Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Simply Supported Beam
Uploaded by
Gelbert SilotOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Simply Supported Beam
Uploaded by
Gelbert SilotCopyright:
Available Formats
Simply supported beam-to-beam connection.
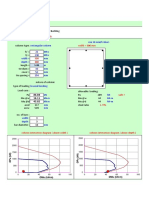
In this example we are going to design a simple (shear) connection between a primary beam IPE400 and a secondary beam IPE300. We are going to use steel S355 and bolts with grade 8.8. The shear force subjected to the connection is 90kN.
Positioning of holes for bolts. (EC3, part 8, table 3.3)
Calculation of the forces subjected to the bolts located at the web of the primary beam.
Firstly, we assume that these bolts transmit only shear force from the secondary to the primary beam. Hence, each of the 6 bolts are subjected to single shear equal to:
Calculation of the forces subjected to the bolts located at the web of the secondary beam.
The shear force is causing a moment to the group of the 3 doubly sheared bolts:
The moment is equivalent with two horizontal forces equal in magnitude and opposite in direction subjected to the edge bolts.
The shear force is distributed equally to the three bolts:
The resultant force at the edge bolts equals to:
Design resistance of the singly sheared bolts @ the web of the primary beam. (EC3, part 8, table 3.4)
We assume that the shear plane passes through the unthreaded portion of the bolt.
Shear resistance:
Bearing resistance:
Check:
Design resistance of the doubly sheared bolts @ the web of the secondary beam. (EC3, part 8, table 3.4)
Shear resistance:
Bearing resistance:
Check:
Design resistance of the angle cleats @ a-a cross-section.
Each of the two angle cleats at the a-a cross-section is subjected to:
Bending resistance: According to EC3, part 1, equation 6.16 we have to check whether the fastener holes in the tension flange will be ignored for the calculation of the bending resistance of the angle cleat.
Hence, we have to ignore the fastener hole at the tension flange for the calculation of the bending
resistance.
Shear resistance (EC3, part 1, equation 6.18):
Moreover, there is no need to reduce the bending resistance of the section because of the shear (EC3, part 1, section 6.2.8 (2)):
Design for block tearing (EC3, part 8, 3.10.2): For a bolt group subject to eccentric loading the design block shear tearing resistance is given by:
Net area subjected to tension:
Net area subjected to shear:
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- SSS Seminar InvitationDocument2 pagesSSS Seminar InvitationGelbert Silot100% (2)
- Tie Beams1Document1 pageTie Beams1Gelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Reinforcing Steel Bars Price List: StructuralDocument1 pageReinforcing Steel Bars Price List: StructuralGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Android Smart TV BOX - (FREE Wireless Mini Keyboard) - Checkout DailyDocument14 pagesAndroid Smart TV BOX - (FREE Wireless Mini Keyboard) - Checkout DailyGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Columnsteel 1Document1 pageColumnsteel 1Gelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Jojo Layout1 PDFDocument1 pageJojo Layout1 PDFGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- 2D Frame Analysis: Analysis of A 2D Frame Subject To Distributed Loads, Point Loads and MomentsDocument26 pages2D Frame Analysis: Analysis of A 2D Frame Subject To Distributed Loads, Point Loads and MomentsGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Beam Girder and Column Rebar Option Is Off, How To Activate This One?Document2 pagesBeam Girder and Column Rebar Option Is Off, How To Activate This One?Gelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Pile StirrupDocument1 pagePile Stirrupbuffyto5377No ratings yet
- (ANALYSIS) Why Filipinos Need To Stay at Home Until June (Or Even Longer) PDFDocument13 pages(ANALYSIS) Why Filipinos Need To Stay at Home Until June (Or Even Longer) PDFGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Latest FormDocument27 pagesLatest FormGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- C 1Document1 pageC 1Gelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- DOH AO 2019-0047 National Standard On The Design, Construction, Operation and Maintenance of A Septic Tank SystemDocument16 pagesDOH AO 2019-0047 National Standard On The Design, Construction, Operation and Maintenance of A Septic Tank SystemMaria Theresa Limos83% (6)
- Structural Drawing PDFDocument1 pageStructural Drawing PDFGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- STAAD ShortcutsDocument3 pagesSTAAD ShortcutsGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- SFB 1Document1 pageSFB 1Gelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- SFB 2Document1 pageSFB 2Gelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- SFB 2Document1 pageSFB 2Gelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- RC ColumnsDocument2 pagesRC ColumnsGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- B 1Document1 pageB 1Gelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Tie Beams2Document1 pageTie Beams2Gelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- C 2Document1 pageC 2Gelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- SFB 1Document1 pageSFB 1Gelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Two Way Slab Design DetailsDocument1 pageTwo Way Slab Design DetailsGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Summary of Bids - MadridDocument1 pageSummary of Bids - MadridGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- 510Document1 page510Gelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Det 11Document1 pageDet 11Gelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Common Shape CodesDocument1 pageCommon Shape CodesIrfanNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow MadridDocument1 pageCash Flow MadridGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Axial ContourDocument1 pageAxial ContourGelbert SilotNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- PR 724 Crawler TractorDocument18 pagesPR 724 Crawler TractorCarlosNo ratings yet
- Koerner. On The Creep GeosynteticDocument6 pagesKoerner. On The Creep GeosynteticSergio Xexo Gonzalez RuizNo ratings yet
- Partbook PC200-10#450640-upDocument922 pagesPartbook PC200-10#450640-upDương Xuân Hiếu100% (1)
- Lect 5 - Mechanism DescriptionDocument15 pagesLect 5 - Mechanism Descriptionjackie delos santosNo ratings yet
- Sinorix™: A6V10867394 - en - c2 Building Technologies 2017-06-06 Control Products and SystemsDocument4 pagesSinorix™: A6V10867394 - en - c2 Building Technologies 2017-06-06 Control Products and SystemsEngineering TFINo ratings yet
- CompAir LeROI CL20-25-30SS,CUB Parts ListDocument59 pagesCompAir LeROI CL20-25-30SS,CUB Parts ListDiana Zar100% (1)
- Archimedes PrincipleDocument4 pagesArchimedes Principleraviteja036No ratings yet
- TRIM AND STABILITY CALCULATION SHEET ANALYSISDocument33 pagesTRIM AND STABILITY CALCULATION SHEET ANALYSISДмитрий ЯрычNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document59 pagesModule 2PSkotsNo ratings yet
- 1411 1502 PDFDocument60 pages1411 1502 PDFAlejandro RagoNo ratings yet
- Shear & Diagonal Tension in BeamsDocument15 pagesShear & Diagonal Tension in BeamsS. M. ZAHIDUR RAHMAN 1301129No ratings yet
- SM Ras-3m23gacv-E Ras-M10 13 16 GK (C) VP-eDocument105 pagesSM Ras-3m23gacv-E Ras-M10 13 16 GK (C) VP-eGoguredNo ratings yet
- Stretch and Recovery Testing Method For Knitted Fabrics: Professional Standard of The People's Republic of ChinaDocument17 pagesStretch and Recovery Testing Method For Knitted Fabrics: Professional Standard of The People's Republic of Chinaoussamawitcher23No ratings yet
- LS Circuit IntroductionDocument18 pagesLS Circuit IntroductionMuhammad DaniNo ratings yet
- LG4HKED-WE-VN53 - Engine Control System 4HK1Document404 pagesLG4HKED-WE-VN53 - Engine Control System 4HK1tuannholtt100% (8)
- Manual Volvo XC90 2005Document17 pagesManual Volvo XC90 2005Diego Alejandro QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Built Up SectionsDocument2 pagesBuilt Up Sectionslisan2053No ratings yet
- Pressure Relief Valve Fig.1319Document2 pagesPressure Relief Valve Fig.1319fernandoNo ratings yet
- Fisher Control Valve Sourcebook - Power and Severe ServiceDocument220 pagesFisher Control Valve Sourcebook - Power and Severe Servicemtrj59No ratings yet
- Gear BoxDocument14 pagesGear Boxarackalfrancis0% (1)
- 6.7L Cummins Maintenance Schedule & Service InformationDocument3 pages6.7L Cummins Maintenance Schedule & Service InformationNick Brady100% (1)
- Structural Design 1: Module inDocument4 pagesStructural Design 1: Module inkangkongNo ratings yet
- Welding DefectsDocument4 pagesWelding DefectsSD Recruiters100% (1)
- Sectional Properties of Rolled Steel Joists (Ref: Is: 808 - 1989 & Is: 12778 - 2004)Document49 pagesSectional Properties of Rolled Steel Joists (Ref: Is: 808 - 1989 & Is: 12778 - 2004)rohitnrgNo ratings yet
- Me-1 To 10 Gf-PodiumDocument10 pagesMe-1 To 10 Gf-PodiumKristina OrmacidoNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase TMDocument39 pages3 Phase TMHari Kishan Nimmu0% (1)
- Ape City March 2013Document60 pagesApe City March 2013DEEPAKNo ratings yet
- Img 20180122 0001 PDFDocument2 pagesImg 20180122 0001 PDFAnonymous vtZNXtACNo ratings yet
- Appendix CDocument3 pagesAppendix CMagin Idelfonso TorreblancaNo ratings yet
- D 6Document47 pagesD 6gilmer flores mamaniNo ratings yet