Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Corporate Finance Pset 1
Uploaded by
zach12345Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Corporate Finance Pset 1
Uploaded by
zach12345Copyright:
Available Formats
Zach Savidge
Problem Set #1: Corporate Finance
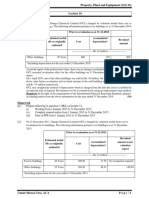
Problem 1
a. 180,000
b. $1.4/per share
c. EBITDA = Net income + Interest + taxes + depreciation & amortization
EBITDA = 140,000 + 0 + 60,000 + 40,000 = 240,000
EBITDA = $240,000
EBITDA is an accrual accounting proxy for cash flow to the firm. It is useful because
it is independent of capital structure and non-cash charges, hence allowing for a
better comparison of operating profitability across firms.
d. The company did not pay out dividends. Dividends would be represented as a
cash outflow in cash from financing activities. Since the cash flow statement shows
there was no net cash flow from financing, dividends could only have been paid if
there was an equal and offsetting inflow from activities classified as cash flow from
financing activities. Since no debt is present on the balance sheet and the question
stipulates that no equity was issued, there were no cash inflows from financing
activities. Hence, the company did not pay out dividends.
e.
Problem 2
a.
Balance Sheet
Assets
Liabilities
Cash
$210,000.00 Paid In Capital
$200,000.00
Inventory $60,000.00 Retained Earnings
$430,000.00
Net PP&E
$360,000.00 Shareholder's Equity
$630,000.00
Total
Assets
$630,000.00 Total Liabilities & Shareholder's Equity
$630,000.00
Income Statement
Sales $600,000.00
COGS $(360,000.00)
Gross Profit $240,000.00
D&A $(40,000.00)
Operating Profit $200,000.00
Loss on Disposal of Assets $(100,000.00)
Pretax Income $100,000.00
Income Tax Expense $(30,000.00)
Net Income $70,000.00
Cash Flow Statement
Operating Activities
Net Income $70,000.00
D&A $40,000.00
Loss on Disposal of Asset $100,000.00
Cash from Operating Activities $210,000.00
Cash from Investing Activities $0
Cash from Financing Activites $0
Change in Cash $210,000.00
b. The companys net income declines by $70,000. This is because the mark-down of
the asset from $100,000 to $0 shows up on the income statement as a loss on
disposal of assets, decreasing pretax income by $100,000. A lower pre-tax income
also incurs a lower tax expense, however. The tax expense declines by $30,000
($100,000 x 30% corporate tax rate). Hence the overall change to net income is
-100,000 + 30,000 = -70,000
c. The companys cash flow increases by $30,000. This is because the write-off of the
asset is a non-cash expense but leads to decline in cash taxes paid. Hence the
companys cash flow from operating activities increases by $30,000 less in taxes
paid.
d. The both the companys assets and liabilities decline by $70,000. On the assets
side, Net PP&E declines by $100,000 due to the write off but cash increases by
$30,000 due to the reduced cash taxes paid. On the liabilities side, retained earnings
declines by $70,000 due to the decline in net income.
Problem 3
a.
According to the VC predictions, the firm will be worth 20 *$10million = $200
million in 5 years.
The VC is targeting a 50% IRR on their $5 million investment, hence they need their
investment in the firm to be worth
million in 5 years.
Therefore the VC will request
of orange bubble.
b. By paying $5 million for 18.98% of the company, the VC valued the firm at
Hence the value of the entrepreneurs stake is ( )
You might also like
- DB Levered Finance Conference: Goodyear Tire PresentationDocument40 pagesDB Levered Finance Conference: Goodyear Tire Presentationzach12345No ratings yet
- Keybank Auto Conference: Goodyear Tire PresentationDocument33 pagesKeybank Auto Conference: Goodyear Tire Presentationzach12345No ratings yet
- Goodyear Tire Q22014 Earning PresentationDocument27 pagesGoodyear Tire Q22014 Earning Presentationzach12345No ratings yet
- Swedish Match CaseDocument6 pagesSwedish Match Casezach12345100% (8)
- Problem Set #1Document3 pagesProblem Set #1zach12345No ratings yet
- Galaxy AlertDocument1 pageGalaxy Alertzach12345No ratings yet
- Conversations in SicilyDocument2 pagesConversations in Sicilyzach12345No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Customer Satisfaction Analysis For A Service Industry of Al-Arafah Islami Bank LimitedDocument25 pagesCustomer Satisfaction Analysis For A Service Industry of Al-Arafah Islami Bank LimitedOmor FarukNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Supply Chain Management On BIDocument12 pagesThe Impact of Supply Chain Management On BIC LeongNo ratings yet
- SAP RE-FX-LA: Navigating New Lease Accounting StandardsDocument16 pagesSAP RE-FX-LA: Navigating New Lease Accounting Standardsanil kumarNo ratings yet
- Employee Satisfaction Case StudyDocument2 pagesEmployee Satisfaction Case StudyMANAN SONEJINo ratings yet
- Aaron Forbes Zachary JohnDocument39 pagesAaron Forbes Zachary JohnAaron ForbesNo ratings yet
- An Industry Overview Is A Document Providing Some Basic Information About An Industry of InterestDocument2 pagesAn Industry Overview Is A Document Providing Some Basic Information About An Industry of InterestLidia Oktarina ChaniagoNo ratings yet
- Report FinalDocument48 pagesReport FinalSantosh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- How To Start A Startup - The Silicon Valley Playbook For Entrepreneurs (PDFDrive)Document307 pagesHow To Start A Startup - The Silicon Valley Playbook For Entrepreneurs (PDFDrive)Hira100% (2)
- Starbucks Teaching Model Using Training Within IndustryDocument17 pagesStarbucks Teaching Model Using Training Within IndustryHowardArzNo ratings yet
- Buying Merchandise: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin Retailing Management, 7/E © 2008 by The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, All Rights ReservedDocument46 pagesBuying Merchandise: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin Retailing Management, 7/E © 2008 by The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, All Rights ReservedTaqdees Shaikh PawaskarNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Financial Management 16th Edition Block Test Bank 1Document27 pagesFoundations of Financial Management 16th Edition Block Test Bank 1john100% (33)
- 52.204-8 Annual Representations and Certifications (Mar 2020)Document6 pages52.204-8 Annual Representations and Certifications (Mar 2020)niraj sainiNo ratings yet
- 1Q BM 3rd Module A.Y. 2021 - 2022Document20 pages1Q BM 3rd Module A.Y. 2021 - 2022Jewel RamosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16Document2 pagesLecture 16Ali OptimisticNo ratings yet
- Extending the Product Life Cycle with Strategic Marketing Mix ChangesDocument6 pagesExtending the Product Life Cycle with Strategic Marketing Mix Changeskashif AliNo ratings yet
- Suzlon Energy: Previous YearsDocument15 pagesSuzlon Energy: Previous YearsSorav SharmaNo ratings yet
- CA Inter FM Super 50 Q by Sanjay Saraf SirDocument129 pagesCA Inter FM Super 50 Q by Sanjay Saraf SirSaroj AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Tax Law IIDocument14 pagesTax Law IIshreya ahujaNo ratings yet
- Jiblr 2005 20 10 535-540Document6 pagesJiblr 2005 20 10 535-540Santanu RoyNo ratings yet
- Law of Contract - Topic 2 Formation of ContractDocument101 pagesLaw of Contract - Topic 2 Formation of Contractnemynemo620No ratings yet
- Cebu EASY General Services Corp.: Leave / Undertime FormDocument2 pagesCebu EASY General Services Corp.: Leave / Undertime FormGrezil Ann Batiancela SabordoNo ratings yet
- Demand (Units) Selling Price Per Unit ($) Cost Per UnitDocument5 pagesDemand (Units) Selling Price Per Unit ($) Cost Per UnitMichael ComunelloNo ratings yet
- Call conferencedel23/09/2019Al ArafahIslami Bank Limited–BANGLADESHDocument9 pagesCall conferencedel23/09/2019Al ArafahIslami Bank Limited–BANGLADESHMd. Helal UddinNo ratings yet
- Subcontracting ProcessDocument11 pagesSubcontracting ProcessRaja100% (1)
- Management vs Leadership; Innovation and Talent Unleash SuccessDocument1 pageManagement vs Leadership; Innovation and Talent Unleash SuccessPraveen UnpluggedNo ratings yet
- Basic Financial Accounting and Reporting: Ishmael Y. Reyes, CPADocument32 pagesBasic Financial Accounting and Reporting: Ishmael Y. Reyes, CPAMicaela EncinasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 For StudentDocument33 pagesChapter 8 For StudentKhánh Đoan NgôNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document6 pagesProblem Set 1Sudisha DasNo ratings yet
- OSP-QF-007 Organizational Chart SAS 2Document1 pageOSP-QF-007 Organizational Chart SAS 2marloncruiseNo ratings yet
- Ayesha Srivastava Erm Graded ProjectDocument7 pagesAyesha Srivastava Erm Graded ProjectAnirudha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet