Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basics of Computer
Uploaded by
tarun06Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basics of Computer
Uploaded by
tarun06Copyright:
Available Formats
Types of Computers
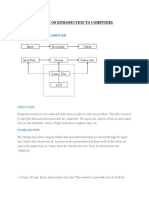
1. Mainframe Computers 2. Mini Computers 3. Micro Computers 4. Super Computers Mainframe Computers work at a high speed, and have a high storage capacity Mini Computers are medium and powerful Computers. Micro Computer are the commonly used as general purpose Computer Data Storage in a Computer 1. 4bits = 1 Nibble 2. 8bits = 1 byte 3. 1024 bytes = 1k or 1kb (kilobyte) 4. 1024KB = 1MB (mega byte) 5. 1024MB = 1GB (Gega byte) 6. 1024GB = 1TBC Terabytes Organization of Computer: 1. Arithmetic and Logical unit 2. Memory unit 3. Control unit 4. Input unit 5. Output unit The Input and Output units are used to receive and display Inputs & Solutions Common i/p & o/p devices : Keyboard, mouse, monitor, printer The CPU (Central Processing Unit) Consists of. 1. ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) 2. CU (Control Unit) 3. MU (Memory Unit) 1. The Control Unit Controls all the activities of the Computer. It sends commands and control signals and finds the sequence of instruction to be executed. 2. Memory Unit is the place where all input data and results are stored. Computer memory is also available in the form of Random Access Memory (RAM) 3. ALU Consists of CKTs for arithmetic operations(+,-,*,/) and logical operations (<,>,>=,<=,==,!=) Connected components of CPU are called peripherals
Storage Devices : 1. Floppy disk 2. Hard disk 3. Compact disk Computer Main Memory : Primary memory RAM (Random Access memory) Secondary memory ROM (Read only memory) Hard disk RAM : It is a temporary storage medium in a computer. The data to be processed by the computer are transferred from a storage devices or a keyboard to RAM results from a executed program are also stored in RAM. The data stored will be erased when the computer is off. ROM (Read only Memory) : This is a non-volatile or data storage medium which stores start up programs (operating systems). This essentially stores the BIOS (Basic Input Operating System) Note : Basically Computer System components communicate it binaries as (0s & 1s, 0 refers OFF state,1 refer ON state) Languages of different Generation Computer. 1. First Generation Language : All the instructions are in the binary form and are referred to as machine level or low level language (LLL). It is very difficult to read the instructions written in binary Eg : 00110101011101110001, 101100001010101 2. Second Generation Language: all the instruction are in the forms of mnemonics. The symbolic instruction language called as Assembly Language. All the symbolic instructions are converted into binaries with the help of translator called Assembles. ASCII (American Standard Code For Information Interchange) is commonly used for translation of source Program into object program
You might also like
- PlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12From EverandPlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12No ratings yet
- Block Diagram of Digital Computer: Central Processing Unit (CPU) 1. 2. 3Document11 pagesBlock Diagram of Digital Computer: Central Processing Unit (CPU) 1. 2. 3desojolNo ratings yet
- PSCP Unit-1Document9 pagesPSCP Unit-1sachin jainNo ratings yet
- BT3 IT - Assembling HardwareDocument10 pagesBT3 IT - Assembling HardwareْNo ratings yet
- Class Xi - CS CH-1Document7 pagesClass Xi - CS CH-1yajur9461No ratings yet
- Computer Science-XI-Chapter1Document28 pagesComputer Science-XI-Chapter1syeda taiba nooraniNo ratings yet
- Computer System & Organization: Unit-IDocument58 pagesComputer System & Organization: Unit-I8D Audio TuneNo ratings yet
- LAB 01-Introduction To Computers-1-7Document7 pagesLAB 01-Introduction To Computers-1-7Mallika Dog54No ratings yet
- BasicComputerSkills NotesDocument31 pagesBasicComputerSkills NotesVanamala MahathiNo ratings yet
- 105-P02 (Compatibility Mode)Document15 pages105-P02 (Compatibility Mode)Ahmad Thariq RahmatullahNo ratings yet
- Computer: - It Is An Electronic Device Which Accepts Data at Its Input, Process It by Doing SomeDocument5 pagesComputer: - It Is An Electronic Device Which Accepts Data at Its Input, Process It by Doing SomePawan NaniNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals SummaryDocument50 pagesComputer Fundamentals SummaryRAMAKRISHNA KRISHNANo ratings yet
- Introduction to Computers Block Diagram and ComponentsDocument5 pagesIntroduction to Computers Block Diagram and ComponentsMULAKALA NIVESH KUMAR VU21CSEN0300028No ratings yet
- Complete C & Data Structure NotesDocument195 pagesComplete C & Data Structure NotesLatchireddy ManojkumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization-C2Document9 pagesComputer Organization-C2irfanahmed.dbaNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND PROCESSING DATADocument11 pagesCOMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND PROCESSING DATAalysonmicheaalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTUREDocument9 pagesChapter1-COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTUREbhuvanalakshmi kNo ratings yet
- Ce Workshop Lab ManualDocument140 pagesCe Workshop Lab Manualvamsi raviNo ratings yet
- Practical 1:-Introduction of Computer HardwareDocument13 pagesPractical 1:-Introduction of Computer HardwareKaveesh NykNo ratings yet
- It Workshop LAB MANUALDocument45 pagesIt Workshop LAB MANUALNanny BoppanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Basic Computer Operations: 1) Computer Accepts Data or Instructions by Way of Input, (INPUT)Document9 pagesChapter 2: Basic Computer Operations: 1) Computer Accepts Data or Instructions by Way of Input, (INPUT)Iqra KhanNo ratings yet
- Inside a Computer's Main Components and FunctionsDocument15 pagesInside a Computer's Main Components and FunctionsMuhamad Irvan SNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Basic Components of ComputerDocument26 pagesUnit 2 Basic Components of ComputerAnurag GoelNo ratings yet
- Chapter No.1 Basics of Information TechnologyDocument17 pagesChapter No.1 Basics of Information TechnologyAmruta DhengaleNo ratings yet
- Computer ApplicationDocument22 pagesComputer ApplicationRIMA CHATURVEDI100% (2)
- Computers, Microprocessors, and Microcontrollers: An IntroductionDocument65 pagesComputers, Microprocessors, and Microcontrollers: An IntroductionHARSHITHA BHAVISETTINo ratings yet
- C Programming BookDocument177 pagesC Programming BookJohn BunyanNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The Computer SystemDocument4 pagesAn Overview of The Computer SystemTerna HonNo ratings yet
- Unit1 NewDocument104 pagesUnit1 NewGayathri potnuru JioNo ratings yet
- First Stage Koya University Software Engineering Department: Academic ComputingDocument22 pagesFirst Stage Koya University Software Engineering Department: Academic ComputingBawar Abid AbdallaNo ratings yet
- GED 101 LecDocument5 pagesGED 101 LecAbbad AliNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of a ComputerDocument11 pagesBlock Diagram of a ComputerMegacable MegacableNo ratings yet
- Computer ApplicationssDocument29 pagesComputer ApplicationssFatima SarwarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document17 pagesLecture 2MUHAMMAD RAHEEL BSSE-FA20-100No ratings yet
- Meeting 2 Inside ComputerDocument16 pagesMeeting 2 Inside ComputerFelix Rizky LesmanaNo ratings yet
- NEW BASIC OF COM KulDocument13 pagesNEW BASIC OF COM KulPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals Lab -1 Components and FunctionsDocument79 pagesComputer Fundamentals Lab -1 Components and Functionsdh_kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1, 2 Part BDocument58 pagesUnit 1, 2 Part BHarish Singh GhughtyalNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Structure of ComputersDocument115 pagesGroup 1 - Structure of ComputersPELAGIO, Angelo Uriel R.100% (1)
- ALU CU Register T: Omputer RganizationDocument7 pagesALU CU Register T: Omputer Rganizationirfanahmed.dbaNo ratings yet
- Computer System Components and OperationsDocument13 pagesComputer System Components and OperationsDik EshNo ratings yet
- 5.input Output Devices and MemoryDocument20 pages5.input Output Devices and MemoryGR FaisalNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument16 pages1 Introductionharikrishna17179No ratings yet
- Computer Science (NEW) Code: 083 Ch1: Comp. System and OrganisationDocument37 pagesComputer Science (NEW) Code: 083 Ch1: Comp. System and OrganisationTeenu GamerzNo ratings yet
- Intel Microprocessors Architecture ProgrDocument4 pagesIntel Microprocessors Architecture ProgrIan MainaNo ratings yet
- p.1 (Digital Computer)Document13 pagesp.1 (Digital Computer)Asakti sinhaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bhs IngDocument4 pagesTugas Bhs IngapriliaNo ratings yet
- MS Office and Computer ApplicationDocument12 pagesMS Office and Computer ApplicationAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document48 pagesUnit 1Sancarapu NagarajuNo ratings yet
- Computer NotesDocument25 pagesComputer NotesRahulNo ratings yet
- Computer SkillsDocument66 pagesComputer SkillsJM (JM)No ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Computer Types: Digital Logic Design and Computer Organization (Dldco)Document37 pagesUNIT-1 Computer Types: Digital Logic Design and Computer Organization (Dldco)surya suryaNo ratings yet
- FundamentalDocument87 pagesFundamentalAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Management and Business TechnologyDocument11 pagesFaculty of Management and Business Technologyvictorjeffry24No ratings yet
- Types and Functional Unit of ComputersDocument4 pagesTypes and Functional Unit of ComputersAqila EbrahimiNo ratings yet
- EE1005 L01 Computers & ProgrammingDocument35 pagesEE1005 L01 Computers & ProgrammingShilin ZhangNo ratings yet
- Computer NotesDocument12 pagesComputer NotesSachinNo ratings yet
- BSC Computer FundamentalsDocument9 pagesBSC Computer FundamentalsbalaNo ratings yet
- Implement For Key Object in HashMapDocument2 pagesImplement For Key Object in HashMaptarun06No ratings yet
- Introduction To String HandlingDocument15 pagesIntroduction To String Handlingtarun06No ratings yet
- Design Patterns in Java: A Design Patterns Are Well-Proved Solution For Solving The Specific Problem/taskDocument1 pageDesign Patterns in Java: A Design Patterns Are Well-Proved Solution For Solving The Specific Problem/tasktarun06No ratings yet
- RectangleDocument34 pagesRectangletarun06No ratings yet
- AOPDocument66 pagesAOPtarun06No ratings yet
- It Has Been Observed That The Struggles For Freedom in India Had Been A Merger of A Whole Series of Political Events Spreading Over Many DecadesDocument4 pagesIt Has Been Observed That The Struggles For Freedom in India Had Been A Merger of A Whole Series of Political Events Spreading Over Many Decadestarun06No ratings yet
- Pid Color Red' Sid NameDocument3 pagesPid Color Red' Sid Nametarun06No ratings yet
- Class ImmutableDocument7 pagesClass Immutabletarun06No ratings yet
- MediaDocument1 pageMediatarun06No ratings yet
- Find Second Highest or Second Maximum Salary of An EmployeeDocument2 pagesFind Second Highest or Second Maximum Salary of An Employeetarun06No ratings yet
- Points From NCERT Books Indian History Part 1Document3 pagesPoints From NCERT Books Indian History Part 1tarun06No ratings yet
- 8 BitsDocument18 pages8 Bitstarun06No ratings yet
- Document 1Document1 pageDocument 1tarun06No ratings yet
- SHRT Question sp2 PDFDocument2 pagesSHRT Question sp2 PDFtarun06No ratings yet
- MacDocument1 pageMactarun06No ratings yet
- Install MatlabDocument1 pageInstall Matlabtarun06No ratings yet
- Assemler 2Document1 pageAssemler 2tarun06No ratings yet
- Low Latency and PredictabilityDocument6 pagesLow Latency and Predictabilitytarun06No ratings yet
- The World Is Not Just Integers: Programming Languages Support Numbers With FractionDocument4 pagesThe World Is Not Just Integers: Programming Languages Support Numbers With Fractiontarun06No ratings yet
- Xilinx Ise 9.1I: ObjectiveDocument11 pagesXilinx Ise 9.1I: Objectivetarun06No ratings yet
- Understanding the Differences Between Using, Drop Pseudo Ops and Open vs Closed SubroutinesDocument2 pagesUnderstanding the Differences Between Using, Drop Pseudo Ops and Open vs Closed Subroutinestarun06No ratings yet
- DCCN1Document2 pagesDCCN1tarun06No ratings yet
- What Are The Advantages of MASM Assembler?Document1 pageWhat Are The Advantages of MASM Assembler?tarun06No ratings yet
- C Plus QuestionsDocument2 pagesC Plus Questionstarun06No ratings yet
- Chapter 4-1Document33 pagesChapter 4-1tarun06No ratings yet
- #Spin - Py: From Import Import DefDocument1 page#Spin - Py: From Import Import Deftarun06No ratings yet
- Python 1Document1 pagePython 1tarun06No ratings yet
- MacroDocument1 pageMacrotarun06No ratings yet
- Skype corporate VP, Birla Sun Life CEO, Bhubaneswar and Imphal airportsDocument1 pageSkype corporate VP, Birla Sun Life CEO, Bhubaneswar and Imphal airportstarun06No ratings yet
- Designing Efficient Irrigation CanalsDocument2 pagesDesigning Efficient Irrigation Canalstarun06No ratings yet
- B-63950en 04 100111Document678 pagesB-63950en 04 100111Ibon Cid Rivera50% (2)
- AP Chemistry - Trends in The Periodic TableDocument3 pagesAP Chemistry - Trends in The Periodic Tableilias1973No ratings yet
- Fig.1 Block Diagram of TransmitterDocument5 pagesFig.1 Block Diagram of TransmitterKranthi KumarNo ratings yet
- DRX-T7445HD-H: Toshiba X-Ray Tube (Water-Cooled Type)Document4 pagesDRX-T7445HD-H: Toshiba X-Ray Tube (Water-Cooled Type)Advanced Medical Group AMGNo ratings yet
- máy cắt sf6 abbDocument7 pagesmáy cắt sf6 abbQuảng Thành NamNo ratings yet
- Inventory list of electronic equipment and accessoriesDocument2 pagesInventory list of electronic equipment and accessoriessmuralirajNo ratings yet
- McIntosh MX406 Car SourceDocument2 pagesMcIntosh MX406 Car SourceNicolus CageNo ratings yet
- XDVDocument54 pagesXDVnachiket1234No ratings yet
- Eng TKR-304E ManualDocument36 pagesEng TKR-304E ManualJean TevesNo ratings yet
- NE91 Project - VC4-ReportDocument8 pagesNE91 Project - VC4-ReportDipak ShahNo ratings yet
- Analogue Electronics 1, DEE 1 Notes - 075733Document137 pagesAnalogue Electronics 1, DEE 1 Notes - 075733Kirimi DanNo ratings yet
- 3MN-00482-0004-REZZA Issue 0 03Document122 pages3MN-00482-0004-REZZA Issue 0 03Yasser El-sammakNo ratings yet
- Micom P341: Interconnection Protection RelayDocument425 pagesMicom P341: Interconnection Protection RelayhudsonNo ratings yet
- Manual de Servicio de Equipo de Sonido de Radio mp3Document46 pagesManual de Servicio de Equipo de Sonido de Radio mp3daniel perezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Systems Programming (CSE 405) Credit: 4 Prerequisite: CSE 301Document25 pagesIntroduction To Systems Programming (CSE 405) Credit: 4 Prerequisite: CSE 301Stricker ManNo ratings yet
- Diamond Like CoatingsDocument24 pagesDiamond Like CoatingscecilchifticaNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual: Epc-50/50E Air-Fuel Controllers Form EPC-50/50e OM 9-12Document46 pagesOperating Manual: Epc-50/50E Air-Fuel Controllers Form EPC-50/50e OM 9-12Esau Jose PabloNo ratings yet
- Weierwei Vev-3288 D Manual Price RangeDocument2 pagesWeierwei Vev-3288 D Manual Price RangeCybertronics Center100% (4)
- LM5116Document37 pagesLM5116Evanier Souza de AlencarNo ratings yet
- Fiery Cws Cofigure Color Work StationDocument90 pagesFiery Cws Cofigure Color Work StationAli VatanNo ratings yet
- Formation Micro Imager ToolDocument25 pagesFormation Micro Imager Toolgee100% (2)
- 0-IBM - Brocade Product Quick Ref Guide (Matrix Mapping) - 23290543Document3 pages0-IBM - Brocade Product Quick Ref Guide (Matrix Mapping) - 23290543Nguyen Van HaiNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Introduction To Android StudioDocument19 pagesLab 1 Introduction To Android StudioYong ShunNo ratings yet
- Power Converters Simulation Lab Manual - (2015-2016)Document41 pagesPower Converters Simulation Lab Manual - (2015-2016)Leela KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Installation QualificationDocument17 pagesInstallation Qualificationtrinath16198067% (6)
- Ceramic - Filter - and - Duplexer - Data - Sheet RALTRONDocument7 pagesCeramic - Filter - and - Duplexer - Data - Sheet RALTRONYung SangNo ratings yet
- Maxximo: Diagnostic Manual MAN-00129Document1 pageMaxximo: Diagnostic Manual MAN-00129LeelaNo ratings yet
- Capacitors: Capacitance Parallel PlateDocument3 pagesCapacitors: Capacitance Parallel Platevictoria schoolNo ratings yet
- Exploded View & Part ListDocument44 pagesExploded View & Part ListGardufNo ratings yet
- 173400Document211 pages173400aiabbasi9615No ratings yet