Professional Documents
Culture Documents
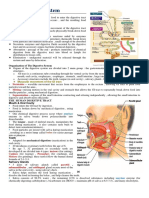
Digestion Is The Mechanical and Chemical Breakdown of
Uploaded by
Himanshu Rajesh PatnekarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Digestion Is The Mechanical and Chemical Breakdown of
Uploaded by
Himanshu Rajesh PatnekarCopyright:
Available Formats
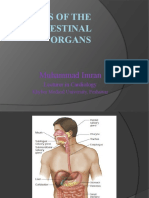
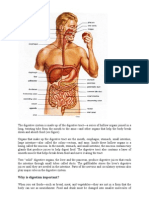
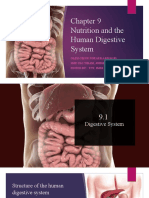
Digestion is the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into smaller components that are more easily absorbed
into a blood stream, for instance. Digestion is a form of catabolism: a breakdown of large food molecules to smaller ones. When food enters the mouth, its digestion starts by the action of mastication, a form of mechanical digestion, and the contact of saliva. Saliva, which is secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down theesophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which are waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes. After some time (typically an hour or two in humans, 46 hours in dogs, somewhat shorter duration in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas, and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K(K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. [1] Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.[2]
Contents
[hide]
1 Digestive systems o 1.1 Secretion systems 1.1.1 Channel transport system 1.1.2 Molecular syringe 1.1.3 Conjugation machinery 1.1.4 Release of outer membrane vesicles o 1.2 Gastrovascular cavity o 1.3 Phagosome o 1.4 Specialised organs and behaviours 1.4.1 Beaks 1.4.2 Tongue 1.4.3 Teeth 1.4.4 Crop 1.4.5 Abomasum 1.4.6 Specialised behaviours o 1.5 In earthworms 2 Overview of vertebrate digestion 3 Human digestion process o 3.1 Phases of gastric secretion o 3.2 Oral cavity o 3.3 Pharynx o 3.4 Esophagus o 3.5 Stomach o 3.6 Small intestine o 3.7 Large intestine 4 Breakdown into nutrients o 4.1 Protein digestion o 4.2 Fat digestion o 4.3 Carbohydrate digestion
o 4.4 DNA and RNA digestion 5 Digestive hormones 6 Significance of pH in digestion 7 Uses of animal's internal organs by humans 8 See also 9 References 10 External links
Digestive systems
You might also like
- Disgestion and NutritionDocument2 pagesDisgestion and NutritionfitraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Human Digestive System: The Mouth and PharynxDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Human Digestive System: The Mouth and Pharynxitachi278No ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of The Digestive Systemangelignacio2209No ratings yet
- DisgestionDocument1 pageDisgestionandressookdeo29No ratings yet
- Nutrition and DigestionDocument8 pagesNutrition and DigestionjeffchegzodNo ratings yet
- Digestion Is The Breaking Down of Chemicals in The Body, Into A Form That Can Be Absorbed. It IsDocument10 pagesDigestion Is The Breaking Down of Chemicals in The Body, Into A Form That Can Be Absorbed. It IsSean McleanNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Finalppt LectureDocument30 pagesDigestive System Finalppt LectureFrancene YepesNo ratings yet
- The Digestion ProcessDocument7 pagesThe Digestion ProcessKim Szydney RachoNo ratings yet
- 35.1 - The Digestive SystemDocument16 pages35.1 - The Digestive SystemMostafa Galal El Din100% (1)
- The Digestive System MODULEDocument3 pagesThe Digestive System MODULEBen Moldenhaur100% (2)
- Food Nutrient Digestion AbsorptionDocument34 pagesFood Nutrient Digestion AbsorptionvinodhknatrajanNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesDigestive Systemapi-208253906100% (1)
- Functions of The Gastrointestinal Organs: Muhammad ImranDocument21 pagesFunctions of The Gastrointestinal Organs: Muhammad ImranSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Digestion. Segmentation Mixes The Chyme With Enzymes From TheDocument3 pagesMechanical Digestion. Segmentation Mixes The Chyme With Enzymes From TheEj OrqueNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System ExplainedDocument4 pagesThe Digestive System ExplainedArash DhillonNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument5 pagesAnaphyAnne BrazilNo ratings yet
- DIGESTIVE SYSTEM BREAKDOWNDocument7 pagesDIGESTIVE SYSTEM BREAKDOWNtheodore_estradaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Digestive SystemJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - DigestionDocument17 pagesChapter 6 - DigestionTrisha100% (1)
- Human Physiology NotesDocument28 pagesHuman Physiology NotesZaraNo ratings yet
- Nutrition-GSCI1045 Lecture - Week 4Document12 pagesNutrition-GSCI1045 Lecture - Week 4Nicholas ObasiNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Breaks Down Food for Cellular UseDocument11 pagesDigestive System Breaks Down Food for Cellular UsePia Sempron100% (1)
- The Digestive System A Level NotesDocument7 pagesThe Digestive System A Level Noteselendria100% (1)
- Human Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesHuman Digestive SystemSyeda NafeezaNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesHuman Digestive SystemSyeda NafeezaNo ratings yet
- Organ Tubuh Manusia EnglishDocument6 pagesOrgan Tubuh Manusia EnglishL-Viva'An Ri-l SpqNo ratings yet
- How Food Is Digested (Alvin Dias)Document7 pagesHow Food Is Digested (Alvin Dias)Alvin Dias NNo ratings yet
- Pancreas: FunctionDocument3 pagesPancreas: FunctionitsankurzNo ratings yet
- Digestive System 2022-23Document28 pagesDigestive System 2022-23Fady Fady100% (1)
- BIOCHEM DigestionDocument53 pagesBIOCHEM DigestionAngelika Perez CunanNo ratings yet
- AbsorbtionDocument2 pagesAbsorbtionÁšhlëy Ålïãh GhåñįęNo ratings yet
- Running Head: 1: The Process of Human DigestionDocument5 pagesRunning Head: 1: The Process of Human Digestiongmelendez2No ratings yet
- Overview of The Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesOverview of The Digestive SystemMehmet SaylıkNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System Chapter SummaryDocument67 pagesHuman Digestive System Chapter SummaryfadilahNo ratings yet
- Digestion: The Digestive SystemDocument66 pagesDigestion: The Digestive SystemTonique GordonNo ratings yet
- Digestion Is The Breakdown of Large, Insoluble Food Molecules Into Small, Water-Soluble Molecules Using Mechanical and Chemical ProcessesDocument14 pagesDigestion Is The Breakdown of Large, Insoluble Food Molecules Into Small, Water-Soluble Molecules Using Mechanical and Chemical ProcessesMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY (Second Term)Document55 pagesBIOLOGY (Second Term)carlaplana2008No ratings yet
- Chemically Digested To Small Molecules That AreDocument14 pagesChemically Digested To Small Molecules That AreVarun WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Human NutritionDocument23 pagesHuman NutritionShechem KumarNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Alimentary Tract of The Digestive System MouthDocument5 pagesDigestive System Alimentary Tract of The Digestive System MouthJoNo ratings yet
- Updated Presentation Note - 082207Document3 pagesUpdated Presentation Note - 082207Joshua AladenikaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition PresentationDocument23 pagesNutrition Presentationanneborja511No ratings yet
- The Anatomy of The StomachDocument33 pagesThe Anatomy of The StomachVictor OmoloNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument5 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionSheehan MathurNo ratings yet
- Part I: Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesPart I: Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemLleana TanNo ratings yet
- Calamba Doctors' College Lecture on Digestion, Absorption, and MetabolismDocument13 pagesCalamba Doctors' College Lecture on Digestion, Absorption, and MetabolismMelody DoriaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument29 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemNadia WidiantiNo ratings yet
- Digestive System A&p BookletDocument11 pagesDigestive System A&p Bookletnurse1990No ratings yet
- Shakila Hamed Report PDFDocument9 pagesShakila Hamed Report PDFShakila HamidNo ratings yet
- M1 Lesson 2Document6 pagesM1 Lesson 2Catherine Sinen ObinqueNo ratings yet
- The Digestive Process: A Concise Guide to the Organs and FunctionsDocument14 pagesThe Digestive Process: A Concise Guide to the Organs and FunctionsRASSaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesDigestive SystemDeepesh BansalNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument43 pagesHuman PhysiologyBlowDatZaZaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System (Unit X)Document44 pagesDigestive System (Unit X)zahraNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument3 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionDJ DannyNo ratings yet
- Unit IV - Digestive and Excretory SystemDocument54 pagesUnit IV - Digestive and Excretory SystemsahilNo ratings yet
- Digestion & Absorption: Anatomy and Processes in Under 40Document3 pagesDigestion & Absorption: Anatomy and Processes in Under 40wajiha raufNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PowerpointDocument65 pagesDigestive System Powerpointapi-263357086No ratings yet
- Leaky Gut Syndrome Stop!: A Complete Guide To Leaky Gut Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & A Holistic System To Eliminate LGS Naturally & PermanentlyFrom EverandLeaky Gut Syndrome Stop!: A Complete Guide To Leaky Gut Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & A Holistic System To Eliminate LGS Naturally & PermanentlyNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Anthe (Senior) - 2016 EnglishDocument16 pagesSample Paper Anthe (Senior) - 2016 EnglishHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- Himanshu Patnekar - B2B A Case 8Document3 pagesHimanshu Patnekar - B2B A Case 8Himanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper: Aakash National Talent Hunt Exam 2015 (Senior)Document1 pageSample Paper: Aakash National Talent Hunt Exam 2015 (Senior)Himanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- 11th Feb 2012Document9 pages11th Feb 2012Himanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- Case 10Document3 pagesCase 10Himanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Anthe-2014Document14 pagesSample Paper Anthe-2014Mitchell Jackson50% (6)
- B2B Marketing: Contributers: Prof. Abhay KardeguddiDocument19 pagesB2B Marketing: Contributers: Prof. Abhay KardeguddiHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument1 pageFood SecurityHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- Li Ka-Shing: at A GlanceDocument2 pagesLi Ka-Shing: at A GlanceHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- 30th Batch Sem III Strategic Business Management (A) Case 05 PDFDocument2 pages30th Batch Sem III Strategic Business Management (A) Case 05 PDFHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- PM - Chapter 5 - R1 Systems Development Cycle Middle & Later Stages 200413Document20 pagesPM - Chapter 5 - R1 Systems Development Cycle Middle & Later Stages 200413Himanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- PLVDocument5 pagesPLVHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- 10 values MBAs must learnDocument3 pages10 values MBAs must learnPoorvi JainNo ratings yet
- RetailandShopperTrendsEmergingMarkets 000 PDFDocument32 pagesRetailandShopperTrendsEmergingMarkets 000 PDFHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- InvitationDocument1 pageInvitationHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- How To Determine ROI - Non Manufacturing Environment PDFDocument4 pagesHow To Determine ROI - Non Manufacturing Environment PDFmoonthinkerNo ratings yet
- Is Africa the New Market of the FutureDocument5 pagesIs Africa the New Market of the FutureHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- LinearDocument3 pagesLinearHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument1 pageIntroductionHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- Instant Food ReportDocument85 pagesInstant Food ReportAks SinhaNo ratings yet
- S&RM Session Plan CasesDocument21 pagesS&RM Session Plan CasesHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument1 pageIntroductionHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- Man HourDocument2 pagesMan HourHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- Word DetailsDocument1 pageWord DetailsHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- QT CasesDocument18 pagesQT CasesHimanshu Rajesh Patnekar0% (1)
- CASE1 AltavoxDocument1 pageCASE1 Altavoxkeberosu8324No ratings yet
- S&RM Session Plan CasesDocument21 pagesS&RM Session Plan CasesHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- Manpower Planning and Recruitment ProcessDocument39 pagesManpower Planning and Recruitment ProcessHimanshu Rajesh PatnekarNo ratings yet
- Blood 2Document13 pagesBlood 2abbaslafeNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument18 pagesDigestive SystemSwit Manrique-De HittaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Transport in Animals (Circulatory System) - Q&ADocument19 pagesChapter 9 - Transport in Animals (Circulatory System) - Q&AAnkith RudreshNo ratings yet
- Reptile CharacteristicsDocument26 pagesReptile CharacteristicsNihal YildrimNo ratings yet
- K6respiration PDFDocument13 pagesK6respiration PDFYS NateNo ratings yet
- L1 - Human BodyDocument40 pagesL1 - Human BodyFikril HakimNo ratings yet
- SLEEP HYGIENE INDEX DrWendieRobbins PDFDocument1 pageSLEEP HYGIENE INDEX DrWendieRobbins PDFrinaldy andriansyahNo ratings yet
- Class IX Biology Respiratory System Review QuestionsDocument6 pagesClass IX Biology Respiratory System Review QuestionsMohammad Farhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Sleep and Elderly BrochureDocument2 pagesSleep and Elderly BrochureMohammedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Respiratory SystemMayden Grace GayatgayNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument17 pagesBlood TransfusionRayne BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Immunohematology-Lab MidtermsDocument9 pagesImmunohematology-Lab MidtermsRachel PlanillaNo ratings yet
- Dry Brushing TechniqueDocument3 pagesDry Brushing Techniqueapi-206772759100% (1)
- CANINE-Canine Transfusion Reactions - Part 2.prevention and TreatmentDocument7 pagesCANINE-Canine Transfusion Reactions - Part 2.prevention and Treatmenttaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Immunohematology Trans by KTRC (Wala Ito Sa Book)Document21 pagesImmunohematology Trans by KTRC (Wala Ito Sa Book)Angelo ErispeNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10Document6 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10SANJEEV KUMARNo ratings yet
- Hedgehog Hibernation Fact SheetDocument3 pagesHedgehog Hibernation Fact SheetHapus NamaNo ratings yet
- Association of Veterinary Hematology and Transfusion Medicine (AVHTM) Transfusion Reaction Small Animal Consensus Statement (TRACS) Part 2 - Prevention and MonitoringDocument22 pagesAssociation of Veterinary Hematology and Transfusion Medicine (AVHTM) Transfusion Reaction Small Animal Consensus Statement (TRACS) Part 2 - Prevention and MonitoringLaboratório de Patologia ClínicaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of SplanchnologyDocument10 pagesIntroduction of Splanchnologyapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Chart ExamDocument2 pagesHuman Body Systems Chart ExamgabrielaNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Module For Grade 11: Earth and Life Science How Animals Survive How Will You Use This Module?Document8 pagesSelf-Learning Module For Grade 11: Earth and Life Science How Animals Survive How Will You Use This Module?MIMOYOUNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternEna Katherine CanonoNo ratings yet
- Tissue Webquest Student ExampleDocument4 pagesTissue Webquest Student Exampleapi-377689746No ratings yet
- AQA A-Level Psychology PYA4: Endogenous Pacemakers and Exogenous ZeitgebersDocument16 pagesAQA A-Level Psychology PYA4: Endogenous Pacemakers and Exogenous ZeitgebersStephan Amaranath100% (5)
- Cardio System 2Document1 pageCardio System 2api-298312370No ratings yet
- Unit 7 Study GuideDocument5 pagesUnit 7 Study GuideSierra MarieNo ratings yet
- PhlebotomyDocument46 pagesPhlebotomyQaiser ZamanNo ratings yet
- GRD121 Anatomy and Physiology B - Course Syllabi (I) TheoryDocument5 pagesGRD121 Anatomy and Physiology B - Course Syllabi (I) TheoryMaryam MohamoudNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AGEDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AGEYum CNo ratings yet
- Improve Memory with Yoga BreathingDocument5 pagesImprove Memory with Yoga Breathingsugu61No ratings yet