Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comac PDF
Uploaded by
Ashutosh KumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Comac PDF
Uploaded by
Ashutosh KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
21.
70
CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE
ship, the modal assurance criterion should approach unity and the value of the modal scale factor can be considered to be reasonable. The modal assurance criterion can indicate only consistency, not validity. If the same errors, random or bias, exist in all modal vector estimates, this is not delineated by the modal assurance criterion. Invalid assumptions are normally the cause of this sort of potential error. Even though the modal assurance criterion is unity, the assumptions involving the system or the modal parameter estimation techniques are not necessarily correct. The assumptions may cause consistent errors in all modal vectors under all test conditions verified by the modal assurance criterion. Coordinate Modal Assurance Criterion (COMAC). An extension of the modal assurance criterion is the coordinate modal assurance criterion (COMAC).42 The COMAC attempts to identify which measurement degrees-of-freedom contribute negatively to a low value of MAC. The COMAC is calculated over a set of mode pairs, analytical versus analytical, experimental versus experimental, or experimental versus analytical. The two modal vectors in each mode pair represent the same modal vector, but the set of mode pairs represents all modes of interest in a given frequency range. For two sets of modes that are to be compared, there is a value of COMAC computed for each (measurement) degree-of-freedom. The coordinate modal assurance criterion (COMAC) is defined as follows:
prpr r = 1 COMACp = N N * pr pr prpr*
r = 1 r = 1
(21.103)
where
pr = modal coefficient from (measured) degree-of-freedom p and modal vector r from one set of modal vectors pr = modal coefficient from (measured) degree-of-freedom p and modal vector r from a second set of modal vectors
The above formulation assumes that there is a match for every mode in the two sets. Only those modes that match between the two sets are included in the computation.
MODAL MODIFICATION PREDICTION
The use of a modal model to predict changes in modal parameters caused by a perturbation (modification) of the system is becoming more of a reality as more measured data are acquired simultaneously. In this validation procedure, a modal model is estimated based upon a complete modal test.This modal model is used as the basis to predict a perturbation to the system that is tested, such as the addition of a mass at a particular point on the structure. Then, the mass is added to the structure and the perturbed system is retested. The predicted and measured data or modal model can be compared and contrasted as a measure of the validity of the underlying modal model.
MODAL COMPLEXITY
Modal complexity is a variation on the use of sensitivity analysis in the validation of a modal model. When a mass is added to a structure, the modal frequencies either should be unaffected or should shift to a slightly lower frequency. Modal overcom-
You might also like
- Modal Assurance CriterionDocument8 pagesModal Assurance CriterionAndres CaroNo ratings yet
- Model-Based Adaptive Critic Designs: Editor's SummaryDocument31 pagesModel-Based Adaptive Critic Designs: Editor's SummaryioncopaeNo ratings yet
- SEM With AMOS and TutorialDocument118 pagesSEM With AMOS and TutorialJohan SampoernoNo ratings yet
- IMAC XV 15th Int 15-5-3 The MAC Revisited UpdatedDocument8 pagesIMAC XV 15th Int 15-5-3 The MAC Revisited UpdatedjaypallaNo ratings yet
- Model Validation - Correlation For UpdatingDocument14 pagesModel Validation - Correlation For Updatingsumatrablackcoffee453No ratings yet
- Model Validation: Correlation For Updating: D J EwinsDocument14 pagesModel Validation: Correlation For Updating: D J EwinsChandan Kumar RayNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Physics-Based and Data-Driven PHM: H. Hanachi, W. Yu, I.Y. Kim and C.K. MechefskeDocument13 pagesHybrid Physics-Based and Data-Driven PHM: H. Hanachi, W. Yu, I.Y. Kim and C.K. MechefskeSudipto RayNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Estimation of Complex SystemsDocument14 pagesHybrid Estimation of Complex SystemsJuan Carlos AmezquitaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Methods For Voltage Sag Performance EstimationDocument5 pagesOverview of Methods For Voltage Sag Performance EstimationJay F. KuizonNo ratings yet
- Structural Damage Detection Employing Best Achievable Eigenvectors in Bayesian FrameworkDocument26 pagesStructural Damage Detection Employing Best Achievable Eigenvectors in Bayesian FrameworkMaker SpaceNo ratings yet
- Determining Optimal Sensor Locations For State and Parameter EstimationDocument15 pagesDetermining Optimal Sensor Locations For State and Parameter EstimationYaqoob AliNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Various Estimation Methods For The Parameters of Michaelis-Menten Equation Based On in Vitro Elimination Kinetic Simulation DataDocument9 pagesComparison of Various Estimation Methods For The Parameters of Michaelis-Menten Equation Based On in Vitro Elimination Kinetic Simulation DataHarshaNo ratings yet
- Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2016.07.011Document26 pagesChemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2016.07.011JessicaNo ratings yet
- Calculation of System Suitability ParametersDocument10 pagesCalculation of System Suitability ParametersMubarak Patel100% (1)
- Model Updating Using Constrained OptimizationDocument9 pagesModel Updating Using Constrained OptimizationHarsh unleashingNo ratings yet
- 56 DorDocument14 pages56 DorAmy GrayNo ratings yet
- Multiple Model Adaptive Control Design For A MIMO Chemical ReactorDocument45 pagesMultiple Model Adaptive Control Design For A MIMO Chemical ReactorFernando RamosNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY 3Document5 pagesCASE STUDY 3vandanavenkat325No ratings yet
- Abstraction and Counterexample-Guided Refinement in Model Checking of Hybrid SystemsDocument22 pagesAbstraction and Counterexample-Guided Refinement in Model Checking of Hybrid Systemszhi.han1091No ratings yet
- Summary of Biostatistics ArticlesDocument4 pagesSummary of Biostatistics ArticlesDerekNo ratings yet
- Hindawi Pso PDFDocument14 pagesHindawi Pso PDFHouda BOUCHAREBNo ratings yet
- Complex Analysis of AerodynamicsDocument17 pagesComplex Analysis of AerodynamicsKannan VenkatNo ratings yet
- Hosmer-Lemeshow Purposeful Selection Macro PerformanceDocument6 pagesHosmer-Lemeshow Purposeful Selection Macro PerformanceMiki DashNo ratings yet
- Markov Algorithms Circumvent Curse of Dimensionality in Stochastic GamesDocument22 pagesMarkov Algorithms Circumvent Curse of Dimensionality in Stochastic Gamesahmed22gouda22No ratings yet
- Probabilistic Small Signal Stability Analysis of Power Systems Based On Hermite Polynomial ApproximationDocument15 pagesProbabilistic Small Signal Stability Analysis of Power Systems Based On Hermite Polynomial ApproximationPooja kNo ratings yet
- Marco P. Tucci David A. Kendrick Hans M. HammanDocument40 pagesMarco P. Tucci David A. Kendrick Hans M. HammanhoahairauNo ratings yet
- MAC-Artigo OriginalDocument7 pagesMAC-Artigo OriginalrompnadegasNo ratings yet
- Design of Indirect MRAS-based Adaptive Control SystemsDocument5 pagesDesign of Indirect MRAS-based Adaptive Control SystemsThiện DũngNo ratings yet
- Probabilistic Control of Nonlinear Uncertain SystemsDocument36 pagesProbabilistic Control of Nonlinear Uncertain SystemsKarad KaradiasNo ratings yet
- IJSOM Volume 5 Issue 4 Pages 289-297Document9 pagesIJSOM Volume 5 Issue 4 Pages 289-297Jabir ArifNo ratings yet
- Analytical Study of Biometrics Normalization and Fusion Techniques For Designing A Multimodal SystemDocument6 pagesAnalytical Study of Biometrics Normalization and Fusion Techniques For Designing A Multimodal SystemijaertNo ratings yet
- Estimating Parameters in A Lumped Parameter System With First Principle Modeling and Dynamic ExperimentsDocument6 pagesEstimating Parameters in A Lumped Parameter System With First Principle Modeling and Dynamic ExperimentsParthiban RajendiranNo ratings yet
- Model Updating in Structural Dynamics - A Generalised Reference Basis ApproachDocument16 pagesModel Updating in Structural Dynamics - A Generalised Reference Basis Approachsumatrablackcoffee453No ratings yet
- Imprtant Hof-Wil-04-hybridDiagnosisDocument14 pagesImprtant Hof-Wil-04-hybridDiagnosisboucharebNo ratings yet
- Choice of Estimator For Distribution System State EstimationDocument13 pagesChoice of Estimator For Distribution System State EstimationFelipe KaewNo ratings yet
- TSP Cmes 41283Document25 pagesTSP Cmes 41283ranim najibNo ratings yet
- Distributed State Estimator - Advances and DemonstrationDocument11 pagesDistributed State Estimator - Advances and DemonstrationThiagarajan RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Measurement-Based Dynamic Load Modeling TechniquesDocument7 pagesEvaluating Measurement-Based Dynamic Load Modeling TechniquesManorath PrasadNo ratings yet
- Statistical Procedures For Measurement Systems Verification and Validation ElsmarDocument15 pagesStatistical Procedures For Measurement Systems Verification and Validation ElsmarEmeka ChieduNo ratings yet
- System Modeling Using A Mamdani Rule Base: University of FloridaDocument7 pagesSystem Modeling Using A Mamdani Rule Base: University of FloridaValy AndyNo ratings yet
- Alvin Imac Xiv 14th Int 14-18-1Document7 pagesAlvin Imac Xiv 14th Int 14-18-1eseemNo ratings yet
- Paper: New Algorithm ofDocument7 pagesPaper: New Algorithm ofAlexander BuenoNo ratings yet
- Modal Assurance Criterion (MAC)Document14 pagesModal Assurance Criterion (MAC)AhsanNo ratings yet
- A Verification Procedure For MSC/NASTRAN Finite Element ModelsDocument22 pagesA Verification Procedure For MSC/NASTRAN Finite Element Modelsdumi_userNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering and Computer Science DepartmentDocument45 pagesElectrical Engineering and Computer Science Departmenteecs.northwestern.eduNo ratings yet
- Bayesion CalibrationDocument16 pagesBayesion CalibrationSyeda Muntaha NaqviNo ratings yet
- Student Grade Prediction Using ML ModelsDocument4 pagesStudent Grade Prediction Using ML ModelsIQRA IMRANNo ratings yet
- An Optimal Measurement Placement Method For Power System Harmonic State EstimationDocument5 pagesAn Optimal Measurement Placement Method For Power System Harmonic State EstimationFabien CallodNo ratings yet
- System Identification Algorithm For Systems With Interval CoefficientsDocument8 pagesSystem Identification Algorithm For Systems With Interval Coefficientseetn1100% (1)
- Ethods For Contingency Screening and Ranking For Voltage Stability Analysis of Power - SystemsDocument7 pagesEthods For Contingency Screening and Ranking For Voltage Stability Analysis of Power - SystemsRameshPatelNo ratings yet
- Observability of Power Systems Based On Fast Pseudorank Calculation of Sparse Sensitivity MatricesDocument6 pagesObservability of Power Systems Based On Fast Pseudorank Calculation of Sparse Sensitivity Matricesjaved shaikh chaandNo ratings yet
- Sobre El Uso de Modelos para La Optimizacion Dinamica en Tiempo RealDocument6 pagesSobre El Uso de Modelos para La Optimizacion Dinamica en Tiempo RealJuan AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Final Project ReportDocument18 pagesFinal Project ReportjstpallavNo ratings yet
- A Verification Procedure For MSC/NASTRAN Finite Element ModelsDocument22 pagesA Verification Procedure For MSC/NASTRAN Finite Element ModelsTomaspockNo ratings yet
- Factorization of Boundary Value Problems Using the Invariant Embedding MethodFrom EverandFactorization of Boundary Value Problems Using the Invariant Embedding MethodNo ratings yet
- Semi-Markov Models: Control of Restorable Systems with Latent FailuresFrom EverandSemi-Markov Models: Control of Restorable Systems with Latent FailuresNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- Emily Schwartz Dallara February 2011Document1 pageEmily Schwartz Dallara February 2011Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- WQ 1Document1 pageWQ 1Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- At 1Document1 pageAt 1Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- TG 1Document1 pageTG 1Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- TG 1Document1 pageTG 1Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- QAW1Document1 pageQAW1Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- SSN 1Document1 pageSSN 1Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- 5 Fuselage and Tail Layout: 4.7 Areas of Flaps and AileronsDocument1 page5 Fuselage and Tail Layout: 4.7 Areas of Flaps and AileronsAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- aircraft loading structural layout simulationDocument1 pageaircraft loading structural layout simulationAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Engine Control On Modern Civil Aircraft: Figure 2.30 Rolls Royce Trent 800 - Overview (Courtesy of Rolls Royce)Document1 pageEngine Control On Modern Civil Aircraft: Figure 2.30 Rolls Royce Trent 800 - Overview (Courtesy of Rolls Royce)Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Mission: Gust and Turbulence RequirementsDocument1 pageMission: Gust and Turbulence RequirementsAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgements Xiii List of Acronyms XV Series Preface Xix 1Document1 pageAcknowledgements Xiii List of Acronyms XV Series Preface Xix 1Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Figure 2.27 Typical Accessory Gearbox: Hydraulic Pump Starter Lube and Scavenge Pump IDGDocument1 pageFigure 2.27 Typical Accessory Gearbox: Hydraulic Pump Starter Lube and Scavenge Pump IDGAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Wing Incidence (i) : C − α C C S SDocument1 page4.5 Wing Incidence (i) : C − α C C S SAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Afdc1 PDFDocument1 pageAfdc1 PDFAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Aerostat Equilibrium and Enhancement ProjectDocument1 pageAerostat Equilibrium and Enhancement ProjectAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgements Xiii List of Acronyms XV Series Preface Xix 1Document1 pageAcknowledgements Xiii List of Acronyms XV Series Preface Xix 1Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- xz02 PDFDocument1 pagexz02 PDFAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Contact Stress Components of Spherical SurfacesDocument1 pageContact Stress Components of Spherical SurfacesAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- xz1 PDFDocument1 pagexz1 PDFAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- V-N Diagram PDFDocument13 pagesV-N Diagram PDFmeku44No ratings yet
- Plate Buckling Analysis112 PDFDocument1 pagePlate Buckling Analysis112 PDFAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Contact Surfaces: For Cylinders in Contact, The Contact Patch Is Rectangular (Half-Width B)Document1 pageCylindrical Contact Surfaces: For Cylinders in Contact, The Contact Patch Is Rectangular (Half-Width B)Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- qq1 PDFDocument2 pagesqq1 PDFAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Solid Sections: Prandtl Stress Function SolutionDocument1 pageTorsion of Solid Sections: Prandtl Stress Function SolutionAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- As01 PDFDocument1 pageAs01 PDFAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- 1702Document1 page1702Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- As 03Document1 pageAs 03Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Cast Defect 01Document1 pageCast Defect 01Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- As 01Document1 pageAs 01Ashutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Earth Air Heat Exchanger PerformanceDocument4 pagesEarth Air Heat Exchanger Performanceviraj shettyNo ratings yet
- Report 4071 - EN6115-4 SPS TITAN (2.1MB)Document34 pagesReport 4071 - EN6115-4 SPS TITAN (2.1MB)pcosro0% (1)
- National Engineering Handbook Chapter 3Document35 pagesNational Engineering Handbook Chapter 3bb8585528No ratings yet
- Cma 4544pf W PDFDocument4 pagesCma 4544pf W PDFAlex RodriguezNo ratings yet
- AN525-Surface Texture Analysis Using Dektak Stylus ProfiDocument4 pagesAN525-Surface Texture Analysis Using Dektak Stylus ProfiNguyễn Hữu PhấnNo ratings yet
- Agilent Vacuum Training GuideDocument27 pagesAgilent Vacuum Training GuidesinytellsNo ratings yet
- SHM & Elasticity: Ba C BC A Ba CDocument13 pagesSHM & Elasticity: Ba C BC A Ba CKrithikaNo ratings yet
- Three Moments of An Explosion 50 Page FridayDocument44 pagesThree Moments of An Explosion 50 Page FridayRandom House Publishing GroupNo ratings yet
- Term Paper of Ele-102: Topic:-Power and Distribution (Transformer'S Application)Document10 pagesTerm Paper of Ele-102: Topic:-Power and Distribution (Transformer'S Application)shailesh singhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Differential EquationsDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Differential EquationsAbdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- INChO2012 Solution of Previous Year Question Papers of Indian National Chemistry Olympiad (INChO)Document9 pagesINChO2012 Solution of Previous Year Question Papers of Indian National Chemistry Olympiad (INChO)Akshay PandeyNo ratings yet
- Louvre Abu DhabiDocument5 pagesLouvre Abu DhabiSharadhi KattiNo ratings yet
- Fusion Cross-Sections - 24 - 11 - 2020Document25 pagesFusion Cross-Sections - 24 - 11 - 2020Isaiah KimNo ratings yet
- Overview of 7FB Turbines PDFDocument22 pagesOverview of 7FB Turbines PDFNikhil MalhotraNo ratings yet
- G 11 Revison 2020 Phy Electrostatics PDFDocument31 pagesG 11 Revison 2020 Phy Electrostatics PDFemihlekamvaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2-1-Calculate Time To Reach Radius of InvestigationDocument12 pagesExercise 2-1-Calculate Time To Reach Radius of InvestigationSohaibSeidNo ratings yet
- The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Mathematics in The Natural SciencesDocument10 pagesThe Unreasonable Effectiveness of Mathematics in The Natural SciencesAshlee AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Aplicações Corantes Naturais - ReviewDocument22 pagesAplicações Corantes Naturais - ReviewIlídiaFerreiraNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Computer Graphics ApplicationsDocument11 pagesIntroduction to Computer Graphics ApplicationsSachin NarangNo ratings yet
- Smart Street Light System Table of ContentsDocument27 pagesSmart Street Light System Table of ContentsMuhammad Solahuddin100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Linear Control (PDFDrive)Document401 pagesFundamentals of Linear Control (PDFDrive)hajibaNo ratings yet
- Construction and Building Materials: Hognon Sogbossi, Jérôme Verdier, Stéphane MultonDocument13 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: Hognon Sogbossi, Jérôme Verdier, Stéphane MultonElber Cuya PillacaNo ratings yet
- Inductance Part 1 - MowryDocument4 pagesInductance Part 1 - MowryJacky FanNo ratings yet
- 1 Syringe Siliconisation Trends Methods Analysis Procedures PDFDocument6 pages1 Syringe Siliconisation Trends Methods Analysis Procedures PDFSofiaProtopsaltiNo ratings yet
- HW5 Work and EnergyDocument20 pagesHW5 Work and EnergyGina G. HarrisNo ratings yet
- Acceptance Test and Clinical Commissioning of CT SDocument8 pagesAcceptance Test and Clinical Commissioning of CT SEskadmas BelayNo ratings yet
- Royal College Term Test Papers 2020 Maths English MediumDocument12 pagesRoyal College Term Test Papers 2020 Maths English MediumSithmi HerathNo ratings yet
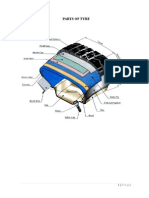
- Tyre ReportDocument19 pagesTyre ReportZachary HuffmanNo ratings yet
- Solid Solution HardeningDocument5 pagesSolid Solution HardeningVasantha SudasinghaNo ratings yet
- Donald Knuth, 1979, Mathematical Typografy, Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. (N.S.) Volume 1, Number 2 (1979), 337-372 PDFDocument36 pagesDonald Knuth, 1979, Mathematical Typografy, Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. (N.S.) Volume 1, Number 2 (1979), 337-372 PDFAndreaNo ratings yet