecule was dialyzed against an excess amount of a solution containing A. After equilibrium was reached, the concentration of A on each side of the dialysis membrane was measured and the ff data obtained. Total concentration of A Solvent Side (M) Macromolecule side(M) 5.1 5.7 10.2 12.8 20.1 23.4 52.2 56.2 105.0 109.1 200 204.7 Determine the binding constant and the total number of binding sites.
4.
The following data were obtained for the variation of Vmax with pH for the fumarase reaction at 298 K (Vmax in arbitrary units) pH 5.2 5.5 6.0 6.5 6.75 7.0 7.5 8.0 Vmax 54 105 184 224 236 230 162 86 Deduce the appropriate pK values.
8.5 33
5.
The following data were obtained for the myosin catalyzed hydrolysis of ATP: Temperature (C) k x 106 (sec 1) Calculate Ea. 39.9 4.67 43.8 7.22 47.1 10.0 50.2 13.9
6.
The equilibrium: I2 + I I3 1 , has been studied using a laserinduced temperature jump technique. Relaxation times were measured at various equilibrium concentrations of reactants at 25C: [I 1] (mM) 0.57 1.58 2.39 2.68 3.45 [I2] (mM) 0.36 0.24 0.39 0.16 0.14 71 50 39 38 32 (ns)
Calculate the constants k1 and k1 for the system at 25C.
You might also like
- Osmosis and Diffusion Lab For AP BioDocument11 pagesOsmosis and Diffusion Lab For AP Bioitssabbyx3No ratings yet
- 2018 AHA Guidelines For Management of Blood CholesterolDocument66 pages2018 AHA Guidelines For Management of Blood CholesterolsarumaxNo ratings yet
- 8 Coenzymes and Vitamins (كيمياء حيوية صيدلانية (1 PDFDocument74 pages8 Coenzymes and Vitamins (كيمياء حيوية صيدلانية (1 PDFmaher100% (1)
- Problem Set - Enzymes From LehningerDocument11 pagesProblem Set - Enzymes From LehningervioletbrownNo ratings yet
- Concise Biochemistry: Fundamental Principles: March 2016Document52 pagesConcise Biochemistry: Fundamental Principles: March 2016Sagar DeshmaniNo ratings yet
- 1.carbohydrates and Lipid Metabolism-Converted - WatermarkDocument97 pages1.carbohydrates and Lipid Metabolism-Converted - WatermarkJuliyamol JoseNo ratings yet
- Biochem HomeworkDocument13 pagesBiochem Homeworkfcukingfranztastik50% (2)
- Practice Kinetics ProblemsDocument1 pagePractice Kinetics ProblemsClint Charles P. Brutas100% (1)
- Diffusion and Osmosis ESL 3Document27 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis ESL 3Katie Isabella100% (1)
- Protein CrystallizationDocument166 pagesProtein CrystallizationElizabeth Znameroski100% (1)
- Enzyme MCQ Study Guide ReviewDocument5 pagesEnzyme MCQ Study Guide ReviewMrs Rehan100% (1)
- SAT II BiologyDocument223 pagesSAT II BiologyAldiyar100% (2)
- Chem 40 Enzyme KineticsDocument85 pagesChem 40 Enzyme KineticsJustine Grace Mariano100% (1)
- Lecture Notes Enzyme 2 Enzyme Kinetics WebDocument29 pagesLecture Notes Enzyme 2 Enzyme Kinetics WebAldren RebaLdeNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Catalysis-Chapter 7 (Part 1)Document22 pagesEnzyme Catalysis-Chapter 7 (Part 1)OmSilence2651No ratings yet
- ENZYMES Problems and SolutionsDocument6 pagesENZYMES Problems and SolutionsChadby GraNaNo50% (2)
- Practical BiochemistryDocument35 pagesPractical BiochemistryMockinjay100% (1)
- MORE Practice For Michaelis-Menten ShitDocument3 pagesMORE Practice For Michaelis-Menten ShitMalcolm Charles100% (1)
- Enzymes: Properties and KineticsDocument59 pagesEnzymes: Properties and Kineticsthamizh555100% (2)
- Solutions for Selected End of Chapter 6 ProblemsDocument6 pagesSolutions for Selected End of Chapter 6 Problemsheyyyale100% (1)
- Potentiometric Titration of Cerium SolutionDocument4 pagesPotentiometric Titration of Cerium SolutionValentin-AngeloUzunov100% (1)
- Optimization of Cellulase Enzyme From Vegetable Waste by Using Trichoderma Atroviride in Solid State FermentationDocument6 pagesOptimization of Cellulase Enzyme From Vegetable Waste by Using Trichoderma Atroviride in Solid State FermentationIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Enzyme Kinetics, Inhibition and ControlDocument23 pagesChapter 12: Enzyme Kinetics, Inhibition and Controlfilippo67% (3)
- Erythropoietin Concentrated Solution (1316)Document5 pagesErythropoietin Concentrated Solution (1316)Mulayam Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Enzyme InhibitionDocument7 pagesEnzyme InhibitionJane Docdoc100% (1)
- Assign#1 Enzyme KineticsDocument1 pageAssign#1 Enzyme KineticsCarla Sibal100% (1)
- Name: Kristine Joy Atos Block: BSN 1-D Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesName: Kristine Joy Atos Block: BSN 1-D Practice ProblemsJenz Hope Segui Novela100% (3)
- Ghid Dislipidemie 2019Document78 pagesGhid Dislipidemie 2019Ema PetrescuNo ratings yet
- 5 Enzyme Kinetics-InhibitionDocument40 pages5 Enzyme Kinetics-InhibitionJoel SmolanoffNo ratings yet
- Michaelis-Menten model accounts for enzyme kineticsDocument11 pagesMichaelis-Menten model accounts for enzyme kineticsPhenyo Mmereki100% (2)
- Assign#2 Enzyme KineticsDocument3 pagesAssign#2 Enzyme KineticsKaren Castro100% (2)
- A.1. Competitive InhibitionDocument5 pagesA.1. Competitive InhibitionFlorecita Cabañog100% (1)
- ENZYME KINETICSDocument11 pagesENZYME KINETICSDianne Villanueva100% (1)
- Excel 2007 TutorialDocument5 pagesExcel 2007 TutorialromelcarvajalNo ratings yet
- BIO307 Lecture 5 (Enzyme Kinetics I)Document11 pagesBIO307 Lecture 5 (Enzyme Kinetics I)Phenyo Mmereki100% (1)
- Enzyme KineticsDocument3 pagesEnzyme KineticsZeny Naranjo100% (2)
- BIOL 112 Practice Final December 2012Document15 pagesBIOL 112 Practice Final December 2012SeoAm HurNo ratings yet
- Che503 PS3 PDFDocument2 pagesChe503 PS3 PDFCarissa TejioNo ratings yet
- Bibc102, Metabolic Biochemistry: Gen-Sheng Feng Fall, 2010Document14 pagesBibc102, Metabolic Biochemistry: Gen-Sheng Feng Fall, 2010cool_trainerNo ratings yet
- Question CH06+answer PDFDocument8 pagesQuestion CH06+answer PDFCris-Anne Juangco III100% (1)
- Voet - Chapt - 12 Properties of EnzymesDocument102 pagesVoet - Chapt - 12 Properties of Enzymestelmo flowNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Kinetics Examples and ProblemsDocument4 pagesEnzyme Kinetics Examples and Problemskiiadizon07100% (1)
- 2-Bacterial Growth Kinetics - F11Document15 pages2-Bacterial Growth Kinetics - F11Suvidha Chib100% (1)
- STRAIN IMPROVEMENT TechniquesDocument28 pagesSTRAIN IMPROVEMENT TechniqueselaiyarajaNo ratings yet
- Microbial Cell Growth and Kinetics PhasesDocument58 pagesMicrobial Cell Growth and Kinetics PhasesKIL170051 STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Cell Growth Kinetics BioprosesDocument24 pagesCell Growth Kinetics BioprosesLuthfi Magecho Sikoembang100% (1)
- Enzyme Immobilization Methods and EffectsDocument3 pagesEnzyme Immobilization Methods and Effectsfintastella0% (1)
- Enzyme KineticsDocument72 pagesEnzyme Kineticsitokki otoya100% (1)
- Enzyme velocity at 1/4 Vmax with 0.5mM KMDocument1 pageEnzyme velocity at 1/4 Vmax with 0.5mM KMfintastellaNo ratings yet
- 4 Bioenergetics and Oxidative Metabolism IIDocument3 pages4 Bioenergetics and Oxidative Metabolism IILinus LiuNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes-Growth Kinetics - Growth PhasesDocument24 pagesLecture Notes-Growth Kinetics - Growth PhasesNhan Nguyen100% (1)
- BCH 314 Tutorial 1 SolutionsDocument9 pagesBCH 314 Tutorial 1 SolutionsvictorNo ratings yet
- Monod Equation ProblemDocument7 pagesMonod Equation Problemeiddnew100% (1)
- Solving Enzyme Kinetics Problems: Sucrose Transport, Vmax vs Km Effects, Carbonic Anhydrase ReactionDocument4 pagesSolving Enzyme Kinetics Problems: Sucrose Transport, Vmax vs Km Effects, Carbonic Anhydrase Reactionbiotech_vidhya100% (1)
- Some Answer of Problemset - 7 - KEYDocument3 pagesSome Answer of Problemset - 7 - KEYNihir PatelNo ratings yet
- Question 1 (37 Marks) : Biochemistry 3 BCH 314Document4 pagesQuestion 1 (37 Marks) : Biochemistry 3 BCH 314victorNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Enzyme ActionDocument2 pagesMechanism of Enzyme ActionBlazy InhumangNo ratings yet
- Sutherland 1991Document7 pagesSutherland 1991Isal AbdussalamNo ratings yet
- MIT Lecture 6 5.07 Biochemistry LectureDocument16 pagesMIT Lecture 6 5.07 Biochemistry LectureakiridoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates SummaryDocument9 pagesCarbohydrates SummaryHarold NagunaNo ratings yet
- Allosteric Enzymes Don't Obey Michaelis-Menten KineticsDocument30 pagesAllosteric Enzymes Don't Obey Michaelis-Menten KineticsFlora D Souza100% (1)
- GlycolysisDocument21 pagesGlycolysisAli AlqumaNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument19 pagesLab Manualanon_467104036No ratings yet
- Hematin-Catalyzed Polymerization of Phenol CompoundsDocument6 pagesHematin-Catalyzed Polymerization of Phenol CompoundsAdrian ParodiNo ratings yet
- Using KSP For The Dissolution of Borax in Water To Determine: G°, H° and S°Document4 pagesUsing KSP For The Dissolution of Borax in Water To Determine: G°, H° and S°Valentin-AngeloUzunov100% (18)
- Fotoderad FlavisDocument4 pagesFotoderad FlavisHylze ChavesNo ratings yet
- 2018 ESC-EACTS Guidelines On Myocardial RevascularizationDocument96 pages2018 ESC-EACTS Guidelines On Myocardial RevascularizationTony Miguel Saba SabaNo ratings yet
- 2016 AHA ACC Periphery Artery Disease GuidelinesDocument56 pages2016 AHA ACC Periphery Artery Disease GuidelinesNika AlizahNo ratings yet
- Orientation 2012 HandoutsDocument4 pagesOrientation 2012 HandoutsChay AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Allergic RhinitisDocument4 pagesAllergic RhinitisChay AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Biochem 124 Problem SetDocument2 pagesBiochem 124 Problem SetKarina NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Making A CritiqueDocument1 pageGuidelines On Making A CritiqueZabrina Tan CuaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Writing FormatDocument5 pagesThesis Writing FormatChay AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Desalting, Concentration, and Buffer Exchange by Dialysis and UltrafiltrationDocument15 pagesDesalting, Concentration, and Buffer Exchange by Dialysis and UltrafiltrationAlejandraBarrónHernándezNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane ProcessesDocument3 pagesCell Membrane ProcessesHyacinth PerezNo ratings yet
- Bio 100 Osmosis Lab ReportDocument4 pagesBio 100 Osmosis Lab Reportapi-249188694No ratings yet
- Lab 41 Diffusion and Osmosis 2006Document14 pagesLab 41 Diffusion and Osmosis 2006S. Spencer50% (2)
- Capillarys / Minicap UrineDocument23 pagesCapillarys / Minicap Urineawlymir0% (1)
- Suppositories SampleDocument20 pagesSuppositories SamplePriyanka S. SutarNo ratings yet
- A Learning Material For BS Biology: Jefferson E. Flores, RN, LPTDocument7 pagesA Learning Material For BS Biology: Jefferson E. Flores, RN, LPTJohn Mark Gallano CanayonNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Concentration of Glucose and Temperature On The Rate of OsmosisDocument4 pagesThe Effects of Concentration of Glucose and Temperature On The Rate of OsmosisAisha Nicole Saito50% (2)
- AP Bio Lab 1Document8 pagesAP Bio Lab 1Paul Jones100% (1)
- Induction BioDocument161 pagesInduction BioFaheem UllahNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Tubing Lab Questions FixedDocument2 pagesDialysis Tubing Lab Questions Fixedapi-23365304250% (2)
- AP Biology Lab 1 ReportDocument6 pagesAP Biology Lab 1 ReportAdriann WilsonNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 1 PH Measurement and Buffer Preparation I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesExperiment # 1 PH Measurement and Buffer Preparation I. ObjectiveschynnaNo ratings yet
- New Lab 3 Manual Fall 2017Document11 pagesNew Lab 3 Manual Fall 2017Kim Jae WonNo ratings yet
- Setting of Cement ProjectDocument20 pagesSetting of Cement ProjectNikhil Solanki 11 ANo ratings yet
- Patent 1 - WO2017122216A1Document61 pagesPatent 1 - WO2017122216A1sci pusatNo ratings yet
- BCH 2333 LAB 1 PDFDocument12 pagesBCH 2333 LAB 1 PDFNupur Vij100% (1)
- Review On Defluoridation Techniques of Water: Piddennavar Renuka, Krishnappa PushpanjaliDocument9 pagesReview On Defluoridation Techniques of Water: Piddennavar Renuka, Krishnappa PushpanjaliSangram PhadtareNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Final Exam ReviewDocument1 pageAP Biology Final Exam Reviewrobertclee1234No ratings yet
- Diafiltration For Desalting or Buffer ExchangeDocument6 pagesDiafiltration For Desalting or Buffer Exchangesharfina02No ratings yet
- Physioex 9.0 Exercise 1 Act 1Document5 pagesPhysioex 9.0 Exercise 1 Act 1Adela LhuzNo ratings yet
- Automated Methods of AnalysisDocument9 pagesAutomated Methods of AnalysisPeerBuxNo ratings yet
- Osmosis & Diffusion Lab GuideDocument4 pagesOsmosis & Diffusion Lab GuideDean DoneenNo ratings yet
- Complex at IonDocument31 pagesComplex at IonShamsuzzaman TanimNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis Lab ResultsDocument4 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis Lab ResultsAmanda YoungNo ratings yet