Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Surface Chemistry: Section-I (Single Option Correct Type, 3 Marks For Each Correct and - 1 For Incorrect)
Uploaded by
Rajeev GangwarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Surface Chemistry: Section-I (Single Option Correct Type, 3 Marks For Each Correct and - 1 For Incorrect)
Uploaded by
Rajeev GangwarCopyright:
Available Formats
Surface Chemistry
Time- 60 mins M.Marks-100
Section-I (Single Option Correct Type, 3 marks for each correct and -1 for incorrect)
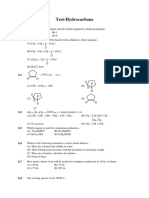
1. Adsorption of gases on solid surface is generally exothermic because: (A) enthalpy is positive (B) entropy decreases (C) entropy increases (D) free energy increases 2. Which forms multimolecular layer during adsorption (A) Physical adsorption (B) Chemisorption (C) Both (A) and (B) (D) None of these 3. Peptization is a process of (A) precipitation of colloidal particles (B) purification of colloids (C) dispersing precipitate into colloidal sols (D) movement of colloidal particles in the electrical field 4. Lyophilic sols are (A) Irreversible sols (B) They are prepared from inorganic compound (C) coagulated by adding electrolytes (D) self-stabilizing 5. Among the following, the surfactant that will form micelles in aqueous solution at the lowest molar concentration at ambinent condition is (A) CH3(CH2)15N+ (CH3)3 Br (B) CH3(CH2)11OSO3Na+ (C) CH3(CH2)6COONa+ (D) CH3(CH2)11N+(CH3)3Br 6. Among the electrolytes Na2SO4, CaCl2, Al2(SO4)3 and NH4Cl, the most effective coagulating agent for Sb2S3 sol is (A) Na2SO4 (B) CaCl2 (C) Al2(SO4)3 (D) NH4Cl 7. In the coagulation of positively charged colloidal solution which of the following has maximum coagulating power? (A) CO32(B) [Fe(CN)6]4(C) PO43(D) Al3+ 8. In the preparation of AgI sol , the excess of AgNO3, is added to potassium iodide solution. The particles of the sol will acquire (A) Negative charge (B) Positive charge (C) No charge (D) Unpredictable 9. Which gas will be adsorbed on a solid to greater extent. (A) A gas having non polar molecule (B) A gas having highest critical temperature (Tc) (C) A gas having lowest critical temperature. (D) A gas having highest critical pressure. 10. Graph between ln (x/m) and ln(p) is straight line inclined at an angle of 45. When pressure is 0.5 atm and intercept is 0.693, what will be the amount of solute adsorbed per gm of adsorbent? (A) 0.5 (B) 1 (C) 2.5 (D) 2
Section-II (One or More Than One Option Correct Type, 4 marks for each correct and -1 for incorrect)
11. Choose the correct reason(s) for the stability of the lyophobic colloidal particles.
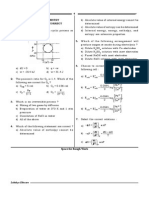
(A) Preferential adsorption of ions of on their surface from the solution (B) Preferential adsorption of solvent on their surface from the solution (C) Attraction between different particles having opposite charges on their surface (D) Potential difference between the fixed layer and the diffused layer of opposite charges around the colloidal particles 12. The given graphs/data I, II, III and IV represent general trends observed for different physisorption and chemisorption processes under mild conditions of temperature and pressure. Which of the following choice(s) about I, II, III and IV is (are) correct ?
(A) I is physisorption and II is chemisorption (B) I is physisorption and III is chemisorption (C) IV is chemisorption and II is chemisorption (D) IV is chemisorption and III is chemisorption 13. When negatively charged colloids like As2S3 sol is added to positively charged Fe(OH)3 sol in suitable amounts (A) Both the sols are precipitated simultaneously (B) This process is called mutual coagulation (C) They becomes positively charged colloids (D) They becomes negatively charged colloids 14. Which of the following statements are true for physiosorption ? (A) Extent of adsorption increases with increase in pressure. (B) It needs activation energy (C) It can be reversed easily (D) It occurs at high temperature 15. Select the correct statements from the following regarding sols (A) Viscosity of lyophilic sols is much higher than that of solvent (B) Surface tension of lyophobic sols is usually low. (C) The particles of lyophilic sols always carry a characteristics charge either positive or negative (D) Hydrophobic sols can easily be coagulated by addition of electrolytes 16. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct (A) Higher the gold number, more protective power of colloid (B) Lower the gold number, more the protective power
(C) Higher the coagulation value, more the coagulation power (D) Lower the coagulation value, higher the coagulation power 17. Which of the following are correct statements (A) Hardy Schulz rule id related to coagulation (B) Brownian movement and Tyndall effect are shown by colloids (C) When liquid is dispersed in liquid, it is called gel. (D) Gold number is a measure of protective power of lyophillic colloid. 18. Freundlich adsorption isotherm is given by the expression x/m= kp1/n . Which of the following conclusions can be drawn from this expression. (A) When 1/n = 0, the adsorption is independent of pressure (B) When 1/ n = 0, the adsorption is directly proportional to pressure. (C) When n = 0, x/ m vs p graph is a line parallel to x-axis. (D) When n = 0, plot of x/ m vs p is a curve19. Which of the following phenomenon occurs when a chalk stick is dipped in ink? (A) adsorption of coloured substance (B) adsorption of solvent (C) absorption and adsorption both of solvent (D) absoprtion of solvent 20. FeCl3 is used to stop bleeding because (A) Fe3+ ions coagulate the blood which is a negatively charges sol. (B) Fe3+ ions coagulate the blood which is a positively charged sol. (C) Cl- ions coagulate the blood which is a positively charged sol (d) Cl- ions coagulate the blood which is a negatively charged sol
Section-III (Comprehensions, 3 marks for each correct and -1 for incorrect)
Passage-1 (for questions 21 to 23) Lyophilic colloidal sols are much more stable than lyopholic colloidal sols. This is due to the extensirely salvation of lyophic colloidal sols, which forms a protective layer out side it & thus prevents it from forming associated colloids. Lyophilic colloidal sols also protect lyophobic colloidal sols from precipitation by the action of electrolytes. This is due to formation of a protective layer by lyophilic sols out side lyophobic sols. Lyophilic sols are also called as protective sols. Gelatin (lyophilic) protect gold sol (lyophobic) from coagulation on addition of sodium chloride solution. Protective powers of different colloidal sols are measured in terms of gold number. It is defined as the amount of protective sol in milligram that prevent the cagulation of 10 ml of a given gold sol on adding 1 ml of 10 % solution of sodium chloride. Thus smaller the gold number of a lyophilic sol, the greater is the protective power. 21. 0.025 gm of starch sol is required to prevent cagulation of 10 ml gold sol when 1 ml of 10 % NaCl solution is added. What is gold number of starch sol (A) 0.025 (B) 2.5 105 (C) 0.25 (D) 25 22. Gold number of haemoglobin is 0.03. Hence 100 ml of gold sol will require haemoglobin so that gold is not cagulated by 1 ml of 10 % NaCl solution (A) 0.03 mg (B) 30 mg (C) 0.30 mg (D) 3 mg 23. [Ag]I Colloidal sol can be coagulated by addition of a suitable cation. 1 mol of [AgI]I requires mol of AgNO3, Pb(NO3)2 & Fe(NO3)3 as (A) 1, 1, 1, (B) 1, 2, 3 (C) 1, 1/2 , 1/3 (D) 6, 3, 2
Passage-II (for questions 24 to 26) If a pair of immiscible liquids such as olive oil and water are mixed and shaken vigorously, a dispersion of very fine droplets of one liquid in the other will result. Such a dispersion is termed emulsion. One of the components in emulsion is water and the other one an oily substance immiscible in water. Emulsion droplets are bigger than sol particles (106 m) and can be seen under an ordinary microscope or sometimes even with a magnifying glass. Emulsions resemble lyophobic sols in some of the properties. Emulsion can be identified by dye-test. 24. In the following emulsion
(A) I is of oil-in-water type and II is of water-in-oil type (B) I is of water-in-oil type and II is of oil-in-water type (C) both are of oil-in-water type (D) both are of water-in-oil type 25. An oil-soluble dye is shaken with the given emulsion under study. We observe that whole background appears coloured. this indicates that emulsion is (A) water-in-oil type (B) oil-in-water type (C) liquid under study is pure oil (D) liquid under study is pure water 26. An oil-soluble dye is shaken with the given emulsion under study. we observe coloured drops when seen under microscope. Thus emulsion is (A) water-in-oil type (B) oil-in-water type (C) liquid under study is pure oil (D) liquid under study is pure water
Section-IV (Matching Type, 1mark for each correct, no negative marking)
27. Match the items of Column I and Column II. Column I Column II (i)Dialysis (a)Cleansing action of soap (ii)Peptisation (b)Coagulation (iii)Emulsification (c)Colloidal sol formation (iv)Electrophoresis (d)Purification
Section-V (Assertion-Reason Type, 4 marks for each correct and -1 for incorrect)
These questions consist of two statements each, printed as assertion and reason, while answering these questions you are required to choose any one of the following responses. (A) If assertion is true but the reason is false. (B) If assertion is false but the reason is true. (C) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is a correct explanation of assertion. (D) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not a correct explanation of assertion. 28. Assertion : Isoelectric point is pH at which colloidal can move towards either of electrode Reason : At isoelectric point, colloidal solution become electrically neutral. 29. Assertion : For adsorption G, H, S all have ve values Reason : Adsorption is a spontaneous exothermic process in which randomness decreases due to force of attraction between adsorbent and adsorbate.
You might also like
- JEE Chemistry - Surface ChemistryDocument16 pagesJEE Chemistry - Surface Chemistryofficial.archit234No ratings yet
- MEO Chemistry Midterm TestbankDocument113 pagesMEO Chemistry Midterm Testbankromaehab201912No ratings yet
- CLASS XII CHEMISTRY SURFACE CHEMISTRY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONSDocument35 pagesCLASS XII CHEMISTRY SURFACE CHEMISTRY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONSManthan K.No ratings yet
- Exercise FinalDocument9 pagesExercise Finald anjilappaNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry GuideDocument19 pagesSurface Chemistry GuideShivang K RaghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Surface ChemistryDocument5 pagesSurface ChemistryRajendra ChikkamathNo ratings yet
- JEE (MAIN + ADVANCED) 2022 REVISION ASSIGNMENT #02 - SURFACE CHEMISTRY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONSDocument6 pagesJEE (MAIN + ADVANCED) 2022 REVISION ASSIGNMENT #02 - SURFACE CHEMISTRY MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONSKrishnaNo ratings yet
- This Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingDocument8 pagesThis Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingvarunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry-03-Assignments (New)Document11 pagesSurface Chemistry-03-Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Single Answer Type QuestionsDocument6 pagesSingle Answer Type Questionspinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- 5 Surface-ChemistryExerciseDocument4 pages5 Surface-ChemistryExercisepinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 10 Study Material English Medium 216233Document15 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 10 Study Material English Medium 216233Âshwin ÂshwinNo ratings yet
- 14-04-08-Svs Surface Chemistry Che - AssignmentDocument10 pages14-04-08-Svs Surface Chemistry Che - AssignmentGadde Gopala Krishna100% (1)
- Solution PDFDocument5 pagesSolution PDFGourab SahaNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry1595054Document18 pagesSurface Chemistry1595054Winter GamingNo ratings yet
- Test Bank SolutionsDocument47 pagesTest Bank SolutionsMohammed AhmedNo ratings yet
- St. Mark's Sr. Sec. Public School, Janakpuri PA-II Exam Class XII Subject: ChemistryDocument22 pagesSt. Mark's Sr. Sec. Public School, Janakpuri PA-II Exam Class XII Subject: ChemistryPp PpNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry MCQsDocument4 pagesSurface Chemistry MCQsAnuj PalNo ratings yet
- 10th ScienceDocument5 pages10th ScienceAkshaya sriNo ratings yet
- JSC Science SQP-4 2023-24Document5 pagesJSC Science SQP-4 2023-24Jayant ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- JSC Science SQP-1 2023-24Document6 pagesJSC Science SQP-1 2023-24Jayant ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry: Cations Accelerate HydrolysisDocument2 pagesSurface Chemistry: Cations Accelerate HydrolysisAnshnuNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, GBN Preboard Examination Iii (2020-21) Class: XII Subject: Chemistry Set - ADocument6 pagesDelhi Public School, GBN Preboard Examination Iii (2020-21) Class: XII Subject: Chemistry Set - AAvinashNo ratings yet
- Unit-5-Surface ChemistryDocument3 pagesUnit-5-Surface ChemistryRSNo ratings yet
- CH1 Soution HHW Worksheet1Document6 pagesCH1 Soution HHW Worksheet1Aaditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- 12th Question FinalDocument9 pages12th Question FinalGKJ kalaiyagamNo ratings yet
- 10th Science Practice TestDocument13 pages10th Science Practice Testavinash960No ratings yet
- Final Revision-STEM Fayoum Chemistry ClubDocument48 pagesFinal Revision-STEM Fayoum Chemistry Clubromaehab201912No ratings yet
- Test 5Document4 pagesTest 5Bad GuyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Pre BoardDocument9 pagesChemistry Pre BoardSahil KhanNo ratings yet
- Sljso 2019 English Full PaperDocument8 pagesSljso 2019 English Full PaperkastonoNo ratings yet
- Oxford Public School Half Yearly Exam Chemistry QuestionsDocument4 pagesOxford Public School Half Yearly Exam Chemistry QuestionsNaruto UzumakiNo ratings yet
- Science X QP Set BDocument7 pagesScience X QP Set BYogesh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Nta Abhyas Test-65 CDocument5 pagesNta Abhyas Test-65 CMIITY EDUNo ratings yet
- Preboard-I Xii A Chemistry Set BDocument8 pagesPreboard-I Xii A Chemistry Set BDiksha TNo ratings yet
- SURFACE CHEMISTRY: ADSORPTION AND COLLOIDSDocument5 pagesSURFACE CHEMISTRY: ADSORPTION AND COLLOIDSHari KotagiriNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper XiiDocument8 pagesSample Paper XiiBKNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - 6Document8 pagesSample Paper - 6rajneesh kumarNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry XII PaperDocument4 pages12 Chemistry XII PaperPrinceNo ratings yet
- Question Ppaer For DavDocument8 pagesQuestion Ppaer For DavAkhilesh KRSNo ratings yet
- Cbse Chemistry Test 5Document6 pagesCbse Chemistry Test 5rajneesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Chem Xii (PB) QPDocument16 pagesChem Xii (PB) QPKojo TiNo ratings yet
- JSC Science SQP-5 2023-24Document5 pagesJSC Science SQP-5 2023-24Jayant ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 06 Term IDocument12 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper Test 06 Term IMayankNo ratings yet
- G-10 Science-05 JunDocument4 pagesG-10 Science-05 JunAman JoshiNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - Term 1 - Science - Final - SendDocument15 pagesGrade 10 - Term 1 - Science - Final - Sendmanasmkw21No ratings yet
- Class 10th PaperDocument11 pagesClass 10th Paperar7218292No ratings yet
- Grades 10 Science SQPDocument6 pagesGrades 10 Science SQPArnav SudhindraNo ratings yet
- Matter Around UsDocument3 pagesMatter Around UsKavi KaviNo ratings yet
- Solution Colligative Properties ExplainedDocument31 pagesSolution Colligative Properties ExplaineddislikeNo ratings yet
- Science X QP Set CDocument7 pagesScience X QP Set CYogesh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Board II Science Exam ReviewDocument8 pagesPre-Board II Science Exam ReviewDIVYANSHI SAINI IX-CNo ratings yet
- Chennai Sahodaya Science Set 1 QP 2022-23 - FOR PRACTICE ONLYDocument7 pagesChennai Sahodaya Science Set 1 QP 2022-23 - FOR PRACTICE ONLYvro hamza100% (14)
- 34 Chemistry SV 2024 Exam-1Document13 pages34 Chemistry SV 2024 Exam-1qzglsefafNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Navi Mumbai Online Assessment September 2021-2022Document10 pagesDelhi Public School Navi Mumbai Online Assessment September 2021-2022Aryaman MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Sljso 2017 EnglishDocument9 pagesSljso 2017 EnglishDayal WeerasooriyaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document43 pagesPaper 1Kathy WongNo ratings yet
- Tional: EdulabzDocument4 pagesTional: Edulabzbhaskar51178No ratings yet
- Volumetric (Ans Key) PDFDocument1 pageVolumetric (Ans Key) PDFRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- XI Advanced Result Dated 12.02.17Document30 pagesXI Advanced Result Dated 12.02.17Rajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Halogen Derivatives SheetDocument6 pagesHalogen Derivatives SheetRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- TestDocument2 pagesTestRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Practical Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesPractical Organic ChemistryRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- KMnO4 & DichromateDocument8 pagesKMnO4 & DichromateRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- PT 3 (Physics)Document51 pagesPT 3 (Physics)Rajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon TestDocument7 pagesHydrocarbon TestRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Chapters Priority For JEE MAINS (Based On Number of Questions Asked From 2002-17)Document1 pageChapters Priority For JEE MAINS (Based On Number of Questions Asked From 2002-17)Rajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Dpps-10 Numerical ConceptDocument1 pageDpps-10 Numerical ConceptRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE Organic Chemistry Aldol CondensationDocument3 pagesIIT-JEE Organic Chemistry Aldol CondensationRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Test 3 AtomicDocument4 pagesTest 3 AtomicRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- KVPY 2010 Stream SA Solved PaperDocument18 pagesKVPY 2010 Stream SA Solved PaperJanaki KrishnanNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE Organic Chemistry Aldol CondensationDocument3 pagesIIT-JEE Organic Chemistry Aldol CondensationRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Maninagar-Target) Section-I (Only One Option Correct)Document4 pagesChemistry (Maninagar-Target) Section-I (Only One Option Correct)Rajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- DPPS-14 Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesDPPS-14 Atomic StructureRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Dpps - 5 Atomic StructureDocument1 pageDpps - 5 Atomic StructureRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- pKa Chart: Strongest Acids and Weakest BasesDocument2 pagespKa Chart: Strongest Acids and Weakest BasesSayNo ratings yet
- Dpps-14 Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesDpps-14 Atomic StructureRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- DPPS-7 Atomic StructureDocument3 pagesDPPS-7 Atomic StructureRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- R - 1 JJJJ JJJJ: Space For Rough WorkDocument1 pageR - 1 JJJJ JJJJ: Space For Rough WorkRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Ethers: Assignment - Stage I Cumulative Skills Multiple Choice Questions 7Document3 pagesEthers: Assignment - Stage I Cumulative Skills Multiple Choice Questions 7Rajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Board Pattern Test Paper - Chemistry (Solid State, Solutions & Electro)Document4 pagesBoard Pattern Test Paper - Chemistry (Solid State, Solutions & Electro)Rajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Dpps - 17 Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesDpps - 17 Atomic StructureRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- DPPS-6 Atomic StructureDocument4 pagesDPPS-6 Atomic StructureRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Dpps-11 Atomic StructureDocument3 pagesDpps-11 Atomic StructureRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- 11-2 Critical TemperatureDocument3 pages11-2 Critical TemperatureAdel AwnNo ratings yet
- Jee Main Paper-2Document8 pagesJee Main Paper-2Rajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Schrodinger Eq NDocument18 pagesSchrodinger Eq NNicole HardyNo ratings yet
- Prof. K.V.Krishna Rao, Apr 2010Document2 pagesProf. K.V.Krishna Rao, Apr 2010Rajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- Ionic Packet For Lab Chem 2010 2011Document16 pagesIonic Packet For Lab Chem 2010 2011Victor BritoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 - OrganohalidesDocument8 pagesExperiment 8 - OrganohalidesOrlando Angelo CerezoNo ratings yet
- 123Document20 pages123Dacy ChowNo ratings yet
- 4CH0 1C MSC 20140821Document28 pages4CH0 1C MSC 20140821Ramy OmarNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument7 pagesIonic BondingDrcreeperPhdNo ratings yet
- DialysisDocument4 pagesDialysisLia PalmaNo ratings yet
- Master DDD 2017Document904 pagesMaster DDD 2017Ainul YuyunNo ratings yet
- ANACHEM Gravimetric Application NotesDocument6 pagesANACHEM Gravimetric Application NotesCASIÑO SHANE VAST ANDREINo ratings yet
- Catalog NAVIMAKS GROUPDocument79 pagesCatalog NAVIMAKS GROUPVesna NikolicNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry ProblemsDocument3 pagesStoichiometry ProblemskjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Jung 2001Document7 pagesJung 2001J Venkat RamanNo ratings yet
- June 2016 (IAL) MS - Unit 5 Edexcel ChemistryDocument31 pagesJune 2016 (IAL) MS - Unit 5 Edexcel ChemistryLeo DennisNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Offset DampeningDocument14 pagesFundamentals of Offset DampeningcarloadugNo ratings yet
- Thesis - Nancy Mduma FINALDocument62 pagesThesis - Nancy Mduma FINALDavid SabaflyNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts - The FundamentalsDocument14 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts - The FundamentalsKirthika SNo ratings yet
- KNO3Document10 pagesKNO3reinhard guevaraNo ratings yet
- Solubility ActivitiesDocument2 pagesSolubility ActivitiesRayian MactalNo ratings yet
- Taller Parcial 1 - Fisica IiiDocument6 pagesTaller Parcial 1 - Fisica IiiJorge CañetesNo ratings yet
- Zirconium 702C and Zirconium 705C PDFDocument2 pagesZirconium 702C and Zirconium 705C PDFgullenariNo ratings yet
- Chlorine Dosing PumpDocument24 pagesChlorine Dosing PumpByron HisseyNo ratings yet
- Iconic Bonding: The Evidence That Ions ExistDocument12 pagesIconic Bonding: The Evidence That Ions ExistKingson_786No ratings yet
- Accelerating AdmixturesDocument5 pagesAccelerating AdmixturesFaraz TariqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab 3Document2 pagesChemistry Lab 3Sherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- ch-29 Que - Paper PDFDocument36 pagesch-29 Que - Paper PDFkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Journal - Copper in Saline WaterDocument34 pagesJournal - Copper in Saline WaterWei Mee HiiNo ratings yet
- Chap 19 No 5Document2 pagesChap 19 No 5api-249777358No ratings yet
- 1 Integración de Desórdenes Electrolíticos y Ácido-Base RB IR Med BahamondeDocument11 pages1 Integración de Desórdenes Electrolíticos y Ácido-Base RB IR Med BahamondeMaría Jose BahamondeNo ratings yet
- Solubility ChartDocument2 pagesSolubility ChartDemonX01No ratings yet
- Ion Exchanger Lab ReportDocument36 pagesIon Exchanger Lab Reporthinman714No ratings yet