Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vnxe VP Operations
Uploaded by
Prakash Lakhera0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views33 pages.
Original Title
vnxe VP Operations
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views33 pagesVnxe VP Operations
Uploaded by
Prakash Lakhera.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 33
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation.
All rights reserved
Upon completion of this module, you should be able to:
Implement Virtual Provisioning
Create Thin and Data Devices
Create Thin Pools
Add Data Devices to Thin Pools
Bind Thin Devices to Thin Pools
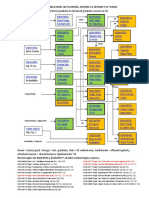
1 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
Upon completion of this lesson, you should be able to:
Implement Virtual Provisioning with SMC
Create Thin and Data Devices
Create Thin Pools
Add Data Devices to Thin Pools
Bind Thin Devices to Thin Pools
Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations 2
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
Like all aspects of storage configuration, the first step is planning. However, with Thin
Devices less planning is required. Users dont have to think about back-end layout and there
is minimal efficiency impact of over-estimating the required capacity.
Later in this module, a review of configuring Thin Devices, Data Devices, and Thin Pools using
SMC and Solutions Enabler is shown. Once the Thin Devices are configured, they can be
mapped, masked, and used like any other device.
Symmetrix VMAXe arrays are pre-configured with Thin Pools and Data Devices, so steps 2-4
would not need to be performed. Instead one would simply create Thin Devices and then
bind them to the appropriate Thin Pool and then mask the same to a host for use. However
for the sake of completeness we will cover the creation of Data Devices and Thin pools in this
module.
3 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
Let us take a look at creating Symmetrix Devices using SMC. Right-click on a Symmetrix,
choose Device Configuration and then Create Device to launch the dialog Device
Configuration - Create Device dialog. On the Symmetrix VMAXe array the Create Device
dialog is used to create Gatekeeper, Thin, Data, and Save devices. Thin and Data devices are
used for Virtual Provisioning. On a VMAXe array the Save devices are used by SRDF/A Delta
Set Extension.
4 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
To create Thin Devices in SMC, Right-click on a Symmetrix, choose Device Configuration and
then Create Device to launch the Create Device dialog.
Click the Thin Device tab in the Create Device dialog and enter the number of devices, the
Configuration (TDEV in this example), the Emulation (FBA, CELERRA_FBA, etc.), Device
capacity in cylinders The drop down list will show you the existing devices sizes on the
Symmetrix.
The device creation dialog also has an option to bind the new Thin Devices to a Thin Pool and
to specify the pre-allocated capacity. In this example we will bind the devices to the SATA_R6
pool.
Please note that if the VMAXe array were setup for SRDFe one would have the option of
creating RDF1+TDEV or RDF2+TDEV devices as well. When create RDF devices the Device
Configuration interface will require adding additional configuration information as it relates
to the creation of RDF devices.
Click Add to Config Session List to add this configuration request to the Config Session view.
The Gatekeeper tab is used to create Gatekeeper devices.
5 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
Symmetrix VMAXe arrays are pre-configured with Data Devices. So typically one would not
have to create new Data Devices.
To create Data Devices in SMC, Right-click on a Symmetrix, choose Device Configuration and
then Create Device to launch the Create Device dialog.
Click the Data Device tab in the Device Configuration Create Device dialog and enter the
number of devices, the Configuration (2-Way Mir, RAID-5 or RAID-6), the Emulation (FBA
only), Device capacity in cylinders The drop down list will show you the existing devices
sizes on the Symmetrix.
Be sure to specify the Disk Group in which the new Data Devices will be created. If you do
not specify a disk group the Data Devices will be spread out over the available disk groups.
The device creation dialog also has an option to add the new Data Devices to a Thin Pool.
The device can also be Enabled (Disabled is the default) when added to the Thin Pool. After
the Data Device is added to the pool the pool can be automatically rebalanced.
Click on Add to Config Session List to add this configuration request to the Config Session
view.
If the VMAXe array were setup for SRDFe one would also see the Save Device tab. The Save
Device tab is used to create Save devices for use by SRDF/A DSE.
6 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
All Configuration tasks in SMC have to be committed by clicking the Commit All button in the
Config Session view.
In this example, 4 thin devices and 4 RAID 6 (6+2) data devices are being created.
The bottom part of the slide are excerpts of the Config Session log. In this example, we can
see that the creation of these devices took about two minutes.
7 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
Symmetrix VMAXe arrays are pre-configured with Thin Pools. So typically one would not have
to create new Thin Pools.
On a VMAXe array SMC can be used to create Thin Pools and SRDF/A DSE Pools. Right click
on a Symmetrix (or the Pools folder under a Symmetrix) and choose Device Pool
Management > Create Device Pool. This will launch the Device Pool Management Create
Device Pool dialog shown on the slide.
To create a Thin Pool, set the pool type to Thin and enter a name. For Thin Pools, the
maximum subscription limit can set.
Optionally, one can add Thin Devices to the pool and enable them. To add devices to the
pool, pick the devices from the Available column and click the Add button to move them the
Target column. The Available column will show Data Devices for Thin Pools. Only disabled
Data Devices will be shown.
The Rebalancing Variance and Maximum Rebalancing Scan Device Range can also be set. We
discussed these features in Module 2. We will discuss the Pool Reserve Capacity setting in
the FAST VP Modules.
8 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
One can create a Thin Pool via SMC with the technique shown on the previous slide.
Alternately one can use the Create Thin Pool Wizard which can be launched from the
Dashboard or the Tasks Page. The Wizard will create the Thin Pool and populate the same
with Data Devices. The wizard will try to use existing data devices which meet the criteria. If
devices do that meet the criteria are not available then the wizard will create the required
data devices and then populate the thin pool.
9 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
To Bind/Unbind Thin Devices to a device pool in SMC, right click on the Thin Pool and choose
Device Pool Management > Bind/Unbind Thin Devices.
All unbound Thin Devices will be listed in the Available column.
To bind a device, highlight it in the Available column and click the Add button to add it to the
Target column. The pre-allocated capacity for the device can also be specified (in Cylinders,
MB or GB). Pre-allocation reserves pool storage before it
is needed, it can be during the bind step or afterwards.
Pre-allocation can be persistent.
To unbind a device, highlight it in the Target column and click the Remove button. Like all the
other configuration tasks, click the Add to Config Session List button and then go to the
Config Session view to commit the task.
10 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
Upon completion of this lesson, you should be able to:
Implement Virtual Provisioning with SMC
Create Thin and Data Devices
Create Thin Pools
Add Data Devices to Thin Pools
Bind Thin Devices to Thin Pools
Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations 11
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
The output on this page is intended to show the Symmetrix VMAXe environment where the
VP operations are going to be performed. Symmetrix 000195900495 is used in the
examples.
The command displays the size of the existing Symmetrix thin devices in the cylinders.
Later in the module, when Thin Devices are created, they will be the same size as these,
which in this case is 1100.
12 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
The syntax related to creating Thin Devices is available in Chapter 1 of the Array Controls
Manual.
It is usually a good idea to use the prepare option in Config Manager to make sure that the
syntax for the command file is in order. Once the prepare is successful, the commit action
makes the necessary changes in the Symmetrix.
13 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
After configuring Thin Devices, they can be viewed using the symdev list command.
Note: that TDEVs are not ready to a host until bound to a Thin Pool.
Note: that DA:IT show NA in that no back-end resources are allocated to Thin Devices.
14 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
Before creating Data Devices we will take a look at a summary of the Disk Groups in this
Symmetrix Array.
We see that this array has SATA, 10K FC, 15K FC and EFD disks in four different disk groups.
We will create some data devices on the 15K FC Disk Group.
15 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
While the example here is for lab demonstration purposes, please remember the
recommendations for configuring Data Devices in production environments.
Data Devices in a pool should be the same size. They should be created on drives the same
size and speed. They should be spread widely across the back-end and should be as large as
practically possible. Please note that in this example we are showing the syntax for creating
RAID1 protected Data Devices. Data devices can also have RAID5 or RAID6 protection. In this
example the Data Devices will be created on Disk Group 3. Which is the 15K FC Disk Group as
seen on the previous slide.
16 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
After configuring Thin Devices, they can be viewed using the symdev list command.
Data Devices are private devices and are not directly visible to a host. Data Devices are
identified by the device type of DT. You can use the -nonpooled option to limit the list to
Data Devices that have not been added to a pool.
17 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
There is no default Thin Pool. Therefore, at least one user defined Thin Pool must be created
before Virtual Provisioning can be used.
All Data Devices in a Thin Pool must have the same emulation and protection type.
18 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
Add Data Devices to the pool and enable them.
19 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
The pool P1 that we had created is listed along with the other thin pools that were already
on the Symmetrix.
Pool P1 is identified as an enabled Thin Pool. The pool is enabled as soon as it contains one
enabled Data Device.
The track numbers reflect the size of two Data Devices, each 1100 cylinders in size. Since
each cylinder comprises of 15 tracks, the actual number is 1100*2*15 = 33000 tracks. At the
moment none of the tracks in Pool P1 are used. There are no thin devices bound to P1.
The Pool Type is T indicating that this is a Thin Pool. The Tech is F indicating that this is a FC
pool.
20 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
There are two options that can be used with the show command to display more information
about the pool. The all option shows information on enabled and disabled Data Devices,
while the detail option includes a listing of the Thin Devices.
21 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
If Thin Devices were to be bound to a pool at the time of creation, the syntax would read as
follows:
create dev count=4, size=1100,
emulation=FBA, config=TDEV,
binding to pool P1;
22 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
In the prior page we bound 4 TDEVs to the pool WB. As a result, one extent, or 12 tracks
were allocated to each TDEV. Also the TDEVs are now ready and available for Read Write
operations once they are mapped and masked to a host.
23 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
The detailed output of the Thin Pool is shown on the slide. The Thin Pool has two enabled
Data Devices.
This slide shows the top part of the output, the rest of the output is shown on the next slide.
24 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
The bottom part of the detailed output shows the correct percentage subscription of the
Thin Devices compared to the pool. Each Thin Device capacity is 16500 tracks, which means
that each TDEV, if filled to capacity would use up 50% of the available TDAT space.
4 Thin Devices filled to capacity would require 200% of the pool space as indicated in the
Subs % column.
25 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
As shown in the syntax for the bind command below, pre-allocation can be done at the
time of binding the Thin Devices to the pool. It is used to reserve storage space in a pool
before the space is actually required. This can be useful when we know in advance that the
device in question will require a certain amount of space.
create dev count=4, size=1100,
emulation=FBA, config=TDEV,
binding to pool P1, preallocate size=1100;
To use the persistent allocation method, add the allocate_type=persistent option to the
syntax.
26 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
The command output shows that additional space has been pre-allocated for the first two
TDEVs in the pool. Nothing has been written to the TDEVs yet.
27 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
The detailed listing of the pool information confirms the existence of the pre-allocated space
for the Data Devices.
This slide shows the top part of the output, the rest of the output is shown on the next slide.
28 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
The bottom part of the detailed listing of the pool information confirms the existence of the
pre-allocated space for the Thin Devices.
29 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
The process of mapping and masking the Thin Devices has not been shown here. We will
cover autoprovisioning in the module 5.
The procedure to map and mask Thin Devices in a VMAX array, is identical to that of regular
devices. After mapping and masking, a reboot (or bus scan) has to be performed in order to
make the devices host visible. Remember to run symcfg discover after the reboot so the new
pdevs are recognized by SYMCLI.
In the Solaris environment, format followed by newfs commands allow a file system to be
created on the Thin Device. The Thin Device is now ready for use.
30 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
As a result of creating a file system on one of the Thin Devices (TDEVs) on Solaris, an
additional (2488 1620) 868 tracks were allocated while 561 tracks (roughly 35 MB) were
written. The Symmetrix array uses a round-robin mechanism to balance the allocation of
extents across all the data devices in the pool that are enabled and that have remaining
unused capacity. In this example we only have two data devices and we that the number of
allocated tracks for each of the data devices is similar.
31 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
Key points covered in this module:
Virtual Provisioning implementation with SMC and SYMCLI
Creation of Thin and Data Devices
Creation of Thin Pools
Addition of Data Devices to Thin Pools
Binding Thin Devices to Thin Pools
32 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
Copyright 2012 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved
1. See slide 14
2. See slide 6, 8, 19
3. See slide 23
4. See slide 5, 10, 26
5. See slide 9
33 Module 3: Virtual Provisioning Operations
You might also like
- Multiprotocol Application Deployment Guide v0 2Document23 pagesMultiprotocol Application Deployment Guide v0 2Prakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- Hitachi Command Suite VSP Gx00 DiscoveryDocument2 pagesHitachi Command Suite VSP Gx00 DiscoveryPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- CIFSDocument44 pagesCIFSPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- VNX DP Power Up VNXDocument6 pagesVNX DP Power Up VNXPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- EMC Security Advisories All EMC Products Current YearDocument3 pagesEMC Security Advisories All EMC Products Current YearPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- VNX DP Upgrading Disk FirmwareDocument6 pagesVNX DP Upgrading Disk FirmwarePrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- VNX P Replace SP Io Module PDFDocument16 pagesVNX P Replace SP Io Module PDFPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- VNX DP Power Down VNXDocument8 pagesVNX DP Power Down VNXPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- VNX P Replace SP Io Module PDFDocument16 pagesVNX P Replace SP Io Module PDFPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- VNX P Replace SP Io Module PDFDocument16 pagesVNX P Replace SP Io Module PDFPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- Hardware Overview-VNX5300Document101 pagesHardware Overview-VNX5300Prakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Base Article: 000517728:: Dsa-2018-018: Dell Emc Isilon Onefs Multiple Vulnerabilities. (000517728)Document3 pagesKnowledge Base Article: 000517728:: Dsa-2018-018: Dell Emc Isilon Onefs Multiple Vulnerabilities. (000517728)Prakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- Brocade Product Training: Fibre Channel Topologies, Terminology and AddressingDocument34 pagesBrocade Product Training: Fibre Channel Topologies, Terminology and AddressingPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- VNXE VP Concept and Planning PDFDocument26 pagesVNXE VP Concept and Planning PDFPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- VMAX Autoprovisioning GroupsDocument44 pagesVMAX Autoprovisioning GroupsPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- Backup Exec 2010 Admin GuideDocument2,060 pagesBackup Exec 2010 Admin Guideafeesh100% (1)
- VMAX Meta Device Symmetrix and Device AttributesDocument52 pagesVMAX Meta Device Symmetrix and Device AttributesPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- VMAXE VP Miscellaneous OperationsDocument28 pagesVMAXE VP Miscellaneous OperationsPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- 300088313Document142 pages300088313Prakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- Brocade Product Training: Fibre Channel Layers and Related ComponentsDocument31 pagesBrocade Product Training: Fibre Channel Layers and Related ComponentsRamana EllamarajuNo ratings yet
- Vblock Systems Basics: Todd SimmonsDocument67 pagesVblock Systems Basics: Todd SimmonsPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- All About DASDDocument126 pagesAll About DASDPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- Information Storage and Management v2: Course DescriptionDocument4 pagesInformation Storage and Management v2: Course DescriptionPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- SANHQ v2 1 FixlistDocument3 pagesSANHQ v2 1 FixlistPrakash LakheraNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Inside ARESDocument338 pagesInside ARESAmit GaragNo ratings yet
- Introduction to SIWES and KAEDCODocument13 pagesIntroduction to SIWES and KAEDCOSamuel Geoffry100% (1)
- Computing Basics Course Covers Everyday Computer UsesDocument33 pagesComputing Basics Course Covers Everyday Computer UsesElias ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Installation DBox enDocument6 pagesInstallation DBox enNuno Pires100% (1)
- MS1500L LPR Data Logger: Metal Samples CompanyDocument68 pagesMS1500L LPR Data Logger: Metal Samples CompanyfornowisNo ratings yet
- TL sf1024Document2 pagesTL sf1024birkzoNo ratings yet
- Thanks For Downloading OperaDocument2 pagesThanks For Downloading OperaAlexis KarampasNo ratings yet
- Emergency Access ManagementDocument5 pagesEmergency Access ManagementPabitraKumarNo ratings yet
- Android TSC Bluetooth/Ethernet library functionsDocument9 pagesAndroid TSC Bluetooth/Ethernet library functionsomar2022No ratings yet
- Brickstream3D Gen2 Datasheet USDocument2 pagesBrickstream3D Gen2 Datasheet USMr. WhiteNo ratings yet
- Alcatel 3G ModemDocument15 pagesAlcatel 3G ModembunaciuneNo ratings yet
- Adint Install (Maxdb)Document20 pagesAdint Install (Maxdb)ELITEKRISHNo ratings yet
- Autoload ClassmapDocument179 pagesAutoload ClassmaprodrigoNo ratings yet
- Recent Topics For ELEN E6713, ELEN E677, & Other Related Topics CoursesDocument1 pageRecent Topics For ELEN E6713, ELEN E677, & Other Related Topics CoursesMangaka DomingosNo ratings yet
- Important: Read First: Release Notes For PRO/II 8.3Document46 pagesImportant: Read First: Release Notes For PRO/II 8.3tinhtinh8204No ratings yet
- GeneTouchMonitor User Guide-2.3Document28 pagesGeneTouchMonitor User Guide-2.3Gas2shackNo ratings yet
- John Cage Prepared Piano: Instruments and InstructionsDocument2 pagesJohn Cage Prepared Piano: Instruments and InstructionstreseisNo ratings yet
- IPcam Webcam Safire WiFi ENDocument31 pagesIPcam Webcam Safire WiFi ENrruuddiiaannttooNo ratings yet
- Edi CockpitDocument2 pagesEdi CockpitLawrence KartodimedjoNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts Catalog: 45E680X1UK-01Document46 pagesSpare Parts Catalog: 45E680X1UK-01Mitica ScurtuNo ratings yet
- Cirrus Perspective Database UpdatesDocument47 pagesCirrus Perspective Database UpdatesJoao AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Honeywell 6150 Honeywell 6160 Install GuideDocument2 pagesHoneywell 6150 Honeywell 6160 Install GuideAlarm Grid Home Security and Alarm Monitoring0% (1)
- E 24256Document226 pagesE 24256yasirhussain86No ratings yet
- Nero Burning ROM v7.2.0.3 Regged Crack ReleaseDocument1 pageNero Burning ROM v7.2.0.3 Regged Crack ReleaseRegina FernandesNo ratings yet
- Extra Exercise Chapter 4 Cache MemoryDocument11 pagesExtra Exercise Chapter 4 Cache MemorySundari MuthuNo ratings yet
- ENSC 351 software installation guideDocument9 pagesENSC 351 software installation guidea bNo ratings yet
- Memjet C6010 Windows UserGuideDocument107 pagesMemjet C6010 Windows UserGuiderendangenakNo ratings yet
- INSPECT STATEMENT VERBSDocument23 pagesINSPECT STATEMENT VERBSJayanthudu SaiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Road DesignDocument8 pagesAdvanced Road DesignZul FadhliNo ratings yet
- Ways To Write To Text FilesDocument13 pagesWays To Write To Text FilesPankaj Pratap SinghNo ratings yet