Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sem 2 Uppp 2014 - 1
Uploaded by
Teoh Ah NgohOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sem 2 Uppp 2014 - 1
Uploaded by
Teoh Ah NgohCopyright:
Available Formats
2
Section A [15 marks]
Four suggested answers labelled A, B, C and D are given for each question in this section. Choose one
correct answer, and write it in the space provided at Page 6
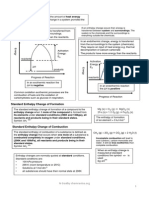
1. Which one of the following equations is correctly associated with the definition of enthalpy change of
formation of carbon monoxide?
A +
C +
2
B + D +
2. Standard combustion enthalpies for 1,2-ethanediol (HOCH
2
CH
2
OH), carbon and hydrogen are
1180.0 kJ mol
1
, 393.7 kJ mol
1
and 285.9 kJ mol
1
respectively. What is the standard formation
enthalpy, in kJ mol
1
, for 1, 2-ethanediol?
A 500.4 C +465.1
B 465.1 D +500.4
3. The lattice energy of sodium chloride is -766 kJ mol
-1
. If the enthalpy of hydration of Na
+
and Cl
-
is
390 and 381 kJ mol
-1
, what is the enthalpy of solution of sodium chloride?
A +5
B 0
C -5
D +766
4. In which of the following reactions does the oxidation number of nitrogen changes from +5 to +1?
A 3 +8
+2
2 +4
+3
B 3 +
+3
C 3 +12
+6
+6
+3
D 3 +
+3
5. The electrode potential of two half-cells are given below:
E = +0.76 V
E = +0.36 V
Which of the following statement is correct with regards to the cells above?
A
is more stable than Fe
2+
(aq)
B
is more stable than Fe
3+
(aq)
C
is a stronger oxidising agent than Fe
3+
(aq)
D
is a stronger reducing agent than Fe
2+
(aq)
3
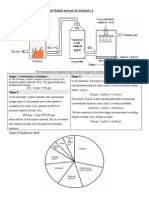
6. Consider the fuel cell below:
Using the following data, determine the e.m.f of the cell.
+2
+2
+4
E = -1.22 V
+2
+4
E = +0.40 V
A - 0.82 V
B - 1.62 V
C + 0.82 V
D +1.62 V
7. Electrolysis is used in effluent treatment. Which of the following groups of ions can be eliminated by
this process?
A Sc
3+
, Cr
3+
, Fe
2+
B Na
+
, Al
3+
, Pb
2+
C Pb
2+
, Cr
3+
, Ni
2+
D Ni
2+
, Cd
2+
, Cr
3+
8. The first ionisation energies of some elements in the Periodic Table are represented in the graph below.
Which statements about this graph are true?
I Element S is in Group 1 of the Periodic Table.
II Atoms of elements Q and U contain two electrons in their valence shells.
III Atoms of element R contain half-filled p orbitals.
IV Element T is a non-conductor.
A I and II only C II and III only
B I and IV only D III and IV only
4
9. Ar, K
+
and Cl
-
are isoelectronic. What is the correct order of increasing size for their radii?
A Ar < Cl
-
< K
+
B K
+
< Ar < Cl
-
C Cl
-
< K
+
< Ar
D K
+
< Cl
-
< Ar
10. Beryllium is the first element in Group 2 of the Periodic Table. By considering the properties of the
Group 2 elements, which statements about beryllium are true?
I Beryllium can form compounds with covalent character.
II The enthalpy change of hydration of Be
2+
is the most exothermic.
III The thermal decomposition temperature of BeCO
3
is the highest.
IV Beryllium sulphate is insoluble in water.
A I and II only
B II and III only
C II and IV only
D III and IV only
11. Which of the following uses of the compounds of Group 2 elements do not correspond?
Compound Use
A Magnesium oxide As refractory bricks in blast furnace
B Magnesium chloride A laxative
C Calcium sulphate As Plaster of Paris
D Barium Sulphate White pigment in paints
12. The diagram below shows part of the structure of a type of silicate.
Which statement is true about this structure?
A The tetrahedral units form a planar structure
B Each silicon atom is bonded tetrahedrally to four oxygen atoms
C The structure is found in the mineral amphibole
D Each tetrahedral unit shares three oxygen atoms
5
13. Aqueous silver nitrate is added to a solution containing I
-
ions. A precipitate, R, is formed. Concentrated
ammonia is then added to R. What is the colour of R and its solubility in concentrated ammonia?
Colour of R Solubility in NH
3
A White Soluble
B White Insoluble
C Yellow Soluble
D Yellow Insoluble
14. In black and white photography, the last step involves a process where the photographic strip is
immersed in an aqueous solution of sodium thiosulphate. What is the role of sodium thiosulphate in this
step?
A To add colour
B To reduce silver ions to silver atoms
C To remove unactivated silver bromide
D To oxidise the bromide ions to bromine atoms.
15. Which reagent when added in excess to an aqueous solution containing copper (II) ions will produce a
dark blue solution as the final product?
A Aqueous ammonia
B Aqueous potassium iodide
C Aqueous sodium hydroxide
D Aqueous potassium hexacyanoferrate(II)
6
MAKTAB SULTAN ABU BAKAR
UJIAN PENILAIAN PRA-PENTAKSIRAN SEM 2 2014
SUBJECT : CHEMISTRY
Name : ____________________________________ Tingkatan : UPPER 6 ____________
Section A
[15 marks]
1 6 11
2 7 12
3 8 13
4 9 14
5 10 15
Section B
[ 15 marks ]
Answer all questions in this section
16. All the period 3 elements (except chlorine and argon) burn in oxygen when heated to form their
respective oxides.
(a) Write the formula of all the oxides with the highest oxidation number. [2 marks]
......
......
......
(b) i. Write balanced equations to illustrate the acid/ base nature for aluminium oxide and silicon(IV)
oxide [3 marks]
......
......
......
......
ii. Explain in terms of bonding why aluminium oxide shows the properties as suggested in (b)(ii)
[2 marks ]
......
......
......
7
17. (a) In the presence of platinum catalyst, NH
3
would burn to produce nitric oxide, NO.
4NH
3
(g) + 5O
2
(g) 4NO (g) + 6H
2
O (g)
Determine the heat of reaction using the following thermochemical equations:
N
2
(g) + O
2
(g) 2NO(g) H
1
= 180.6 kJ
N
2
(g) + 3H
2
(g) 2NH
3
(g) H
2
= -91.8 kJ
2H
2
(g) + O
2
(g) 2H
2
O(g) H
3
= -483.7 kJ [2 marks]
(b) Construct the Born- Haber cycle for the formation of magnesium fluoride by using the data given
below. [6 marks]
Enthalpy of atomisation of magnesium +148 kJmol
-1
Enthalpy of atomisation of fluorine +159 kJmol
-1
First ionisation energy of magnesium +738 kJmol
-1
Second ionisation energy of magnesium +1450 kJmol
-1
Electron affinity of fluorine -328 kJmol
-1
Standard enthalpy of formation of magnesium fluoride -1123 kJmol
-1
8
SECTION C
[30 marks]
Answer any two questions below
18. (a) The electromotive force, E
0
cell
for the following cell is +0.80V.
Pt(s) I H
2
(g, 1atm) / H
+
(aq,1M) II Ag
+
(aq, 1M) I Ag (s)
i. Draw a labelled diagram of the cell. Indicate the direction of flows of electrons in your diagram.
[3 marks]
ii. Determine the standarad reduction (redox) potential of silver. [2 marks]
iii. Given the Nernst equation is
Q lg
n
059 . 0
E E
0
+ =
where Q is the reaction quotients
If the acid in the above cell is replaced by hydrochloric acid, the electromotive force of the cell is
+1.20 V at 25
0
C and 1.0 atm. Determine the concentration and the pH of the hydrochloric acid used.
[4 marks]
(b) i. What do you understand by the term anodisation of aluminium ? [1 mark]
ii. The thickness of the oxide layer of an aluminium object of total surface area 2500 cm
2
is to be
increased by 0.005cm. Calculate the quantity of electric charge required.
[ Density of aluminium oxide = 4.00 gcm
-3
] [5 marks ]
19. The group 14 elements include carbon (C), germanium (Ge), silicon (Si), tin (Sn) and lead (Pb).
(a) i. Explain the trends of metallic characteristics of group 14. [1 mark]
ii. Diamond are known as one of the allotropes of carbon. Explain why diamond cannot conduct
electricity but lead can. [2 marks]
iii. When going down Group 14, melting point decrease. Compare and explain why melting point of
lead is higher than tin based on the atomic radius and structure. [2 marks]
(b) i. Explain the use of lead(IV) oxide as an oxidizing agent. [3 marks]
ii. Explain why carbon tetrachloride does not react with water. [1 mark]
iii. When water is added to silicon tetrachloride, white fumes are released and a white solid is left
behind. Explain this observation. [1 mark]
(c) i. Explain why the +2 oxidation state of lead is more stable than the +4 oxidation state. [3 marks]
ii. Carbon burns in air to form carbon dioxide but lead burns in air to form lead monoxide. Explain
why. [2 marks]
Element C (diamond) Si Ge Sn Pb
Melting point(
o
C) 3730 1410 937 232 327
9
20. Transition elements occupy the central part of the Periodic Table, bridging the gap between the
active s-block metals and p-block metals.
(a) The first four ionization energies of three different elements X,Y and Z are shown in the table below.
Elements
Ionisation energy
First Second Third Fourth
X 655 4309 6421 7980
Y 976 1700 7900 14000
Z 757 1640 3230 5100
Which of the elements is a transition element? Explain your answer. [2marks]
(b) i. An aqueous solution of potassium thiocyanate is added to an aqueous solution of iron (lll) ions.
Write an equation for the reaction and state the color changes observed. [2 marks]
ii. Copper exhibits two important oxidation states, +1 and +2. Explain why copper(l) compounds are
mostly white while copper (ll) compounds are coloured. [3 marks]
(c) The stability constants, expressed as their logarithms, of the complex ion [CuCl
4
]
2-
and [Cu(NH3)
4
]
2+
are 5.6 and 13.2 respectively.
i. Give state the IUPAC name for [CuCl
4
]
2-
[1 mark]
ii. Explain what happens when an aqueous solution of ammonia is added to an aqueous solution of
[CuCl
4
]
2-
. [4 marks]
iii. Predict the stability constants, expressed as their logarithms, of the complex ion [Cu(EDTA)]
2-
, and
give a reason for your answer. [3 marks]
10
Section A
[15 marks]
1 A 6 D 11 B
2 B 7 D 12 B
3 C 8 C 13 D
4 B 9 B 14 C
5 B / D 10 A 15 A
16. a) Na2O ; MgO ; Al2O3 ; SiO2 ; P4O10 ;
SO3 3 and above [1] All correct [2]
b) i. Al2O3 + 6 HCl 2 AlCl3 + 3H2O [1]
Al2O3 + 2 NaOH + 3 H2O 2 NaAl(OH)4 [1]
SiO2 + 2NaOH Na2SiO3 + H2O [1]
ii. - Al2O3 is ionic bond [1]
- Al
3+
has high charge density / polarising
power [1]
17. a) 2N2 + 2O2 4NO (g) H1 = + 361.2
4 NH3 2N2 + 6H2 H2 = + 183.6
6H2 + 3 O2 6 H2O H3 = - 1451.1 [1]
4 NH3 + 5O2 4NO + 6H2O
H = -906.3 kJ [1]
b) ii. Born Haber cycle [6]
E Mg
2+
(g) + 2 F(g) + 2e
-
2 x Hatom of F [1] 2x EA of F [1]
Mg
2+
(g) + F2 (g) +2 e
-
1
st
HIE of Mg [1] Mg
2+
(g) + 2F
-
(g)
+ 2
nd
HIE of Mg
Mg (g) + F2 (g)
Hatom of Mg [1] LE [1]
Mg (s) + F2 (g)
Hf [1]
___MgF2 (s)
18. a) m1 : Half cell of H2 [1]
m2 : Half cell of Ag [1]
m3 : salt bridge [1]
ii.m4 : Ecell = Ered Eoxi @ + 0.80 V 0.00 [1]
m5 : Ecell = + 0.80 V [1]
iii.
m6 :
2
2
] 1 [
] H [
lg
2
0592 . 0
V 80 . 0 V 20 . 1
+
+
=
[1]
m7 : [H
+
] = 1.75 x 10
-7
mol dm
-3
[1]
m8 : pH = - lg [H
+
] @ - lg 3.77 x 10
-6
[1]
m9 : pH = 6.77 [1]
b) m10 : i. Anodisation : coating Al metal with
Al2O3, during electrolysis with the Al metal as
the anode [1]
ii. V of Al2O3 increased = 2500 x 0.005
= 12.5 cm
3
m11 : m of Al2O3 = 12.5 cm
3
x 4.00 g cm
-3
@ 50 g [1]
m12 : mol Al2O3 = 50 / 102 @ 0.490 mol [1]
Half equation at anode :
m13 : 2 H2O O2 + 4 H
+
+ 4 e
-
@ [1]
4 Al + 3 O2 2 Al2O3 @
2Al2O3 = 3O2 = 12e- / 1Al2O3 = 3/2O2 = 6e
-
m14 : mol of e- = 2.94 mol [1]
m15 : Q = mol of e- x F @ 2.94 x 96500 [1]
m16 : 2.84 x 10
5
C (3 s.f. w unit) [1]
19.a) m1 : i. metallic character increaase [1]
m2 : ii. all / 4 valence electron of C formed
covalent bond [1]
m3 : - lead can delocalised electron [1]
m4 : iii. atomic radius Sn smaller than Pb [1]
m5 : Pb is more close pack than Sn / Pb has
face center cubic while Sn is tetragonal [1]
b) m6 : i. Pb, +2 O.S more stable than +4 [1]
m7 : Pb
4+
is reduce to form Pb
2+
[1]
m8 : PbO2 + 4 HCl PbCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O [1]
or PbO2 + H2SO4 PbSO4 + 1/2O2 + H2O
m9 : ii. C does not have empty d orbitals to
coordinate water molecules [1]
m10 : iii. SiCl4 hydrolyse in water [1]
m11 : - SiCl4 + 2H2O SiO2 + 4 HCl [1]
or SiCl4 + 4H2O Si(OH)4 + 4 HCl
c) m 12 : i. due to inert pair effect [1]
m13 : - electron in 6s
2
remain stable and
unreactive in the filled sub- shell [1]
m14 : ii. C is more stable in +4 @ eq :
C + O2 CO2 [1]
m15 : - Pb + 1/2 O2 PbO [1]
20. a) m1 : - Z is transition metal [1]
m2 : - succesive ionisation energy increase
gradually as eff. nuclear charge increase [1]
b) m3 : i.yellow change to blood red soln [1]
m4 : [Fe(H2O)6]
3+
+ SCN
-
[Fe(SCN)(H2O)5]
2+
+ H2O [1]
m5 : ii. Cu
+
has full-filled 3d orbital / 3d
10
[1]
m6 : - Cu
2+
has partially filled 3d orb / 3d
9
[1]
m7 : - splitting of 3d orbital occur /
@ d-d transition occur [1]
c) m8 : i. tetrachlorocuprate (II) ion [1]
m9 : ii. Yellow turns a deep blue colour. [1]
m10 : [CuCl4]
2
(aq) + 4 NH3(aq)
[Cu(NH3)4]
2+
(aq) + 4 Cl
(aq) [1]
m11 : - [Cu(NH3)4]
2+
is more stable than
[CuCl4]
2
as K is higher [1]
m12 : - NH3 is stronger ligand than Cl
-
[1]
m13 : iii. - K of [Cu(EDTA)]
2
(> 13.2) [1]
m14 : - [EDTA]
4
is a polydentate ligand [1]
m15 : - has stronger chelating effect / hold
stronger to center metal ion [1]
2
2
0
] [
] [
lg
2
0592 . 0
+
+
=
Ag
H
E E
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Mechanical and Metallurgical Failure MechanismsDocument105 pagesMechanical and Metallurgical Failure MechanismsMohammad Hamdani100% (1)
- Food ChemistryDocument42 pagesFood ChemistryAashay Patil75% (4)
- 03 04 Faradays Laws of Electrolysis and ApplicationsDocument12 pages03 04 Faradays Laws of Electrolysis and ApplicationsTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- A Method For Cleaning Ancient Coins.Document36 pagesA Method For Cleaning Ancient Coins.S. RollNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - All of QuestionbankDocument36 pagesTopic 4 - All of Questionbankraghad100% (2)
- Vitamin C in FruitDocument10 pagesVitamin C in FruitWoon BingNo ratings yet
- CDI 2018 Board ConfidentialDocument18 pagesCDI 2018 Board ConfidentialJohn Mark Manahan50% (2)
- AFS Thermal Analysis of CupsDocument12 pagesAFS Thermal Analysis of Cupsyash_ganatraNo ratings yet
- Energetics Unit 2 Chemistry AS LevelDocument9 pagesEnergetics Unit 2 Chemistry AS LevelMuradNo ratings yet
- Energetics Unit 2 Chemistry AS LevelDocument9 pagesEnergetics Unit 2 Chemistry AS LevelMuradNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9Document6 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 9Suriati Bt A Rashid100% (1)
- STPMchemistry Scheme of Work (6atas) Paper 2Document8 pagesSTPMchemistry Scheme of Work (6atas) Paper 2Teoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- Exercise: SMK Seksyen 10 Kota Damansara 47810 Petaling Jaya, SelangorDocument3 pagesExercise: SMK Seksyen 10 Kota Damansara 47810 Petaling Jaya, SelangorTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 Chapter 3 Practice AnswerDocument2 pagesSem 1 Chapter 3 Practice AnswerTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument10 pagesBasic ConceptsTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- Sem 2 Final 2014Document5 pagesSem 2 Final 2014Teoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- Soft WaterDocument3 pagesSoft WaterTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- Unit: Three Topic Sub-Topic Objectives: E-Learning and Teacher EducationDocument2 pagesUnit: Three Topic Sub-Topic Objectives: E-Learning and Teacher EducationTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- Soft WaterDocument3 pagesSoft WaterTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- 4.6, 4.7 Exam Questions MsDocument20 pages4.6, 4.7 Exam Questions MsTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Energetics DatabaseDocument23 pages2.1 Energetics DatabaseskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- HarianDocument1 pageHarianTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- Young Teacher Programme 1Document3 pagesYoung Teacher Programme 1Teoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- Structured Questions: Chapter 7: Asid and BasesDocument2 pagesStructured Questions: Chapter 7: Asid and BasesTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- 6 Extr 1Document9 pages6 Extr 1Teoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- LBP6000 LBP6018 E-Manual - LNKDocument12 pagesLBP6000 LBP6018 E-Manual - LNKTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- Echem TutDocument8 pagesEchem TutTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- MATA PELAJARAN SENARAI NAMA PELAJAR-PELAJAR PU1SNDocument2 pagesMATA PELAJARAN SENARAI NAMA PELAJAR-PELAJAR PU1SNTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- Chemistry A2 AQA NotesDocument21 pagesChemistry A2 AQA NotesJalal Kazemi ◄▬No ratings yet
- Q Trial Chemistry Sem 3 STPM 2013Document14 pagesQ Trial Chemistry Sem 3 STPM 2013Teoh Ah Ngoh100% (1)
- Slide Ch1 (Phy)Document1 pageSlide Ch1 (Phy)Teoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- Find formulas and balance equations for chemistry problemsDocument2 pagesFind formulas and balance equations for chemistry problemsTeoh Ah NgohNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts in ChemistryDocument19 pagesSome Basic Concepts in Chemistryg_ayyanarNo ratings yet
- EP 10.8 - Air MedicinalDocument2 pagesEP 10.8 - Air MedicinalXuan Nhi NguyenNo ratings yet
- 1 4 2 1 1 PDFDocument9 pages1 4 2 1 1 PDFVikash ChachanNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab ReportDocument9 pagesBio Lab Reportapi-298082264No ratings yet
- Wood CoatingDocument6 pagesWood CoatingnancytalaatNo ratings yet
- AFCAT GK Questions 2019Document19 pagesAFCAT GK Questions 2019Krishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- Cadwell MoldesDocument34 pagesCadwell MoldesjaimeyzNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds QDocument8 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds QMuthoni WachiraNo ratings yet
- United States Patent: (75) Inventors: Prashant Anil Tatake, Mumbai (IN)Document8 pagesUnited States Patent: (75) Inventors: Prashant Anil Tatake, Mumbai (IN)angsalcautzarNo ratings yet
- SPE 154255 ECO-GSAI "Gravity Stable Air Injection" Pilot Test, An Enhanced Oil Recovery Opportunity To Be Implemented in Chichimene Field - ColombiaDocument6 pagesSPE 154255 ECO-GSAI "Gravity Stable Air Injection" Pilot Test, An Enhanced Oil Recovery Opportunity To Be Implemented in Chichimene Field - ColombiaFredy Andres Narvaez BohorquezNo ratings yet
- General Studies: Do Not Open This Booklet Until You Are Asked To Do SoDocument59 pagesGeneral Studies: Do Not Open This Booklet Until You Are Asked To Do SoBhargav Chowdary GangarapuNo ratings yet
- Transition Elements Chemistry Part IIDocument2 pagesTransition Elements Chemistry Part IIShaveeto KhanNo ratings yet
- ENERGOL GR-XP 200 msds 영문Document4 pagesENERGOL GR-XP 200 msds 영문thisbaboNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Paper MOM STD 8Document7 pagesMock Test Paper MOM STD 8Dr Mohan SavadeNo ratings yet
- Pengolahan Air Laut Dengan Menggunakan Karbon Aktif Dari Akar MangroveDocument6 pagesPengolahan Air Laut Dengan Menggunakan Karbon Aktif Dari Akar MangroveImaNo ratings yet
- Every Day Science MCQS1Document34 pagesEvery Day Science MCQS1Agha Khan DurraniNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Analysis ReportDocument19 pagesCertificate of Analysis ReportakloioNo ratings yet
- Avl Sa2Document125 pagesAvl Sa2coldness_13No ratings yet
- State of The Art of Hydrogen Production Via Pyrolysis of Natural GasDocument9 pagesState of The Art of Hydrogen Production Via Pyrolysis of Natural Gaskyrillos wahbaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Nitrogen Ratio in The Soil PDFDocument3 pagesCarbon Nitrogen Ratio in The Soil PDFguru9anandNo ratings yet
- Dehradun Public School ASSIGNMENT (2019 - 2020) Subject: Science (086) Class - IxDocument4 pagesDehradun Public School ASSIGNMENT (2019 - 2020) Subject: Science (086) Class - Ixbadnight4uNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Education in The 21st CenturyDocument106 pagesChemistry Education in The 21st CenturyAbhishek BansalNo ratings yet
- XIX. Chemistry, High SchoolDocument25 pagesXIX. Chemistry, High SchoolJane TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Graphene Patent Search and Analysis ReportDocument31 pagesGraphene Patent Search and Analysis ReportRobin LuniyaNo ratings yet