Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circulatory Systems (29:08)
Uploaded by
Brian TranCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circulatory Systems (29:08)
Uploaded by
Brian TranCopyright:
Available Formats
Circulatory Systems (29/08) In multi-cellular animals there are a variety of transport systems that exist (eg.
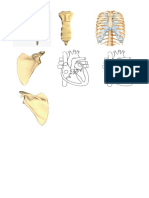
open or closed systems). These systems transport requirements (nutrients) to cells wastes away from cells. In Humans: There are two major circulatory systems humans: Cardiovascular system & Lymphatic system Cardiovascular System Role: is to transport substance such as hormones, antibodies, nutrients (eg. glucose, amino acids, minerals, vitamins), oxygen to cells and wastes (carbon dioxide, urea) away from cells. Structure: the Human Cardiovascular System is a double circulatory system (it has two major circuits): 1. Pulmonary Circuit (blood travels between the heart and lungs) a small circuit 2. Systemic Circuit (blood travels between the heart and the rest of the body) a large multi-branched circuit There are three major parts to the cardiovascular system: 1. Heart (muscular pump) 2. Blood Vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries) 3. Blood (plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets) 1. Heart Is a muscular pump Is 4 chambered. Each separated by a combination of the septum (central wall and atrio-ventricular valve. o Two receiving chambers at the top of the heart called the aorta. Blood enters the chambers via veins (vena cava and pulmonary veins) o Two pumping chambers at the base of the heart called ventricles. Blood leaves these via arteries (pulmonary artery and aorta) o The right side of the heart transports deoxygenated blood o The left side of the heart transports oxygenated blood. How does the Heart work? (30/08) THE CARDIAC CYCLE (steps involved in a complete heart beat): There are two major phases in a cardiac cycle: Systole and Diastole. Systole refers to ventricular c____ while Diastole refers to ventricular r__________. The step involved in a Cardiac Cycle: 1. Blood enters the atria 2. SA Node (pacemaker) sends electrical impulse across the walls of the atria causing atrial contractions. 3. Blood travels into ventricles through open atrio ventricular (AV) valves. 4. AV valves close causing blood to transport through (producing Lub sound). 5. AV Node (at base of right atrium) relays the electrical impulses through the septum and walls of the ventricle causing ventricular contractions.
6. Blood travels into the major aartery leaving the heart through open semilunar valves. 7. Semilunar valves close preventing backflow of blood into the ventricles (blood travels through produces the Dub sound). 2. Blood Vessels (02/09/13) There are three major types i) arteries ii) veins iii) capillaries Arteries: transport blood away from the heart have thick muscrlar walls normall transport oxygenated blood do not have valves transport blood under high pressure Veins: transport blood towards the heart have thinner walls wide diameter lumen normally transport deoxygenated blood do have valves transport blood under very low pressure (using the process called milking involving alternating valve and skeletal muscle action) Capillaries: are branched networks that connect small arteries (arterioles) to small veins (venules) thin diameter, walls are 1 cell thick and are leaky sites of nutrient / gas exchange 3. Blood Is the fluid transport medium made of plasma (liquid component), red blood cells (erythocytes), many types of white blood cells (leucocytes), platelets (thrombocytes), plasma proteins etc. Component Drawing / Description Function 1. Plasma Straw coloured liquid, Contains water, nutrients, wastes, proteins 2. Red Blood Cells Biconcave discs (Erythocytes) No nucleus but are filled with haemoglobin 3. White Blood cells Large cells nucleated Platelets Small, irregular in shape, nunnucleated
You might also like
- Curio GuideDocument8 pagesCurio GuideBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Week ? NotesDocument5 pagesMental Health Week ? NotesBrian TranNo ratings yet
- See The World - Beautiful and StrangeDocument1 pageSee The World - Beautiful and StrangeBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Tbis Is Christmas by Sara Bareilles Also Performed by Waitress Broadway Cast 2016 On Carols For A CureDocument1 pageTbis Is Christmas by Sara Bareilles Also Performed by Waitress Broadway Cast 2016 On Carols For A CureBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Blue Flashcards AnatomyDocument1 pageBlue Flashcards AnatomyBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Ohio in SummerDocument1 pageOhio in SummerBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Andante Andante Please Love Me Now AbbaDocument1 pageAndante Andante Please Love Me Now AbbaBrian TranNo ratings yet
- You've Got To Get Up Every Mornin' With A Smile On Your Face and Show The World All The Love in Your 3Document1 pageYou've Got To Get Up Every Mornin' With A Smile On Your Face and Show The World All The Love in Your 3Brian TranNo ratings yet
- AndanteDocument1 pageAndanteBrian TranNo ratings yet
- AndanteDocument1 pageAndanteBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Sara Bareilles Sittin' On The Dock of The Bay Wasting TimeDocument1 pageSara Bareilles Sittin' On The Dock of The Bay Wasting TimeBrian TranNo ratings yet
- EoS Question GuesstimationDocument1 pageEoS Question GuesstimationBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Student Study PlannerDocument2 pagesStudent Study PlannerBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Musc1700 Pop Music Recommended ReadingDocument1 pageMusc1700 Pop Music Recommended ReadingBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 Quarter 2 Quarter 3 Quarter 4Document1 pageQuarter 1 Quarter 2 Quarter 3 Quarter 4Brian TranNo ratings yet
- Jupiter of Drops Page 1Document1 pageJupiter of Drops Page 1Brian TranNo ratings yet
- Blue Flashcards AnatomyDocument1 pageBlue Flashcards AnatomyBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Bryce Dallas Howard Is Amazing The Jurassic World. Claire Dearing Is LifeDocument1 pageBryce Dallas Howard Is Amazing The Jurassic World. Claire Dearing Is LifeBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Motion Under Constant AccelerationDocument3 pagesMotion Under Constant AccelerationBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Onsciousness: Consciousness Can Be ObservedDocument6 pagesOnsciousness: Consciousness Can Be ObservedBrian TranNo ratings yet
- A Short History of Nearly Everything - Bill BrysonDocument1 pageA Short History of Nearly Everything - Bill BrysonBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Onsciousness: Consciousness Can Be ObservedDocument6 pagesOnsciousness: Consciousness Can Be ObservedBrian TranNo ratings yet
- A Short History of Nearly Everything - Bill BrysonDocument1 pageA Short History of Nearly Everything - Bill BrysonBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Homework GuideDocument1 pageHomework GuideBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Ethical QuestionsDocument8 pagesEthical QuestionsBrian TranNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System (06:09)Document1 pageLymphatic System (06:09)Brian TranNo ratings yet
- Printing Instructions: - Use A Colour Printer - Use White A4 Paper or Card - Ensure The Page Scaling Is Set To 'None'Document1 pagePrinting Instructions: - Use A Colour Printer - Use White A4 Paper or Card - Ensure The Page Scaling Is Set To 'None'Brian TranNo ratings yet
- Biology - Respiratory Systems (Breathing)Document1 pageBiology - Respiratory Systems (Breathing)Brian TranNo ratings yet
- BibliographyDocument1 pageBibliographyBrian TranNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Cariogram E BookDocument90 pagesCariogram E BookAlifianNo ratings yet
- WHO Top 10 Causes of DeathDocument4 pagesWHO Top 10 Causes of DeathMas IyoNo ratings yet
- 038-80sonodiag Complete English 602 PDFDocument81 pages038-80sonodiag Complete English 602 PDFMihaellaBoncătăNo ratings yet
- What Is The Female Reproductive System?: External PartsDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Female Reproductive System?: External PartsKeneth Dave AglibutNo ratings yet
- Warfarin LeafletDocument2 pagesWarfarin LeafletchampbeeNo ratings yet
- Clinical ChemistryDocument10 pagesClinical ChemistryChristina AtefNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain ProtocolDocument7 pagesChest Pain Protocolomar kmr97No ratings yet
- The Potential Use of Biomarkers in Predicting Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney InjuryDocument17 pagesThe Potential Use of Biomarkers in Predicting Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injuryumie khoirunNo ratings yet
- Estimated Time of Death:: Cooling of The BodyDocument2 pagesEstimated Time of Death:: Cooling of The BodynoramalinaabdmanafNo ratings yet
- By S/A Zekariyas G/Eysus: Addis Ababa University, Chs School of AnesthesiaDocument51 pagesBy S/A Zekariyas G/Eysus: Addis Ababa University, Chs School of Anesthesiaagatakassa0% (1)
- Medical Report: Reason RequestedDocument4 pagesMedical Report: Reason RequestedWebmaster0% (1)
- IKMAN NURHAKIM XII IPS 3 - Explanation Text BDRDocument2 pagesIKMAN NURHAKIM XII IPS 3 - Explanation Text BDRikman nibosNo ratings yet
- Impetigo PDFDocument7 pagesImpetigo PDFdestraNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG Interpretation Review Questions Flashcards - QuizletDocument5 pagesBasic ECG Interpretation Review Questions Flashcards - Quizletdina sharafNo ratings yet
- Macroradiography (Enlargement Technique) in The Radiology of The Ear, Nose and ThroatDocument10 pagesMacroradiography (Enlargement Technique) in The Radiology of The Ear, Nose and ThroatGenta EftaNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthesia For The Dental Hygienist 2nd Edition Logothetis Test BankDocument12 pagesLocal Anesthesia For The Dental Hygienist 2nd Edition Logothetis Test BankJessicaPorterfqmei100% (18)
- Kaplan Spikes 2010Document4 pagesKaplan Spikes 2010Asrini Widya AnomNo ratings yet
- Emergency Life Support AlgorithmDocument43 pagesEmergency Life Support AlgorithmDADASDSANo ratings yet
- Management of FebrileDocument9 pagesManagement of FebrileNur AiniNo ratings yet
- The Perio-Restorative InterrelationshipexpandingDocument8 pagesThe Perio-Restorative InterrelationshipexpandingErdeli StefaniaNo ratings yet
- Ecg PDFDocument2 pagesEcg PDFNaveen SharmaNo ratings yet
- 9 Top Benefits of KarakkayaDocument4 pages9 Top Benefits of KarakkayaAcharla SatyanarayanaNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument13 pagesAntibioticsJOrgeNo ratings yet
- Spermac Stain Analysis of Human SpermDocument5 pagesSpermac Stain Analysis of Human SpermNatasyaNo ratings yet
- Essential Blood Test Reference SheetDocument1 pageEssential Blood Test Reference Sheetd3nny89No ratings yet
- Trauma Guideline ManualDocument157 pagesTrauma Guideline Manualsgod34No ratings yet
- Angiography Basics and Seldinger TechniqueDocument33 pagesAngiography Basics and Seldinger TechniqueTsz Him James WongNo ratings yet
- London Core Review Course - (Thurs 18 May - Sun 21 May 2017) - TimetableDocument5 pagesLondon Core Review Course - (Thurs 18 May - Sun 21 May 2017) - Timetablelondon_core_reviewNo ratings yet
- TheTruth About Food Grade Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 by James Paul RoguskiDocument86 pagesTheTruth About Food Grade Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 by James Paul RoguskiTheRazorsEdge80% (5)
- Unseen PassageDocument7 pagesUnseen PassageChanya SardanaNo ratings yet