Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Examining Peripheral Nerves
Uploaded by
Nur Atiqah ZainalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Examining Peripheral Nerves
Uploaded by
Nur Atiqah ZainalCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Goals of examining peripheral nerve: -what nerves involve (median/ Ulnar/ Radial) -level of the lesions (High/ low) -Causes of the injury (from scars or deformity present) # Must know anatomyyy.... Anatomy is very important!! Median Nerve 1. Motor Flexor compartment of the forearm: -Flexor pollicis longus (Flex the thumb) -Flexor digitorum profundus(Index finger: Flex index finger)(DIP joint) -Flexor digitorum superficialis(PIP joint) -Flexor Carpi Radialis (Flexion of the wrist: make a fist, flex wrist and resist at the radial side) Hand -L: 1st and 2nd lumbricals -O: opponent Pollucis -A: Abductor Pollucis brevis -F: Flexor Pollicis brevis 2. Sensory -Lateral 3 fingers -Thenar muscle LOOK -Wasting: thenar (both hands at the eye level) / Radial side of arm - Scars -Benedict sign: finger pointing -Ape hand deformity -Deformity FEEL -Feel for all the muscle bulk involved -If there are scars present: check for tenderness over the scar
MOVE 1. Motor -Flexion(flexion of wrist at radial side) -Opposition (Do Ok sign)(lawan OK sign dgn patient) -abduction (ask the patient to point his thumb towards the nose then resist) * if all 3 have problems : Median nerve Palsy ( to answer what nerve involve) 2. Sensory (must use sharp orange stick) - Lateral 3 of fingers (First test on chest for the sharpness, then test on both thumb, and test on lateral and medial of 3 fingers: ask for any reduce sensation) * if reduced confirmed median nerve palsy. -Then proceed with checking for sensation over the thenar( still need to proceed as if sensory on thenar still intact, the lesion is after the branches5 cm above wrist joint:palmar cutaneous branch-superficial to flexor retinaculum)Carpal tunnel - sensation here intact #if FDP & FDS are paralyzed: High lesion (elbow) Ape-like hand: thenar muscle paralysed. Thus, lack ability to oppose and abduct. Special test for carpal tunnel synd: Tinels sign- tap carpal bone(pin and needle-positive sign), Phalens test-(numbness-positive sign) put dorsal of hands together for 1 minute , flexion compression test-flex the wrist joint and compress median nerve at carpal bones for 30 seconds 30 second- median nerve 1-muscle wasting thenar 2-muscle wasting radial forearm(spared if lower lesion) 3-lawan OK sign 4-lawan thumb abduction 5-lawan flexion of DIP joint on index finger(spared if lower lesion)
6-lawan wrist flexion on radial side(spared if lower lesion) 7-sensation 3 jari 8-sensation thenar(spared if carpal tunnel)
ULNAR NERVE 1. Motor -Flexor Carpi Ulnaris : flex the hand at the wrist (ulnar side) -Ulnar of Flexor digitorum Profundus : flexes the fingers -Hands: Hypothenar/ 3th and 4th lumbricals (flex MCP and extend IP)/Adductor pollicis/Interrosei muscle 2. Sensory -ulnar 1 of the fingers -Dorsal of the hand over the ulnar side
LOOK -wasting of hypothenar, -guttering over the dorsal and ulnar half of the forearm (feel the muscle bulk) - scar -Clawing of the ring and little fingers. FEEL -Muscle bulk of nerve innervations -If scars or deformity present, palpate for tenderness MOVE 1. Motor -Interroseous muscle : PAD (card test) and DAB -Adductor pollicis : Froment test: put both palm of the hands together, and MUST test both sides together.(positive sign-patient flex IP joint of thumb on the affected hand) -Flexor digitorum Profundus: Flex distal phalanx of little finger
-FCU: Flex the wrist at ulnar side *if it is intact:Low lesion (at the wrist:wrist laceration), but if FCU and medial half of FDP affected it is a high lesion (at the elbow-medial epicondyle) . 2.Sensory : -same technique with median nerve , but over the ulnar 1 of the fingers, hypothenar ). - ulnar side dorsal aspect Ulnar Claw: Hyperextension of MCP joint of little and ring fingers due to paralysis of 3rd and 4rd lumbricals .Flexion of DIP and PIP by FDP Ulnar Paradox: the higher the lesion the less claw is. -why: if in high lesion, the flexor digitorum profundus will be paralysed. Guyon canal sydrome: entrapment of ulnar nerve at guyon canal Guyon canal: between flexor retinaculum and palmar carpal ligament Cubital tunnel syndrome: entrapment ulnar nerve at cubital fossa. 30 saat - Ulnar nerve 1-muscle wasting hypothenar 2-guttering 3-muscle wasting ulnar forearm 4-card test 5-froments test 6-5th DIP joint flexion (spared in lower lesion) 7-wrist flexion on ulnar side (spared in lower lesion) 8-sensation ulnar 1 9-sensation at dorsal ulnar side special test ulnar nerve- tinels sign and nerve compression at: 1- carpal bone on the ulnar side 2-behind medial epicondyle of humerus
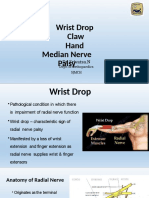
RADIAL NERVE 1.Motor -Triceps -Brachioradialis -Supinator -Extensor pollicis longus -Abductor pollicis longus -Extensor pollicis brevis -Extensor carpi radialis -Extensor carpi ulnaris -Extensor digitorum/digiti minimi/ 2.Sensory -First web space of dorsal part
LOOK -scars -no muscle wasting -Observe for wrist drop (deformity) FEEL -Triceps and extensors wasting MOVE 1.Motor -Ask the patient to extend the wrist -Check for finger drop (ask the pt to flex the wrist n extend the fingers) -Thumb extension against resistance If involved PIN: able to extend the wrist weakly(radial deviation-ECRL supply by radial N before become PIN) with finger drop. If all drop (wrist and finger) :proceed to check for elbow extension Finger drop: low lesion Wrist drop: high lesion Saturday night palsy: higher palsy
2.Sensation -At first web space If intact: lower lesion 30 second radial nerve: 1-muscle wasting triceps 2-thumb extention 3-finger extention 4-wrist extension (spared if lower lesion-with radial deviation) 5-elbow extension (spared if lower lesion) 6-sensation 1st dorsal web space(spared if lower lesion)
You might also like
- Peripheral Nerve Examination (Final)Document2 pagesPeripheral Nerve Examination (Final)Nurul Amalina OsmanNo ratings yet
- Wrist Anatomy: Bones Quiz - What Bones Comprise The Wrist? Joints Quiz - What Joints Comprise The Wrist?Document63 pagesWrist Anatomy: Bones Quiz - What Bones Comprise The Wrist? Joints Quiz - What Joints Comprise The Wrist?Mnn SaabNo ratings yet
- Claw Hand, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandClaw Hand, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Ankle and Foot Examination PDFDocument16 pagesAnkle and Foot Examination PDFainizatiNo ratings yet
- Traumatology Orthopaedic EXAMDocument219 pagesTraumatology Orthopaedic EXAMElo GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Ankle Examination Orthopaedics McraeDocument6 pagesAnkle Examination Orthopaedics McraeHafizah HoshniNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Imaging: A Practical Approach: Adam Greenspan 6th EditionDocument11 pagesOrthopedic Imaging: A Practical Approach: Adam Greenspan 6th EditionNovien WilindaNo ratings yet
- Hip ExaminationDocument84 pagesHip ExaminationDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Elbow Anatomy & Biomechanics - Shoulder & Elbow - OrthobulletsDocument10 pagesElbow Anatomy & Biomechanics - Shoulder & Elbow - OrthobulletsShashank VermaNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Exam Notes Apu PDFDocument6 pagesOrthopedic Exam Notes Apu PDFabiramirajalaksmiNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic examination techniques and common conditionsDocument226 pagesOrthopedic examination techniques and common conditionsMandisa Ndlovu Tenego0% (1)
- Osce Grand RoundDocument32 pagesOsce Grand Rounddoos1No ratings yet
- Perthes Disease: A Rare Childhood Hip ConditionDocument4 pagesPerthes Disease: A Rare Childhood Hip ConditionMohamed HamoodNo ratings yet
- SCOLIOSISDocument19 pagesSCOLIOSISEspers BluesNo ratings yet
- Shoulder DislocationDocument29 pagesShoulder DislocationAndaleeb ZehraNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Surgery Fractures and Dislocations: Tomas Kurakovas MF LL Group 29Document13 pagesOrthopaedic Surgery Fractures and Dislocations: Tomas Kurakovas MF LL Group 29Tomas Kurakovas100% (1)
- Ficat and Arlet staging of hip AVNDocument6 pagesFicat and Arlet staging of hip AVNFernando Sugiarto0% (1)
- Approach To FractureDocument17 pagesApproach To FractureRebecca WongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3e Pathological GaitDocument8 pagesChapter 3e Pathological GaitpodmmgfNo ratings yet
- Common CasesDocument44 pagesCommon CasesRebecca WongNo ratings yet
- Paediatrics OrthopaedicsDocument5 pagesPaediatrics OrthopaedicsGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Exam Guide: Inspection, Palpation, ROM, Neurovascular, Special TestsDocument12 pagesShoulder Exam Guide: Inspection, Palpation, ROM, Neurovascular, Special Testsckyew64No ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Examination GuideDocument60 pagesOrthopaedic Examination Guideanand100% (2)
- Ankle Arthrodesis - Screw FixationDocument26 pagesAnkle Arthrodesis - Screw FixationChristopher HoodNo ratings yet
- Gpe - 017.1 - Orthopaedic ExaminationDocument3 pagesGpe - 017.1 - Orthopaedic ExaminationImiey Eleena HanumNo ratings yet
- Upper Extremity FracturesDocument80 pagesUpper Extremity FracturesSidan EmozieNo ratings yet
- Principles of Tendon Transfer in The Hand and ForearmDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Tendon Transfer in The Hand and Forearm'Ema Surya PertiwiNo ratings yet
- DR - O. K. A. SamuelsDocument76 pagesDR - O. K. A. Samuelsgdudex118811No ratings yet
- 1.26 (Surgery) Orthopedic Pathology - OncologyDocument7 pages1.26 (Surgery) Orthopedic Pathology - OncologyLeo Mari Go LimNo ratings yet
- Orthopedics Notes NeetpgDocument4 pagesOrthopedics Notes NeetpgGIST (Gujarat Institute of Science & Technology)No ratings yet
- Thoracolumbar Spine Trauma Classification and ManagementDocument29 pagesThoracolumbar Spine Trauma Classification and ManagementFernaldi Anggadha100% (1)
- Skeletal System GuideDocument11 pagesSkeletal System GuideEllaDelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic EssaysDocument139 pagesOrthopaedic EssaysDuncan Jackson100% (1)
- Dr. Sunil Kumar Sharma Senior Resident, Dept. of Neurology G.M.C., KOTADocument67 pagesDr. Sunil Kumar Sharma Senior Resident, Dept. of Neurology G.M.C., KOTAsuckeydluffyNo ratings yet
- Why Every Spine Fusion Can Be A Deformity?Document88 pagesWhy Every Spine Fusion Can Be A Deformity?PaulMcAfeeNo ratings yet
- Examination of Hand & Common Hand InjuriesDocument165 pagesExamination of Hand & Common Hand InjuriesPriya GK100% (1)
- Kamars RadiologyDocument135 pagesKamars RadiologyNayantara Nair100% (1)
- IvdpDocument89 pagesIvdpFelix SabuNo ratings yet
- Tendon TransferDocument1 pageTendon TransferPandi Smart VjNo ratings yet
- Basic Science OITE ReviewDocument91 pagesBasic Science OITE ReviewICH KhuyNo ratings yet
- Spine ExaminationDocument46 pagesSpine ExaminationRatish Mishra100% (1)
- How To Examine The Wrist and HandDocument7 pagesHow To Examine The Wrist and HandSurgicalgownNo ratings yet
- AAOS Orthopaedic Knowledge Update 8Document763 pagesAAOS Orthopaedic Knowledge Update 8Hiohi LianaNo ratings yet
- The Talonavicular and Subtalar Joints The Calcaneopedal Unit ConceptDocument11 pagesThe Talonavicular and Subtalar Joints The Calcaneopedal Unit ConceptAnonymous kdBDppigENo ratings yet
- Fractures of Spine and Pelvis2007Document70 pagesFractures of Spine and Pelvis2007api-19916399No ratings yet
- Spine Examination: Mario Johan Heryputra 11.2012.208Document29 pagesSpine Examination: Mario Johan Heryputra 11.2012.208Mario Johan Heryputra100% (1)
- Orthopedic History Taking: DR - Kholoud Al-ZainDocument30 pagesOrthopedic History Taking: DR - Kholoud Al-ZainKaizar EnnisNo ratings yet
- Proximal Femoral NewDocument34 pagesProximal Femoral NewHimanshu HemantNo ratings yet
- Alingment in TKRDocument3 pagesAlingment in TKRdeepak100% (1)
- Ortopedic TestsDocument4 pagesOrtopedic TestsdocfinNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Dislocation DraftDocument26 pagesShoulder Dislocation Drafthusnajihah18No ratings yet
- Ankle Foot OrthosisDocument4 pagesAnkle Foot Orthosis楊畯凱No ratings yet
- Orthopath Final ReviewDocument16 pagesOrthopath Final ReviewharrischoeNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic InfectionsDocument6 pagesOrthopaedic InfectionsSurgicalgownNo ratings yet
- Queens Orthopedic Inpatient Trauma PDFDocument27 pagesQueens Orthopedic Inpatient Trauma PDFRema AmerNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Management in Cerebral Palsy, 2nd EditionFrom EverandOrthopaedic Management in Cerebral Palsy, 2nd EditionHelen Meeks HorstmannRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Current Challenges with their Evolving Solutions in Surgical Practice in West Africa: A ReaderFrom EverandCurrent Challenges with their Evolving Solutions in Surgical Practice in West Africa: A ReaderNo ratings yet
- Avascular Necrosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAvascular Necrosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Tendon Transfers For Radial, Median, and Ulnar Nerve Palsy: Review ArticleDocument10 pagesTendon Transfers For Radial, Median, and Ulnar Nerve Palsy: Review ArticleDavidBeatonComuladaNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Tendon TransfersDocument12 pagesGeneral Principles of Tendon TransfersHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Paid Orthobullet MCQs - HandDocument130 pagesPaid Orthobullet MCQs - HandShiKid COMIX-GAMENo ratings yet
- Atlas of Human Anatomy: Prof. Dr. Med. Petra Köpf-Maier, BerlinDocument14 pagesAtlas of Human Anatomy: Prof. Dr. Med. Petra Köpf-Maier, BerlinEspoire LibertéNo ratings yet
- Examining Peripheral NervesDocument6 pagesExamining Peripheral NervesNur Atiqah ZainalNo ratings yet
- 1-Acute Osteomyelitis Is Commonly Caused By:: A. Staph Aureus. B. S. Pyogenes. C. H. Influenzae. D. SalmonellaDocument41 pages1-Acute Osteomyelitis Is Commonly Caused By:: A. Staph Aureus. B. S. Pyogenes. C. H. Influenzae. D. Salmonellaملك عيسىNo ratings yet
- Pre and Post Operative Physiotherapy Management in Tendon Transfer of HandDocument59 pagesPre and Post Operative Physiotherapy Management in Tendon Transfer of HandjothiNo ratings yet
- Tendon Transfers: by DR Krishna BhattDocument89 pagesTendon Transfers: by DR Krishna Bhattvenkata ramakrishnaiahNo ratings yet
- Claw HandDocument16 pagesClaw HandArum MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Hand SurgeryDocument566 pagesAtlas of Hand SurgeryCostea Hincu100% (2)
- Correction of The Claw HandDocument14 pagesCorrection of The Claw HandAbdelhakim MareiNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve Injury in Upper LimbDocument29 pagesPeripheral Nerve Injury in Upper Limbvenkata ramakrishnaiahNo ratings yet
- Wrist Drop Claw Hand Median Nerve Palsy: Dr. Srivatsa.NDocument46 pagesWrist Drop Claw Hand Median Nerve Palsy: Dr. Srivatsa.NMurali KarthikkNo ratings yet
- Tendon TransferDocument6 pagesTendon TransferMd Ahsanuzzaman PinkuNo ratings yet