Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differences in Clinical Manifestations of Primary and Secondary Hemostasis Disorders
Uploaded by
Mischa Vlăsceanu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views7 pages1. Defects of primary hemostasis (platelet defects) cause bleeding immediately after trauma in superficial sites, while defects of secondary hemostasis (plasma protein defects) cause delayed bleeding in deep sites.
2. Physical findings in primary hemostasis defects include petechiae and ecchymoses, while secondary hemostasis defects cause hematomas and hemarthroses.
3. Defects of primary hemostasis usually have an autosomal dominant family history, while defects of secondary hemostasis often have an autosomal or X-linked recessive family history.
Original Description:
Hemostaza
Original Title
Hemostaza
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Defects of primary hemostasis (platelet defects) cause bleeding immediately after trauma in superficial sites, while defects of secondary hemostasis (plasma protein defects) cause delayed bleeding in deep sites.
2. Physical findings in primary hemostasis defects include petechiae and ecchymoses, while secondary hemostasis defects cause hematomas and hemarthroses.
3. Defects of primary hemostasis usually have an autosomal dominant family history, while defects of secondary hemostasis often have an autosomal or X-linked recessive family history.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views7 pagesDifferences in Clinical Manifestations of Primary and Secondary Hemostasis Disorders
Uploaded by
Mischa Vlăsceanu1. Defects of primary hemostasis (platelet defects) cause bleeding immediately after trauma in superficial sites, while defects of secondary hemostasis (plasma protein defects) cause delayed bleeding in deep sites.
2. Physical findings in primary hemostasis defects include petechiae and ecchymoses, while secondary hemostasis defects cause hematomas and hemarthroses.
3. Defects of primary hemostasis usually have an autosomal dominant family history, while defects of secondary hemostasis often have an autosomal or X-linked recessive family history.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Differences in the Clinical Manifestations of Disorders of Primary and Secondary Hemostasis
Manifestations Defects of Primary Hemostasis
(Platelet Defects)
Defects of Secondary Hemostasis (Plasma Protein
Defects)
Onset of bleeding after trauma Immediate Delayed (hours or days)
Sites of bleeding Superficial skin, mucous membranes, nose, gastrointestinal
and genitourinary tracts
Deep (joints, muscle, retroperitoneum)
Physical findings Petechiae, ecchymoses Hematomas, hemarthroses
Family history Autosomal dominant Autosomal or X-linked recessive
Response to therapy Immediate; local measures effective Requires sustained systemic therapy
EXPLORAREA HEMOSTAZEI PRIMARE
TESTELE DE SCREENING :
Timpul de sangerare - TS
Numararea placutelor sanguine
Primary Hemostatic (Platelet) Disorders
1. Defects of platelet adhesion
- von Willebrand's disease
- Bernard-Soulier syndrome (absence or dysfunction of GpIb/IX)
2. Defects of platelet aggregation
- Glanzmann's thrombasthenia (absence or dysfunction of GpIIb/IIIa)
3. Defects of platelet release
Decreased cyclooxygenase activity
- Drug-induced (aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents)
- Congenital
Granule storage pool defects
- Congenital
- Acquired
Uremia
Platelet coating (e.g., penicillin or paraproteins)
4. Defect of platelet coagulant activity
- Scott's syndrome
Evaluation of Platelet Function
Bleeding time
Modified Ivy method
Skin incision (time to stop bleeding)
Global screen of platelet role in hemostasis
von Willebrand factor assays
vWF Ag (immunoassay of total vWF protein)
vWF R:Cof (bioassay of vWF that measures ability of patient plasma to support agglutination of normal platelets in the presence of ristocetin)
Factor VIII (coagulation assay of factor VIII bound and carried by plasma vWF)
Platelet aggregometry
Measures platelet aggregation in response to a panel of agonists, usually ADP, collagen, arachidonic acid, and epinephrine
Membrane glycoproteins
Presence of glycoproteins Ib-IX and IIb-IIIa can be measured using monoclonal antibodies and flow cytometry
Platelet granule content
Dense granules (electron microscopy or uptake and retention of radiolabeled serotonin)
Alpha granules (electron microscopy and/or immunoassays for platelet-associated proteins - vWF, fibrinogen, platelet factor four
EXPLORAREA HEMOSTAZEI SECUNDARE (COAGULAREA)
TESTE DE SCREENING :
TCG TC (aPTT)
TIMPUL DE PROTROMBINA (QUICK) = PT
TIMPUL DE TROMBINA
FIBRINOGENEMIA
Relationship between Secondary Hemostatic Disorders and Coagulation Test Abnormalities
Prolonged partial thromboplastin time (PTT)
No clinical bleeding (factors XII, HMWK, PK)
Mild or rare bleeding (factor XI)
Frequent, severe bleeding (factors VIII and IX)
Prolonged prothrombin time (PT)
Factor VII deficiency
Vitamin K deficiency - early
Warfarin anticoagulant ingestion
Prolonged PTT and PT
Factor II, V, or X deficiency
Vitamin K deficiency - late
Warfarin anticoagulant ingestion
Prolonged thrombin time (TT)
Mild or rare bleeding, afibrinogenemia
Frequent, severe bleeding, dysfibrinogenemia
Heparin-like inhibitors or heparin administration
Prolonged PT and/or PTT not corrected with normal plasma
Specific or nonspecific inhibitor syndromes
Clot solubility in 5 M urea
Factor XIII deficiency
Inhibitors or defective cross-linking
Rapid clot lysis
a2 plasmin inhibitor
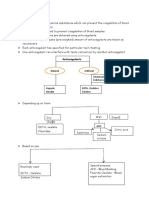
Dg. diferential : deficit de FPC / deficit de VK
TESTUL KOLLER
DEFICIT FPC DEFICIT DE VK
APTT / PT APTT / PT
Administrare de VK (i.m.)
8 12 ore
APTT / PT (nu se corecteaza) APTT / PT = N (se corecteaza)
TEST KOLLER (-) TEST KOLLER (+)
EXPLORAREA FIBRINOLIZEI
TLCS
TLCE
D-DIMER
SEMNIFICATIA D-DIMERULUI
SINDROM FIBRINOLITIC SINDROM FIBRINOLITIC
PRIMAR SECUNDAR
APTT = N APTT
PT = N PT
TT = N TT
Fibrinogenemie (disproportionat) Fibrinogenemie
Tr-citopenie Tr-citopenie
TLCS, TLCE TLCS, TLCE
PDF +++ PDF +++
D-Dimer = N D-Dimer
You might also like
- Hemostaza LPDocument7 pagesHemostaza LPmischa_vlasceanuNo ratings yet
- Approach To Coagulation DisordersDocument20 pagesApproach To Coagulation DisordersTri P BukerNo ratings yet
- Platelet, Coagulation, and Bleeding Disorder Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument11 pagesPlatelet, Coagulation, and Bleeding Disorder Diagnosis and TreatmentSara AshurstNo ratings yet
- Hemostatic Test: Rahajuningsih D. SetiabudyDocument17 pagesHemostatic Test: Rahajuningsih D. Setiabudyyuuna_wellerNo ratings yet
- CLG Chapter5 PDFDocument5 pagesCLG Chapter5 PDFIberisNo ratings yet
- Hemostaza LPDocument12 pagesHemostaza LPmoto24100% (1)
- Finals Topic-7 Hema-2 Mixing-Studies 3CDocument2 pagesFinals Topic-7 Hema-2 Mixing-Studies 3CFRANCIS ANDREI H. MIRANo ratings yet
- Interpreting Thromboelastography (TEG) - RK - MDDocument1 pageInterpreting Thromboelastography (TEG) - RK - MDNicolas HortonNo ratings yet
- Test For Secondary HemostasisDocument32 pagesTest For Secondary Hemostasistitania izaNo ratings yet
- Coagulation DisordersDocument20 pagesCoagulation DisordersAnuj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Venous Thromboembolism (Vte) : Abdullah Al Dahbali, Mpharm, PHDDocument23 pagesVenous Thromboembolism (Vte) : Abdullah Al Dahbali, Mpharm, PHDعزالدين الطيارNo ratings yet
- Test For Secondary HemostasisDocument32 pagesTest For Secondary Hemostasistitania izaNo ratings yet
- REVALIDA COMPRE HEMA2LAB MIXING STUDIES UnivSantoTomasDocument4 pagesREVALIDA COMPRE HEMA2LAB MIXING STUDIES UnivSantoTomasJemimah CainoyNo ratings yet
- Lab EvalDocument4 pagesLab EvalCecilio Manzo IINo ratings yet
- For Secondary: IeiviqstasisDocument68 pagesFor Secondary: IeiviqstasisMichelle San Miguel FeguroNo ratings yet
- Follow Up Tgl/Jam S O A PDocument2 pagesFollow Up Tgl/Jam S O A PGabriellaNo ratings yet
- AntiArrhythmic DrugsDocument7 pagesAntiArrhythmic DrugsKAZI RAHATNo ratings yet
- PT Aptt CoagulationDocument6 pagesPT Aptt Coagulationशिवराज शैटिNo ratings yet
- Hemostaticdisorders Associatedwith Hepatobiliarydisease: Cynthia R.L. WebsterDocument15 pagesHemostaticdisorders Associatedwith Hepatobiliarydisease: Cynthia R.L. WebsterJuan DuasoNo ratings yet
- Hemostatic TestDocument21 pagesHemostatic TestVitrosa Yosepta SeraNo ratings yet
- Coag Made EasyDocument16 pagesCoag Made EasyBrian RobertsNo ratings yet
- Ischemic PreconditioningDocument36 pagesIschemic PreconditioninghirschmedNo ratings yet
- Uecm3243 Topic 1Document16 pagesUecm3243 Topic 1YU XUAN LEENo ratings yet
- ADK Final Version-UpdatedDocument135 pagesADK Final Version-UpdatedDaal ChawlNo ratings yet
- Formulae Sheet Fundamental Constants: R 0.08314 DM Bar K Mol R 0.08206 DM Atm K Mol R 8.314 J K MolDocument6 pagesFormulae Sheet Fundamental Constants: R 0.08314 DM Bar K Mol R 0.08206 DM Atm K Mol R 8.314 J K MolPauline NgNo ratings yet
- Cerebro Vascular AttackDocument10 pagesCerebro Vascular AttackKalyan Babu VakaNo ratings yet
- What's New 20dec2022 ( (Autorecovered-310036581311017056) )Document19 pagesWhat's New 20dec2022 ( (Autorecovered-310036581311017056) )Abir HarmouchNo ratings yet
- Coagulation Made EasyDocument27 pagesCoagulation Made EasyHaris TanNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY ASSESSMENT OF HEMOSTASISDocument24 pagesLABORATORY ASSESSMENT OF HEMOSTASISrisantosa9823No ratings yet
- Anticoagulant Drugs Blood Clotting TestsDocument3 pagesAnticoagulant Drugs Blood Clotting TestsKristin DouglasNo ratings yet
- SYCDW 2011 Coag Made EasyDocument17 pagesSYCDW 2011 Coag Made EasyAnonymous wZYRDrClNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet: Systolic DiastolicDocument3 pagesFormula Sheet: Systolic DiastolicJames LaiNo ratings yet
- ASD For TKV Sem-4Document35 pagesASD For TKV Sem-4Aulia SriyantiNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument4 pagesElectrolyte ImbalanceBharathbushan V MandiriNo ratings yet
- Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction: An Overview of The Technique and Its ApplicationsDocument17 pagesReverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction: An Overview of The Technique and Its ApplicationsItzelOchoaNo ratings yet
- Think Coag Think Tcoag: Catalogue Your Coagulation CompanyDocument32 pagesThink Coag Think Tcoag: Catalogue Your Coagulation CompanysandraNo ratings yet
- Approach To Thrombocytopenia and ItpDocument73 pagesApproach To Thrombocytopenia and ItpDharaneedhar AdepuNo ratings yet
- Advances in The Diagnosis and Treatment of ThrombocytopeniaDocument50 pagesAdvances in The Diagnosis and Treatment of ThrombocytopeniaLetnanCapungNo ratings yet
- Cascading Knapsack Inequalities - Hidden Structures in Some Inventory-Production-Distribution ProblemsDocument20 pagesCascading Knapsack Inequalities - Hidden Structures in Some Inventory-Production-Distribution ProblemsManuelRamosNo ratings yet
- Massive Transfusion Phone Log INITIAL PHONE CALL (MP Activation Call)Document1 pageMassive Transfusion Phone Log INITIAL PHONE CALL (MP Activation Call)Jack WyattNo ratings yet
- Queueing SystemDocument67 pagesQueueing SystembalwantNo ratings yet
- SYCDW 2011 Coag Made EasyDocument17 pagesSYCDW 2011 Coag Made EasyRose KasidiNo ratings yet
- Coagulation and HemostasisDocument72 pagesCoagulation and HemostasisBiniyam AsratNo ratings yet
- BTCTDocument6 pagesBTCTnoha83No ratings yet
- Drug Moa PK Use Se Ci Blood Coagulation: AnticoagulantsDocument4 pagesDrug Moa PK Use Se Ci Blood Coagulation: AnticoagulantsYusoff RamdzanNo ratings yet
- Coagulation Disorders-First Aid Book: SS DX TXDocument6 pagesCoagulation Disorders-First Aid Book: SS DX TXMAINo ratings yet
- Echocardiography Evaluation For The Tricuspid ValveDocument48 pagesEchocardiography Evaluation For The Tricuspid ValveSofia KusumadewiNo ratings yet
- Mixing Studies 1pp 08-13-15.pptx 0 PDFDocument49 pagesMixing Studies 1pp 08-13-15.pptx 0 PDFKholifah LintangNo ratings yet
- Coag Made EasyDocument27 pagesCoag Made Easyniko hizkiaNo ratings yet
- PDF Nursing Care PlanDocument16 pagesPDF Nursing Care PlanMichael MabiniNo ratings yet
- October 31,2019: TH TH TH THDocument4 pagesOctober 31,2019: TH TH TH THYoussry JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Role of Bleeding Time and Clotting Time in Preoperative Hemostasis EvaluationDocument7 pagesRole of Bleeding Time and Clotting Time in Preoperative Hemostasis EvaluationAfin WiraNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Humaclot ProDocument8 pagesService Manual Humaclot ProHuy Trung GiápNo ratings yet
- Result Interpretation: Flags, Masks, Messages & RBC/PLT AnalysisDocument63 pagesResult Interpretation: Flags, Masks, Messages & RBC/PLT AnalysisMarcellia Angelina100% (1)
- Laboratory Hemostatic DisordersDocument41 pagesLaboratory Hemostatic DisordersYohanna SinuhajiNo ratings yet
- Physiology Slides UsmleDocument46 pagesPhysiology Slides Usmlejustseas100% (1)
- Follow Up Pasien PscbaDocument10 pagesFollow Up Pasien PscbaDexzalNo ratings yet
- Sunday Academic MeetDocument22 pagesSunday Academic MeetSrinivasan YashrajNo ratings yet
- TRP Channels as Therapeutic Targets: From Basic Science to Clinical UseFrom EverandTRP Channels as Therapeutic Targets: From Basic Science to Clinical UseArpad SzallasiNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Haematology 1 6 PDFDocument23 pagesRevision Notes Haematology 1 6 PDFCattrainuhNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument14 pagesCardiovascular System Multiple Choice QuestionsnyRonak45No ratings yet
- Thromboembolic Disease During PregnancyDocument17 pagesThromboembolic Disease During PregnancyYaacoub ChahineNo ratings yet
- Makalah INFLAMASIDocument12 pagesMakalah INFLAMASIAshifa QuamilaNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation and Hemostasis in Neurosurgery PDFDocument404 pagesAnticoagulation and Hemostasis in Neurosurgery PDFAleksandar DimovskiNo ratings yet
- TT Test LabDocument2 pagesTT Test LabSamantha ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- Blood Chapter SummaryDocument4 pagesBlood Chapter SummaryPhilline ReyesNo ratings yet
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument193 pagesDeep Vein Thrombosisdoctor_pepper0% (1)
- Venous ThromboembolismDocument14 pagesVenous ThromboembolismCélia BetkaouiNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)Document24 pagesDisseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)Atiya HajjajNo ratings yet
- IVD Product GroupingDocument35 pagesIVD Product GroupingoytNo ratings yet
- AnticoagulantsDocument4 pagesAnticoagulantsArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Why Is A Prothrombin Time Test Performed?: WarfarinDocument6 pagesWhy Is A Prothrombin Time Test Performed?: WarfarinMamta ShindeNo ratings yet
- 2015-Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis PDFDocument997 pages2015-Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis PDFnikospapaioannouNo ratings yet
- Acute Biologic CrisisDocument385 pagesAcute Biologic CrisisSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Lesson plan on nursing management of hemorrhageDocument35 pagesLesson plan on nursing management of hemorrhageDr-Sanjay Singhania93% (15)
- An Overview of Therapeutic Plasma ExchangeDocument65 pagesAn Overview of Therapeutic Plasma ExchangesayednourNo ratings yet
- Hemostatic AgentsDocument18 pagesHemostatic AgentshariNo ratings yet
- J 1538-7836 2004 01009 XDocument7 pagesJ 1538-7836 2004 01009 XAdriana BaceuNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis ReviewerDocument14 pagesHemostasis ReviewerDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- Elsevier - Anaesthesiology Clinics - Vol.26, Issues 1 - Obstetric Anesthesia (2008) PDFDocument230 pagesElsevier - Anaesthesiology Clinics - Vol.26, Issues 1 - Obstetric Anesthesia (2008) PDFMila KarmilaNo ratings yet
- HemophiliaA Research PaperDocument7 pagesHemophiliaA Research PaperShanePooleNo ratings yet
- MT Activity 1Document18 pagesMT Activity 1Luigie TorresNo ratings yet
- Paper: A Label-Free Aptamer-Based Nanogap Capacitive Biosensor With Greatly Diminished Electrode Polarization EffectsDocument11 pagesPaper: A Label-Free Aptamer-Based Nanogap Capacitive Biosensor With Greatly Diminished Electrode Polarization EffectsLakshmipriya GopinathNo ratings yet
- MSN 571 Mid-Term Pharmacology QuestionsDocument13 pagesMSN 571 Mid-Term Pharmacology QuestionsNelson MandelaNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and Thrombosis: OutlineDocument11 pagesHemostasis and Thrombosis: OutlineManila MedNo ratings yet
- Anti Haemostatic MechanismDocument29 pagesAnti Haemostatic MechanismDorin PathakNo ratings yet
- Vessel Due FDocument2 pagesVessel Due Fianecunar88% (8)
- Guyton Chapter 36Document6 pagesGuyton Chapter 36g_komolafe100% (1)
- CVD Q's & A'sDocument9 pagesCVD Q's & A'sAlan TaylorNo ratings yet