Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Direct and Reported Speech
Uploaded by
Marta Alcaraz CanteroOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Direct and Reported Speech
Uploaded by
Marta Alcaraz CanteroCopyright:
Available Formats
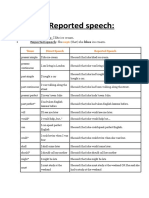
Direct and Reported Speech (El estilo directo y indirecto)
Cuando queremos comunicar o informar de lo que otra persona ha dicho, hay dos maneras de hacerlo: utilizando el estilo directo o el estilo indirecto.
Direct Speech (El estilo directo) Cuando queremos informar exactamente lo que otra persona ha dicho, utilizamos el estilo directo. Con este estilo lo que la persona ha dicho se coloca entre comillas ("...") y deber ser palabra por palabra.
Ejemplos: "I am going to London next week," she said. ("Voy a Londres la semana que viene," ella dijo.) "Do you have a pen I could borrow," he asked. ("Tienes un bolgrafo que puedas prestarme," l
pregunt.)
Alice said, "I love to dance." (Alice dijo, "Me encanta bailar.") Chris asked, "Would you like to have dinner with me tomorrow night?" (Chris pregunt, "Te
gustara cenar conmigo maana por la noche?")
Reported Speech (El estilo indirecto) El estilo indirecto, a diferencia del estilo directo, no utiliza las comillas y no necesita ser palabra por palabra. En general, cuando se usa el estilo indirecto, el tiempo verbal cambia. A continuacin tienes un explicacin de los cambios que sufren los tiempos verbales. A veces se usa "that" en las frases afirmativas y negativas para introducir lo que ha dicho la otra persona. Por otro lado, en las frases interrogativas se puede usar "if" o "whether".
Direct Speech
Reported Speech
Present Simple "He's American," she said. "I'm happy to see you," Mary said. " He asked, "Are you busy tonight?" Present Continuous "Dan is living in San Francisco," she said.
Past Simple She said he was American. Mary said that she was happy to see me. He asked me if I was busy tonight. Past Continuous She saidDan was living in San Francisco.
" He said, "I'm making dinner." "Why are you working so hard?" they asked. Past Simple "We went to the movies last night," he said.
He told me that he was making dinner. They asked me why I was working so hard. Past Perfect Simple He told me they had gone to the movies last night. Greg said that he hadn't gone to work yesterday. She asked me if I had bought a new car. Past Perfect Continuous Vicki told me she'd been working last night. They said that they hadn't been waiting long. He asked if I'd been sleeping when he called. Past Perfect Simple Heather told me that she'd already eaten. They said they hadn't been to China. I asked her whether she'd worked there before. Past Perfect Continuous He said he'd been studying English for two years. Steve told me that they'd been dating for over a year.
" Greg said, "I didn't go to work yesterday." "Did you buy a new car?" she asked. Past Continuous "I was working late last night," Vicki said. " They said, "we weren't waiting long." " He asked, "were you sleeping when I called?" Present Perfect Simple " Heather said, "I've already eaten." "We haven't been to China," they said. "Have you worked here before?" I asked. Present Perfect Continuous "I've been studying English for two years," he said. " Steve said, "we've been dating for over a year now."
"Have you been waiting long?" they asked. They asked whether I'd been waiting long. Past Perfect Simple "I'd been to Chicago before for work," he said. Past Perfect Continuous " She said, "I'd been dancing for years before the accident." Past Perfect Simple (*NO CHANGE) He said that he'd been to Chicago before for work. Past Perfect Continuous (*NO CHANGE) She said she'd been dancing for years before the accident.
Nota: Cuando hablamos de algo que no ha cambiado (todava es verdad) o que es en el futuro, no tenemos que cambiar el tiempo verbal.
Ejemplos:
"I'm 30 years old," she said. She said she is 30 years old. Dave said, "Kelly is sick." Dave said Kelly is sick. "We are going to Tokyo next week," they said. They said they are going to Tokyo next week.
"I'll cut my hair tomorrow," Nina said. Nina said she is cutting her hair tomorrow.
Modal Verbs (Los verbos modales)
El tiempo verbal cambia en el estilo indirecto tambin con algunos de los verbos modales:
Direct Speech
Indirect Speech
Will "I'll go to the movies tomorrow," John said. "Will you help me move?" she asked. Can " Debra said, "Allen can work tomorrow."
Would John said he would go to the movies tomorrow. She asked me if I would help her move. Could Debra said Allen could work tomorrow.
"Can you open the window, please?", he asked. He asked me if I could open the window. Must "You must wear your seatbelt," mom said. " She said, "You must work tomorrow." Shall "Shall we go to the beach today?" Tom asked. Had to My mom said I had to wear my seatbelt. She said I had to work tomorrow. Should Tom asked if we should go to the beach today. She asked me what we should do tonight. Might/Could Jane said she might not be in class tomorrow. The boy asked if he could use the bathroom.
"What shall we do tonight?" she asked. May " Jane said, "I may not be in class tomorrow." " the boy asked. "May I use the bathroom, please?" the boy asked.
Nota: Con "would", "could", "should", "might" y "ought to", el tiempo no cambia.
You might also like
- Direct & Report Speech (Chismes)Document3 pagesDirect & Report Speech (Chismes)visnjikrizNo ratings yet
- Curso de Ingles - English Lesson - Direct and Reported Speech (Lección de Inglés - El Estilo Directo y Indirecto)Document4 pagesCurso de Ingles - English Lesson - Direct and Reported Speech (Lección de Inglés - El Estilo Directo y Indirecto)David OrtizNo ratings yet
- Direct and Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect and Reported SpeechNestor Portes MorellNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesReported SpeechJaviera Gálvez PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Direct and Reported SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Reported Speechgutyy86341No ratings yet
- Direct and Reported SpeechDocument18 pagesDirect and Reported SpeechAndres Onfire100% (1)
- Direct Speech and Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect Speech and Reported SpeechCati Lara CazorlaNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech TensesDocument2 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech TensesJoseph Polo MartinezNo ratings yet
- This or That Complete Sentences ActivityDocument8 pagesThis or That Complete Sentences ActivityvakimuNo ratings yet
- Modo Directo e IndirectoDocument3 pagesModo Directo e IndirectoKirsis Mata VegaNo ratings yet
- Que Es El Reported SpeechDocument5 pagesQue Es El Reported SpeechCYBERDEIBYSMARQUEZNo ratings yet
- El Estilo Indirecto, A Diferencia Del Estilo Directo, No Utiliza Las Comillas y No Necesita Ser Palabra Por Palabra. enDocument2 pagesEl Estilo Indirecto, A Diferencia Del Estilo Directo, No Utiliza Las Comillas y No Necesita Ser Palabra Por Palabra. enDany OjedaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesReported SpeechEDUARD MUÑOZ CENIZONo ratings yet
- U1 - Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesU1 - Reported SpeechManuel Del AngelNo ratings yet
- Estilo IndirectoDocument4 pagesEstilo IndirectoVictoria Gómez PeláezNo ratings yet
- Exercises - Unit 10Document22 pagesExercises - Unit 10Judith RguezNo ratings yet
- Reporter SpeechDocument15 pagesReporter SpeechAnonymous Lw1e6SmivNo ratings yet
- Penjelasan Tentang Direct and Indirect Speech TerlengkapDocument11 pagesPenjelasan Tentang Direct and Indirect Speech TerlengkapHasby HasbyNo ratings yet
- Fadiyawyni B IngggrisDocument14 pagesFadiyawyni B IngggrisCindy HarapannNo ratings yet
- Nama: Shafira Ananda NIM: 204840132: StatementsDocument7 pagesNama: Shafira Ananda NIM: 204840132: StatementsShafira AnandaNo ratings yet
- Elvira Agnestia Ningrum (B.ingg)Document6 pagesElvira Agnestia Ningrum (B.ingg)Elvira AgnestiaNNo ratings yet
- Exercice SDocument10 pagesExercice SSylvia RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: That If WhetherDocument2 pagesReported Speech: That If WhetherMarlon OchoaNo ratings yet
- Backshift in Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesBackshift in Reported SpeechPablo CorderoNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech - TiaraDocument6 pagesReported Speech - Tiarariani.tiaraNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect John Said-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesDirect and Indirect John Said-WPS OfficeM Zaib SNo ratings yet
- Tense Direct Speech Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesTense Direct Speech Reported SpeechAnca IonNo ratings yet
- EXERCISESDocument8 pagesEXERCISESShafira AnandaNo ratings yet
- TRABAJOS AiavDocument7 pagesTRABAJOS AiavDiana AndradeNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: The House Was Built in 1975Document6 pagesUnit 6: The House Was Built in 1975YunliNo ratings yet
- Is Was: Reported Speech (El Estilo Indirecto)Document6 pagesIs Was: Reported Speech (El Estilo Indirecto)EvensJeanNo ratings yet
- 10 Contoh Soal Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument4 pages10 Contoh Soal Direct and Indirect SpeechIrma Shinta100% (2)
- Reported Speech:: Direct Speech: I Like Ice Cream. Reported Speech: SheDocument3 pagesReported Speech:: Direct Speech: I Like Ice Cream. Reported Speech: SheTik JustinaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument10 pagesReported SpeechDANIELA CEBALLOSNo ratings yet
- Direct and IndirectaDocument2 pagesDirect and IndirectaLovely Diosa BatnagNo ratings yet
- Grammar Reported SpeechDocument10 pagesGrammar Reported Speechmovilnet1999999No ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument1 pageReported SpeechJuan HGNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech - Rules and ExercisesDocument6 pagesReported Speech - Rules and Exercisesanasmateussa2078No ratings yet
- Reported Speech TensesDocument4 pagesReported Speech TensesTR ProductionNo ratings yet
- 6 - Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument4 pages6 - Direct and Indirect SpeechBharathiNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeecheditfotiNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech AnswersDocument19 pagesReported Speech AnswersAroa Viana0% (1)
- Reported Speech (El Estilo Indirecto) : BeforeDocument10 pagesReported Speech (El Estilo Indirecto) : Beforekoalaelena21No ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechUzaahRdzSnttNo ratings yet
- Use Direct and Indirect Speech AppropriatelyDocument2 pagesUse Direct and Indirect Speech AppropriatelyMarielle Villagonzalo100% (2)
- Tense Direct Speech Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesTense Direct Speech Reported SpeechChristeena HoàngNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechHasib QureshiNo ratings yet
- Direct Indirect Speech PatternDocument11 pagesDirect Indirect Speech PatternVinit Kapoor100% (1)
- Indirect Speech or Reported Speech 2Document21 pagesIndirect Speech or Reported Speech 2Constanza Farfán100% (1)
- Reported SpeechDocument15 pagesReported SpeechОльга ЮрьеваNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument10 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechseraNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech ConversionsDocument8 pagesReported Speech ConversionsJhonaly Karin Flores MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Reported questions, requests and pronouns explainedDocument14 pagesReported questions, requests and pronouns explainedFikri HaikalNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv ModificadaDocument9 pagesUnit Iv Modificadawalquiria cabezaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar - SpeechDocument7 pagesEnglish Grammar - SpeechAisy AstarinaNo ratings yet
- Veronica and Susan Telepathic Connection of Two Friends: A tale of two friendsFrom EverandVeronica and Susan Telepathic Connection of Two Friends: A tale of two friendsNo ratings yet
- Countable vs Uncountable NounsDocument12 pagesCountable vs Uncountable NounsMiguel Angel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Expressing IntentionDocument19 pagesExpressing IntentionChristineNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - Resub - MiguelLaricoCondoriDocument8 pagesAssignment 2 - Resub - MiguelLaricoCondoriMIGUEL ANGEL LARICO CONDORINo ratings yet
- Nominal and Verbal Sentences in ArabicDocument7 pagesNominal and Verbal Sentences in ArabicSerendipity EnglishNo ratings yet
- Past TenseDocument11 pagesPast TenseMuhammad Ilham SyaputraNo ratings yet
- Paraphrasing GuideDocument5 pagesParaphrasing GuideErica SouzaNo ratings yet
- Common Irregular Verbs GroupedDocument3 pagesCommon Irregular Verbs Groupedapi-236095657No ratings yet
- GerundDocument18 pagesGerundBecik Uswatun HasanahNo ratings yet
- Anindita Engish Assignment Using Template - 7Document4 pagesAnindita Engish Assignment Using Template - 7NewbieGamers - নিউবি গেমার্সNo ratings yet
- 1 GrammarDocument14 pages1 GrammarJoseph Edrick SayNo ratings yet
- Grammar and Vocabulary GuideDocument85 pagesGrammar and Vocabulary GuideLingüini Meddina VazNo ratings yet
- Saturday, September 2nd 2023, StudentsDocument6 pagesSaturday, September 2nd 2023, StudentsArturo MontielNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Literacy Curriculum PDFDocument19 pagesGrade 4 Literacy Curriculum PDFhlariveeNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Second Half TestDocument2 pages9th Class Second Half TestAli UsmanNo ratings yet
- TagDocument5 pagesTagKennyHuancaÑahueNo ratings yet
- GNS 101 Past QuestionsDocument57 pagesGNS 101 Past QuestionsIbraheem AribidesiNo ratings yet
- Portafolio InglesDocument11 pagesPortafolio InglesMax CtNo ratings yet
- Chapter X-Noun and Noun Clause In...Document14 pagesChapter X-Noun and Noun Clause In...Midori YuriNo ratings yet
- Practise Your TensesDocument67 pagesPractise Your Tensesanjreem100% (2)
- Keep AddingDocument1 pageKeep AddingSamir BantalNo ratings yet
- Past Simple and Comparatives Grammar QuizDocument2 pagesPast Simple and Comparatives Grammar QuizAlba SGNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test of Standard Written EnglishDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Test of Standard Written EnglishRania Sayed0% (2)
- Contractions Grammar ChartDocument2 pagesContractions Grammar ChartGuillermo LeosNo ratings yet
- 8.2.21 KS1 English Paddingtons Post Part 1Document20 pages8.2.21 KS1 English Paddingtons Post Part 1moizmohamed028No ratings yet
- Nivel 2 Speak Out StarterDocument13 pagesNivel 2 Speak Out StarterRafet TanrıoğluNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and AdverbsDocument16 pagesAdjectives and AdverbsNelson LunaNo ratings yet
- List of Verbs (Basic) : English Vocabulary - Vocabulario de InglésDocument8 pagesList of Verbs (Basic) : English Vocabulary - Vocabulario de InglésLily AraveugNo ratings yet
- Formulas and Examples of Past Future TenseDocument3 pagesFormulas and Examples of Past Future TenseNoviPrincessCandyCandyNo ratings yet
- Library: Transcriber's NoteDocument122 pagesLibrary: Transcriber's NoteGutenberg.org100% (3)
- Answers Grammar - Present Simple Tense - Verb To BEDocument6 pagesAnswers Grammar - Present Simple Tense - Verb To BEMaju NavarroNo ratings yet