Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comb Manual Oxymitter 4000 Addendum 200412 2
Uploaded by
Best KvansOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Comb Manual Oxymitter 4000 Addendum 200412 2
Uploaded by
Best KvansCopyright:
Available Formats
Instruction Bulletin Addendum For Pressure-Balanced In Situ Oxygen Probes
Instruction Bulletin Addendum IB PB1000
Oxymitter 4000 Part no. Serial no. Order no.
Applicability: Used with pressure-balancing option, p/n 3D39811 (50 psig maximum process pressure). This product option may be utilized with Rosemount Analyticals Oxymitter 4000/5000 O2 analyzer or with Rosemount Analyticals CENELEC World Class O2 Analyzer. This may also be used with 3081/4081FG high temperature systems (remote mounted only) and may be used in conjunction with optional Isolation Valving System Oxy-Iso 1000
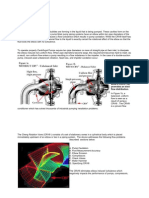
General Rosemount Analyticals line of in situ oxygen analyzers utilize zirconium oxide sensing technology, which is sensitive to pressure variations in the process. The ZrO2 sensing cell develops and EMF O2 relative to content based upon the Nernst Equation: EMF = KT log10 (P1/P2) + C where: P2 is the partial pressure of oxygen on the flue gas side P1 is the partial pressure of oxygen on the reference side T is the absolute temperature K is a constant C is the cell constant. Rosemount Analyticals Oxymitter and World Class probes place the sensing cell at the end of an in situ probe that inserts directly into the process gas stream. This arrangement provides for fast response and is also very resistant to pluggage from particulate material, or the acids that frequently condense out of normal flue gas. The ZrO2 sensing technology is sensitive to pressure changes of the process, and one can expect an output change of approximately 1% of reading (not 1 % FS, or 1% O2) for every 4 inches of H2O pressure or vacuum in the process. The pressure errors of a few psi can be calibrated by calibrating the probe in the installed, pressurized condition. However, pressure fluctuations from the calibrated state will induce errors. A better accommodation for pressurized processes is to balance the process pressure with reference air (common instrument air) inside of the oxygen probe (see following page). The sensing cell will have the same pressure on both sides, eliminating any pressureinduced error. Pressure fluctuations in the process will be balanced, maintaining the most accurate O2 reading throughout normal operating conditions. Rosemount Analyticals Oxymitter 4000/5000 probes (both hazardous area and general purpose styles) and the CENELEC World Class probes are suitable for pressure balancing. Process pressure is routed to a balancing relay via a nitrogen purge system or via the probes internal calibration gas line. The balancing relay duplicates the process pressure with instrument air and this is routed to the reference side of the probe (inside of the probe). This pressure balancing system is integrally mounted to the probe and gauges are provided to confirm proper balancing operation.
Preferred Arrangement Utilizing N2 Purge into the Process and Representing Process Pressure
Ambient
Proces s
Probe Tube
Sensing Cell
Check Valve (if Autocal system is utilized)
Diaphrag m
N2 Purge into Process
Diffusion Element, and Optional Flame Arrestor
Balancing Relay
Pressure Regulator, Instrument Air set to above max. process pressure
Installation notes for N2 Purge Arrangement Install T for N2 tap as close to process as possible. Calibration Gas Fitting- capped tight between calibrations If autocal system is utilized, or if cal gas lines are permanently installed, use check valve kit, p/n 7307A56G02 Reference Gas InletPiped to pressure/balancing system Reference Gas Exhaust- Capped, turn open from tight Operation Note- Set N2 pressure regulator to 10 PSI above maximum process pressure
Integral Pressure Balancing Arrangement- Manual Calibration Ambient Process
Probe Tube Sensing Cell
Calibration Gas Line/Process Tap Selector CG Valve Flowmeter Cal Gas
Gages Diaphragm
(manually applied)
Diffusion Element, and Optional Flame Arrestor
Balancing Relay
Pressure set to above Regulator, process max. pressure
Instrument Air
1
If N2 purge is unavailable, the probes calibration gas line may be utilized as the process pressure tap for the Balancing Relay. Ensure that all parts wetted by process gases are well insulated to prevent condensation.
Integral Pressure Balancing Arrangement- Auto Calibration Probe Tube Sensing Cell Ambient Proces s
Calibration Gas Line/Process Tap
Check Valve
Gage s Diaphrag m
CG Flowmeter Cal Gas
(from Autocal system)
Diffusion Element, and Optional Flame Arrestor
Balancing Relay Reference Air Pressure Regulator, Instrument Air at Process set to above max. Pressure process pressure
An optional isolation valving system facilitates the insertion and withdrawal of the probe for service while the process is under pressure. This valving system is recommended if the process cannot be shut down for probe maintenance.
Unpacking Probe will be shipped with the pressure-balancing valving option mounted and tested.
Installation of Pressure Balancing System Reference Air Follow standard instructions in the instruction bulletin for the mechanical installation of the probe system. Instrument air is required and must be piped into the pressure regulator provided on the pressure balancing assembly. Set this pressure regulator to 50 psi. Reference air exhaust port should be capped loosely, turn open from tight. Calibration Gases If the probe system will be manually calibrated, ensure that the blocking valve is shut except during calibration. When calibrating, connect bottles to the bottom part of the calibration gas flowmeter and set bottle pressure regulators to 50 psi. If an automatic calibration system will be used, mount the SPS, IMPS or MPS per standard instruction bulletin and pipe calibration gas outlet line to the check valve provided on the probe (per page 3 of the appendix). If an automatic calibration system will be used, again set the pressure regulator on the calibration gas bottles to 50 psi. Any time the calibration gases will be permanently connected, ensure that a check valve is provided to prevent the migration of process flue gases back down the calibration gas line. To prevent corrosion from condensation of process gases insulate all process wetted parts; including the probe flange, the calibration gas/process line and balancing relay. If this is an outdoor installation where rain and snow will be present, cover the entire probe electronics (Oxymitter) or probe junction box (CENELEC World Class) to inhibit the cooling effect of precipitation. Electrical Follow the probe electrical installation instructions in the Instruction Manual. Note that electrical penetrations into the CENELEC World Class probe will be under pressure, and must be sealed. The normal procedures for installing probes into hazardous areas are usually sufficient to maintain pressure inside a probe. The Oxymitter utilizes an internal bulkhead which isolates the terminations side of the probe from the pressure balancing system. The termination side cover can be removed and the wires disconnected while the system is under pressure. Do not remove the electronics side cover while the process is under pressure, and the pressure balancing system is active.
Note: The pressure balancing system must be connected and operational at all times. If an optional isolation valving system is utilized for inserting or withdrawing the probe while the process is under pressure, the pressure balancing system must be active at all times until the gate valve is closed. This may require an installation whereby the reference instrument air lines and electrical cables can ride back and forth with the probe. See Instruction Bulletin Addendum for Isolation Valving System, IB ISO1000 for more information. Calibration gas lines may be removed for probe installation or removal.
Start-up and Operation Pressure Balancing system works automatically, and requires no adjustment. Two pressure gages are provided with the system, and should always read very close to the same pressure. Reference gas side gage may read 1-2 PSI lower than the process side gage. Consult the troubleshooting table whenever these gages do not read the same. For most accurate operation, calibrate the probe after the process is up, and at operating temperature and pressure. Caution: The inside of the probe is pressurized. If using the CENELEC World Class product do not unscrew the junction box cover or the electrical penetrations until reference gas pressure is bled off. If using the Oxymitter, do not unscrew the electronics side cover while pressurized. Oxymitter terminations side cover may be opened while pressurized. Operational Note: Some catalyst regeneration applications (notably the UOP CCR process) use nitrogen in the process. During shutdown, the O2 is completely displaced with N2 for some period of time. Residual CO and other combustible components can build up on the diffuser and cell of the probe. When coming back on line, the probe will read zero percent O2 until these components are burned completely off the heated probe. We recommend that nitrogen be bled down the probes calibration gas line at 5 SCFH during any periods where the probes O2 reading approaches zero. This flow may be removed and the cal gas line capped tightly when the unit comes back on line. This will insure that the O2 reading will respond normally as air is reintroduced into the process.
Pressure Balancing System Troubleshooting The pressure balancing system will operate without periodic adjustment. Whenever the probe is taken out of service, inspect the pressure balancing system for condensation or particulate pluggage in the lines. Most surfaces that are in contact with the process gases are stainless steel, but condensate can still corrode stainless steel. If condensation is found, insulate the process lines to keep them warm. Leaks are the most likely problems in the pressure-balancing system.
Symptom O2 ocillates up and down repeatedly and at a frequency greater than the normal process O2 changes, (up and down every few seconds).
O2 reading increases above normal readings.
Diagnosis Watch the two pressure gages on the pressure balancing system. If needles are not stable and do not follow each other, there is a hole in the balancing relay diaphram or in the process tap/cal gas line feeding the balancing relay. Disassemble and bench test the balancing relay to isolate the leak. Disassemble probe and look for leaks in the calibration gas line.
Cause Diaphram on balancing relay or process tap has a hole in it.
Correction Replace balancing relay or process tap.
Process tap/calibration gas line has a hole in it or the elastomer tube has popped off. Process gas is mixing with reference air inside the probe.
For disassembly of pressure balancing system, see page 9.
Spare Parts Lists Balancing Relay Block Valve Check Valve Calibration Gas Flowmeter Cal Gas/Process Dial Gage Reference Air Dial Gage Reference Air Pressure Regulator Mounting Bar Bracket 1A99408H01 3526B30H01 7307A56G02 771B635H01 1A99410H03 1A99410H01 1A99094H01 4851B62H01 4851B61H01
Pressure Balancing System Detail
Optional Isolation Valve (probe uninstalled)
Oxygen probe
Reference Air Press. Gage Process Gage Block Valve Cal Gas Flowmeter
Disassembly of Pressure Balancing System
Mounting Bar Booster Relay Bracket Reference Air Pressure Regulator Fig, 8
1) Disconnect instrument air supply line at the pressure regulator. 2) Disconnect the instrument air reference line out of the balancing relay and into the probe. 3) Disconnect the calibration gas line into the flowmeter. 4) Disconnect the calibration gas line from probe into balancing relay. 5) Remove the entire pressure balancing assembly from the mounting bar that is welded to the probe flange. 6) Unscrew calibration gas assembly feeding into the balancing relay, including the CG flowmeter, valve (or check valve if an autocal system is utilized), and tee fitting. 7) Remove balancing relay from mounting bracket. 8) Unscrew reference gas assembly from balancing relay, including the instrument air reference gas pressure regulator, and gage. Assembly procedure is reverse of disassembly procedure.
You might also like
- INTS2 B WebDocument17 pagesINTS2 B WebBest KvansNo ratings yet
- Boiler Aux.Document58 pagesBoiler Aux.Best KvansNo ratings yet
- Elect Et Syllabus 2013 For SJVNDocument3 pagesElect Et Syllabus 2013 For SJVNBest KvansNo ratings yet
- Comb Manual Oxymitter 4000 Addendum 200412 2Document10 pagesComb Manual Oxymitter 4000 Addendum 200412 2Best KvansNo ratings yet
- SJVN - Nic.in Recdata Sample Paper Etrecruitment 2013Document9 pagesSJVN - Nic.in Recdata Sample Paper Etrecruitment 2013Deepak Kumar SahooNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- HW 200Document40 pagesHW 200Nguyễn Trọng HùngNo ratings yet
- CRV ApplicationsDocument13 pagesCRV ApplicationsMuhammad AdnanNo ratings yet
- So, You Think You Know Shuttle Valves?Document6 pagesSo, You Think You Know Shuttle Valves?AkileshNo ratings yet
- LPG Carbon Dioxide Fire Suppression System Installation Manual .Document50 pagesLPG Carbon Dioxide Fire Suppression System Installation Manual .hrhgk100% (4)
- Calculating pipe friction losses using equivalent pipe lengthsDocument4 pagesCalculating pipe friction losses using equivalent pipe lengthsWasantha JayarathnaNo ratings yet
- Valvula Check Wafer 250psiDocument1 pageValvula Check Wafer 250psiOscar Fernandez SanchezNo ratings yet
- XXI Paper HAZOP ErrorsDocument6 pagesXXI Paper HAZOP ErrorsravisankarNo ratings yet
- Watermist Engineering ManualDocument97 pagesWatermist Engineering ManualDragan CvetkovićNo ratings yet
- Apollo Valves Marine Valvescat - MACA9000Document12 pagesApollo Valves Marine Valvescat - MACA9000Michael MangadaNo ratings yet
- ATIQ ReportDocument48 pagesATIQ ReportAdeel Aslam RajpootNo ratings yet
- Valves Member ListDocument168 pagesValves Member Listrkpatel40No ratings yet
- Aquarium Plumbing Basics - Reef AquariumDocument29 pagesAquarium Plumbing Basics - Reef AquariumKanashibi Ogawa100% (1)
- API 521 7 Edition Ballot Item 6.1 New Work Item - Potential ASME Code ViolationsDocument14 pagesAPI 521 7 Edition Ballot Item 6.1 New Work Item - Potential ASME Code ViolationsAyadi_AymanNo ratings yet
- 5-EN 4050-A (Dig) - 2F1CDocument9 pages5-EN 4050-A (Dig) - 2F1Cabuzer1981No ratings yet
- Axial Flow Check ValveDocument2 pagesAxial Flow Check ValveProject MarsysNo ratings yet
- Clean Cut Trainning ManualDocument205 pagesClean Cut Trainning ManualPETROPATH FLUIDS INDIA PVT. LTD.No ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument62 pagesProject ReportAll_regNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Valves GuideDocument13 pagesPneumatic Valves GuideShehab NaeemNo ratings yet
- APT10 and APT14: For Effective Condensate Drainage and RemovalDocument12 pagesAPT10 and APT14: For Effective Condensate Drainage and RemovalwimpievdsNo ratings yet
- Manual Installation Instructions Bulletin 642-jDocument24 pagesManual Installation Instructions Bulletin 642-jReinaldo RamirezNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas MetersDocument22 pagesNatural Gas MetersIslami AdaNo ratings yet
- Basic Boiler Mountings and Their FunctionDocument5 pagesBasic Boiler Mountings and Their FunctionChristian Cuevas100% (4)
- Strainer Brochure ADocument11 pagesStrainer Brochure AsitaNo ratings yet
- CEU 228 Oct15 PDFDocument11 pagesCEU 228 Oct15 PDFMohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- Enquiry - Fire Hydrant SystemDocument9 pagesEnquiry - Fire Hydrant Systemrkpatel40No ratings yet
- 2) Ata 12 B737NG Ground Handling and ServicingDocument40 pages2) Ata 12 B737NG Ground Handling and ServicingAmberNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Force Feed Lubrication System Upgrade GuideDocument4 pagesEnhanced Force Feed Lubrication System Upgrade GuideIl Il Il IlNo ratings yet
- Bottom Blowdown: Download The (295 KB) Try Answering The For This Tutorial View The Complete Collection ofDocument8 pagesBottom Blowdown: Download The (295 KB) Try Answering The For This Tutorial View The Complete Collection ofsenaNo ratings yet
- Reliance Water Controls Hoseguard Bib Tap HTAP217008 520-041-0001Document2 pagesReliance Water Controls Hoseguard Bib Tap HTAP217008 520-041-0001AdvancedWaterCompanyNo ratings yet
- Bendix TP-3DC Tractor Protection Valve With Double Check: DescriptionDocument8 pagesBendix TP-3DC Tractor Protection Valve With Double Check: DescriptionPototoNo ratings yet