Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prezentare
Uploaded by
Sandu CristianOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prezentare
Uploaded by
Sandu CristianCopyright:
Available Formats
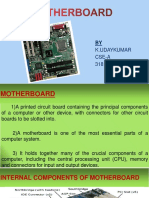
Slide 2: A motherboard is a very complex piece of hardware on witch all the other PC hardware components are mounted .
Slide 3: Motherboard elements Slide 4: CPU socket is a mechanical component that provides electrical and mechanical connection between a device (usually a microprocessor) and a printed circuit board. Motherboards are divided according to the processors socket, which is commonly referred to as the existing number of contacts for the processor pins. Slide 5: A chipset refers to a group of integrated circuits manufactured to work together. In most cases, they are manufactured in a single product. There are two chipsets: graphics chipset. The main component of the video card, coordinating the boards activities. motherboard chipset. For the motherboard, the chipset is the main component, greatly influencing motherboars performance by coordinating the essential components of the system. It has two main components, Northbridge and Southbridge, both performing distinct functions. Slide 6: In this slide are the two main components of the socket: at the top is the north bridge. This connects to the following: CPU, memory slots, AGP and PCI Express slot . At the bottom is southbridge with connects : hard drives, network card, USB ports, PCI slots and computer sound card. Slide 7: BIOS (Basic Input Output System) links the physical components and operating system. BIOS performs three basic functions: it inspects all hardware components at startup. Loads the Operating system Links the operating system to the hardware devices Slide 8: AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) is an interconnection for graphics accelerators, used mainly for 3D graphics and playback videos. AGP technology improves system performance by providing a fast way between graphics controller and system memory. AGP is a port, not a bus because a bus can connect multiple devices, while AGP is a connection point to point only between the CPU and video adapter. Slide 9: PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) is an interconnection system between a microprocessor and attached devices in expansion
slots. The PCI ports can connect components such as modems, network cards, video card, sound card, etc. . Slide 10: PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a standardized card expansion intended to replace the old PCI, PCI-X, and AGP standards. PCIe 3.0 is the latest standard for expansion cards, which is available on mainstream PCs. Slide 11: RAM (Random Access Memory ) is the volatile memory of a computer. The data stored in it is lost when the power supply is interrupted. This is not a disadvantage because the function of RAM is to store data when the computer is runnying and therefore not to store data for long periods of time. RAM appears as a small plate ("module") that holds several memory chips. The RAM module is attacked to the motherboard by a Memory interface slot. Slide 12: RAID stands for "Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks" or "Redundant Array of Independent Disks", which describes a configuration (array) with multiple disks designed to provide error tolerance and improved data access times . There are three main types of RAID: "mirroring" (= mirror copy of data on multiple disks) "data striping" (interlaced = data splitting on multiple disks) "Error Correction" (with error correction, where additional verification discs store information necessary for detecting and correcting errors). Slide 13: IDE (Intelligent Drive Electronics or Integrated Drive Electronics) is an interface for mass storage devices. The controller is integrated in the disk or CD-ROM.
You might also like
- Plan Managerial Emil PetrescuDocument16 pagesPlan Managerial Emil PetrescuSandu CristianNo ratings yet
- 6361403c9497b 101 Tips For Writing Attention Getting HeadlinesDocument28 pages6361403c9497b 101 Tips For Writing Attention Getting HeadlinesSandu CristianNo ratings yet
- New Schematic Project 7/12/2018Document1 pageNew Schematic Project 7/12/2018Sandu CristianNo ratings yet
- LM 2596Document45 pagesLM 2596Rafael PereiraNo ratings yet
- Releul EASYDocument15 pagesReleul EASYSandu CristianNo ratings yet
- LM 2596Document45 pagesLM 2596Rafael PereiraNo ratings yet
- Automatic Gain ControlDocument9 pagesAutomatic Gain ControlMareedu Ramya DeepthiNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument11 pagesDatasheetSandu CristianNo ratings yet
- Program Constatari 2011Document1 pageProgram Constatari 2011Sandu CristianNo ratings yet
- Serii Fourier TeorieDocument7 pagesSerii Fourier TeorieSandu CristianNo ratings yet
- Facultatea de Inginerie Electrica: MotherboardDocument13 pagesFacultatea de Inginerie Electrica: MotherboardSandu CristianNo ratings yet
- Attiny 2313Document226 pagesAttiny 2313api-241773043No ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Analog Filters - A Signal Processing PDFDocument453 pagesDesign and Analysis of Analog Filters - A Signal Processing PDFAntoniaMariaNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- ListaDocument1,388 pagesListagleisonclNo ratings yet
- Soal MGMP Bahasa Inggris (10 Soal)Document3 pagesSoal MGMP Bahasa Inggris (10 Soal)Fida Rizki Khoirunisa0% (1)
- MOTHERBOARDDocument13 pagesMOTHERBOARDUday HrudaiNo ratings yet
- UsbFix ReportDocument3 pagesUsbFix ReportzubadiNo ratings yet
- Dream StudioDocument16 pagesDream StudioAditya JaybhayeNo ratings yet
- ICTL Test2Document2 pagesICTL Test2Fweeda MkNo ratings yet
- Inventario de Sala de Cómputo Ie: 88301 Jesus de NazarethDocument4 pagesInventario de Sala de Cómputo Ie: 88301 Jesus de NazarethAurelio Botello AlegreNo ratings yet
- Motherboard and BiosDocument26 pagesMotherboard and BiosJoseph Mediano PogoyNo ratings yet
- NAEG10063768466 InvoiceDocument1 pageNAEG10063768466 InvoiceAlaaNo ratings yet
- FP CLOCK - csproj.FileListAbsoluteDocument14 pagesFP CLOCK - csproj.FileListAbsolutePhi Huỳnh NgôNo ratings yet
- Poster 2Document1 pagePoster 2Anderson MendesNo ratings yet
- Practical Techniques For Laptop RepairDocument3 pagesPractical Techniques For Laptop RepairGary FilbeeNo ratings yet
- Tecra 8100 Disassembly GuideDocument13 pagesTecra 8100 Disassembly GuideevilgreenieNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument44 pagesOperating SystemMaricel Fraga AzcarragaNo ratings yet
- Ipxpv-D3: Motherboard Layout ReferenceDocument6 pagesIpxpv-D3: Motherboard Layout ReferenceE Moy LandaNo ratings yet
- Mainboard j601cfr2Document18 pagesMainboard j601cfr2Ho Thanh BinhNo ratings yet
- Build a Custom PC for Rs. 64,546Document1 pageBuild a Custom PC for Rs. 64,546Vishnu Vardhan Reddy BaitintiNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor and Firmware HistoryDocument8 pagesMicroprocessor and Firmware HistoryjdbdavidNo ratings yet
- Rocky-4782 V1.5Document52 pagesRocky-4782 V1.5migbonNo ratings yet
- 3.2.2.5 Lab - Boot The ComputerDocument3 pages3.2.2.5 Lab - Boot The ComputerCsongor KissNo ratings yet
- Compaq Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesCompaq Schematic DiagramQuenitoLucianoJoãoNo ratings yet
- 5 Tools To Easily Install FreeDOS or MS-DOS Onto USB For BIOS Flashing - Raymond - CCDocument5 pages5 Tools To Easily Install FreeDOS or MS-DOS Onto USB For BIOS Flashing - Raymond - CCVincent PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing CF-19 Overview, Accessories & Mounting OptionsDocument18 pagesMobile Computing CF-19 Overview, Accessories & Mounting OptionsPeter Terrett100% (2)
- Packing Slip for Order 254034175Document4 pagesPacking Slip for Order 254034175josemx4No ratings yet
- PC Express Laptop Pricelist - Dec 1 2022Document9 pagesPC Express Laptop Pricelist - Dec 1 2022Angelo123No ratings yet
- Lapsing of Company Ex - 2012Document6 pagesLapsing of Company Ex - 2012Ma Teresa B. CerezoNo ratings yet
- Aggregated app crash reportDocument18 pagesAggregated app crash reportMelissa DillonNo ratings yet
- VIC20 Penultimate Cartridge User Guide 0.3Document2 pagesVIC20 Penultimate Cartridge User Guide 0.3Komitsu ArmsterNo ratings yet
- System Requirements Allplan 2017Document1 pageSystem Requirements Allplan 2017Marko PopovićNo ratings yet
- Mainboard Ms - 7046M1Document30 pagesMainboard Ms - 7046M1Ho Thanh BinhNo ratings yet