Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIMC Adult DKA Protocol 2012
Uploaded by
djizhieeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BIMC Adult DKA Protocol 2012
Uploaded by
djizhieeCopyright:
Available Formats
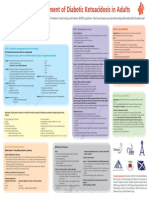
BIMC Adult DKA Protocol, Page 1 of 5 BIMC ADULT DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS (DKA) PROTOCOL Aim: To establish a protocol for
adults with diabetic ketoacidosis. Rationale: Diabetic ketoacidosis is one of the most serious acute complications of diabetes. Therapy is time sensitive and should be instituted as soon as possible. Having a unified protocol will allow for rapid identification of DKA and early initiation of treatment in the emergency department (ED) which can be continued until resolution of acidosis in the ED or once the patient is admitted to the hospital. Eligibility: Adults (age18) with DKA are characterized by the triad of hyperglycemia, an anion gap metabolic acidosis and ketonemia/ketouria. If adult patients meet the DKA criteria, they should be enrolled in the DKA protocol and categorized into either mild versus moderate-severe DKA. DKA Criteria 1. FS 250 2. AG 12 3. Ketonemia/ketouria DKA Severity Mild: Venous pH 7.25 Moderate-Severe: Venous pH < 7.25 When patients come from the ED into the hospital and the protocol has already been initiated, the protocol should be followed to completion. Please complete documentation on ER flow sheet. Goals: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Glucose level less than 250mg/dL Anion gap (AG) less than or equal to 12 Volume resuscitation Electrolyte management Patient off continuous insulin infusion and back on home regimen or appropriate alternative
Protocol: A. Once enrolled, all patients should get 1. An assessment for shock status a. If in shock SBP<90 or MAP<65, intravenous fluid (IVF) resuscitation 20cc/kg wide open b. If not in shock, IVF NS 1L over 1st hour, then 1L over 1-2hr, and another 1L over 1-2hrs for goal IVF NS 4L by 5-9 hours 2. Initiation of an insulin drip accordingly for moderate-severe vs. mild DKA a. moderate-severe: bolus 0.1U/kg and maintenance drip at 0.1 U/kg/hr b. mild: no bolus and maintenance rate 0.14U/kg/hr 3. Checks of fingerstick glucose (FSG) hourly 4. Check of basic metabolic panel (BMP) every 4 hours 5. Check of initial CBC 6. Correction of potassium and magnesium as follows: a. K 5.5: observe b. 4.5 K < 5.5: IV potassium repletion c. 3.3 K < 4.5: IV and PO potassium repletion d. K < 3.3: IV and PO potassium repletion + add 40meq of KCL to NS infusion 7. A urinalysis and blood cultures before antibiotics (if indicated)
BIMC Adult DKA Protocol, Page 2 of 5 8. A chest x-ray (if indicated) 9. Blood pressure, heart rate and oxygen saturation monitoring per ED/ICU protocol 10. Supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation (if required) B. If glucose still greater than 250: 1. If FSG decreased by 75-100 over last hour, maintain current insulin infusion rate 2. If FSG decreased by less that 75-100 over last hour, increase insulin drip by 1 unit per hour 3. Continue to check FSG hourly and BMP every four hours C. If glucose less than/equal to 250, but anion gap is greater than 12: 1. Decrease insulin drip to current rate 2. Initiate D5 NS at 150cc/hr 3. Titrate D5 NS to keep glucose 150-250 mg/dL until acidosis resolves (anion gap 12) 4. Continue to check FSG hourly and BMP every four hours D. If glucose less than/equal to 250 and anion gap is less than/equal to 12: 1. Test to see that patient can tolerate food If patient is able to tolerate food: 2. Administer subcutaneous long-acting insulin in one of following doses: a. home dose of long acting insulin and meal coverage b. 0.5-0.8U/kg as daily dose for insulin nave50% long acting & 50% divided in 3 doses for with-meal short acting insulin (for example: 70kg man to get 0.7*70U/day = 49U/day ~25U Lantus and ~25U/3 = ~8U regular insulin before meals) 3. Discontinue both insulin infusion and D5 NS infusion 1-2 hours after administration of long-acting insulin If patient is UNABLE to tolerate food: 4. Continue insulin drip 5. Continue IVF D5 NS fluid 6. Goal FSG 120-180 E. If hypoglycemic (FSG150) 1. If FSG <70 a. Administer 1 ampule of D50 b. Hold insulin drip for 15min and recheck FSG c. If FSG >100, re-start insulin drip reduced rate ( rate) d. Goal FSG > 150 2. If FSG 70-150 a. If patient is still has acidosis (AG >12): i. Switch IVF from D5 NS to D10 NS and start at 150ml/hr ii. Hold insulin drip for 15min and recheck FSG iii. If FSG >100, re-start insulin drip reduced rate ( rate) iv. Goal FSG > 150 b. If patient no longer has acidosis (AG 12): i. Increase IVF D5 NS rate by 50-150ml/hr ii. Hold insulin drip for 15min and recheck FSG iii. If FSG >100, re-start insulin drip reduced rate ( rate) iv. Goal FSG > 150
BIMC Adult DKA Protocol, Page 3 of 5
BIMC Adult DKA Protocol, Page 4 of 5
* volume expansion is key & must occur simultaneously, see Volume Resuscitation
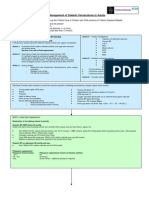
Adult Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatment Algorithm
Acute Phase
Check glucose 250 mg/dL <250 mg/dL
Severe (VBG pH<7.25) Bolus 0.1U/kg Insulin and start drip at 0.1U/kg/hr Mild (VBG pH7.25) Insulin drip 0.14U/kg/hr
Did glucose by 75-100 over last hour? no yes
1. IV insulin by 1 unit/hr Keep IV insulin at current rate
(If on D5, may need )
Assess acidosis: AG 12 (or known baseline)
* If next SMA not done, assume still acidotic
yes
IV insulin to current rate Start D5NS (or D5NS) at 150ml/hr Keep glucose 150-250 until Acidosis resolves
no
2.
3.
Enter Transition Phase
Transition Phase
Is patient able to eat? test a few bites of food no Maintain IV insulin & D5 at current rate until can eat Check glucose q1-hour yes Feed & Provide SQ insulin
Start
Option #1: Start home dose of long acting insulin and meal coverage Option #2: Start 0.5-0.8U/kg as daily dose for insulin nave (50% long acting; 50% subdivided in 3 for with-meal short acting insulin) After 1-2 hours: Discontinue IV insulin & D5 infusions
BIMC Adult DKA Protocol, Page 5 of 5
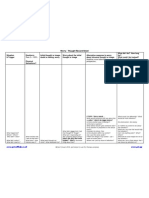
Laboratory Work-Up
Initially (time=0) Absolute Blood glucose (fingerstick) Complete metabolic panel (SMA20 and magnesium) VBG for pH (mild vs severe DKA) CBC Urinalysis, EKG, CXR (DKA trigger) Lactate (other cause of AG) Serum/urine ketones Recommended HbA1C Repetition Frequency Every 1 hour Every 4 hours (SMA10 with magnesium and phosphorus)
Every 4 hours until normal
Volume Resuscitation
Patients in shock SBP<90 or MAP<65
20cc/kg NS wide open Consider addition of vasopressors Evaluate for cause other than hypovolemia
1L NS over 1st hour then 1L NS over 1-2 hours then 1L NS over 1-2 hours then 1L NS over 2-4 hours Should have 4L in by 5-9 hours
* may need to be adjusted for patients with ESRD or CHF
Patients not in shock*
Electrolyte Repletion
Potassium (Patients are most often total body K+ depleted)
K+ 5.5 4.5 K+ < 5.5
3.3 K+ < 4.5 K+ < 3.3 observe IV Potassium repletion Consider adding 20meq of KCL to NS infusion IV Potassium repletion Consider adding 40meq of KCL to NS infusion IV/PO Potassium repletion Consider adding 40meq of KCL to NS infusion Hold insulin and give 20-30meq/hr until >3.3**
**only if able to recheck K within 1hr in ICU or ER setting via VBG/ABG
Magnesium & Phosphorus: Aggressively replete (goal Mg>1.6, Ph>2.5)
You might also like
- Managing Anaphylactic Shock Journal of Modern Pharmacy 2006Document3 pagesManaging Anaphylactic Shock Journal of Modern Pharmacy 2006Saputro AbdiNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Treatment ProcedureDocument4 pagesAnaphylaxis Treatment ProcedureIvy Jorene Roman RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain Protocol StepsDocument4 pagesChest Pain Protocol StepsArul ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Atls SpineDocument11 pagesAtls SpineRonald David EvansNo ratings yet
- GEA ProtocolsDocument101 pagesGEA Protocolsffbrians100% (1)
- Informed Consent For Lasik SurgeryDocument2 pagesInformed Consent For Lasik SurgeryMoerieda RinquestNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Head InjuryDocument9 pagesPediatric Head InjuryAndy WijayaNo ratings yet
- Guideline of ExtravasationDocument35 pagesGuideline of ExtravasationAura Lorena Rivas Zambrano100% (1)
- ACLS Study GuideDocument30 pagesACLS Study GuidemmmmzNo ratings yet
- AHA ACLS Written Test: Ready To Study? Start With FlashcardsDocument8 pagesAHA ACLS Written Test: Ready To Study? Start With FlashcardssallyNo ratings yet
- Surgical Cricothyrotomy (Assist)Document5 pagesSurgical Cricothyrotomy (Assist)ydtrgnNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Document1 pageAnaphylaxis Algorithm 2021Shawn Gaurav JhaNo ratings yet
- BLS MCQDocument8 pagesBLS MCQAmit BhowmikNo ratings yet
- BLS Healthcare Provider AlgorithmDocument7 pagesBLS Healthcare Provider AlgorithmyuniNo ratings yet
- Role Play Code BlueDocument2 pagesRole Play Code BlueKrzia TehNo ratings yet
- 3 Combined AHA BLS ACLS Updates CombinedDocument5 pages3 Combined AHA BLS ACLS Updates Combinedamanrup randhawa100% (1)
- NHS Lanarkshire Major Haemorrhage GuideDocument3 pagesNHS Lanarkshire Major Haemorrhage GuideleicesterbugNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Initial Assessment and Resuscitation Skill Station Guidance1 2010Document4 pages8.1 Initial Assessment and Resuscitation Skill Station Guidance1 2010brianed231No ratings yet
- Common Medical EmergenciesDocument9 pagesCommon Medical EmergenciesKURIMAONGNo ratings yet
- CPRDocument4 pagesCPRjeetNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument29 pagesCardiopulmonary ResuscitationSarahNo ratings yet
- Harris Regional ICU Daily Sedation Vacation GuidelinesDocument1 pageHarris Regional ICU Daily Sedation Vacation GuidelinesFebri Yudha Adhi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- How To Organize An ACLS Course PresentationDocument19 pagesHow To Organize An ACLS Course PresentationAzhar MohamedNo ratings yet
- Internship Manual For MBBSDocument29 pagesInternship Manual For MBBSKoustav ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Trauma in Pregnancy:: Get One Buy OneDocument46 pagesTrauma in Pregnancy:: Get One Buy OneJudi Januadi Endjun, MD, ObsGyn100% (1)
- Cant Intubate Cant VentilateDocument6 pagesCant Intubate Cant Ventilatedannyromero2712No ratings yet
- Bicarbonate Therapy in Severe Metabolic AcidosisDocument39 pagesBicarbonate Therapy in Severe Metabolic AcidosisRoberto UrquizaNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Power Point Slide Presentation - The Guidelines - Implementation For The FutureDocument25 pagesSepsis Power Point Slide Presentation - The Guidelines - Implementation For The Futuremontie13No ratings yet
- Pepp Als PretestDocument4 pagesPepp Als PretestDave BoppNo ratings yet
- 4 Phases of IV Fluid Therapy FinalDocument29 pages4 Phases of IV Fluid Therapy FinalLuqmanul Hakim Junaidden100% (1)
- Poster 10 PALS 01 01 ENG V20100927 PDFDocument1 pagePoster 10 PALS 01 01 ENG V20100927 PDFAndy XiaoNo ratings yet
- Algorithm-ACLS Electrical Cardioversion 200612Document1 pageAlgorithm-ACLS Electrical Cardioversion 200612Kavya ShreeNo ratings yet
- 2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Acute Coronary Syndromes AlgorithmDocument1 page2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Acute Coronary Syndromes Algorithmms_lezahNo ratings yet
- BLS ALGORITHM As of February 2023Document2 pagesBLS ALGORITHM As of February 2023Mark Jason Rodriguez, RNNo ratings yet
- BLS Mock Mark SheetDocument1 pageBLS Mock Mark Sheetatse1885No ratings yet
- Adult Basic Life Support Algorithm For Healthcare ProvidersDocument1 pageAdult Basic Life Support Algorithm For Healthcare ProvidersKavya ShreeNo ratings yet
- Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation: Dr. Sebastian ValceaDocument16 pagesCardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation: Dr. Sebastian ValceaAna MariaNo ratings yet
- Questions FinalDocument3 pagesQuestions FinalKeerthi Chowdary AmaraneniNo ratings yet
- AIPGMEE 1st Counselling 2011Document121 pagesAIPGMEE 1st Counselling 2011tarungupta2001No ratings yet
- 17 - Enhanced Recovery PrinciplesDocument7 pages17 - Enhanced Recovery Principlesbocah_britpopNo ratings yet
- The Main Principles:: A B C D EDocument4 pagesThe Main Principles:: A B C D EHatem FaroukNo ratings yet
- Ambulance Response Protocol DraftDocument3 pagesAmbulance Response Protocol DraftCommand CenterNo ratings yet
- Securement Device ChartDocument2 pagesSecurement Device ChartpacsolanoNo ratings yet
- Mechanical ThrombectomyDocument58 pagesMechanical Thrombectomyres.uditacharyaNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Fibrillation/ Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia AlgorithmDocument2 pagesVentricular Fibrillation/ Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia AlgorithmsafasayedNo ratings yet
- ACLS Online Training Material: Unit One: General ConceptsDocument34 pagesACLS Online Training Material: Unit One: General ConceptsJohn JenjinsNo ratings yet
- Protocol For The Management of Choking in AdultsDocument3 pagesProtocol For The Management of Choking in AdultsSarinah RynaNo ratings yet
- Checklist of Nonverbal Pain IndicatorsDocument41 pagesChecklist of Nonverbal Pain IndicatorsantipaticoNo ratings yet
- PalsDocument1 pagePalslordroentgenNo ratings yet
- Trauma in PregnancyDocument34 pagesTrauma in PregnancyOlulode Olufemi SNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of BLS: Muhammad SaleemDocument27 pagesBasic Concept of BLS: Muhammad Saleemms khanNo ratings yet
- نقابة التمريض الفلسطينية 7Document11 pagesنقابة التمريض الفلسطينية 7أبوأحمد الحكيمNo ratings yet
- Truspected Stroke AlgorithmDocument4 pagesTruspected Stroke Algorithmtri wahyunoNo ratings yet
- Management of Shock: Role of Inotropic & Vasoactive DrugsDocument50 pagesManagement of Shock: Role of Inotropic & Vasoactive DrugsbajaocNo ratings yet
- ACLS Full LectureDocument47 pagesACLS Full LectureAdhydeva Purusanti100% (3)
- PRE ANAESTHETIC ASSESSMENT New 1Document41 pagesPRE ANAESTHETIC ASSESSMENT New 1lokeswara reddyNo ratings yet
- Bls - Fbao - First AidDocument172 pagesBls - Fbao - First AidMaria Regina Castro Gabriel100% (1)
- GUIDELINES FOR MANAGING DIABETESDocument1 pageGUIDELINES FOR MANAGING DIABETESthapanNo ratings yet
- DKA Protocol TGDocument11 pagesDKA Protocol TGabelNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (D.K.A) Beaumont Hospital Protocol: DiagnosisDocument1 pageDiabetic Ketoacidosis (D.K.A) Beaumont Hospital Protocol: Diagnosislouglee9174100% (1)
- Heart Failure Clinical Pathway GuideDocument7 pagesHeart Failure Clinical Pathway GuidedjizhieeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway StrokeDocument8 pagesClinical Pathway StrokedjizhieeNo ratings yet
- Acute Ischemic Stroke PathwayDocument50 pagesAcute Ischemic Stroke PathwaydjizhieeNo ratings yet
- All About Partial Seizures PDFDocument6 pagesAll About Partial Seizures PDFdjizhieeNo ratings yet
- 36x60 Advocate Health Care Vertical TemplateDocument1 page36x60 Advocate Health Care Vertical TemplatedjizhieeNo ratings yet
- Acute Ischemic Stroke PathwayDocument50 pagesAcute Ischemic Stroke PathwaydjizhieeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway StrokeDocument8 pagesClinical Pathway StrokedjizhieeNo ratings yet
- Public Relation Alert!Document31 pagesPublic Relation Alert!djizhieeNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Clinical Pathway GuideDocument7 pagesHeart Failure Clinical Pathway GuidedjizhieeNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Clinical Pathway GuideDocument7 pagesHeart Failure Clinical Pathway GuidedjizhieeNo ratings yet
- International Travel Health ITH - 2009Document252 pagesInternational Travel Health ITH - 2009djizhieeNo ratings yet
- TocDocument727 pagesTocdjizhiee100% (1)
- ARIA Report 2008Document196 pagesARIA Report 2008jasbroNo ratings yet
- 18x24 PosterDocument1 page18x24 PosterdjizhieeNo ratings yet
- CondylomaDocument4 pagesCondylomaOchabianconeriNo ratings yet
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic Non-Ketotic StateDocument5 pagesHyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic Non-Ketotic StatedjizhieeNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Transcranial Direct Current ... (Previ A Impressió) PDFDocument12 pagesThe Effects of Transcranial Direct Current ... (Previ A Impressió) PDFdjizhieeNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in The Medical Community (Part 1) - Dr. Khotibuddin - 18 April 2012Document29 pagesNutrition in The Medical Community (Part 1) - Dr. Khotibuddin - 18 April 2012djizhieeNo ratings yet
- CASP Diagnostic Test Checklist 31.05.13Document6 pagesCASP Diagnostic Test Checklist 31.05.13itho23No ratings yet
- Dka Management of Dka in Adults March 20101Document24 pagesDka Management of Dka in Adults March 20101djizhieeNo ratings yet
- Aria Rhinitis Allergic Pocket GuideDocument8 pagesAria Rhinitis Allergic Pocket GuideAlfani FajarNo ratings yet
- Pathway KeratitisDocument16 pagesPathway Keratitisdjizhiee100% (1)
- Aria Rhinitis Allergic Pocket GuideDocument8 pagesAria Rhinitis Allergic Pocket GuideAlfani FajarNo ratings yet
- Joint British Diabetes Societies Inpatient Care Group - The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Adults - Pathway PosterDocument1 pageJoint British Diabetes Societies Inpatient Care Group - The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Adults - Pathway PosterAllison Nadine MarchandNo ratings yet
- Dka Guidelines - 2012Document4 pagesDka Guidelines - 2012djizhieeNo ratings yet
- Joint British Diabetes Societies Inpatient Care Group - The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Adults - Pathway PosterDocument1 pageJoint British Diabetes Societies Inpatient Care Group - The Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Adults - Pathway PosterAllison Nadine MarchandNo ratings yet
- DokDocument1 pageDokdjizhieeNo ratings yet
- MMR SKills Lab 1Document3 pagesMMR SKills Lab 1djizhieeNo ratings yet
- Pre-Op NPO and Traditional Post-Op Diet Advancement: Time To Move OnDocument7 pagesPre-Op NPO and Traditional Post-Op Diet Advancement: Time To Move OnDaru KristiyonoNo ratings yet
- Return To Running ProgramDocument1 pageReturn To Running ProgramMark DingleNo ratings yet
- Bateman Fonagy 2008 Mentalization Based Treatment For BPDDocument16 pagesBateman Fonagy 2008 Mentalization Based Treatment For BPDCamila Piña SanhuezaNo ratings yet
- Brexpiprazole: A Review of A New Treatment Option For Schizophrenia and Major Depressive DisorderDocument6 pagesBrexpiprazole: A Review of A New Treatment Option For Schizophrenia and Major Depressive DisorderLuis Pablo HsNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Practice Math Problems Answer KeyDocument3 pagesPediatric Practice Math Problems Answer KeyKaren Hutchinson50% (2)
- ATLS COURSE OVERVIEW: PURPOSE, HISTORY, AND CONCEPTSDocument12 pagesATLS COURSE OVERVIEW: PURPOSE, HISTORY, AND CONCEPTSALberta YosheNo ratings yet
- Jurnal PDPH Anest RisaDocument15 pagesJurnal PDPH Anest Risaadit rifqiNo ratings yet
- Bronson at Home Advanced Illness Management ProgramDocument15 pagesBronson at Home Advanced Illness Management Programapi-262307733No ratings yet
- Pityriasis AlbaDocument6 pagesPityriasis AlbaLee Eng SiangNo ratings yet
- Orem's Self-Care Deficit Nursing TheoryDocument30 pagesOrem's Self-Care Deficit Nursing TheoryDairyl Tagaro100% (1)
- Hunkin 2020Document11 pagesHunkin 2020Alex LazoNo ratings yet
- Edema Paru Kardiogenik Akut Kak TiaraDocument8 pagesEdema Paru Kardiogenik Akut Kak TiaraTyara LarisaNo ratings yet
- Drug AdministrationDocument8 pagesDrug AdministrationKATE LAWRENCE BITANTOSNo ratings yet
- Effect of Mcconnell Taping On Pain, Rom & Grip Strength in Patients With Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex InjuryDocument9 pagesEffect of Mcconnell Taping On Pain, Rom & Grip Strength in Patients With Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex InjuryDr. Krishna N. SharmaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Lower Body Stabilization and Diff Writing Tools On Handwriting in PX With CP PDFDocument8 pagesEffect of Lower Body Stabilization and Diff Writing Tools On Handwriting in PX With CP PDFRainNo ratings yet
- Sternotomi PDFDocument11 pagesSternotomi PDFHeri PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Informed Consent FormDocument2 pagesInformed Consent FormSaroja RoyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Superintendent DutiesDocument7 pagesNursing Superintendent DutiesSrinivas Polikepati100% (1)
- Wilderness Remote First Aid ManualDocument128 pagesWilderness Remote First Aid Manualcr4zyvi3t100% (3)
- Tranquil Eyes Kit User ManualDocument27 pagesTranquil Eyes Kit User ManualJj TreyNo ratings yet
- Arthritis Psoriatica, Arthropathic: Psoriasis or Psoriatic ArthropathyDocument13 pagesArthritis Psoriatica, Arthropathic: Psoriasis or Psoriatic ArthropathyGrace de RamosNo ratings yet
- Crown Prep Goodacre PDFDocument14 pagesCrown Prep Goodacre PDFRuben SosaNo ratings yet
- Word Power Made EasyDocument22 pagesWord Power Made Easynagendra67% (3)
- Expander Cable TrainingDocument3 pagesExpander Cable Trainingjec35No ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument11 pagesNarrative Reportwhatss upNo ratings yet
- Kazdin 2007 PDFDocument29 pagesKazdin 2007 PDFDaniela UrreaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDan MandigNo ratings yet
- GAD Thought Record SheetDocument1 pageGAD Thought Record SheetpanickedchickNo ratings yet
- Heti 2021 IPPE POSTER VOLTEIODocument1 pageHeti 2021 IPPE POSTER VOLTEIOAline SartiNo ratings yet
- Week 14 LEC Interdisciplinary Mental Health Team Collaboration BAUTISTADocument51 pagesWeek 14 LEC Interdisciplinary Mental Health Team Collaboration BAUTISTAAngelica GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Autism Ethiopia PDFDocument13 pagesAutism Ethiopia PDFAnonymous ae0Sceo100% (3)