Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2012 Probability Past IB Questions
Uploaded by
Victor O. WijayaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2012 Probability Past IB Questions
Uploaded by
Victor O. WijayaCopyright:
Available Formats
Probability past IB questions 1. Events A and B have probabilities P(A) = 0.4, P (B) = 0.65, and P(A B) = 0.85.
. (a) (b) (c) Calculate P(A B). State with a reason whether events A and B are independent. State with a reason whether events A and B are mutually exclusive.
(Total 6 marks)
2.
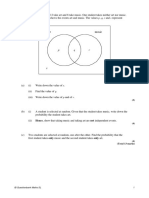
On a particular day 100 children are asked to make a note of what they drank that day. They are given three choices: water (W), coffee (C) or fruit juice (F) 1 child drank only water. 6 children drank only coffee. 8 children drank only fruit juice. 5 children drank all three. 7 children drank water and coffee only. 53 children drank coffee and fruit juice only. 18 children drank water and fruit juice only. (a) Represent the above information on a Venn Diagram.
(4)
(b)
How many children drank none of the above?
(2)
(c)
A child is chosen at random. Find the probability that the child drank (i) (ii) (iii) coffee; water or fruit juice but not coffee; no fruit juice, given that the child did drink water.
(4)
(d)
Two children are chosen at random. Find the probability that both children drank all three choices.
(3) (Total 13 marks)
3.
Neil has three dogs. Two are brown and one is grey. When he feeds the dogs, Neil uses three bowls and gives them out randomly. There are two red bowls and one yellow bowl. This information is shown on the tree diagram below. 2 3 2 3 1 3 B ro w n 1 3 2 G re y 3 1 3 (a) One of the dogs is chosen at random. (i) (ii) Find P (the dog is grey and has the yellow bowl). Find P (the dog does not get the yellow bowl).
(3)
R ed
Y e llo w R ed
Y e llo w
(b)
Neil often takes the dogs to the park after they have eaten. He has noticed that the grey dog plays with a stick for a quarter of the time and both brown dogs play with sticks for half of the time. This information is shown on the tree diagram below. S tic k 2 3 1 3 G re y N o s tic k
B ro w n
N o s tic k S tic k
(i)
Copy the tree diagram and add the four missing probability values on the branches that refer to playing with a stick.
During a trip to the park, one of the dogs is chosen at random. (ii) (iii) (iv) Find P (the dog is grey or is playing with a stick, but not both). Find P (the dog is grey given that the dog is playing with a stick). Find P (the dog is grey and was fed from the yellow bowl and is not playing with a stick).
(9) (Total 12 marks)
4.
There are 49 mice in a pet shop. 30 mice are white. 27 mice are male. 18 mice have short tails. 8 mice are white and have short tails. 11 mice are male and have short tails. 7 mice are male but neither white nor short-tailed. 5 mice have all three characteristics and 2 have none. Copy the diagram below to your examination script. S 3 5 W U W re p re s e n ts w h ite m ic e . M re p re s e n ts m a le m ic e . S re p re s e n ts s h o rt-ta ile d m ic e .
M (a) (b) Complete the diagram, using the information given in the question.
(4)
Find (i) (ii)
n(M W) n(M S)
(3)
Two mice are chosen without replacement. (c) Find P (both mice are short-tailed).
(2) (Total 9 marks)
5.
When Geraldine travels to work she can travel either by car ( C), bus (B) or train (T). She travels by car on one day in five. She uses the bus 50% of the time. The probabilities of her being late (L) when travelling by car, bus or train are 0.05, 0.12 and 0.08 respectively. (a) Copy the tree diagram below and fill in all the probabilities, where NL represents not late, to represent this information.
(5)
C 0 .2 B
L NL L NL L
T NL (b) (c) (d) Find the probability that Geraldine travels by bus and is late.
(1)
Find the probability that Geraldine is late.
(3)
Find the probability that Geraldine travelled by train, given that she is late.
(3) (Total 12 marks)
6.
Claire and Kate both wish to go to the cinema but one of them has to stay at home to baby-sit. The probability that Kate goes to the cinema is 0.2. If Kate does not go Claire goes. If Kate goes to the cinema the probability that she is late home is 0.3. If Claire goes to the cinema the probability that she is late home is 0.6. (a) Copy and complete the probability tree diagram below. L a te 0 .3 K a te 0 .2 ... N o t L a te L a te
... ... C la ire ... (b) Calculate the probability that (i) (ii)
N o t L a te
(3)
Kate goes to the cinema and is not late;
(2)
the person who goes to the cinema arrives home late.
(3) (Total 8 marks)
7.
Let F be the set of all families that have exactly 2 children. (a) Assuming P(boy) = P(girl), copy and complete the following tree diagram, for families with 2 children. B oy
1 2
B oy G irl B oy G irl
G irl
(2)
(b)
What is the probability that a family chosen at random from F has exactly (i) (ii) (iii) 2 boys? 2 boys, if it is known that the first child is a boy? 2 boys, if it is known that there is a boy in the family?
(3) (Total 5 marks)
8.
The sets A, B and C are subsets of U. They are defined as follows: U = {positive integers less than 16} A = {prime numbers} B = {factors of 36} C = {multiples of 4}
(a)
List the elements (if any) of the following: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) A; B; C; A B C.
(4)
(b)
(i) (ii)
Draw a Venn diagram showing the relationship between the sets U, A, B and C. Write the elements of sets U, A, B and C in the appropriate places on the Venn diagram.
(4)
(c)
From the Venn diagram, list the elements of each of the following (i) (ii) (iii) A (B C); (A B); (A B) C.
(3)
(d)
Find the probability that a number chosen at random from the universal set U will be (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) a prime number; a prime number, but not a factor of 36; a factor of 36 or a multiple of 4, but not a prime number; a prime number, given that it is a factor of 36.
(6) (Total 17 marks)
9.
The data in the table below refers to a sample of 60 randomly chosen plants. Growth rate high low total dark 3 8 11 Classification by environment light 8 9 17 shady 14 18 32 total 25 35 60
(a)
(i)
Find the probability of a plant being in a shady environment.
(ii)
Find the probability of a plant having a low growth rate and being in a dark environment.
(iii)
Find the probability of a plant not being in a dark environment.
(5)
(b)
A plant is chosen at random from the above group. Find the probability that the chosen plant has (i) (ii) a high growth rate or is in a dark environment, but not both a light environment, given that it has a high growth rate.
(4)
(c)
The 60 plants in the above group were then classified according to leaf type. It was found that 15 of the plants had type A leaves, 37 had type B leaves and 8 had type C leaves. Two plants were randomly selected from this group. Find the probability that (i) (ii) both plants had type C leaves neither of the plants had type B leaves.
(5) (Total 14 marks)
10
10.
The Venn diagram below shows the number of students studying Science ( S), Mathematics (M) and History (H) out of a group of 20 college students. Some of the students do not study any of these subjects, 8 study Science, 10 study Mathematics and 9 study History. U S 4 2 1 3 3 H 1 A M
(a)
(i) (ii) (iii)
How many students belong to the region labelled A? Describe in words the region labelled A. How many students do not study any of the three subjects?
(5)
(b)
Draw a sketch of the Venn diagram above and shade the region which represents S H.
(1)
(c)
Calculate n(S H).
(2)
This group of students is to compete in an annual quiz evening which tests knowledge of Mathematics, Science and History. The names of the twenty students are written on pieces of paper and then put into a bag. (d) One name is randomly selected from the bag. Calculate the probability that the student selected studies (i) (ii) all three subjects; History or Science.
(2)
11
(e)
A team of two students is to be randomly selected to compete in the quiz evening. The first student selected will be the captain of the team. Calculate the probability that (i) (ii) (iii) the captain studies all three subjects and the other team member does not study any of the three subjects; one student studies Science only and the other student studies History only; the second student selected studies History, given that the captain studies History and Mathematics.
(5) (Total 15 marks)
11.
There are two biscuit tins on a shelf. The red tin contains three chocolate biscuits and seven plain biscuits. The blue tin contains one chocolate biscuit and nine plain biscuits. (a) A child reaches into the red tin and randomly selects a biscuit. The child returns that biscuit to the tin, shakes the tin, and then selects another biscuit. Find the probability that (i) (ii) both biscuits chosen are chocolate.
(2)
one of the biscuits is plain and the other biscuit is chocolate.
(3)
12
(b)
A second child chooses a biscuit from the blue tin. The child eats the biscuit and chooses another one from the blue tin. The tree diagram below represents the possible outcomes for this event. C
10 P C 9 10 P a b (i) (ii) (iii) Write down the values of a and b.
(2)
Find the probability that both biscuits are chocolate.
(1)
What is the probability that at least one of the biscuits is chocolate?
(3)
(c)
Suppose that before the two children arrived, their brother randomly selected one of the biscuit tins and took out one biscuit. Calculate the probability that this biscuit was chocolate.
(4) (Total 15 marks)
13
12.
A school jazz band contains three different musical instruments saxophone (S), clarinet (C) and drums (D). Students in the band are able to play one, two or three different instruments. In a class of 40 IB students, 25 belong to the jazz band. Out of these 25 3 can play all three instruments 5 can play the saxophone and clarinet only 5 can play at least the clarinet and drums 7 can play at least the saxophone and drums 16 can play the saxophone 12 can play the clarinet. (a) Draw a Venn Diagram and clearly indicate the numbers in each region.
(5)
(b)
Show that the number of students who play the drums only is 5.
(2)
(c)
Find the probability that a student chosen at random from the IB class plays only the saxophone.
(2)
(d)
Find the probability that a student chosen at random from the IB class plays either the clarinet or drums or both.
(2)
(e)
Given that a student plays the saxophone, find the probability that he also plays the clarinet.
(3) (Total 14 marks)
14
13.
When Andy plays tennis, 65% of his first serves go into the correct area of the court. If the first serve goes into the correct area, his chance of winning the point is 90 %. If his first serve does not go into the correct area, Andy is allowed a second serve and, of these, 80% go into the correct area. If the second serve goes into the correct area, his chance of winning the point is 60 %. If neither serve goes into the correct area, Andy loses the point. (a) Complete the tree diagram below. W in ..... F irs t se rv e in
0 .6 5
0 .1
L ose Second se rv e in 0 .6 0 .4 W in
0 .3 5 F irs t se rv e out 0 .8
L ose
0 .2
Second se rv e out
..... L ose
(2)
(b)
Find the probability that Andy loses the point.
(4) (Total 6 marks)
15
14.
Today Philip intends to go walking. The probability of good weather (G) is good, the probability he will go walking (W) is the probability he will go walking is (a)
3 . If the weather is 4
17 . If the weather forecast is not good (NG) 20
1 . 5
Complete the probability tree diagram to illustrate this information. W 17 20 G 3 4 N W W
N G
N W
(b)
What is the probability that Philip will go walking?
(Total 8 marks)
16
15.
Jim drives to work each day through two sets of traffic lights. The probability of the first set of traffic lights being red is 0.65. If the first set is red then the probability that the next set of traffic lights is red is 0.46. If the first set is not red, the probability that the next set is red is 0.72. re d
red 0 .6 5 not re d re d not red
not re d (a) (b) Complete the tree diagram above. Calculate the probability that the second set of traffic lights is red.
(Total 8 marks)
17
16.
Two identical dice have sides numbered one to six. The dice are weighted. All the numbers except the four have equal probability of appearing on top. The four is three times as likely as each of the other numbers to appear on top. The tree diagram below shows some of the probabilities. a 8 one tw o 1 8 1 8 b 8 fo u r 1 8 s ix 1 8 fiv e th re e
(a)
Find the values of a and b in the diagram.
(b)
Both dice are thrown. Calculate the probability that two fours appear on top.
(c)
One of the dice is thrown once. The result is not a two or a three. What is the probability that it is a six?
(Total 8 marks)
18
You might also like
- Glee Volume 1 Season 1 Glee PDFDocument117 pagesGlee Volume 1 Season 1 Glee PDFmarkNo ratings yet
- 1519886-Twin Peaks ThemeDocument2 pages1519886-Twin Peaks ThemeChristopher Bignamini0% (1)
- Vocal Mutation in Adolescent Male - Assisting Boys Through Vocal ChangeDocument8 pagesVocal Mutation in Adolescent Male - Assisting Boys Through Vocal ChangeAine MulveyNo ratings yet
- Flute DuetsDocument12 pagesFlute DuetsMarta Souto Caride50% (4)
- Functions Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesFunctions Practice ProblemstaengooNo ratings yet
- Tok EssayDocument7 pagesTok Essayapi-648772994No ratings yet
- IB Math Probability Practice(b) 11/36(C2Document13 pagesIB Math Probability Practice(b) 11/36(C2Abdullah AmbusaidiNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Sudoku Bk 1: A Fun Way to Develop, Enhance, and Review Students’ Algebraic SkillsFrom EverandAlgebraic Sudoku Bk 1: A Fun Way to Develop, Enhance, and Review Students’ Algebraic SkillsNo ratings yet
- Possible C3 Questions From Past Papers P1P3Document20 pagesPossible C3 Questions From Past Papers P1P3PXLIV100% (1)
- Math IB Revision Functions & EquationsDocument26 pagesMath IB Revision Functions & Equationsmykiri79100% (1)
- Vectors Review IB Paper 2 QuestionsDocument4 pagesVectors Review IB Paper 2 QuestionsJasmine YimNo ratings yet
- Arrival of The Queen of ShebaDocument9 pagesArrival of The Queen of ShebaLiam ClinkNo ratings yet
- Kinematics WorksheetDocument6 pagesKinematics WorksheetDIPAKSHINo ratings yet
- Revision 12 IB Paper 1Document293 pagesRevision 12 IB Paper 1SiddharthChoksi100% (7)
- All Trig Revision QusDocument11 pagesAll Trig Revision QusAlan WaiNo ratings yet
- I Am Glad To See You PDFDocument18 pagesI Am Glad To See You PDFPercy Galindo Panez Tinoco100% (2)
- IB REVIEW - Integration 2012Document6 pagesIB REVIEW - Integration 2012makunjapNo ratings yet
- IB HL Math ProblemsDocument43 pagesIB HL Math ProblemsAngelaNo ratings yet
- IBSL Circular Functions and Trig QsDocument6 pagesIBSL Circular Functions and Trig QsJashkirat VirdiNo ratings yet
- IB Maths Worksheet ProbabilityDocument14 pagesIB Maths Worksheet Probabilityhans100% (2)
- Venn Diagram Probability ProblemsDocument40 pagesVenn Diagram Probability Problemstaimoor2No ratings yet
- IB Math HL Series SummaryDocument2 pagesIB Math HL Series Summarystong15100% (1)
- IB Math SL Statistics ReviewDocument11 pagesIB Math SL Statistics ReviewJorgeNo ratings yet
- Notes For Comp ExamDocument8 pagesNotes For Comp ExammikeNo ratings yet
- IB Math SL Arithmetic Geometric Sequences Series ReviewDocument8 pagesIB Math SL Arithmetic Geometric Sequences Series ReviewDiana Oblitas Zanabria100% (1)
- EXS 1-2-25v1 HL Exponents LogarithmsDocument2 pagesEXS 1-2-25v1 HL Exponents LogarithmsRaivat ShahNo ratings yet
- IB Math HL Syllabus 19-20Document3 pagesIB Math HL Syllabus 19-20Arthur BragaNo ratings yet
- Pocas Soluciones Fabio Critto - Mathematics Higher Level (Core) 3rd Ed. (For Use With The International Baccalaureate Diploma Programme)Document48 pagesPocas Soluciones Fabio Critto - Mathematics Higher Level (Core) 3rd Ed. (For Use With The International Baccalaureate Diploma Programme)J Eduardo T OntanedaNo ratings yet
- MathHL QB3 T2Document25 pagesMathHL QB3 T2Nikola PetrovicNo ratings yet
- IB Maths HL Mini Topic Exam:: AlgebraDocument6 pagesIB Maths HL Mini Topic Exam:: Algebraomar triveñoNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Test 3. FunctionsDocument8 pagesTest 3. FunctionsNeelamNo ratings yet
- 3.4 The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra, Sum and Product of The Zeros of PolynomialsDocument4 pages3.4 The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra, Sum and Product of The Zeros of PolynomialsAryan WaghdhareNo ratings yet
- IB Physics HL - 2025 Questionbank - Thermal Energy TransfersDocument35 pagesIB Physics HL - 2025 Questionbank - Thermal Energy TransfersRahul Sharma100% (1)
- IB Math HL Induction Test ReviewDocument6 pagesIB Math HL Induction Test ReviewEdward100% (3)
- IB Chemistry HL Summer AssignmentDocument4 pagesIB Chemistry HL Summer AssignmentVal B100% (1)
- BartokDocument116 pagesBartokJosé PinhoNo ratings yet
- Bivariate StatisticsDocument6 pagesBivariate StatisticstahsansaminNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Tle 6 (Home Economics)Document7 pagesSummative Test in Tle 6 (Home Economics)Mary Ann Corpuz100% (2)
- IB Related RatesDocument8 pagesIB Related RatesVidhiGondaliaNo ratings yet
- Inthinking - AI HL Paper 1Document17 pagesInthinking - AI HL Paper 1Pearl NarangNo ratings yet
- Test 7. Statistics - ProbabilityDocument4 pagesTest 7. Statistics - ProbabilityValentina TarabukinaNo ratings yet
- HKExcel Math AI SL NoteDocument60 pagesHKExcel Math AI SL Noteyara hazemNo ratings yet
- IBDP Arithmetic Sequence WorksheetDocument3 pagesIBDP Arithmetic Sequence WorksheetbalajibabutNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Differentiation 1Document69 pagesCalculus - Differentiation 1Amina Rakha HassanNo ratings yet
- IB TOK EssayDocument7 pagesIB TOK Essaypomegranateandkiwi100% (1)
- Arcs and Sectors FormulaeDocument5 pagesArcs and Sectors FormulaeDileep NaraharasettyNo ratings yet
- IB Math Studies Internal Assessment-2Document20 pagesIB Math Studies Internal Assessment-2Clay CarpenterNo ratings yet
- Sketching functions and finding inversesDocument17 pagesSketching functions and finding inversestoh tim lamNo ratings yet
- 2017 H2 Prelim (Graphs and Transformations)Document21 pages2017 H2 Prelim (Graphs and Transformations)toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument1 pageQuadratic EquationEmyRaNo ratings yet
- Sample IB Questions ThermalDocument8 pagesSample IB Questions ThermalEthan KangNo ratings yet
- IB Math HL Binomial Expansion Counting ProblemsDocument2 pagesIB Math HL Binomial Expansion Counting ProblemsMohd Uvais100% (1)
- Oxidation Reduction Past PaperDocument8 pagesOxidation Reduction Past Paperrainbow100% (1)
- Logarithms and Exponets Worksheet Exam Style PDFDocument2 pagesLogarithms and Exponets Worksheet Exam Style PDFYuan CuiNo ratings yet
- HL Year 1 Random Trig Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesHL Year 1 Random Trig Practice ProblemslilyNo ratings yet
- Assign Sheet TrigDocument3 pagesAssign Sheet TrigChirag Hablani100% (1)
- Maths IADocument2 pagesMaths IALoic RobillotNo ratings yet
- Ib Practice Integration QuestionsDocument5 pagesIb Practice Integration QuestionsSaket GudimellaNo ratings yet
- Exploring the Geometry of Ancient Japanese Sangaku PuzzlesDocument5 pagesExploring the Geometry of Ancient Japanese Sangaku PuzzlesKavin RukNo ratings yet
- Math IB Revision Differentiation BasicsDocument3 pagesMath IB Revision Differentiation Basicsmykiri79100% (1)
- 2.2 Even Odd FunctionsDocument4 pages2.2 Even Odd FunctionsMuhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- POPULATION TRENDS IN CHINADocument2 pagesPOPULATION TRENDS IN CHINAMongoosiaNo ratings yet
- DIFFERENTIATION AND CURVESDocument8 pagesDIFFERENTIATION AND CURVESDileep Naraharasetty0% (1)
- 2017 H2 Prelim (Vectors)Document28 pages2017 H2 Prelim (Vectors)toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- Tables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39From EverandTables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39No ratings yet
- Born This Way: Becoming, Being, and Understanding ScientistsFrom EverandBorn This Way: Becoming, Being, and Understanding ScientistsNo ratings yet
- Hush Chords by Deep Purple at Ultimate-Guitar - ComDocument4 pagesHush Chords by Deep Purple at Ultimate-Guitar - Comfedderico_sdNo ratings yet
- Philippine Folk DanceDocument15 pagesPhilippine Folk DanceEdzel M. RamirezNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - H.O.P.E. 3Document15 pagesWeek 1 - H.O.P.E. 3do san namNo ratings yet
- Blanchot - Ars NovaDocument10 pagesBlanchot - Ars NovaRobs CamaraNo ratings yet
- KG1 Early Years Plan: All About MeDocument7 pagesKG1 Early Years Plan: All About MeAnonymous eynRrXPNo ratings yet
- Music 8Document49 pagesMusic 8Vanessa LoberianoNo ratings yet
- Ball Room Dance: Presentation OF Group 1Document23 pagesBall Room Dance: Presentation OF Group 1heartNo ratings yet
- Mynta Ka SngiDocument4 pagesMynta Ka SngiKLYPTO DNo ratings yet
- In The Hall Of The Mountain KingDocument11 pagesIn The Hall Of The Mountain KingOliviaWienertNo ratings yet
- Piano VirtualDocument14 pagesPiano Virtual4_Javier_4No ratings yet
- Bounce Now HSW Level 3Document28 pagesBounce Now HSW Level 3Marita Castro GonzàlesNo ratings yet
- Course Pack MUSIC FINALSDocument18 pagesCourse Pack MUSIC FINALSGranules ExNo ratings yet
- OcnosHble HHcrpyMeHTbr poK-My3brKr4Document84 pagesOcnosHble HHcrpyMeHTbr poK-My3brKr4DJVLADIMIR7No ratings yet
- The Weekender 08-24-2011Document79 pagesThe Weekender 08-24-2011The Times LeaderNo ratings yet
- Can To Feel The Love TonightDocument2 pagesCan To Feel The Love TonightAleksandar SakanarskiNo ratings yet
- 2nd AEMC International Chamber Music Competition PDFDocument2 pages2nd AEMC International Chamber Music Competition PDFAlessio BenvenutoNo ratings yet
- Crusell Clarinet Concerto Nr3 Op11 Solopart PDFDocument9 pagesCrusell Clarinet Concerto Nr3 Op11 Solopart PDFKe XuNo ratings yet
- What is DramaDocument25 pagesWhat is DramaMonica AbagaNo ratings yet
- OCL, Samson and DelilahDocument3 pagesOCL, Samson and DelilahRadman RastiNo ratings yet
- Pink Floyd SongsDocument4 pagesPink Floyd SongsA_Valsamis0% (1)
- Vocal Posture and Breathing Lesson Plan 2Document3 pagesVocal Posture and Breathing Lesson Plan 2api-499585530No ratings yet